Study on Trace Element Characteristics in Otoliths of Pacific Saury (Cololabis saira) in Northwest Pacific Ocean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
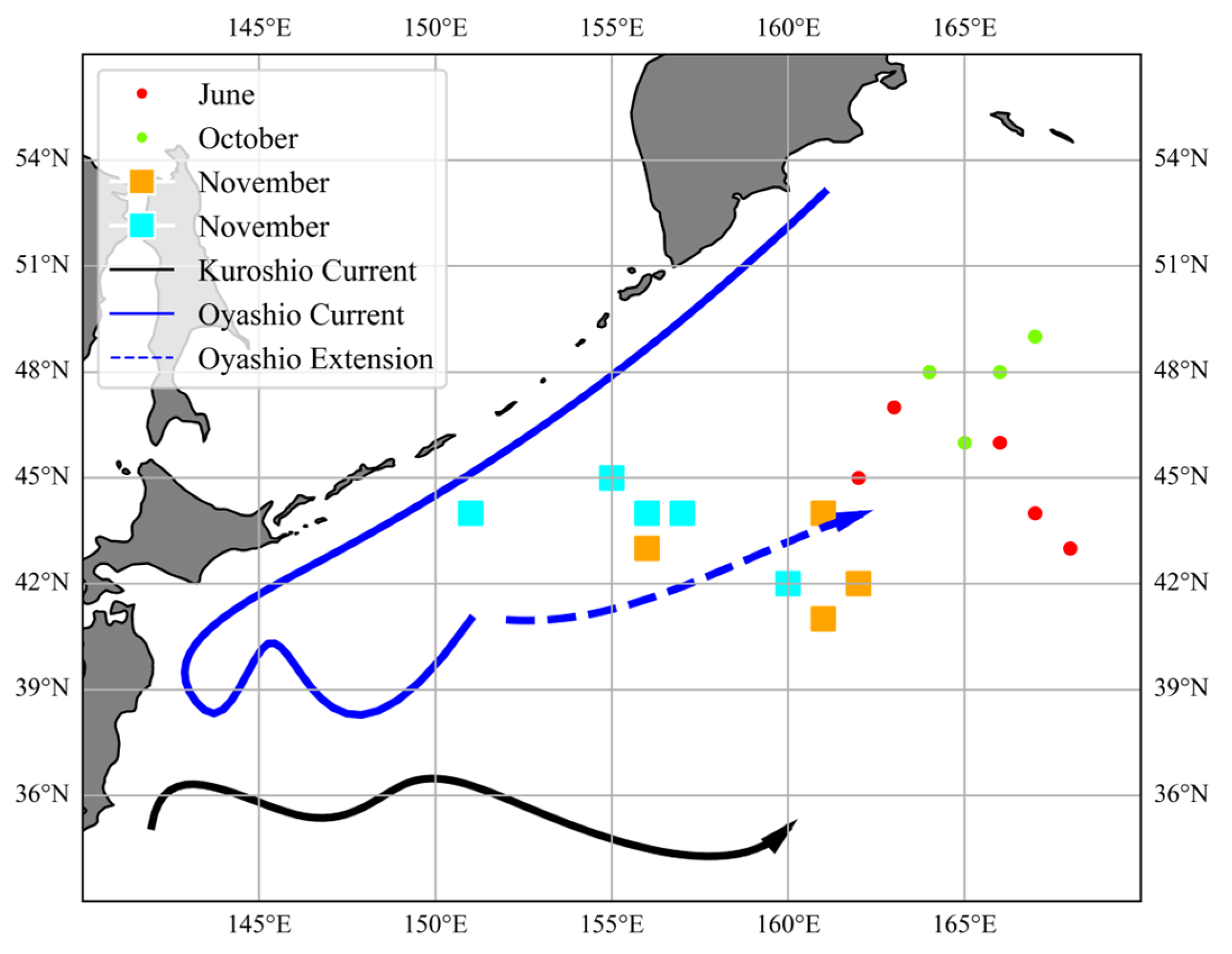
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Environmental Data
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.3.1. Basic Biological Measurements
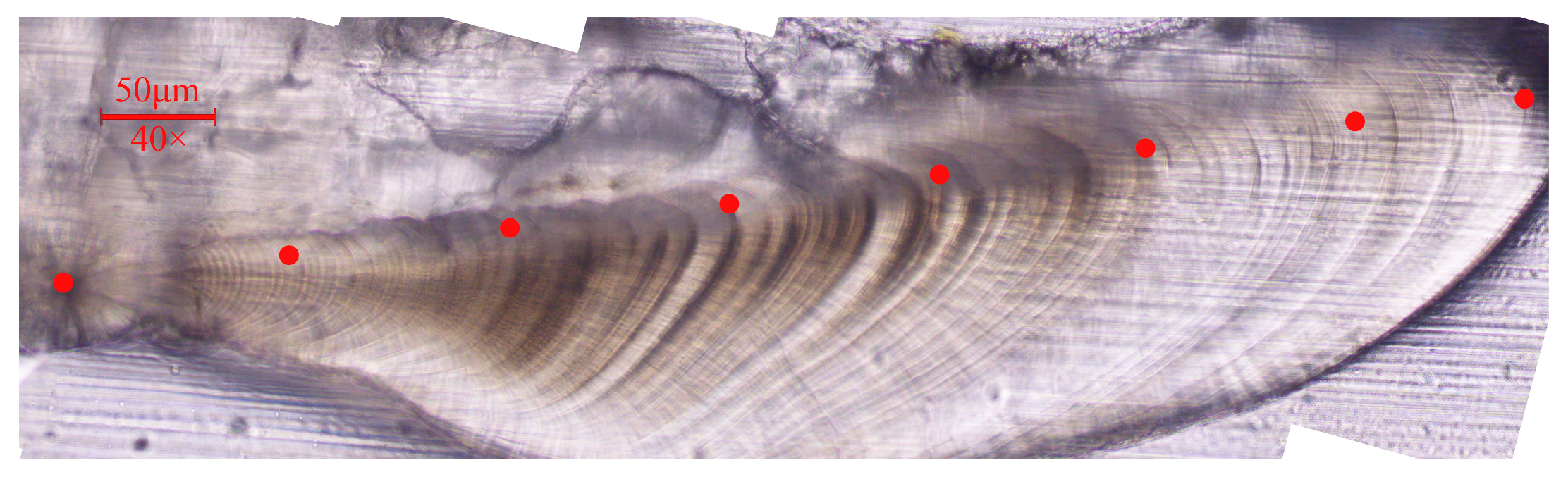
2.3.2. Daily Age Determination
2.3.3. Otolith Trace Element Measurement
