Isolation, Identification, and Virulence Properties of Enterobacter bugandensis Pathogen from Big-Belly Seahorse Hippocampus abdominalis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial Isolation
2.3. Bacterial Identification
2.3.1. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis
2.3.2. Genomic Sequencing Analysis
2.3.3. Phenotypic Identification
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assay
2.5. Pathogenicity-Related Gene Assay
2.6. Experimental Seahorses
2.7. Experimental Pathogenicity Assay
2.8. Median Lethal Dose Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Isolation
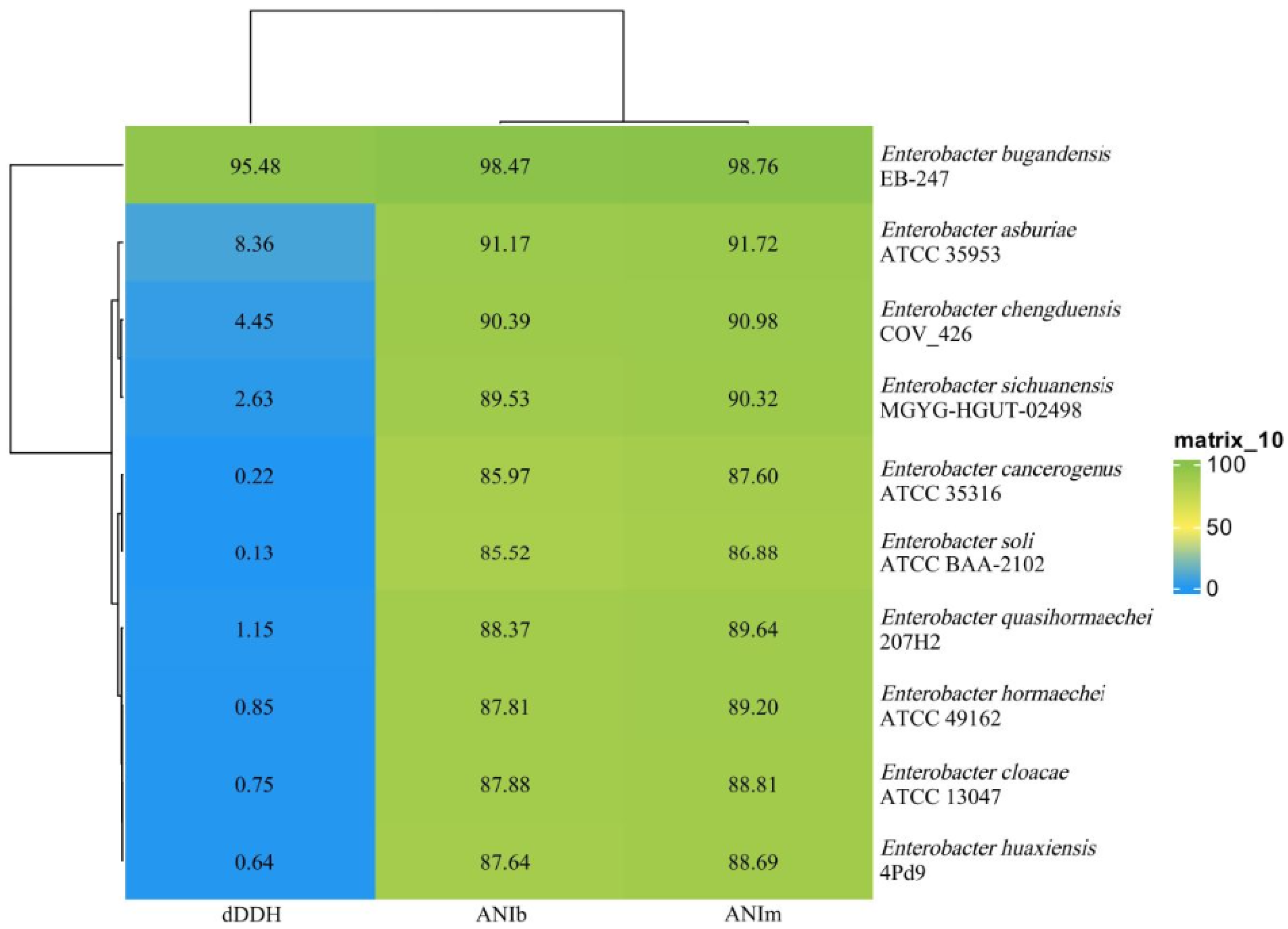
3.2. Bacterial Identification
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Assessment
3.4. Pathogenicity-Related Genes
3.5. Experimental Pathogenicity
3.6. Virulence Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, N.; Kim, S.Y.; Rho, S.; Ko, J.Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-fatigue activity of a mixture of seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) hydrolysate and red ginseng. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ryu, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Lee, H.J. Brassicasterol from edible aquacultural Hippocampus abdominalis exerts an anti-cancer effect by dual-targeting AKT and AR signaling in prostate cancer. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molagoda, N.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Sung, J.; Kim, G.Y. Ethanolic extract of Hippocampus abdominalis exerts anti-melanogenic effects in B16F10 melanoma cells and zebrafish larvae by activating the ERK signaling pathway. Cosmetics 2019, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.M.C. Improving initial survival in cultured seahorses, Hippocampus abdominalis Leeson, 1827 (Teleostei: Syngnathidae). Aquaculture 2000, 190, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.B.; Qi, J.F.; Lin, J.B.; Chen, X.X.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Y.Y. Artificial propagation and seedling technique of Hippocampus abdominalis. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Fernand, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Wang, L.; Lee, S.H.; Ko, S.C.; Kang, M.C.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Jeon, Y.J. Free radical scavenging activity of the peptide from the alcalase hydrolysate of the edible aquacultural seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis). J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldewey, H.J.; Martin-Smith, K.M. A global review of seahorse aquaculture. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzymińska, S.; Koczura, R.; Mokracka, J.; Puton, T.; Kaznowski, A. Isolates of the Enterobacter cloacae complex induce apoptosis of human intestinal epithelial cells. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 49, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Bakhshi, B.; Peerayeh, S.N. Particular distribution of Enterobacter cloacae strains isolated from urinary tract infection within clonal complexes. Iran. Biomed. J. 2016, 20, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, N.B.; Doijad, S.P.; Schultze, T.; Mannala, G.K.; Yao, Y.C.; Jaiswal, S.; Ryan, D.; Suar, M.; Gwozdzinski, K.; Bunk, B.; et al. Enterobacter bugandensis: A novel enterobacterial species associated with severe clinical infection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.F.; Yang, G.Y.; Gao, Q.; Xia, Z.L.; Pu, J.W.; Shen, P.J.; Huang, Z.Y. Identification and isolation of a novel bacterial pathogen (Enterobacter cloacae) from diseased larvae of giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2015, 46, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, V.T.; Santiago, T.C.; Vijavan, K.K.; Alavandi, S.V.; Raj, V.S.; Rajan, J.J.S.; Sanjuktha, M.; Kalaimani, N. Involvement of Enterobacter cloacae in the mortality of the fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 46, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Prasad, K.P.; Raman, R.P.; Kumar, S.; Purushothaman, C.S. Association of Enterobacter cloacae in the mortality of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878) reared in culture pond in Bhimavaram, Andhra Pradesh, India. Indian J. Fish. 2013, 60, 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.J.; Zhang, H.H.