Evaluation of Three Atlantic Salmon Strains for Resistance to Copepodid Sea Lice Attachment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish and Husbandry
2.2. Sea Lice Collection and Rearing
2.3. Sea Lice Exposure Challenge
2.4. Lice Enumeration
2.5. Transcriptomic Profiling
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
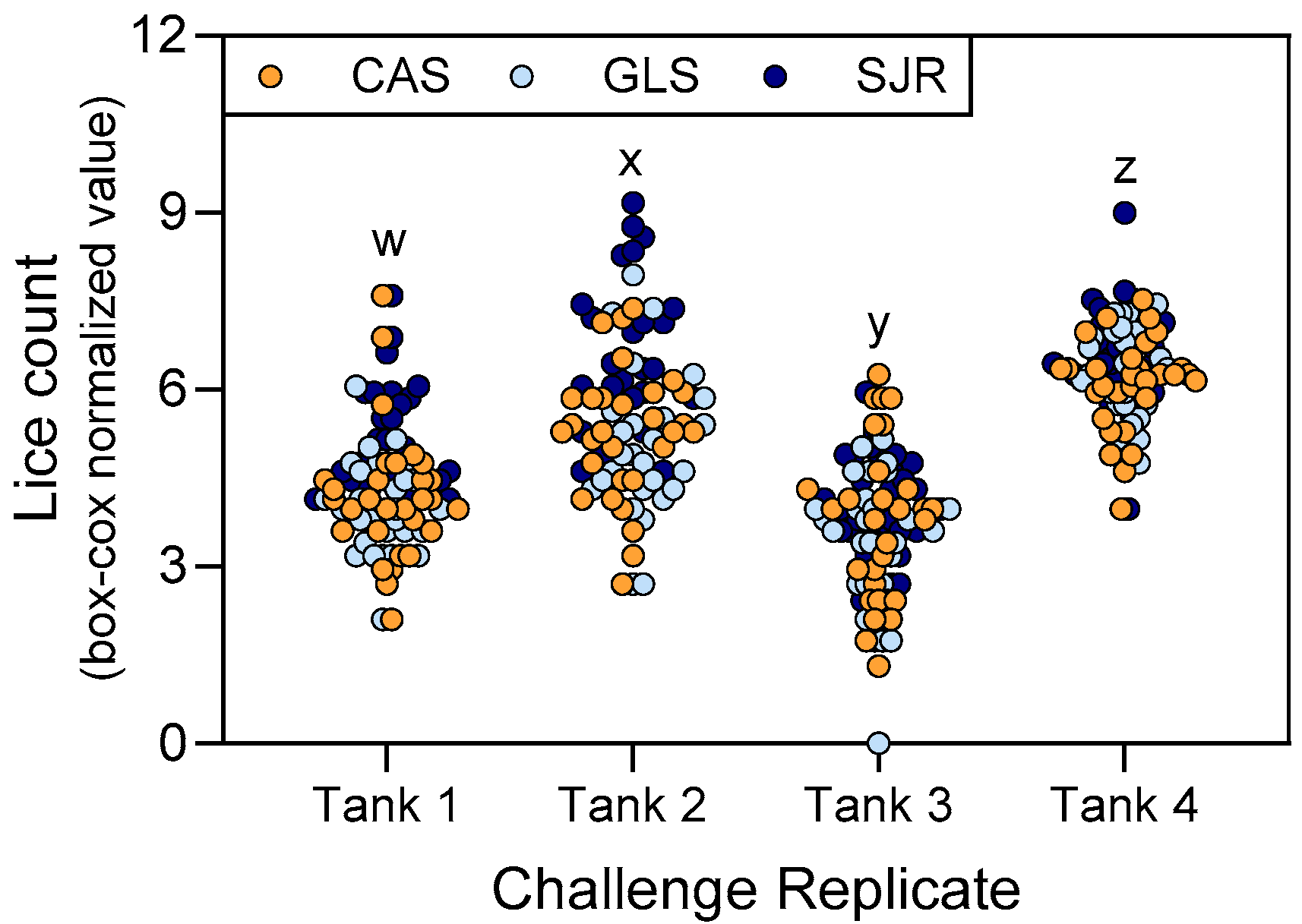
3.1. Challenge Produced High Variation in Sea Lice Attachment Among Replicate Tanks
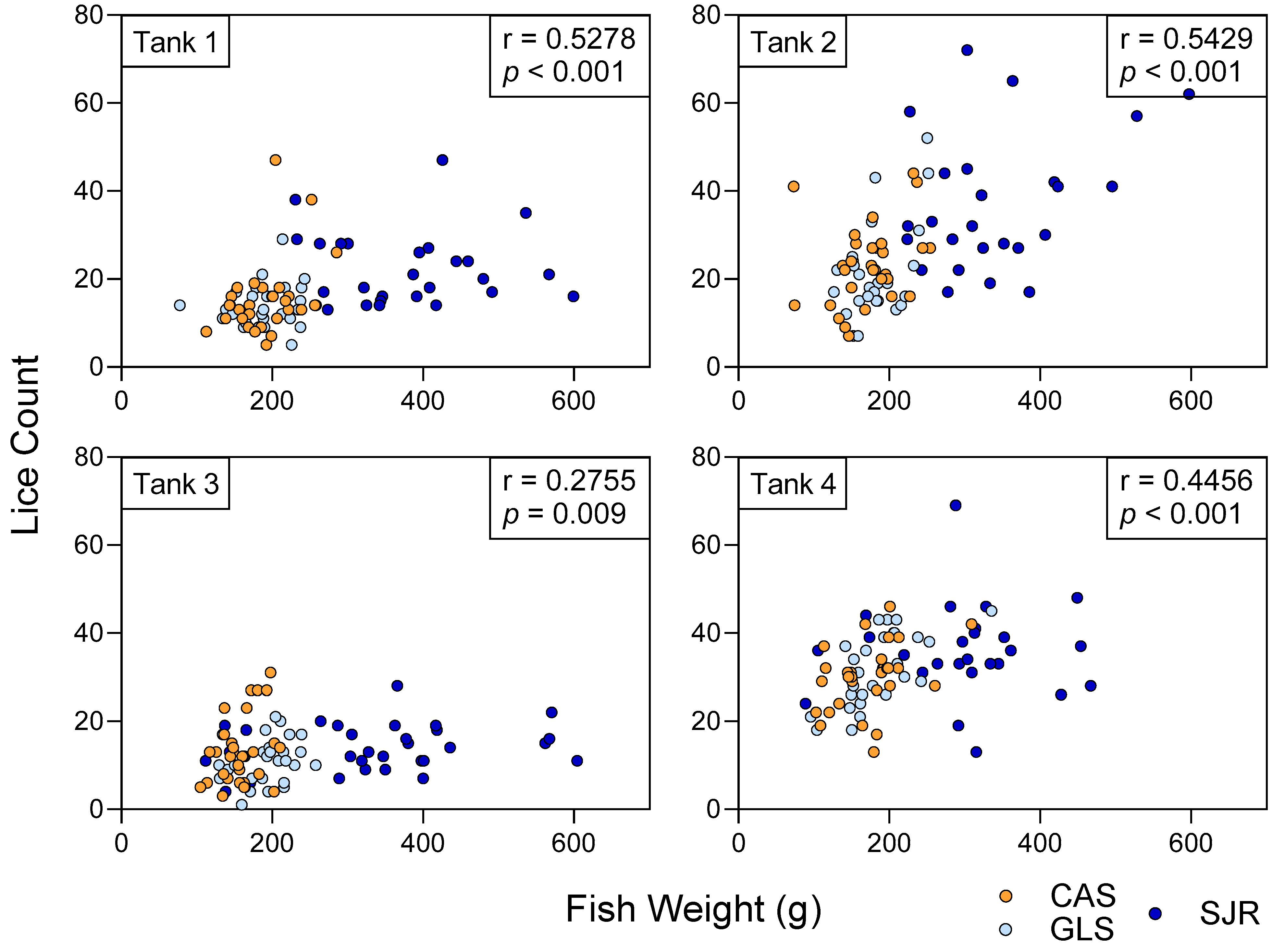
3.2. Copepodid Attachment Was Correlated with the Size (Weight) of Host Fish
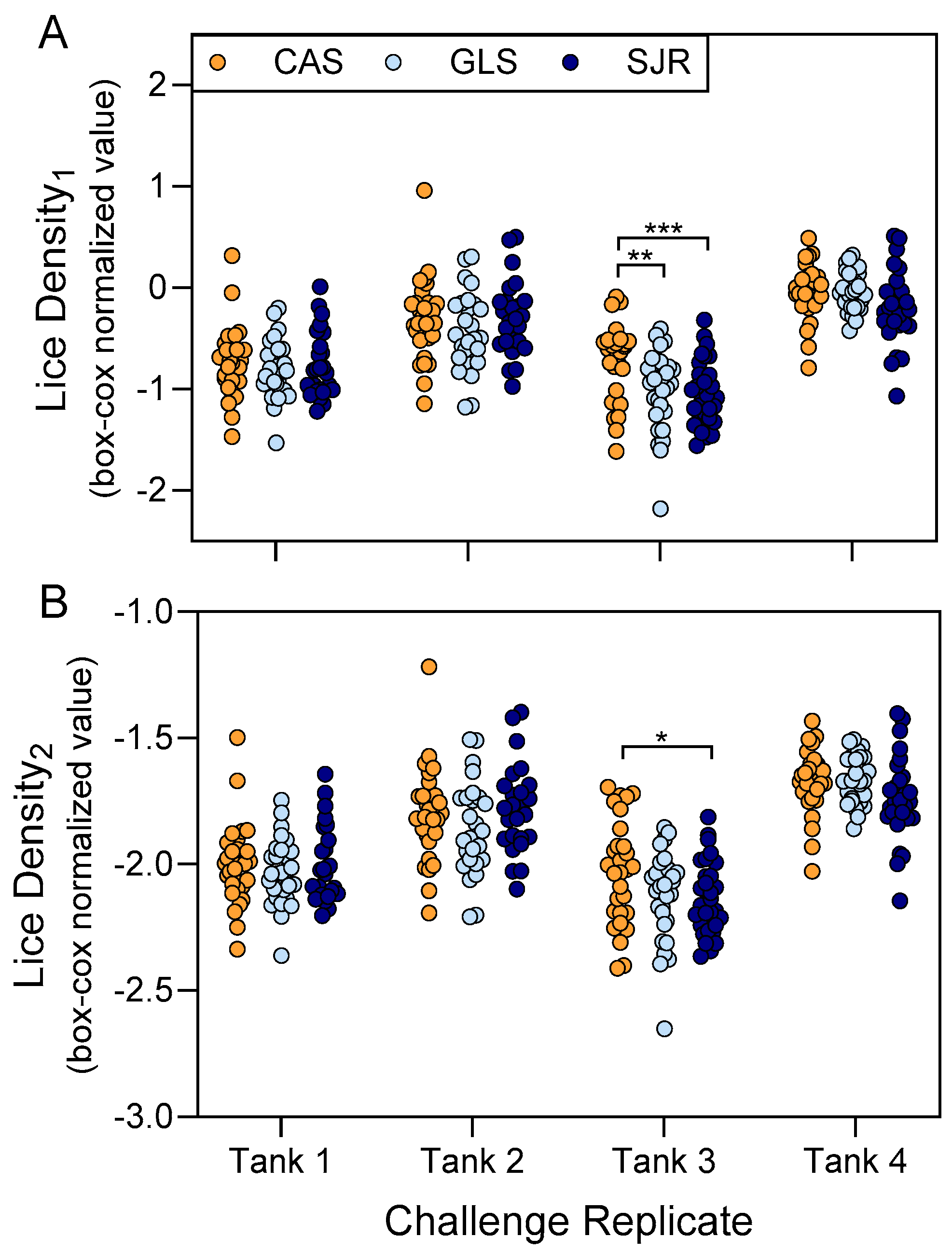
3.3. Strain History of Sea Lice Exposure Contributed Minimally to Differences in Copepodid Attachment Density
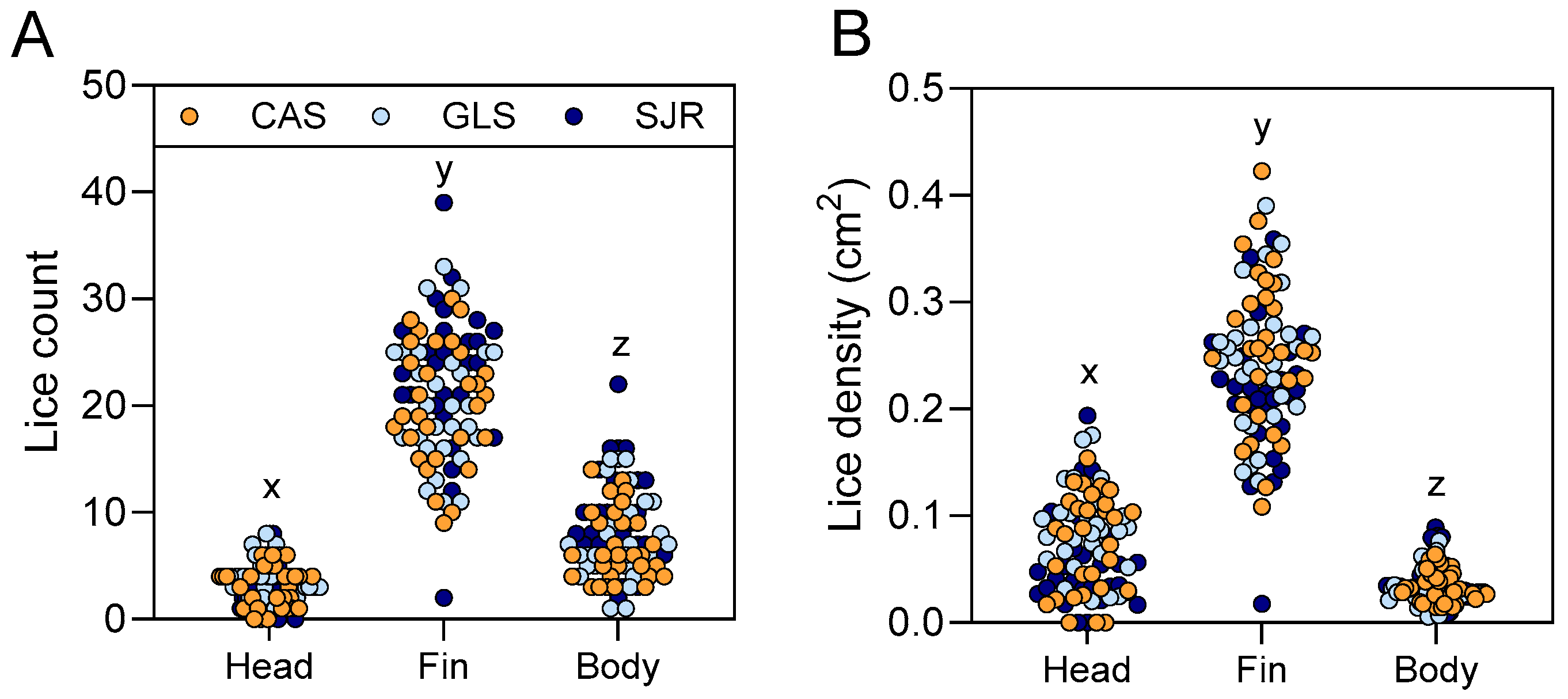
3.4. Copepodid Settlement Occurred More on Fins Relative to Head or Body Independent of Atlantic Salmon Strain
3.5. Atlantic Salmon Strain Was Not a Major Source of Skin/Fin Transcriptome Variation Following Sea Lice Attachment in This Study
3.6. Sea Lice Transcriptomes Were Suggested to Vary Based on Host Atlantic Salmon Strain
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NCWMAC | National Cold Water Marine Aquaculture |
| SJR | Saint John River |
| GLS | Grand Lakes Stream |
| CAS | Casco Hatchery |
| dpi | Days post infestation |
| LC | Lice count |
| BW | Body weight |
| LD1 | Lice density as defined by Gjerde et al. 2011 [47] |
| LD2 | Lice per cm2 |
| SA | Surface area |
References
- Abolofia, J.; Asche, F.; Wilen, J.E. The Cost of Lice: Quantifying the Impacts of Parasitic Sea Lice on Farmed Salmon. Mar. Resour. Econ. 2017, 32, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxaspen, K.; Karlsen, Ø.; Svåsand, T.; Asplin, L. Impacts of sea lice. In Sea Lice Biology and Control; Treasurer, J., Bricknell, I., Bron, J., Eds.; 5M Books: Essex, UK, 2022; p. 531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Sogn-Grundvåg, G.; Tveterås, R. The impact of parasitic sea lice on harvest quantities and sizes of farmed salmon. Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.; Oldham, T.; Kristiansen, T.S.; Oppedal, F.; Stien, L.H. Declining size-at-harvest in Norwegian salmon aquaculture: Lice, disease, and the role of stunboats. Aquaculture 2022, 559, 738440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walde, C.S.; Stormoen, M.; Pettersen, J.M.; Persson, D.; Røsæg, M.V.; Bang Jensen, B. How delousing affects the short-term growth of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J. The global economic cost of sea lice to the salmonid farming industry. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandal, P.O.; Egidius, E. Preliminary report on oral treatment against salmon lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, with Neguvon. Aquaculture 1977, 10, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandal, P.O.; Egidius, E. Treatment of salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis Krøyer, 1838) with Neguvon®—Description of method and equipment. Aquaculture 1979, 18, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.; Richards, R.H.; Sommerville, C. Current practices in the chemotherapeutic control of sea lice infestations in aquaculture: A review. J. Fish Dis. 1993, 16, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M. The Availability and use of chemotherapeutic sea lice control products. Contrib. Zool. 2000, 69, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M. Management of Sea Lice on Farmed Salmon with Veterinary Medicines and Biological Control Strategies. Int. Anim. Health J. 2015, 2, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Myhre Jensen, E.; Horsberg, T.E.; Sevatdal, S.; Helgesen, K.O. Trends in de-lousing of Norwegian farmed salmon from 2000–2019—Consumption of medicines, salmon louse resistance and non-medicinal control methods. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stene, A.; Carrozzo Hellevik, C.; Fjørtoft, H.B.; Philis, G. Considering elements of natural strategies to control salmon lice infestation in marine cage culture. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2022, 14, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, A.W. Sea lice—Major pathogens of farmed atlantic salmon. Parasitol. Today 1989, 5, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, S.; Geitung, L.; Oppedal, F.; Barrett, L.T. Salmon lice survive the straight shooter: A commercial scale sea cage trial of laser delousing. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M.; Oppedal, F.; Ditria, E.; Wright, D.W. The effectiveness of hyposaline treatments against host-attached salmon lice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geitung, L.; Oppedal, F.; Stien, L.H.; Dempster, T.; Karlsbakk, E.; Nola, V.; Wright, D.W. Snorkel sea-cage technology decreases salmon louse infestation by 75% in a full-cycle commercial test. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, K.; Oppedal, F.; Stien, L.H.; Moltumyr, L.; Wright, D.W.; Dempster, T. Thermal delousing with cold water: Effects on salmon lice removal and salmon welfare. Aquaculture 2019, 505, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, K.; Barrett, L.T.; Oppedal, F.; Kristiansen, T.S.; Dempster, T. Sea lice removal by cleaner fish in salmon aquaculture: A review of the evidence base. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2020, 12, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.T.; Overton, K.; Stien, L.H.; Oppedal, F.; Dempster, T. Effect of cleaner fish on sea lice in Norwegian salmon aquaculture: A national scale data analysis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, E.; Pontefract, N.; Rawling, M.; Valdenegro, V.; Aasum, E.; Andujar, L.V.; Migaud, H.; Castex, M.; Merrifield, D. Dietary supplementation with a specific mannan-rich yeast parietal fraction enhances the gut and skin mucosal barriers of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and reduces its susceptibility to sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Reynolds, P. In lumpfish We Trust? The Efficacy of Lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus to Control Lepeophtheirus salmonis Infestations on Farmed Atlantic Salmon: A Review. Fishes 2022, 7, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Balseiro, P.; Handeland, S.; Godø, O.R. Follow-Up Study on Acoustic De-Licing of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar): Lepeophtheirus salmonis and Caligus elongatus Dynamics over Four Consecutive Production Cycles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Barrett, L.T.; Mangor-Jensen, A.; Nola, V.; Harboe, T.; Folkedal, O. Effect of water temperature and exposure duration on detachment rate of salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis); testing the relevant thermal spectrum used for delousing. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, R.L.; Pietrak, M.R.; Milligan, M.M.; Gao, G.; Tsuruta, S.; Fragomeni, B.O.; Long, R.L.; Peterson, B.C.; Palti, Y. Genetic architecture and accuracy of predicted genomic breeding values for sea lice resistance in the St John River aquaculture strain of North American Atlantic salmon. Aquaculture 2024, 586, 740819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.A.; Whyte, S.K.; Purcell, S.L.; Hay, T.; Taylor, R.G.; Balder, R.; Gagné, N.; Dalvin, S.; Fast, M.D. The impact of functional feed on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) systemic immune response to high and low levels of sea lice infection (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) and co-infection with infectious salmon anemia virus. Comp. Immunol. Rep. 2024, 6, 200147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onabanjo, O.; Meuwissen, T.; Aslam, M.L.; Schmitt, A.O.; Dagnachew, B. Use of whole-genome sequence data for fine mapping and genomic prediction of sea louse resistance in Atlantic salmon. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1381333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, A.; Phillips, B.L.; Oppedal, F.; Bui, S.; Overton, K.; Dempster, T. Parasites under pressure: Salmon lice have the capacity to adapt to depth-based preventions in aquaculture. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungfeldt, L.E.R.; Quintela, M.; Besnier, F.; Nilsen, F.; Glover, K.A. A pedigree-based experiment reveals variation in salinity and thermal tolerance in the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Evol. Appl. 2017, 10, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Horsberg, T.E. Sensitivity towards low salinity determined by bioassay in the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae). Aquaculture 2020, 514, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Horsberg, T.E. In vitro bioassay methods to test the efficacy of thermal treatment on the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasurer, J.; Bravo, S. An introduction to sea lice control. In Sea Lice Biology and Control; Treasurer, J., Bricknell, I., Bron, J., Eds.; 5M Book: Essex, UK, 2022; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, K.A.; Hamre, L.A.; Skaala, O.; Nilsen, F. A comparison of sea louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) infection levels in farmed and wild Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) stocks. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolstad, K.; Heuch, P.A.; Gjerde, B.; Gjedrem, T.; Salte, R. Genetic variation in resistance of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) to the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Aquaculture 2005, 247, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsairidou, S.; Robledo, D.; Houston, R.D. Selective breeding for improved resistance to sea lice in farmed salmonids. In Sea Lice Biology and Control; Treasurer, J., Bricknell, I., Bron, J., Eds.; 5M Books: Essex, UK, 2022; p. 374. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.C.; Burr, G.S.; Pietrak, M.R.; Proestou, D.A. Genetic Improvement of North American Atlantic Salmon and the Eastern Oyster at the USDA-ARS National Cold Water Marine Aquaculture Center. N. Am. J. Aquacult. 2020, 82, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holborn, M.K.; Rochus, C.M.; Ang, K.P.; Elliott, J.A.K.; Leadbeater, S.; Powell, F.; Boulding, E.G. Family-based genome wide association analysis for salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) resistance in North American Atlantic salmon using a 50 K SNP array. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Hamilton, A.; Tinch, A.E.; Guy, D.R.; Bron, J.E.; Taggart, J.B.; Gharbi, K.; Stear, M.; Matika, O.; Pong-Wong, R.; et al. Genomic prediction of host resistance to sea lice in farmed Atlantic salmon populations. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2016, 48, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, M.; Braden, L. Salmon-louse interaction and immunological consequences for the host. In Sea Lice Biology and Control; Treasurer, J., Bricknell, I., Bron, J., Eds.; 5M Books: Essex, UK, 2022; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, S.; Oppedal, F.; Sievers, M.; Dempster, T. Behaviour in the toolbox to outsmart parasites and improve fish welfare in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 11, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, L.H.J.; Pike, A.W.; Houlihan, D.F.; McVicar, A.H. Comparison of the susceptibility of sea trout (Salmo trutta L.) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) to sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Kroyer, 1837)) infections. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1997, 54, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, J.E.; Sommerville, C.; Jones, M.; Rae, G.H. The Settlement and Attachment of Early Stages of the Salmon Louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda, Caligidae) on the Salmon Host, Salmo salar. J. Zool. 1991, 224, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsing, F.; Solstorm, D.; Oppedal, F.; Solstorm, F.; Dempster, T. Gone with the flow: Current velocities mediate parasitic infestation of an aquatic host. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, M.D.; Ross, N.W.; Muise, D.M.; Johnson, S.C. Differential gene expression in Atlantic salmon infected with Lepeophtheirus salmonis. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2006, 18, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, H.J.; Skugor, S.; Bjelland, A.K.; Radunovic, S.; Wadsworth, S.; Koppang, E.O.; Evensen, Ø. Contrasting expression of immune genes in scaled and scaleless skin of Atlantic salmon infected with young stages of Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 67, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, S.; Hamre, L.A.; Skern-Mauritzen, R.; Dalvin, S.; Bron, J.E. Sea Lice Behaviour. In Sea Lice Biology and Control; Treasurer, J., Bricknell, I., Bron, J., Eds.; 5M Books: Essex, UK, 2022; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerde, B.; Ødegård, J.; Thorland, I. Estimates of genetic variation in the susceptibility of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) to the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Aquaculture 2011, 314, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, C.; Brady, D.C.; Bricknell, I. Landing strips: Model development for estimating body surface area of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2017, 473, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, B.; Mordue-Luntz, A.J.; Fryer, R.J.; Pert, C.C.; Bricknell, I.R. Determination of the surface area of a fish. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, S.; Dalvin, S.; Dempster, T.; Skulstad, O.F.; Edvardsen, R.B.; Wargelius, A.; Oppedal, F. Susceptibility, behaviour, and retention of the parasitic salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) differ with Atlantic salmon population origin. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, S.; Halttunen, E.; Mohn, A.M.; Vågseth, T.; Oppedal, F. Salmon lice evasion, susceptibility, retention, and development differ amongst host salmonid species. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 75, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, S.; Oppedal, F.; Samsing, F.; Dempster, T. Behaviour in Atlantic salmon confers protection against an ectoparasite. J. Zool. 2017, 304, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ødegård, J.; Medina, M.; Torgersen, J.S.; Korsvoll, S.A.; Deerenberg, R.; Yáñez, J.M.; Cichero, D.; Lopez, P.; Moen, T.; Kjøglum, S. Genetic selection for reduced parasite load in Atlantic salmon: Zero-sum game or a tool for group-level protection against sea lice? Aquaculture 2024, 581, 740438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietrak, M.R.; Delomas, T.A.; Lifgren, D.; Polinski, M.P. Evaluation of Three Atlantic Salmon Strains for Resistance to Copepodid Sea Lice Attachment. Fishes 2025, 10, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070334
Pietrak MR, Delomas TA, Lifgren D, Polinski MP. Evaluation of Three Atlantic Salmon Strains for Resistance to Copepodid Sea Lice Attachment. Fishes. 2025; 10(7):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070334
Chicago/Turabian StylePietrak, Michael R., Thomas A. Delomas, Demitri Lifgren, and Mark P. Polinski. 2025. "Evaluation of Three Atlantic Salmon Strains for Resistance to Copepodid Sea Lice Attachment" Fishes 10, no. 7: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070334
APA StylePietrak, M. R., Delomas, T. A., Lifgren, D., & Polinski, M. P. (2025). Evaluation of Three Atlantic Salmon Strains for Resistance to Copepodid Sea Lice Attachment. Fishes, 10(7), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070334