2.4. Data Preprocessing
2.4.1. Classification of Different Life History Stages by Daily Age
2.4.2. Back-Calculation of Dates
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.5.1. Differential Analysis
2.5.2. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trace Element Characteristics of Otoliths
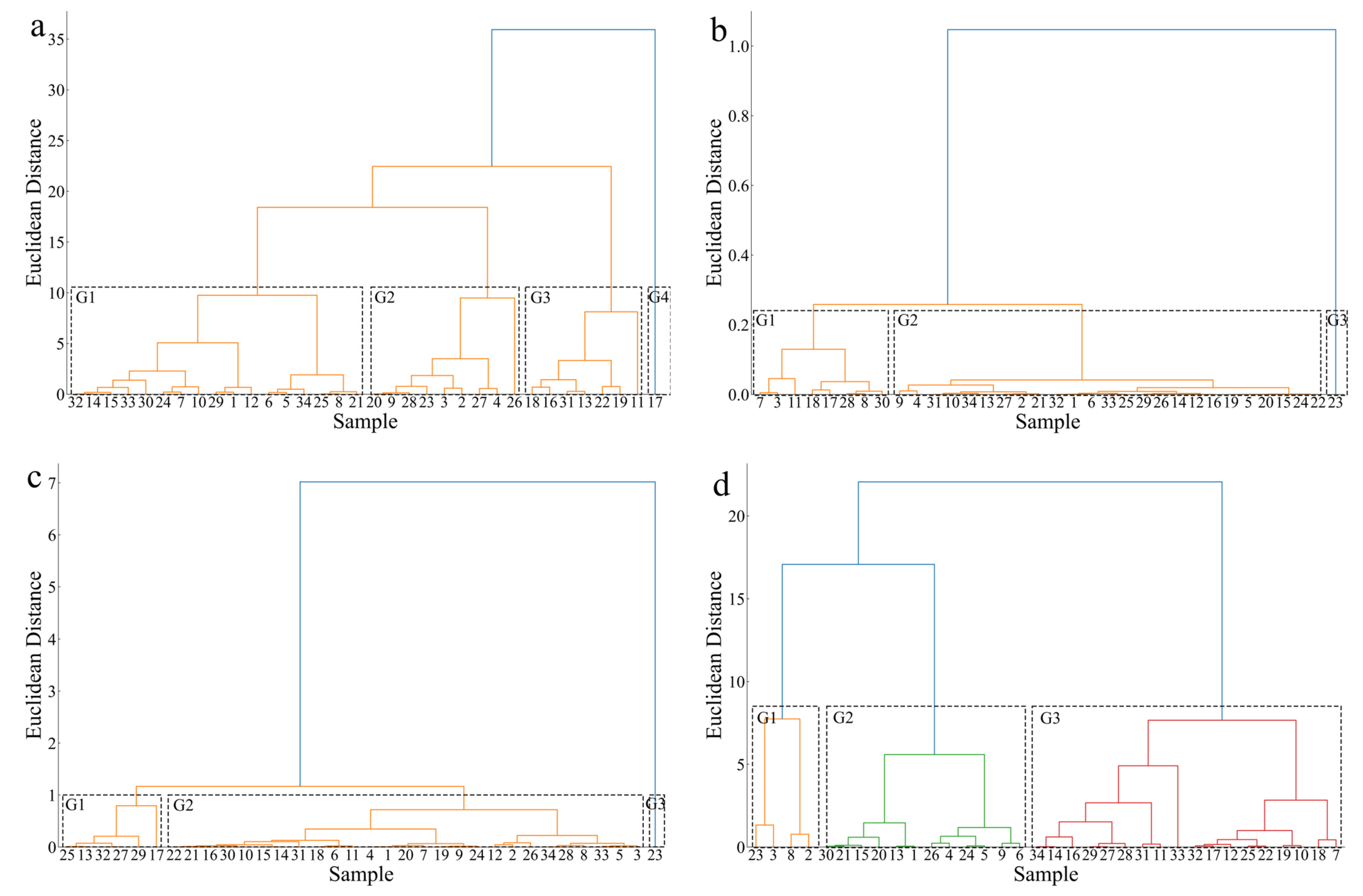
3.2. Distribution of Characteristics Between Sexes
3.3. Distribution Characteristics of Otolith Core Regions
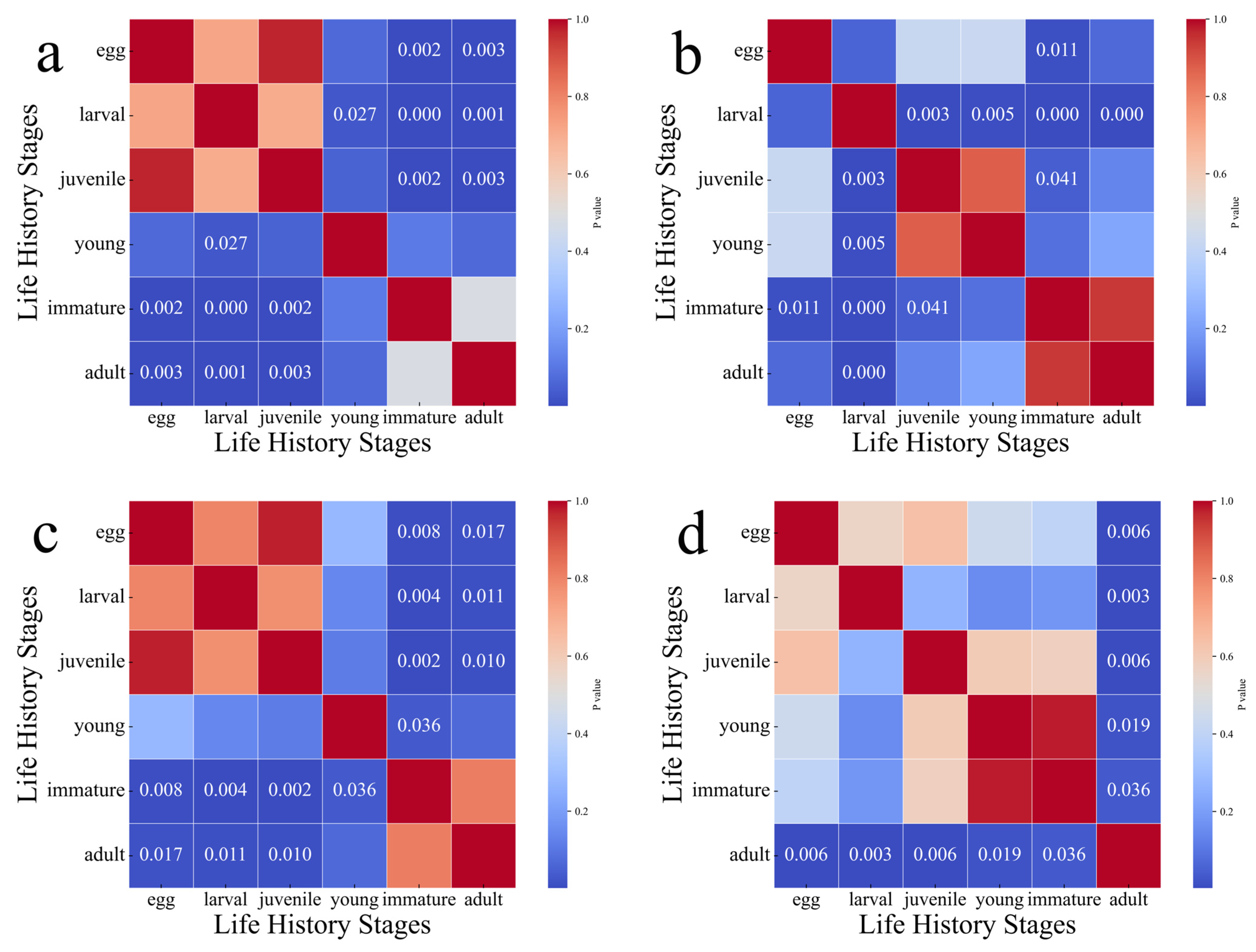