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, N.; Li, X.X.; Liu, X.D.; Yang, H.; Wei, W.H.; Zhang, X.J. Enterobacter cloacae associated with mass mortality in zoea of giant freshwater prawns Macrobrachium rosenbergii and control with specific chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins (lgY). Aquaculture 2019, 501, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.P.; An, J.; Ou, R.J.; Lu, L.Q.; Ai, X.H.; Yang, Y.B. Enterobacter aerogenes: An emerging pathogen for enteritis in farmed channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Isr. J. Aquac.—Bamidgeh 2017, 69, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.G.; Lipton, A.P.; Ríos-Escalante, P.D.L.; Ibáñez-Arancibia, E. Isolation and characterization of bacterial pathogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter cloacae from the moribund fish, Etroplus maculatus. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2021, 12, 1332–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; Xu, N.; Ai, X. Identification of a multi-resistant Enterobacer cloacae strain from diseased crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Phenotypic and genomic insights into the pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance of an Enterobacter roggenkampii strain isolated from diseased silver arowana (Osteoglossum bicirrhosum). J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condon, K.; Huerlimann, R.; Charles, T.; Lowrey, R.; Arbon, P.; Jerry, D.R. Using bacterial whole genome sequencing to identify toxin genes associated with disease outbreaks in black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) aquaculture production. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Wang, F.; Jia, L.W.; Yan, H.S.; Gao, L.K.; Tian, Y.N.; Su, X.L.; Zhang, X.; Lv, C.H.; Ma, Z.H.; et al. Edwardsiella piscicida infection reshapes the intestinal microbiome and metabolome of big-belly seahorses: Mechanistic insights of synergistic actions of virulence factors. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1135588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Dahanayake, P.S.; De Zoysa, M.; Heo, G.J. Phylogenetic characteristics, virulence properties and antibiogram profile of motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from ornamental guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.D.; Sun, H.S.; Bai, X.F.; Lin, Q.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, D.C. HC2 of Pseudomonas sp. induced enteritis in Hippocampus japonicus. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2027–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.X.; Qiu, Q.T.; Song, Y.P.; Huang, K.J.; Jin, S.; Xie, J.S.; Zhao, Q.S.; Xu, Y.J. Isolation, identification and pathogenic characteristics of bacterial pathogens from cultured Hippocampus kuda with skin ulcers. J. Agric. Catastroph. 2021, 11, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Yong, P.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Xie, S.D.; Fan, Y.S.; Zang, L.; Cui, L.W.; Sun, J.H. Isolation, identification, and histopathological analysis of Vibrio tubiashii from lined seahorse Hippocampus erectus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2019, 133, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, S.K.; Bai, X.H.; Luo, Z.; Liu, J.B.; Ke, K. Pathogenic Photobacterium sp. induces mortality in the lined seahorse (Hippocampus erectus): China’s first case report. Isr. J. Aquac.—Bamidgeh 2022, 74, 1584678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, Z.Q. Three different viruses observed from the tissues of diseased mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1999, 44, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.L.; He, Y.W.; Li, Y.; Ren, T.R.