Ontogenetic and Sex-Specific Isotopic Niches of Blue Sharks (Prionace glauca) in the Northwestern Pacific
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
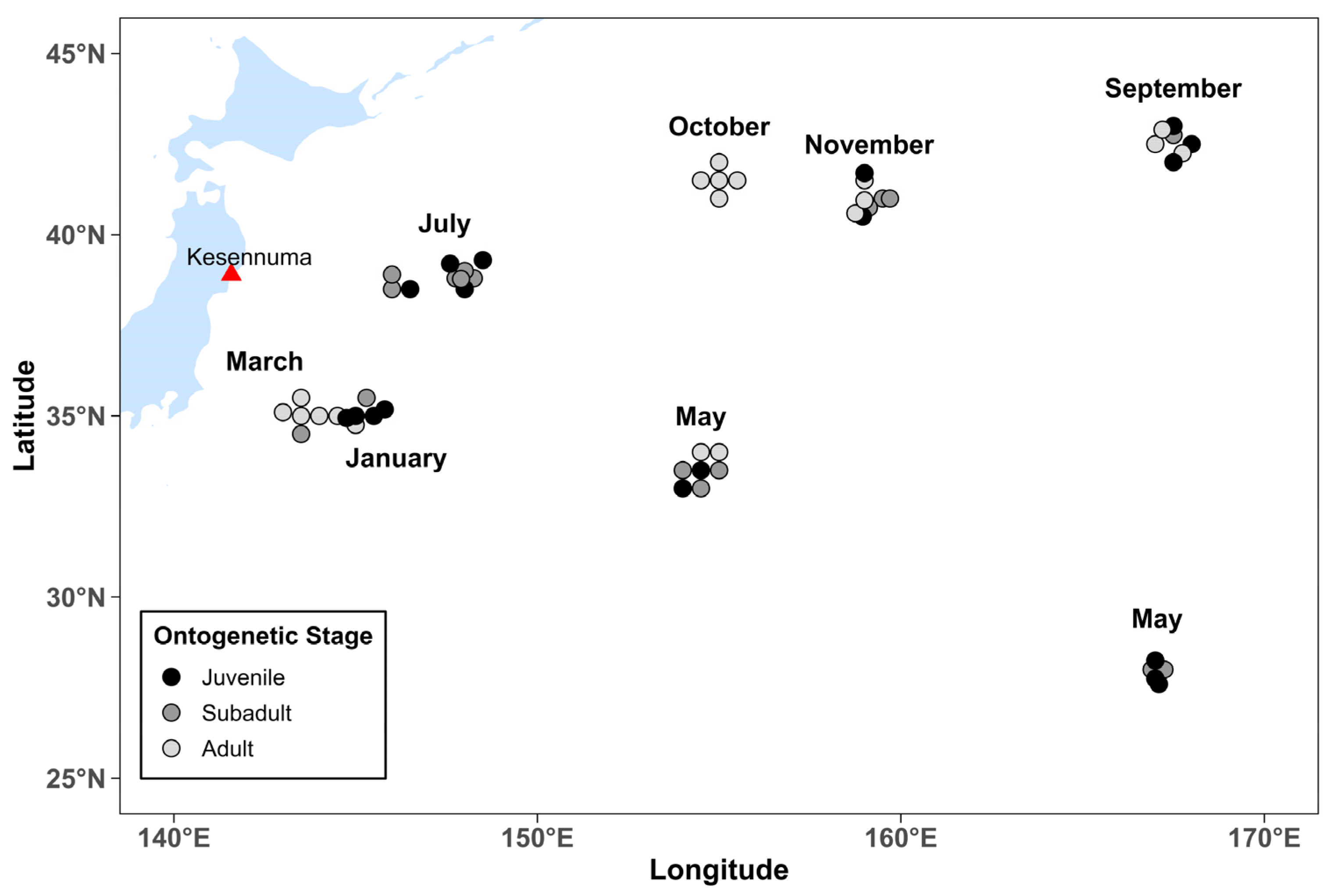
2.1. Sampling
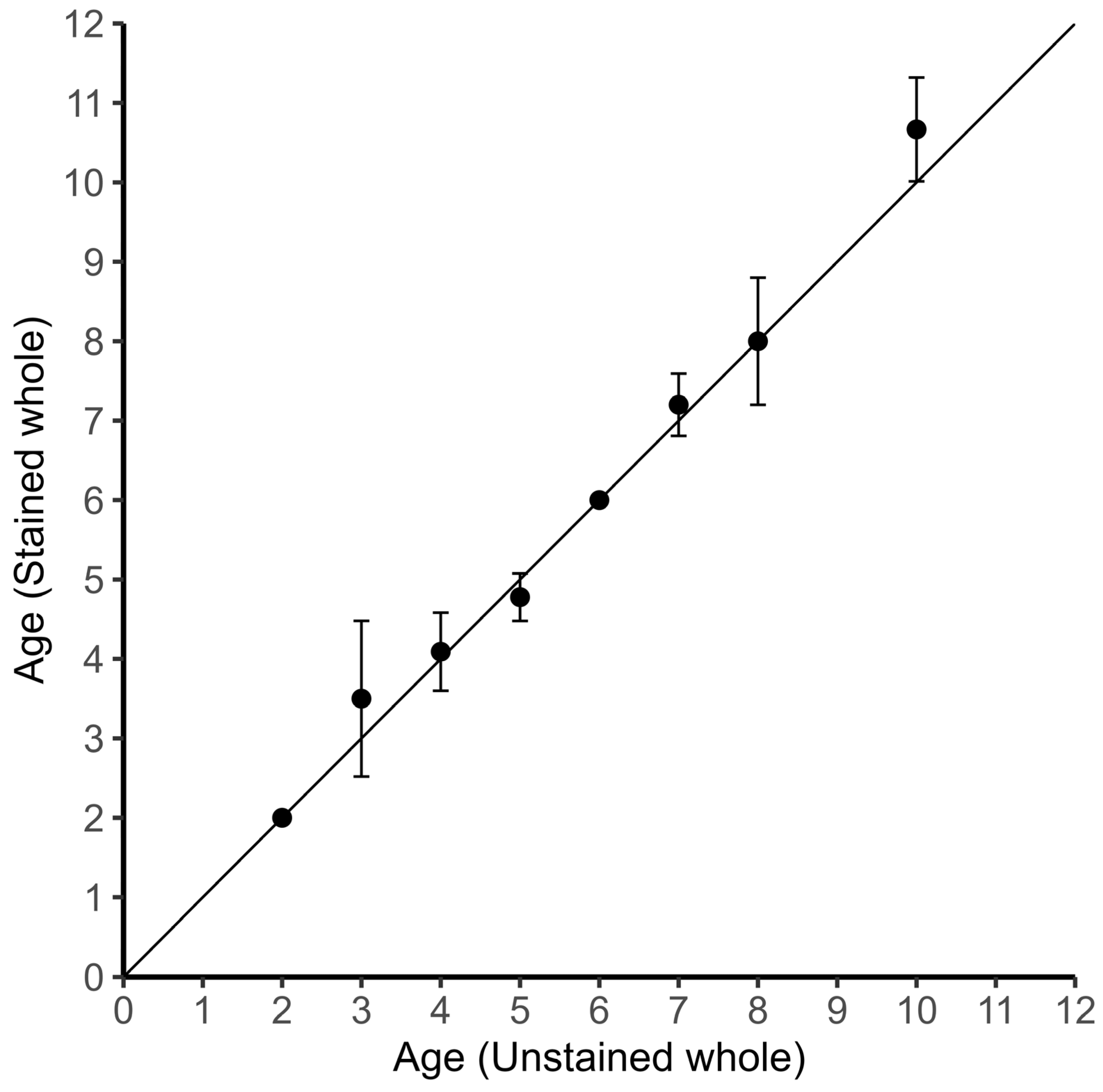
2.2. Age Estimation
2.3. Relative Age-Group Classification
2.4. Stable Isotope Analysis Procedures
2.5. Niche Breadth and Isotopic Overlap Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Age Determination and Verification
3.2. Seasonal Variation in Body Size
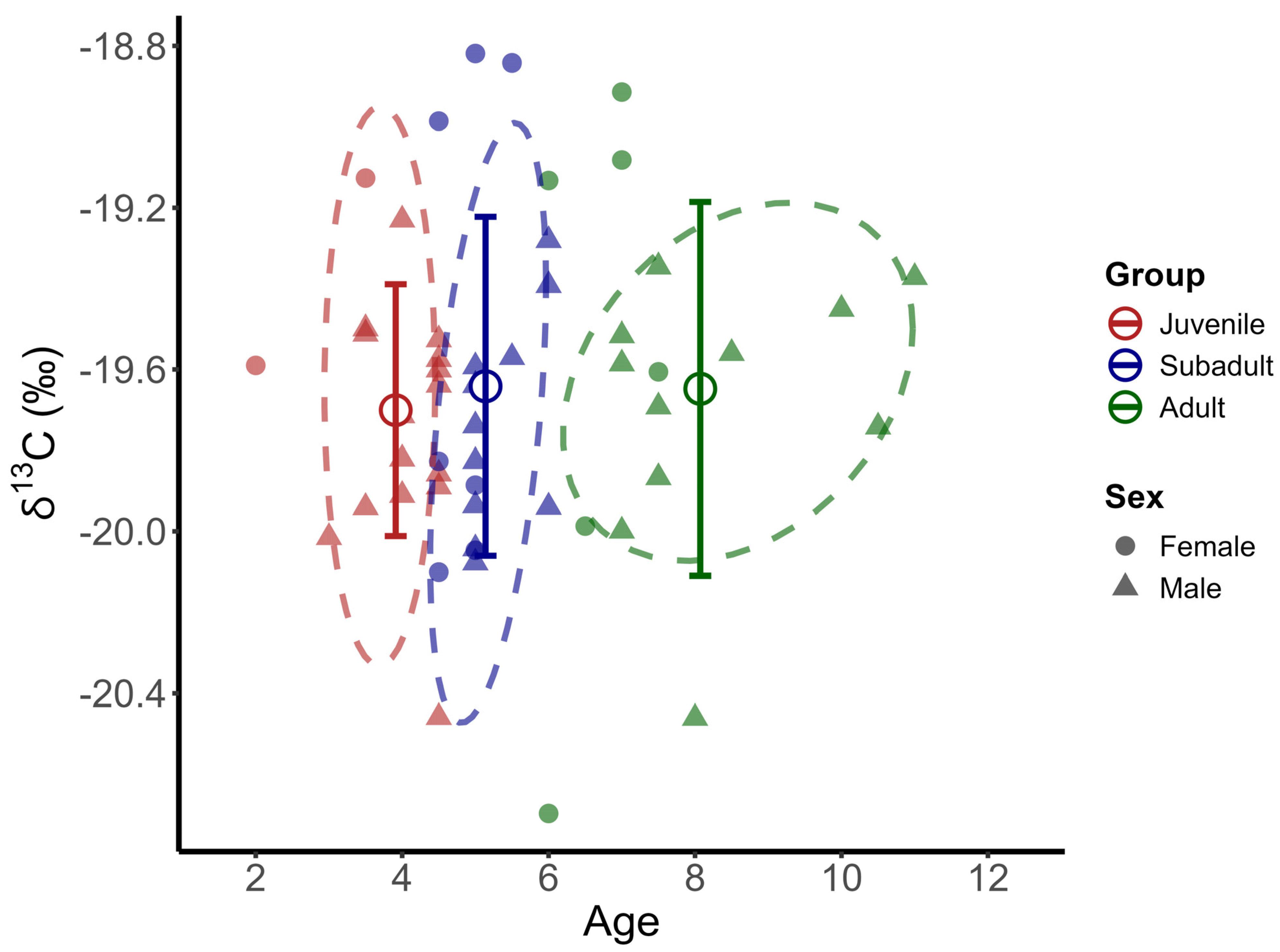
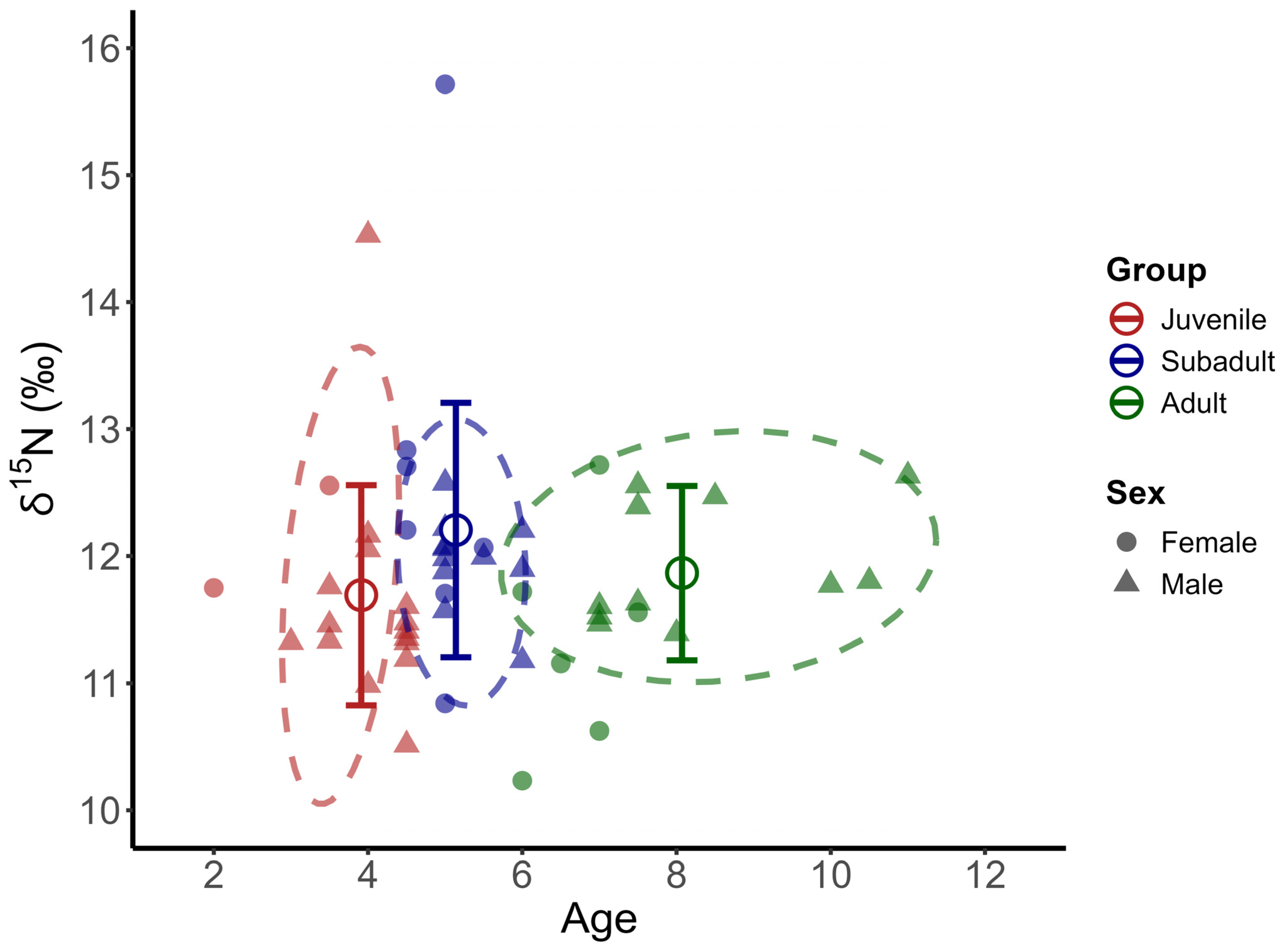
3.3. Stable Isotopic Results
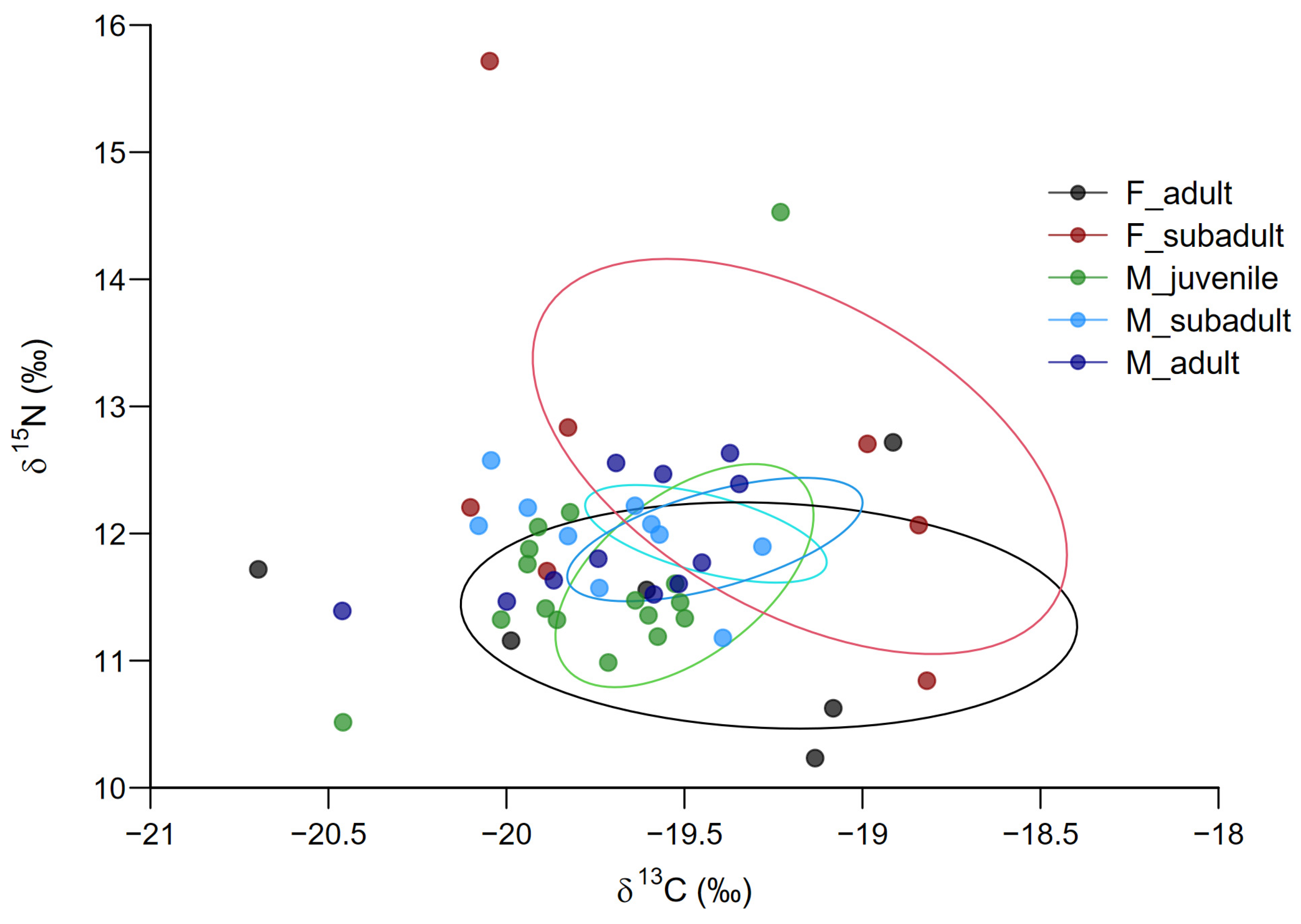
3.4. Isotopic Niche Breadth and Overlap
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Patterns
4.2. Food Sources
4.3. Trophic Levels
4.4. Niche Breadth and Isotopic Overlap
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sih, A.; Cote, J.; Evans, M.; Fogarty, S.; Pruitt, J. Ecological implications of behavioural syndromes. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, S.R.; Bell, A.M.; Bolnick, D.I.; Ratnieks, F.L. An evolutionary ecology of individual differences. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Svanbäck, R.; Fordyce, J.A.; Yang, L.H.; Davis, J.M.; Hulsey, C.D.; Forister, M.L. The ecology of individuals: Incidence and implications of individual specialization. Am. Nat. 2003, 161, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réale, D.; Garant, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Bergeron, P.; Careau, V.; Montiglio, P.O. Personality and the emergence of the pace-of-life syndrome concept at the population level. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, A.B.; Goldman, K.J.; Litvin, S.Y.; Madigan, D.J.; Bigman, J.S.; Swithenbank, A.M.; Kline, T.C., Jr.; Block, B.A. Stable isotope analysis of vertebrae reveals ontogenetic changes in habitat in an endothermic pelagic shark. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20141446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasby-Lucas, N.; Dewar, H.; Sosa-Nishizaki, O.; Wilson, C.; Hyde, J.R.; Vetter, R.D.; Wraith, J.; Block, B.A.; Kinney, M.J.; Sippel, T.; et al. Movements of electronically tagged shortfin mako sharks (Isurus oxyrinchus) in the eastern North Pacific Ocean. Anim. Biotelemetry 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosal, A.P.; Cartamil, D.P.; Wegner, N.C.; Lam, C.H.; Hastings, P.A. Movement ecology of young-of-the-year blue sharks Prionace glauca and shortfin makos Isurus oxyrinchus within a putative binational nursery area. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 623, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.P.; Handy, R.D.; Gruber, S.H. Ontogenetic diet shifts and prey selection in nursery bound lemon sharks, Negaprion brevirostris, indicate a flexible foraging tactic. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2012, 95, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfil, R.; Clarke, S.; Nakano, H. The biology and ecology of the oceanic whitetip shark, Carcharhinus longimanus. In Sharks of the Open Ocean: Biology, Fisheries and Conservation; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, M.; Bengil, E.G.T.; Palmer, J.L.; Beton, D.; Çağlar, Ç.; Godley, B.J.; Özkan, M.; Snape, R.T.E.; Broderick, A.C. Diversity and distribution of elasmobranchs in the coastal waters of Cyprus: Using bycatch data to inform management and conservation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1181437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2022-2; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Fowler, S.L.; Musick, J.A.; Cavanagh, R.D.; Kyne, P.M.; Harrison, L.R.; Carlson, J.K.; Davidson, L.N.; Fordham, S.V.; Francis, M.P.; et al. Extinction risk and conservation of the world’s sharks and rays. eLife 2014, 3, e00590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Seki, M.P. Synopsis of biological data on the blue shark, Prionace glauca Linnaeus. Bull. Fish. Res. Agency Jpn. 2003, 2003, 18–55. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.R.; Wetklo, M.; Supernault, J.; Taguchi, M.; Yokawa, K.; Sosa-Nishizaki, O.; Withler, R.E. Genetic analysis of stock structure of blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the north Pacific ocean. Fish. Res. 2015, 172, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.J.; Quintans, M.; Ramos-Cartelle, A.; Mejuto, J. Movements and environmental preferences of the shortfin mako, Isurus oxyrinchus, in the southeastern Pacific Ocean. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, L.; Dando, M.; Fowler, S. A Field Guide to the Sharks of the World; Collins: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés, E. Standardized diet compositions and trophic levels of sharks. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1999, 56, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.R.; Knip, D.M.; Simpfendorfer, C.A.; Dulvy, N.K. Sizing up the ecological role of sharks as predators. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 495, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.; Meléndez, R.; Barría, P. Preliminary diet analysis of the blue shark Prionace glauca in the eastern South Pacific. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2010, 45, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, Y.; Nakatsuka, S.; Ohshimo, S. Feeding Habits of the Blue Shark (Prionace glauca) in the Northwestern Pacific Based on Stomach Contents and Stable Isotope Ratios. Pac. Sci. 2018, 72, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preti, A.; Soykan, C.U.; Dewar, H.; Wells, R.D.; Spear, N.; Kohin, S. Comparative feeding ecology of shortfin mako, blue and thresher sharks in the California Current. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2012, 95, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Aguilar, S.B.; Escobar-Sánchez, O.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Abitia-Cárdenas, L.A. Trophic ecology of the blue shark (Prionace glauca) based on stable isotopes (δ13C and δ15N) and stomach content. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2016, 96, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.R.; Clarke, D.C.; Martins, H.R.; Silva, H.M. The Diet of the Blue Shark (Prionace glauca L.) in Azorean Waters. 1996. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.3/1491 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Rosas-Luis, R.; Navarro, J.; Loor-Andrade, P.; Forero, M.G. Feeding ecology and trophic relationships of pelagic sharks and billfishes coexisting in the central eastern Pacific Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 573, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaida, U.; Sosa-Nishizaki, O. Food and feeding habits of the blue shark Prionace glauca caught off Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico, with a review on its feeding. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2010, 90, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, Y.; Kanaiwa, M.; Ohshimo, S.; Takahashi, N.; Kai, M.; Yokawa, K. Relative abundance trend of the blue shark Prionace glauca based on Japanese distant-water and offshore longliner activity in the North Pacific. Fish. Sci. 2016, 82, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, I.F.; Darvell, B.W. Shark fishing vs. conservation: Analysis and synthesis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfadyen, G. Blue Shark: Economic Valuation of the Global Market for Blue Shark Products and Interdependent. 2022. Available online: https://coilink.org/20.500.12592/tvmxxs (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Kai, M. Spatio-temporal changes in catch rates of pelagic sharks caught by Japanese research and training vessels in the western and central North Pacific. Fish. Res. 2019, 216, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.I.; Woodley, C.M.; Brudek, R.L. A Preliminary Evaluation of the Status of Shark Species; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Aires-da-Silva, A.M.; Gallucci, V.F. Demographic and risk analyses applied to management and conservation of the blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the North Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2007, 58, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.C.; McAllister, M.K.; Milner-Gulland, E.J.; Kirkwood, G.P.; Michielsens, C.G.J.; Agnew, D.J.; Pikitch, E.K.; Nakano, H.; Shivji, M.S. Global estimates of shark catches using trade records from commercial markets. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, C.L.; Barreto, R.; Carlson, J.; Fernando, D.; Fordham, S.; Francis, M.P.; Herman, K.; Jabado, R.W.; Liu, K.M.; Marshall, A.; et al. Prionace glauca . IUCN Red List Threat. Species 2019, 2019, e.T39381A2915850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubodera, T.; Watanabe, H.; Ichii, T. Feeding habits of the blue shark, Prionace glauca, and salmon shark, Lamna ditropis, in the transition region of the Western North Pacific. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2007, 17, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, E.; Herzka, S.Z.; Sosa-Nishizaki, O.; Lowe, C.G.; O’Sullivan, J.B. Stable isotope analysis of juvenile white sharks inside a nursery area reveals foraging in demersal-inshore habitats and trophic overlap with sympatric sharks. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 687738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, N.E.; MacNeil, M.A.; Olin, J.A.; McMeans, B.C.; Kinney, M.J.; Chapman, D.D.; Fisk, A.T. Stable isotopes and elasmobranchs: Tissue types, methods, applications and assumptions. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 1449–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.; López, L.; Coll, M.; Barría, C.; Sáez-Liante, R. Short-and long-term importance of small sharks in the diet of the rare deep-sea shark Dalatias licha. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L.; Tinker, M.T.; Estes, J.A.; Koch, P.L. Ontogenetic and among-individual variation in foraging strategies of northeast Pacific white sharks based on stable isotope analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hette-Tronquart, N. Isotopic niche is not equal to trophic niche. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1987–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, D.J.; Carlisle, A.B.; Dewar, H.; Snodgrass, O.E.; Litvin, S.Y.; Micheli, F.; Block, B.A. Stable isotope analysis challenges wasp-waist food web assumptions in an upwelling pelagic ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, Y.; Chen, X.; Dai, X.; Zhu, J. Trophic ecology of sharks in the mid-east Pacific ocean inferred from stable isotopes. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2014, 13, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estupiñán-Montaño, C.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Sánchez-González, A.; Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Delgado-Huertas, A.; Páez-Rosas, D. Dietary ontogeny of the blue shark, Prionace glauca, based on the analysis of δ13C and δ15N in vertebrae. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo-Silva, C.J.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Delgado-Huertas, A. Trophic inferences of blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the Mexican Pacific from stable isotope analysis in teeth. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabehagasoa, N.; Lorrain, A.; Bach, P.; Potier, M.; Jaquemet, S.; Richard, P.; Ménard, F. Isotopic niches of the blue shark Prionace glauca and the silky shark Carcharhinus falciformis in the southwestern Indian Ocean. Endanger. Species Res. 2012, 17, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Cardador, L.; Garcia-Barcelona, S.; Macias, D.; Druon, J.N.; Coll, M.; Navarro, J. The relative importance of biological and environmental factors on the trophodynamics of a pelagic marine predator, the blue shark (Prionace glauca). Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 183, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailliet, G.M.; Smith, W.D.; Mollet, H.F.; Goldman, K.J. Age and growth studies of chondrichthyan fishes: The need for consistency in terminology, verification, validation, and growth function fitting. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2006, 77, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.E. Age Determination of Elasmobranchs, with Special Reference to Mediterranean Species: A Technical Manual. In General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean; Studies and Reviews; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; Volume 94, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami, Y.; Semba, Y.; Tanaka, S. Age determination and growth of the blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the western North Pacific Ocean. Fish. Bull. 2019, 117, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megalofonou, P.; Damalas, D.; De Metrio, G. Biological characteristics of blue shark, Prionace glauca, in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2009, 89, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomal, G.B.; Natanson, L.J. Age and growth of the blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the North Atlantic Ocean. Fish. Bull.-Natl. Ocean. Atmos. Adm. 2003, 101, 627–639. [Google Scholar]