3.4. Distribution of Characteristics Across Life History Stages
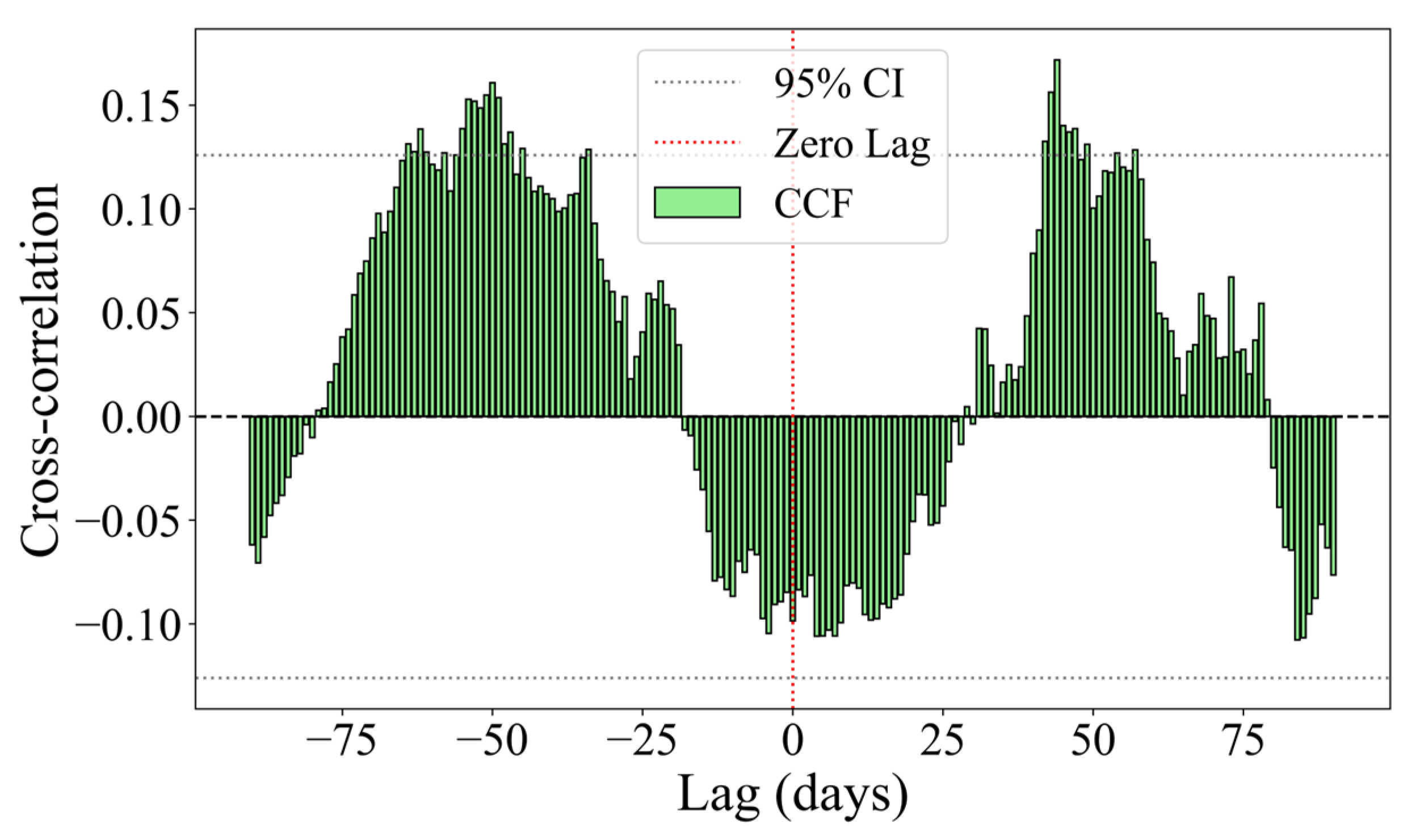
3.5. Relationship Between Otolith Sr/Ca Values and SST
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship Between Otolith Core Sr/Ca, Ba/Ca, Mg/Ca, and Na/Ca Values and Hatching Characteristics
4.2. Relationship Between Otolith Trace Element Values and Life History
4.3. Relationship Between Otolith Trace Element Values and Migration Patterns
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- There were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in the otolith Sr/Ca, Ba/Ca, Mg/Ca, and Na/Ca values between male and female Pacific saury, but there were significant differences (p < 0.05) across different life history stages. These results suggest that Pacific saury in the same area may originate from multiple spawning grounds, while individuals from different fishing locations may share common spawning areas. This confirms the phenomenon of mixed populations among different geographic groups of Pacific saury.
- (2)
- The young stage (91~180 d) marks the beginning of independent migration for Pacific saury. Significant changes in the otolith Sr/Ca values before and after this life history stage reflect the environmental changes experienced by Pacific saury around this time. Additionally, significant changes in the Mg/Ca and Na/Ca values during the adult stage may reflect physiological behaviors such as feeding, spawning, and reproduction.