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.B.; Jiang, D.H.; Hsiang, T.; Zheng, L. Two new biocontrol agents against clubroot caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.B.; Liu, B.H.; Xie, Y.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, W.H.; Yuan, J.Y.; He, G.Z.; Chen, Y.X.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.J.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, D.; Cai, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, F.; Li, C.L.; Huang, X.H. Complete genome sequence analysis of Brevibacillus laterosporus Bl-zj reflects its potential algicidal response. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcher, A.L.; Bratke, K.A.; Powers, E.C.; Salzberg, S.L. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besemer, J.; Borodovsky, M. GeneMark: Web software for gene finding in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA genes in genomic sequences. In Gene Prediction; Kollmar, M., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1962, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.S.; Han, F.; Yu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.J. Complete genome sequence of the Pseudomonas oleovorans strain ODT-83 isolated from oyster. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.F.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.P.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; et al. CARD 2017: Expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouts, D.E. Phage finder: Automated identification and classification of prophage regions in complete bacterial genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 34, 5839–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, S.M.; Amer, M.A. Pseudocitrobacter cyperus, a novel bacterial species recovered from Cyperus alternifolius in Egypt. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Jiang, X.; Yuan, N.; Zhang, W. Separation and identification spoilage microorganisms in the soft can of rice pudding. Food Res. Dev. 2015, 36, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doijad, S.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Yao, Y.C.; Pati, N.B.; Falgenhauer, L.; Hain, T.; Foesel, B.U.; Abt, B.; Overmann, J.; Mirambo, M.M.; et al. Enterobacter bugandensis sp. nov., isolated from neonatal blood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated from Aquatic Animals, Approved Guideline; CLSI document VET03-A; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, Twenty-Second Informational Supplement, CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, Thirty-Fifth Edition, CLSI Supplement M100TM.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.H.; Zheng, D.D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, W.; Cao, Z.; Xu, B.; Wang, G.; Luo, M. High correlation between genotypes and phenotypes of environmental bacteria Comamonas testosterone strains. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China. Circular of the General Office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs on printing and distributing the guidelines on identification and safety evaluation of direct-fed microbials and fermented-food-derived bacterial strains. Gaz. Minist. Agric. Rural. Aff. People’s Repub. China 2021, 11, 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, G.; Korenaga, H.; Nagamine, R.; Kono, T.; Shimokawa, H.; Itami, T.; Sakai, M. Immune stimulant effects of a nucleotide-rich baker’s yeast extract in the Kuruma shrimp, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Aquaculture 2012, 366, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, C.L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.R.; Xu, L.; Ye, H.B. Identification of Vibrio ponticus as a bacterial pathogen of coral trout Plectropomus leopardus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1089247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xiao, M.; Li, J.; Mao, Z.F.; Zhang, C.Z.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhu, M.J.; Jian, S.Q.; Zhao, D.X. Effects of Aeromonas hydrophila stimulation on immunity of Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Fish. Sci. 2020, 39, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Bu, L.; Jin, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y. Outbreak of vibriosis caused by Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus in farmed seahorse Hippocampus kuda in China. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Wang, F.; Chen, G.Z.; Yang, B.Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, K.; Hou, Y.P. Edwardsiella tarda induces enteritis in farmed seahorses (Hippocampus erectus): An experimental model and its evaluation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildberg, A.; Mikkelsen, H. Effects of supplementing the feed to Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) fry with lactic acid bacteria and immuno-stimulating peptides during a challenge trial with Vibrio anguillarum. Aquaculture 1998, 167, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Zheng, F.R.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, P.Y.; Xin, M.S. Identification and characterization of the pathogen associated with skin ulcer syndrome in lined seahorse, Hippocampus erectus. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denham, B.E. Concluding Communication. In Categorical Statistics for Communication Research; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, G.; Luo, W.; Lin, Q. A novel pathogenic bacteria (Vibrio fortis) causing enteritis in cultured seahorses, Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.L.; Mourino, J.L.P.; Fezer, G.F.; Neto, C.C.B.; Garcia, P.; Silva, B.C.; Jatobá, A.; Vieira, F.N. Isolation and experimental infection with Vibrio alginolyticus in the sea horse, Hippocampus reidi Ginsburg, 1933 (Osteichthyes: Syngnathidae) in Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2010, 70, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.H.; Zheng, L.Y.; Huang, Z.C.; Lin, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, C. Identification and characterization of pathogen Vibrio rotiferianus, a pathogen isolated from Hippocampus erectus with tail-rot disease. J. Fish. Sci. China 2017, 24, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.Y.; Yang, N.; Feng, H.M.; Huang, H.; Wu, Y.T. Isolation, identification and biological control of enteritis pathogenic bacteria from Hippocampus kuda. Genom. App. Biol. 2018, 37, 5317–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.X.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, L.B.; Zhou, B.B.; Ye, D.D.; Zheng, X.K.; Lin, Y.S.; Zeng, W.L.; Zhou, T.L.; Ye, J.Z. Cluster differences in antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation, mobility, and virulence of clinical Enteroacter cloacae complex. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 814831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.J.; Huang, H.; Yang, N.; Feng, H.M.; Li, Y.; Han, B.B. Isolation, identification, and biological control in vitro of tail rot pathogen strain from Hippocampus kuda. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.H.; Hao, S.; Fu, J.P.; Sun, H.C.; Luo, Z. Identification of Mycobacterium chelonae from lined seahorse Hippocampus erectus and histopathological analysis. Fishes 2023, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagui, G.S.; Moreira, N.; Santos, D.V.; Paschoalato, C.; Sierra, J.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.; Darini, A.C.; Andrade, L.N.; Segura-Muoz, S. Multidrug-resistant Enterobacter spp. in wastewater and surface water: Molecular characterization of β-lactam resistance and metal tolerance genes. Environ. Res. 2023, 233, 116443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S.S.; Kc, R.; Leong, K.W.; Mac Aogain, M.; O’Toole, R.F. A step-by-step beginner’s protocol for whole genome sequencing of human bacterial pathogens. J. Biol. Methods 2019, 6, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Bezdan, D.; Sielaff, A.C.; Wheeler, K.; Mason, C.E.; Venkateswaran, K. Multi-drug resistant Enterobacter bugandensis species isolated from the International Space Station and comparative genomic analyses with human pathogenic strains. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Christensen, H.; Arahal, D.R.; Costa, M.S.; Rooney, A.P.; Yi, H.; Xu, X.W.; Meyer, S.D.; et al. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.D. A comprehensive description of the TolC effect on the antimicrobial susceptibility profile in Enterobacter bugandensis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1036933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Xie, T.F.; Wu, Q.P.; Li, Y.P.; Lei, T.; Zhang, J.M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Chen, M.T.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis reveals the potential risk of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from ready-to-eat foods in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Dortet, L.; Poirel, L. Carbapenem resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Here is the storm! Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mshana, S.E.; Gerwing, L.; Minde, M.; Hain, T.; Domann, E.; Lyamuya, E.; Chakraborty, T.; Imirzalioglu, C. Outbreak of a novel Enterobacter sp. carrying blaCTX-M-15 in a neonatal unit of a tertiary care hospital in Tanzania. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, C.; Sielaff, A.C.; Frey, K.G.; Allen, J.E.; Singh, N.; Jaing, C.; Wheeler, K.; Venkateswaran, K. Detection of antimicrobial resistance genes associated with the International Space Station environmental surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paytubi, S.; Aznar, S.; Madrid, C.; Balsalobre, C.; Dillon, S.C.; Dorman, C.J.; Juáarez, A. A novel role for antibiotic resistance plasmids in facilitating Salmonella adaptation to non-host environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.C.; Yang, W.; Deng, H.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.Y.; Yi, L.X.; Kuang, Q.H.; Xu, R.; Li, D.; Li, R.N.; et al. Matrine reverses the resistance of Haemophilus parasuis to cefaclor by inhibiting the mutations in penicillin-binding protein genes (ftsI and mrcA). Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1364339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.G.; Paterson, D.L.; Young, B.; Lye, D.C.; Davis, J.S.; Schneider, K.; Yilmaz, M.; Dinleyici, R.; Runnegar, N.; Henderson, A.; et al. Meropenem versus piperacillin-tazobactam for definitive treatment of bloodstream infections caused by AmpC β-Lactamase-producing Enterobacter spp., Citrobacter freundii, Morganella morganii, Providencia spp., or Serratia marcescens: A pilot multicenter randomized controlled trial (MERINO-2). Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratu, S.; Landman, D.; George, A.; Salvani, J.; Quale, J. Correlation of the expression of acrB and the regulatory genes marA, soxS and ramA with antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae endemic to New York city. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Ager-Wick, E.; Kumar, J.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I.; Peng, B.; Evensen, O.; Sorum, H.; Munang’andu, H.M. Aeromonas species isolated from aquatic organisms, insects, chicken, and humans in India show similar antimicrobial resistance profiles. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1008870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ning, J.A.; Sajid, A.; Cheng, G.Y.; Yuan, Z.H.; Hao, H.H. The nature and epidemiology of OqxAB, a multidrug efflux pump. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.J.G.; Morrell, B.; Campos, G.L.; Valvano, M.A. Distribution and diversity of type VI secretion system clusters in Enterobacter bugandensis and Enterobacter cloacae. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Shang, D.W.; Yu, X.H.; Cui, P.; Yang, Y.J.; Sun, J.H. Isolation, identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from Hippocampus erectus. J. Tianjin Agric. Univ. 2022, 29, 52–56, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulla, K.M.A.; Al-Muhanna, A.S. PCR determination of some virulence gene among Enterobacter cloacae isolated from gall-bladder infections. J. Fish. Sci. 2023, 10, 4425–4430. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, K.; Selander, R.K. Intergeneric transfer and recombination of the6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase gene (gnd) in enteric bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10227–10231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Schellhorn, H.E. Role of RpoS in virulence of pathogens. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, B.; Dong, X.; Sheng, A.; Zhang, X. A mutation in rcsB, a gene encoding the core component of the Rcs cascade, enhances the virulence of Edwardsiella tarda. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.H.; Sun, L. The global regulatory effect of Edwardsiella tarda Fur on iron acquisition, stress resistance, and host infection: A proteomics-based interpretation. J. Proteom. 2016, 140, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Dong, J.F.; Li, R.Q.; Li, L.; Zou, Q.H. Roles of the Hcp family proteins in the pathogenicity of Salmonella typhimurium 14028s. Virulence 2020, 11, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.Q.; Xu, H.D.; Su, Y.L.; Liu, S.L.; Xu, L.W.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J.J.; Cheng, C.H.; Feng, J. Horizontal gene transfer contributes to virulence and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio harveyi 345 based on complete genome sequence analysis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhas, M.; van der Meer, J.R.; Gaillard, M.; Harding, R.M.; Hood, D.W.; Crook, D.W. Genomic islands: Tools of bacterial horizontal gene transfer and evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napit, R.; Gurung, A.; Poudel, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Manandhar, P.; Sharma, A.N.; Raut, S.; Pradhan, S.M.; Joshi, J.; Poyet, M.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of human, animal, and environmental samples identifies potential emerging pathogens, profiles antibiotic resistance genes, and reveals horizontal gene transfer dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishii, K.; Morozumi, M.; Chiba, N.; Ono, A.; Ubukata, K. Direct detection by real-time PCR of ftsI gene mutations affecting MICs of β-lactam agents for Haemophilus influenzae isolates from meningitis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2011, 17, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, X.; Luo, C.; Zou, C.; Liu, X. The beginning of the rpoB gene in addition to the rifampin resistance determination region might be needed for identifying refampin/refabutin cross-resistance in multidrug-resistance Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Southern China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 50, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yeh, H.W.; Lan, C.Y. Role of the BaeSR two-component system in the regulation of Acinetobacter baumannii adeAB genes and its correlation with tigecycline susceptibility. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.N.; Wang, F.; Su, X.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Ma, Z.H.; Gao, L.K.; Yan, H.S.; Xue, Y.Y.; Lv, C.H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Supplementation with Enterococcus faecium enhances growth performance, intestinal health and immunity of big-belly seahorses (Hippocampus abdominalis) during diet conversion. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnip, E.R.; Widanarni, W.; Meryandini, A. Selection of lactic acid bacteria as a probiotic and evaluated its performance on gnotobiotic catfish Clarias sp. J. Akuakultur Indones. 2018, 17, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyaningsih, S.; Prayitno, S.B. Patogenisity Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from catfish (Clarias gariepinus) from Boyolali. J. Aquac. Manag. Technol. 2014, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xia, X.D. PhoP/PhoQ Two-Component System Contributes to Intestinal Inflammation Induced by Cronobacter sakazakii in Neonatal Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.T.; Mekalanos, J.J. In vivo actin cross-linking induced by Vibrio cholerae type VI secretion system is associated with intestinal inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4365–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.P.; He, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.B.; Ai, X.H. Hafnia alvei: A pathogen causing infectious intussusception syndrome (IIS) in farmed channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Isr. J. Aquac.—Bamidgeh 2016, 68, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Feature | Genome |