- Başusta, N.; Demirhan, S.A.; Çiçek, E.; Başusta, A.; Kuleli, T. Age and growth of the common guitarfish, Rhinobatos rhinobatos, in Iskenderun Bay (north-eastern Mediterranean, Turkey). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2008, 88, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, M.J.; Carvalho, F.; Kai, M.; Semba, Y.; Liu, K.M.; Tsai, W.P.; Leonardo, C.G.; Horacio, H.A.; Daniel, C.C.; Teo, S.L.H. Cluster Analysis Used to Re-Examine Fleet Definitions of North Pacific Fisheries with Spatiotemporal Consideration of Blue Shark Size and Sex Data. 2022. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/40453 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Nakano, H. Age, reproduction and migration of blue shark Prionace in the north Pacific ocean. Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Far Seas Fish. 1994, 31, 141–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.L.; Koch, P.L. Methods to collect, preserve, and prepare elasmobranch tissues for stable isotope analysis. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2012, 95, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiffman, D.S.; Gallagher, A.J.; Boyle, M.D.; Hammerschlag-Peyer, C.M.; Hammerschlag, N. Stable isotope analysis as a tool for elasmobranch conservation research: A primer for non-specialists. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, M.; Tokuhiro, T.; Suyama, Y. On the urea content and the ammonia formation of the muscle of sharkfish. I. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1950, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, Y.; Kurashima, A.; Shiozaki, K.; Hiraoka, Y.; Semba, Y.; Ohshimo, S.; Nakano, H.; Kai, M. New insights into spatial segregation by sex and life-history stage in blue sharks Prionace glauca in the northwestern Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 696, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshimo, S.; Madigan, D.J.; Kodama, T.; Tanaka, H.; Komoto, K.; Suyama, S.; Ono, T.; Yamakawa, T. Isoscapes reveal patterns of δ13C and δ15N of pelagic forage fish and squid in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 175, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, J.A.; Rice, A.N.; Lutcavage, M.E.; Skomal, G.B. Predicting trophic position in sharks of the north-west Atlantic Ocean using stable isotope analysis. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2003, 83, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, F.G.; Scharold, J.V.; Kalmijn, A.J. Movements of blue sharks (Prionace glauca) in depth and course. Mar. Biol. 1990, 106, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, K.C.; Castilho, P.C.; Morrissette, J.M.; Landeira-Fernandez, A.M.; Holts, D.B.; Schallert, R.J.; Goldman, K.J.; Block, B.A. Satellite tagging and cardiac physiology reveal niche expansion in salmon sharks. Science 2005, 310, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Kubodera, T.; Moku, M.; Kawaguchi, K. Diel vertical migration of squid in the warm core ring and cold water masses in the transition region of the western North Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 315, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubodera, T. Cephalopod fauna off Sanriku and Joban districts, northeastern Japan. In Memoirs of the National Science Museum, Tokyo; National Science Museum: Tokyo, Japan, 1996; Volume 29, pp. 187–207. [Google Scholar]
- Carbonara, P.; Prato, G.; Alfonso, S.; Bottaro, M.; Hinrichs, T.; Krumme, U.; Neglia, C.; Niedermüller, S.; Toomey, L.; Zupa, W. Blue shark vertical movement patterns in the Central Mediterranean: Bycatch mitigation windows revealed from pop-up satellite archival tag data. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2024, 34, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rincón, R.O.; Acosta-Pachón, T.A. Effect of environmental factors, fish size, and baseline on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope variability in Thunnus alalunga, T. albacares, and T. obesus in the Pacific Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 203, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricas, T.C. Relationships of the blue shark, Prionace glauca, and its prey species near Santa Catalina Island, California. Fish. Bull. 1979, 77, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Scharf, F.S.; Juanes, F.; Rountree, R.A. Predator size-prey size relationships of marine fish predators: Interspecific variation and effects of ontogeny and body size on trophic-niche breadth. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 208, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, F.F. On the role of dense aggregations of males and juveniles in the functional structure of the range of the blue shark Prionace glauca. J. Ichthyol. 2006, 46, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, N.E.; Brush, J.; McCarthy, I.D.; Fisk, A.T. δ15N and δ13C diet–tissue discrimination factors for large sharks under semi-controlled conditions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 155, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goñi, N.; Arrizabalaga, H. Seasonal and interannual variability of fat content of juvenile albacore (Thunnus alalunga) and bluefin (Thunnus thynnus) tunas during their feeding migration to the Bay of Biscay. Prog. Oceanogr. 2010, 86, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudo, J.J.; Wetherbee, B.M.; Wood, A.D.; Weng, K.; Howey-Jordan, L.A.; Harvey, G.M.; Shivji, M.S. Vertical movements of shortfin mako sharks Isurus oxyrinchus in the western North Atlantic Ocean are strongly influenced by temperature. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 547, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altabet, M.A. Nitrogen isotopic evidence for micronutrient control of fractional NO3− utilization in the equatorial Pacific. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, D.M.; Granger, J.; DiFiore, P.J.; Lehmann, M.M.; Ho, R.; Cane, G.; Van Geen, A. Coupled nitrogen and oxygen isotope measurements of nitrate along the eastern North Pacific margin. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethybridge, H.; Choy, C.A.; Logan, J.M.; Allain, V.; Lorrain, A.; Bodin, N.; Somes, C.J.; Young, J.; Ménard, F.; Langlais, C.; et al. A global meta-analysis of marine predator nitrogen stable isotopes: Relationships between trophic structure and environmental conditions. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, D.J.; Shipley, O.N.; Carlisle, A.B.; Dewar, H.; Snodgrass, O.E.; Hussey, N.E. Isotopic tracers suggest limited trans-oceanic movements and regional residency in North Pacific blue sharks (Prionace glauca). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 653606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niella, Y.; Raoult, V.; Gaston, T.; Peddemors, V.M.; Harcourt, R.; Smoothey, A.F. Overcoming multi-year impacts of maternal isotope signatures using multi-tracers and fast turnover tissues in juvenile sharks. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.M.; Lutcavage, M.E. Stable isotope dynamics in elasmobranch fishes. Hydrobiologia 2010, 644, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musyl, M.K.; Brill, R.; Curran, D.S.; Fragoso, N.M.; McNaughton, L.; Nielsen, A.; Kikkawa, B.S.; Moyes, C.D. Postrelease survival, vertical and horizontal movements, and thermal habitats of five species of pelagic sharks in the central Pacific Ocean. Fish. Bull. 2011, 109, 341–368. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, S.M.; Scales, K.L.; Bograd, S.J.; Briscoe, D.K.; Dewar, H.; Hazen, E.L.; Lewison, R.L.; Welch, H.; Crowder, L.B. Seasonal spatial segregation in blue sharks (Prionace glauca) by sex and size class in the Northeast Pacific Ocean. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, H.L., Jr. Reproduction in the blue shark, Prionace glauca. Fish. Bull. 1979, 77, 445–470. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeperre, F.; Aires-da-Silva, A.; Fontes, J.; Santos, M.; Serrão Santos, R.; Afonso, P. Movements of blue sharks (Prionace glauca ) across their life history. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howey, L.A.; Wetherbee, B.M.; Tolentino, E.R.; Shivji, M.S. Biogeophysical and physiological processes drive movement patterns in a marine predator. Mov. Ecol. 2017, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druon, J.N.; Campana, S.; Vandeperre, F.; Hazin, F.H.; Bowlby, H.; Coelho, R.; Queiroz, N.; Serena, F.; Abascal, F.; Damalas, D.; et al. Global-scale environmental niche and habitat of blue shark (Prionace glauca) by size and sex: A pivotal step to improving stock management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 828412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearmouth, V.J.; Sims, D.W. Sexual segregation in marine fish, reptiles, birds and mammals: Behaviour patterns, mechanisms and conservation implications. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2008, 54, 107–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazin, F.H.; Kihara, K.; Otsuka, K.; Boeckman, C.E.; Leal, E.C. Reproduction of the blue shark Prionace glauca in the south-western equatorial Atlantic Ocean. Fish. Sci. 1994, 60, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fujinami, Y.; Shiozaki, K.; Hiraoka, Y.; Semba, Y.; Ohshimo, S.; Kai, M. Seasonal migrations of pregnant blue sharks Prionace glauca in the northwestern Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 658, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimley, A.P. The determinants of sexual segregation in the scalloped hammerhead shark, Sphyrna lewini. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1987, 18, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, J. Indicators of the spatial distribution of blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the North Pacific. WCPFC-SC14-2018/SA WP-09. In Proceedings of the 14th Regular Session of the Scientific Committee, Busan, Republic of Korea, 21 July 2018; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- McCord, M.E.; Campana, S.E. A quantitative assessment of the diet of the blue shark (Prionace glauca) off Nova Scotia, Canada. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 2003, 32, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sex | Age-Defined Group | n | δ13C (‰) Mean ± SE | CV_δ13C (%) | δ15N (‰) Mean ± SE | CV_δ15N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Juvenile | 2 | −19.36 ± 0.23 | 1.69 | 12.15 ± 0.40 | 4.69 |
| F | Subadult | 7 | −19.50 ± 0.22 | 3.02 | 12.58 ± 0.58 | 12.16 |
| F | Adult | 6 | −19.57 ± 0.28 | 3.47 | 11.33 ± 0.36 | 7.75 |
| M | Juvenile | 16 | −19.76 ± 0.07 | 1.44 | 11.65 ± 0.22 | 7.44 |
| M | Subadult | 10 | −19.71 ± 0.08 | 1.35 | 11.97 ± 0.12 | 3.16 |
| M | Adult | 11 | −19.69 ± 0.10 | 1.65 | 11.93 ± 0.14 | 4.02 |
| Age-Defined Group | Juvenile | Subadult | Adult |
|---|---|---|---|
| Juvenile | - | 0.014 | 0.530 |
| Subadult | - | 0.148 | |
| Adult | - |
| Category | M_Juvenile | M_Subadult | M_Adult | F_Subadult | F_Adult | Isotopic Niche SEAc (95% Credible Interval) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M_juvenile | - | 32.03 | 51.93 | 20.89 | 29.52 | 0.70 (0.43–1.15) |
| M_subadult | - | 40.78 | 9.81 | 12.43 | 0.29 (0.16–0.57) | |
| M_adult | - | 14.68 | 18.72 | 0.44 (0.25–0.84) | ||
| F_subadult | - | 50.20 | 2.33 (0.96–4.98) | |||
| F_adult | - | 2.95 (1.41–6.43) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, P.; Katayama, S.; Murakami, H.; Ryan, T.A. Ontogenetic and Sex-Specific Isotopic Niches of Blue Sharks (Prionace glauca) in the Northwestern Pacific. Fishes 2025, 10, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080402
Ding P, Katayama S, Murakami H, Ryan TA. Ontogenetic and Sex-Specific Isotopic Niches of Blue Sharks (Prionace glauca) in the Northwestern Pacific. Fishes. 2025; 10(8):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080402
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Pengpeng, Satoshi Katayama, Hiroaki Murakami, and Tah Andrew Ryan. 2025. "Ontogenetic and Sex-Specific Isotopic Niches of Blue Sharks (Prionace glauca) in the Northwestern Pacific" Fishes 10, no. 8: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080402
APA StyleDing, P., Katayama, S., Murakami, H., & Ryan, T. A. (2025). Ontogenetic and Sex-Specific Isotopic Niches of Blue Sharks (Prionace glauca) in the Northwestern Pacific. Fishes, 10(8), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080402