- (3)
- A significant nonlinear lagged negative correlation was found between the otolith Sr/Ca values and SST (p < 0.05, r < 0), speculating that the migration pattern of Pacific saury exhibits seasonal variation. The timing of migration may approximately correspond to SST inflection points. Some individuals may also undergo vertical migration across water layers during specific life stages. The maximum cross-correlation lag between the Sr/Ca values and the SST was 44 days, suggesting that SST changes precede otolith Sr/Ca variations by about 44 days. This implies that environmental changes may drive Sr/Ca fluctuations in otoliths after a deposition delay, confirming that the water temperature is a key environmental factor in studying Pacific saury migrations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.; Akamine, T.; Suda, M. Variations in the abundance of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) from the northwestern Pacific in relation to oceanic-climate changes. Fish. Res. 2003, 60, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhu, Q.C.; Hua, C.X. Fishing ground distribution of saury and its correlation with marine environment factors in the Northern Pacific high sea in 2013. J. Shang Ocean Univ. 2015, 24, 773–782. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.C.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, B.J.; Li, F. Relationship between fishing ground of Pacific saury and vertical temperature in the north Pacific Ocean. Hebei Fish. 2022, 44, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.; Tong, J.; Ma, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Lyu, S.; Chen, X. Reimagining habitat suitability modeling for Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) in the Northwest Pacific Ocean through acoustic data analysis from fishing vessels. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.X.; Zhu, Q.C.; Xu, W.; Song, L.M.; Li, F. Review of the life history, resources and fishing grounds of the Pacific saury in the North Pacific Ocean. J. Fish. Sci. China 2019, 26, 811–821. [Google Scholar]
- North Pacific Fisheries Commission: About NPFC. Available online: https://www.npfc.int/about_npfc (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Liang, J.W.; Hua, C.X.; Chen, X.J.; Yang, N.; Zhao, Z.F.; Hu, G.Y.; Li, J.H. On habitat changes of Cololabis saira based on carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes technology. Mar. Fish. 2023, 45, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Tian, S.Q.; Chen, X.J. Review of research methods for migration and distribution of aquatic animals. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 1678–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Elsdon, T.; Wells, B.; Campana, S.; Gillanders, B.; Jones, C.; Limburg, K.; Secor, D.; Thorrold, S.; Walther, B. Otolith Chemistry to Describe Movements and Life-History Parameters of Fishes: Hypotheses, Assumptions, Limitations and Inferences. In Oceanography and Marine Biology; Gibson, R., Atkinson, R., Gordon, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 297–330. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.H. Preliminary Study on Growth, Mortality, and Resource Status of Pacific Saury in the Northwest Pacific Ocean; SHOU: Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Tian, H.; Cao, C.; Watanabe, Y.; Tian, Y. Different growth patterns reveal the potential origins of two Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) groups in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Fish. Res. 2024, 272, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, T.; Kurita, Y.; Suyama, S.; Ambe, D. Estimating the spawning ground of Pacific saury Cololabis saira by using the distribution and geographical variation in maturation status of adult fish during the main spawning season. Fish. Oceanogr. 2021, 30, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, T.; Nakagami, M.; Suyama, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Kidokoro, H. Geographical differences in the stable isotope ratios of Pacific saury in the North Pacific Ocean. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, H.; Suyama, S.; Vijai, D.; Kidokoro, H.; Naya, M.; Fuji, T.; Sakai, M. Predicting the timing of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) immigration to Japanese fishing grounds: A new approach based on natural tags in otolith annual rings. Fish. Res. 2019, 209, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, S.; Nakagami, M.; Naya, M.; Ueno, Y. Migration route of Pacific saury Cololabis saira inferred from the otolith hyaline zone. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S. Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: Pathways, mechanisms and applications. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 188, 263–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, H.B.; Tang, J.H.; Zhong, X.M.; Liu, P.T.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; Chen, T.T. Application of otolith microchemistry on reconstruction of migratory patterns and stock discrimination in marine fishes. Chin. Bull. Life Sci. 2015, 27, 953–959. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.W. Study on Habitat Evaluation of Cololabis Saira in the Northwest Pacific Based on Biogeochemical Technology; SHOU: Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.A. Effects of water temperature and barium concentration on otolith composition along a salinity gradient: Implications for migratory reconstructions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 405, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ložys, L.; Shiao, J.-C.; Iizuka, Y.; Minde, A.; Pūtys, Ž.; Jakubavičiūtė, E.; Dainys, J.; Gorfine, H.; Tzeng, W.-N. Habitat use and migratory behaviour of pikeperch Sander lucioperca in Lithuanian and Latvian waters as inferred from otolith Sr: Ca ratios. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.C.; Gu, R.B.; Liu, H.B.; Jiang, T.; Du, F.K.; Nie, Z.J.; Yang, J.; Xu, P. Fluctuation of Sr/Ca in otoliths of Coilia nasus in the Yangtze River and the validation for the anadromous migratory history. J. Fish. China. 2014, 38, 939–945. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.H. Trophic Niche and Otolith Microchemistry of Major Fish in the Pearl River Estuary Qi’ao Mangrove Water Area; DLOU: Dalian, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.J.; Tang, X.Y.; Yan, X.J.; Song, W.H.; Zhou, Y.D.; Zhang, H.L.; Jiang, R.J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T. Speculation of migration routes of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea based on otolith microchemistry. Haiyang Xuebao 2023, 45, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, A.; Taylor, M.D.; Barnes, T.C.; Johnson, D.D.; Gillanders, B.M. Habitat transitions by a large coastal sciaenid across life history stages, resolved using otolith chemistry. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.L. Analysis of Inter-Annual Variation in Individual Growth and Habitat of Scomber Japonicus in the East China Sea Based on Otolith Information; SHOU: Shanghai, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Caccavo, J.; Ashford, J.R.; Ryan, S.; Papetti, C.; Schröder, M.; Zane, L. Spatial structuring and life history connectivity of Antarctic silverfish along the southern continental shelf of the Weddell Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 624, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Morphological Characteristics and Differences of Trace Elements of Collichthys Lucidus Otoliths in the Yellow and East China Sea; SHOU: Shanghai, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Kong, X.; Zhao, W.X.; Yu, C.Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.X.; Liu, H.J.; Song, A.H. Microchemical characteristics of otoliths and stock discrimination of Hexagrammos otakii from the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Mar. Sci. 2023, 47, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, S.Z.; Amano, H.; Yu, X.; Cao, L.; Shirai, K.; Otake, T.; Tsukamoto, K. Multiple laser ablations on otolith nuclei for ICPMS to elementally fingerprint fish stocks: A case study. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2011, 42, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S.E.; Fowler, A.J.; Jones, C.M. Otolith Elemental Fingerprinting for Stock Identification of Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua) Using Laser Ablation ICPMS. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 51, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolé, F.G.; Thompson, G.A.; Vargas, C.V.; Leisen, M.; Barra, F.; Volpedo, A.V.; Avigliano, E. Fish stocks of Urophycis brasiliensis revealed by otolith fingerprint and shape in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 229, 106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S. Study on the Age, Growth and Otolith Microchemistry of Pacific Saury (Cololabis saira) in the Northwest Pacific Ocean; SHOU: Shanghai, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa, H.; Nishikawa, S.; Ishizaki, H.; Wakamatsu, T.; Ishikawa, Y. Detection of the Oyashio and Kuroshio fronts under the projected climate change in the 21st century. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2020, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.X.; Gao, Y.Z.; Zhu, Q.C.; Zhou, Y.F.; Li, S.S. Age and growth of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) in the northwest Pacific Ocean based on otolith microstructure. Haiyang Xuebao 2017, 39, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.G.; Chen, H.H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Z.; Huang, H.X.; Li, J.H.; Gao, C.X. Reconstruction of habitat history of Pennahia argentata in the offshore waters of southern Zhejiang based on otolith microchemical Sr/Ca. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2024, 33, 768–775. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Akamine, T.; Suda, M. Modeling the influence of oceanic-climatic changes on the dynamics of Pacific saury in the northwestern Pacific using a life cycle model. Fish. Oceanogr. 