|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 4,821,486 |
| Plasmid | 0 |
| Chromosome | 1 |
| GC content (%) | 55.91 |
| Number of CDS | 4438 |
| Gene average length (bp) | 971.21 |
| Number of tRNAs | 83 |
| Number of 5S rRNAs | 9 |
| Number of 16S rRNAs | 8 |
| Number of 23S rRNAs | 8 |
| sRNAs | 181 |
| Repeated regions (%) | 0.29 |
| Number of repeats | 104 |
| Number of GIs | 12 |
| Number of prophages | 4 |
| Number of IS | 1 |
| Characterization | Isolate H4 | E. bugandensis Strain EB-247 a |
|---|---|---|
| Voges–Proskauer | - | - |
| Arginine dihydrolase | + | + |
| Lysine decarboxylase | - | - |
| Ornithine decarboxylase | + | + |
| β-galactosidase | + | + |
| Urease | - | - |
| Phenylalanine deaminase | - | ND |
| Indole production | - | - |
| H2S production | - | - |
| Gelatin hydrolysis | - | - |
| Citrate utilization | + | + |
| Glucose fermentation | + | + |
| Sucrose fermentation | + | + |
| Mannitol fermentation | + | + |
| Rhamnose fermentation | + | + |
| Melibiose fermentation | + | + |
| Arabinose fermentation | + | + |
| Inositol fermentation | + | + |
| Sorbitol fermentation | + | + |
| Amygdalin fermentation | - | - |
| Antimicrobial Category | Antimicrobial Agent | Content (μg/disc) | Zone Diameter Breakpoints (mm) | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | Susceptibility | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | I | R | |||||
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 10 | ≥15 | 13–14 | ≤12 | 16.20 ± 0.26 d | S |
| Kanamycin | 30 | ≥18 | 14–17 | ≤13 | 19.43 ± 0.42 c | S | |
| Cephalosporins | Cefazolin | 30 | ≥23 | 20–22 | ≤19 | 0 ± 0 f | R |
| Cefuroxime | 30 | ≥18 | 15–17 | ≤14 | 0 ± 0 f | R | |
| Ceftazidine | 30 | ≥21 | 18–20 | ≤17 | 0 ± 0 f | R | |
| Penicillins | Ampicillin | 10 | ≥17 | 14–16 | ≤13 | 0 ± 0 f | R |
| Piperacillin | 100 | ≥21 | 25–29 | ≤17 | 0 ± 0 f | R | |
| Quinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 5 | ≥21 | 22–25 | ≤15 | 30.43 ± 0.21 a | S |
| Sulfonamides | Cotrimoxazole * | 23.75/1.25 | ≥16 | 11–15 | ≤10 | 21.80 ± 0.52 b | S |
| Tetracyclines | Doxycycline * | 30 | ≥14 | 11–13 | ≤10 | 0 ± 0 f | R |
| Minocycline | 30 | ≥16 | 13–15 | ≤12 | 0 ± 0 f | R | |
| Tetracycline * | 30 | ≥15 | 12–14 | ≤11 | 9.43 ± 0.42 e | R | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, H.; Teng, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Diao, J.; Yu, L.; Gai, C.; et al. Isolation, Identification, and Virulence Properties of Enterobacter bugandensis Pathogen from Big-Belly Seahorse Hippocampus abdominalis. Fishes 2025, 10, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080411
Ye H, Teng C, Yang Y, Liu Y, Li L, Fan Y, Wang Y, Diao J, Yu L, Gai C, et al. Isolation, Identification, and Virulence Properties of Enterobacter bugandensis Pathogen from Big-Belly Seahorse Hippocampus abdominalis. Fishes. 2025; 10(8):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080411
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Haibin, Chenhao Teng, Yueqi Yang, Yiyao Liu, Li Li, Ying Fan, Youhong Wang, Jing Diao, Lingling Yu, Chunlei Gai, and et al. 2025. "Isolation, Identification, and Virulence Properties of Enterobacter bugandensis Pathogen from Big-Belly Seahorse Hippocampus abdominalis" Fishes 10, no. 8: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080411
APA StyleYe, H., Teng, C., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Li, L., Fan, Y., Wang, Y., Diao, J., Yu, L., Gai, C., & Cao, H. (2025). Isolation, Identification, and Virulence Properties of Enterobacter bugandensis Pathogen from Big-Belly Seahorse Hippocampus abdominalis. Fishes, 10(8), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080411