2004, 13, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, N.; Yu, J.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.J. Preliminary study on the migration characteristic of two loligo species in the northern South China Sea based on otolith microchemistry. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2021, 52, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Matsuyama, M. Migratory routes of the swordtip squid Uroteuthis edulis inferred from statolith analysis. Aquat. Biol. 2015, 24, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.B.; Huang, Y.C. Reproductive biology of Cololabis saira (Brevoort, 1856) in the Northwest Pacific: Female maturity and spawning migration. BioScience. 2011, 53, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 8588—2024; Fundamental Terms of Fishery Resource Sciences. National Technical Committee 156 on Aquaculture of Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Suyama, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Meguro, T.; Shimazaki, K. Estimation of the Age and Growth of Pacific Saury Cololabis saira in the Central North Pacific Ocean determined by Otolith Daily Growth Increments. Nippon. Suisan Gakk. 1992, 58, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iwahashi, M.; Isoda, Y.; Ito, S.; Oozeki, Y.; Suyama, S. Estimation of seasonal spawning ground locations and ambient sea surface temperatures for eggs and larvae of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) in the western North Pacific. Fish. Oceanogr. 2006, 15, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.J. Preliminary analysis of trace elements in Scomberomorus niphonius otoliths in waters adjacent to the Yangtze Estuary. Mar. Fish. 2022, 44, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipkin, A.I.; Campana, S.E.; FitzGerald, J.; Thorrold, S.R. Spatial and temporal variation in elemental signatures of statoliths from the Patagonian longfin squid (Loligo gahi). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Nin, B.; Geffen, A.J.; Pérez-Mayol, S.; Palmer, M.; González-Quirós, R.; Grau, A. Seasonal and ontogenic migrations of meagre (Argyrosomus regius) determined by otolith geochemical signatures. Fish. Res. 2012, 127–128, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.A.; Li, X.F. Relationship between Cololabis saira fishery distribution patterns and sea surface temperature front in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. J. Fish. China 2018, 42, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, L.L.; Zhu, Q.C.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y. Study on biological characteristics of Cololabis saira in the high seas of Northwest Pacific Ocean. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 198–201. [Google Scholar]

| Sampling Month | June | July | August | September | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body length/mm | 238~287 | 266~288 | 268~305 | 259~303 | |
| Daily age/d | 145~428 | 102~438 | 197~374 | 199~381 | |
| Sr/Ca, mmol·mol−1 | 7.72 ± 1.41 | 7.50 ± 1.30 | 7.18 ± 1.03 | 7.11 ± 1.20 | |
| Ba/Ca, mmol·mol−1 | 0.012 ± 0.017 | 0.007 ± 0.008 | 0.013 ± 0.023 | 0.026 ± 0.043 | |
| Mg/Ca, mmol·mol−1 | 0.10 ± 0.15 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.13 | |
| Na/Ca, mmol·mol−1 | 7.39 ± 0.90 | 7.68 ± 0.44 | 7.38 ± 0.56 | 7.25 ± 0.99 | |
| Sample size | 9 | 7 | 8 | 10 | |
| Breeding season | Spring | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Summer | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | |
| Autumn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Winter | 6 | 1 | 5 | 6 | |
| Sex | Female | 3 | 6 | 3 | 4 |
| Male | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Area | Sr/Ca | Ba/Ca | Mg/Ca | Na/Ca | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | p | H | p | H | p | H | p | |
| Core area | 0.019 | 0.890 | 0.744 | 0.388 | 0.686 | 0.408 | 0.744 | 0.388 |
| Entire area | 2.018 | 0.155 | 0.723 | 0.395 | 0.340 | 0.560 | 0.046 | 0.830 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, C.; He, J.; Zhu, Q.; Li, F. Study on Trace Element Characteristics in Otoliths of Pacific Saury (Cololabis saira) in Northwest Pacific Ocean. Fishes 2025, 10, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090425
Hua C, He J, Zhu Q, Li F. Study on Trace Element Characteristics in Otoliths of Pacific Saury (Cololabis saira) in Northwest Pacific Ocean. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090425
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Chuanxiang, Jialin He, Qingcheng Zhu, and Fei Li. 2025. "Study on Trace Element Characteristics in Otoliths of Pacific Saury (Cololabis saira) in Northwest Pacific Ocean" Fishes 10, no. 9: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090425
APA StyleHua, C., He, J., Zhu, Q., & Li, F. (2025). Study on Trace Element Characteristics in Otoliths of Pacific Saury (Cololabis saira) in Northwest Pacific Ocean. Fishes, 10(9), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090425





