Comparative Analysis of Different Body Composition, Mucus Biochemical Indices, and Body Color in Five Strains of Larimichthys crocea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish
2.2. Analysis of Population Genetic Diversity
2.3. The Body Composition
2.4. Mucus Samples Collecting and Analyzing Parameters
2.5. Skin Samples Collecting and Analyzing Parameters
2.6. Real-Time PCR Quantitative
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diversity Analysis of Populations
3.2. The Body Components
3.3. The Mucus Antioxidant Indices
3.4. The Mucus Immune Indices
3.5. Histological Analysis of the Skin
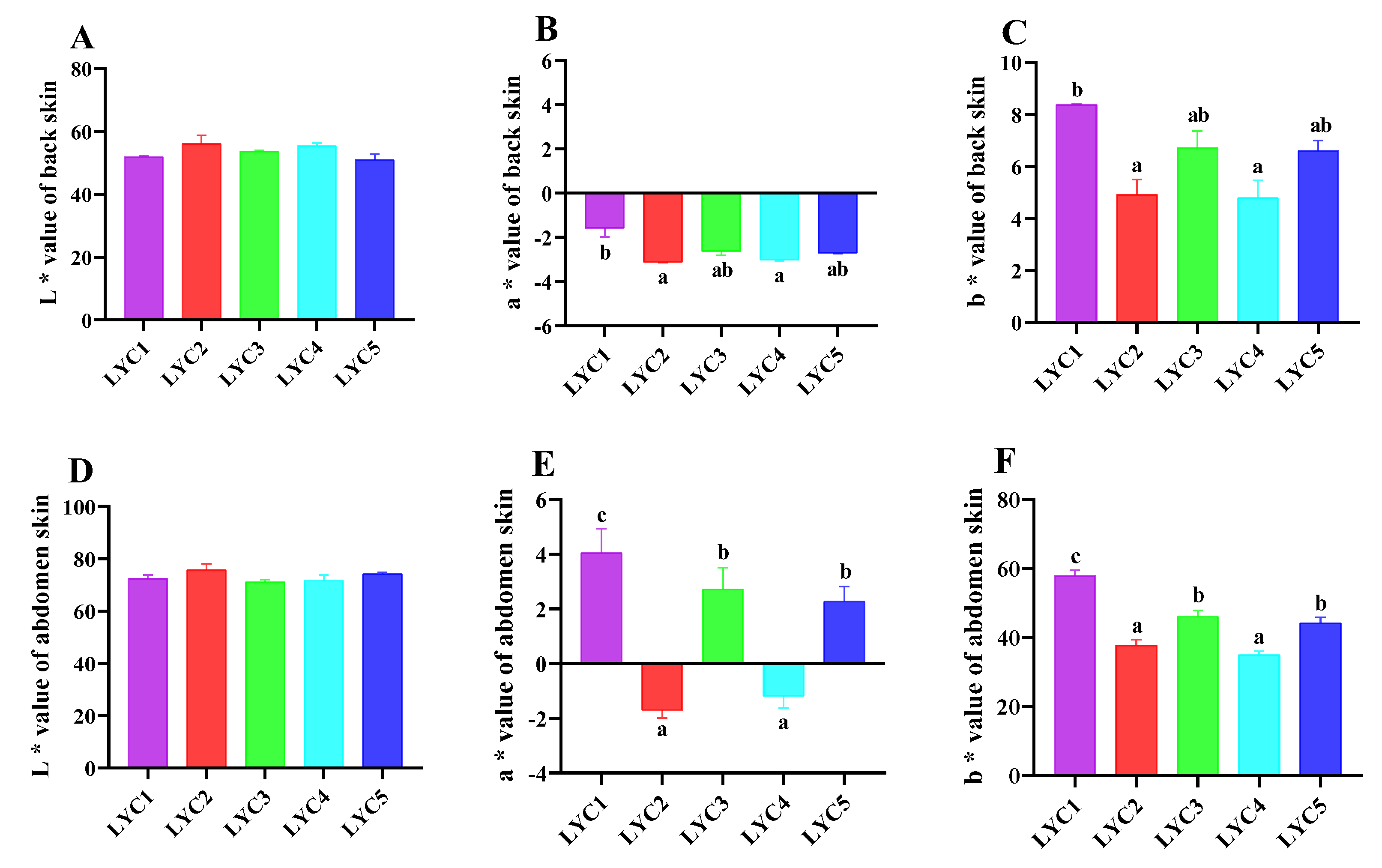
3.6. Skin Chroma Value
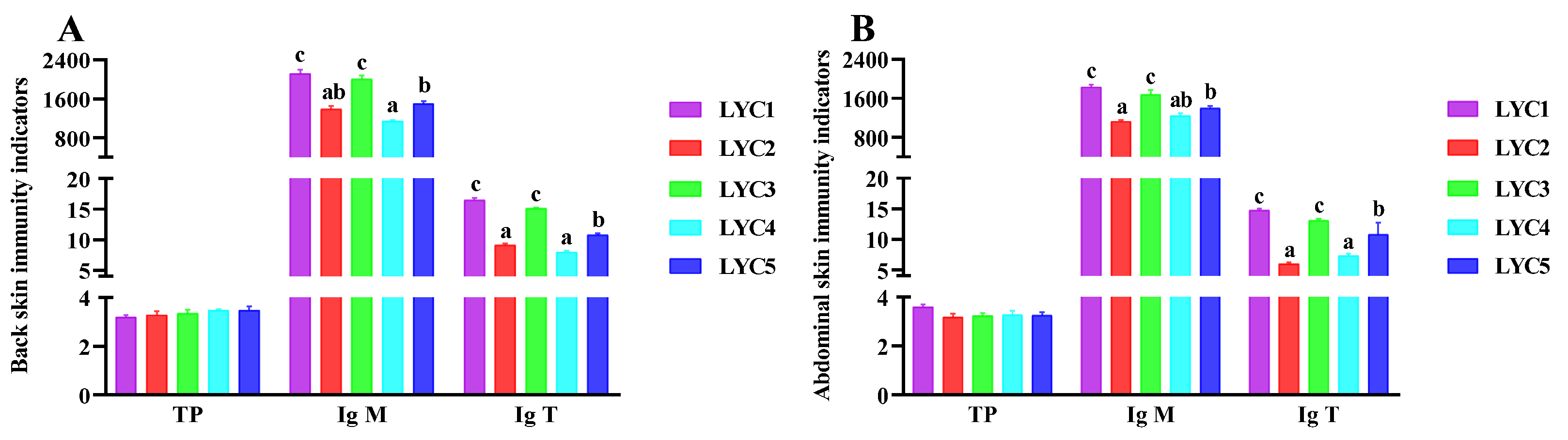
3.7. Skin Immune Indicators
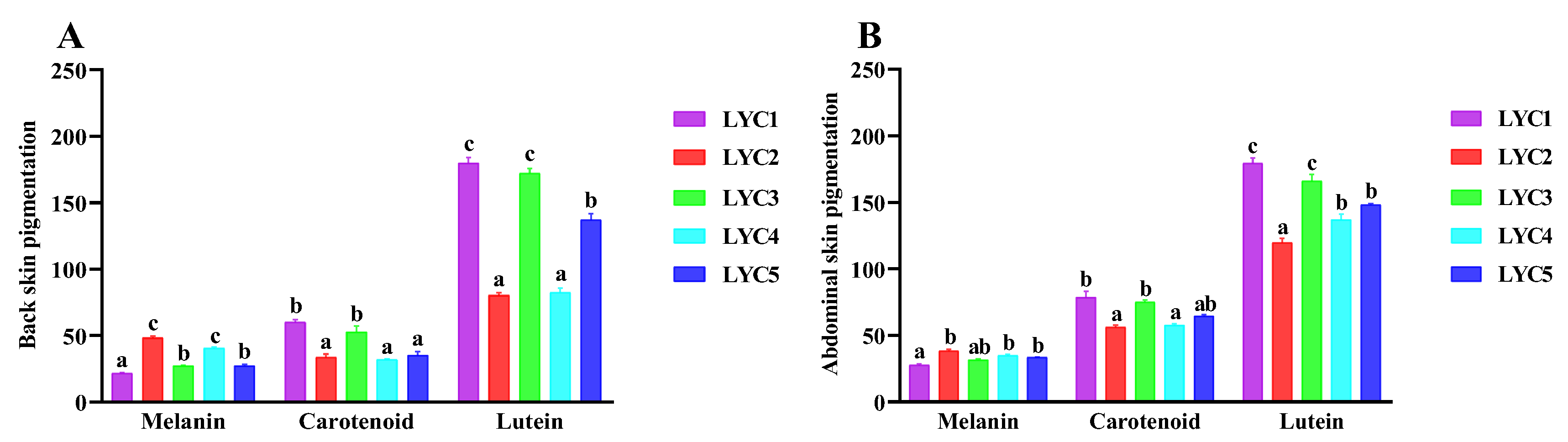
3.8. Skin Pigmentation
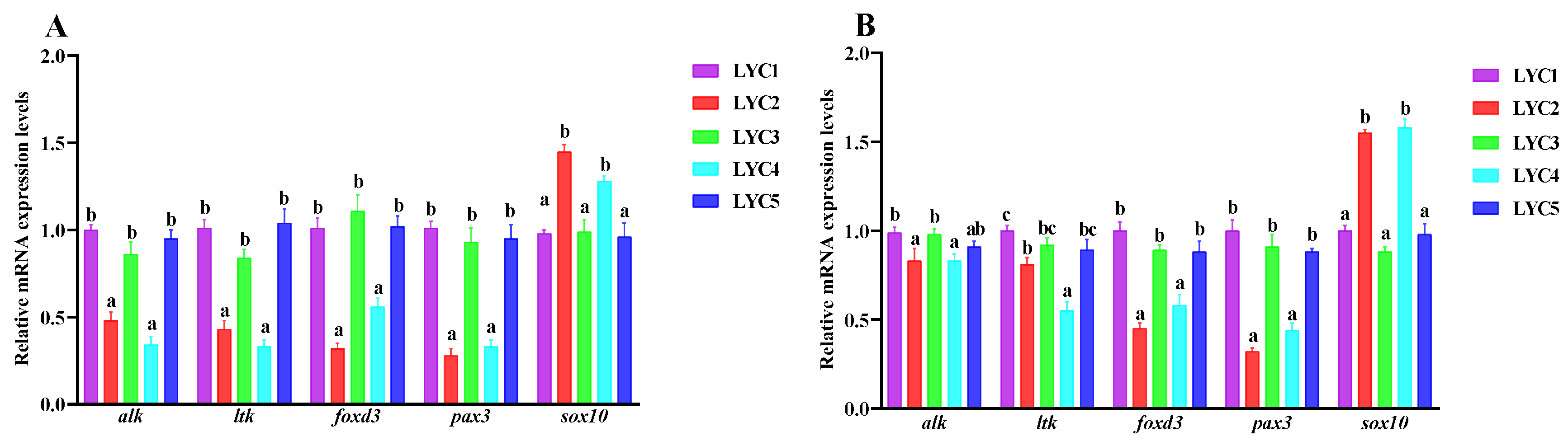
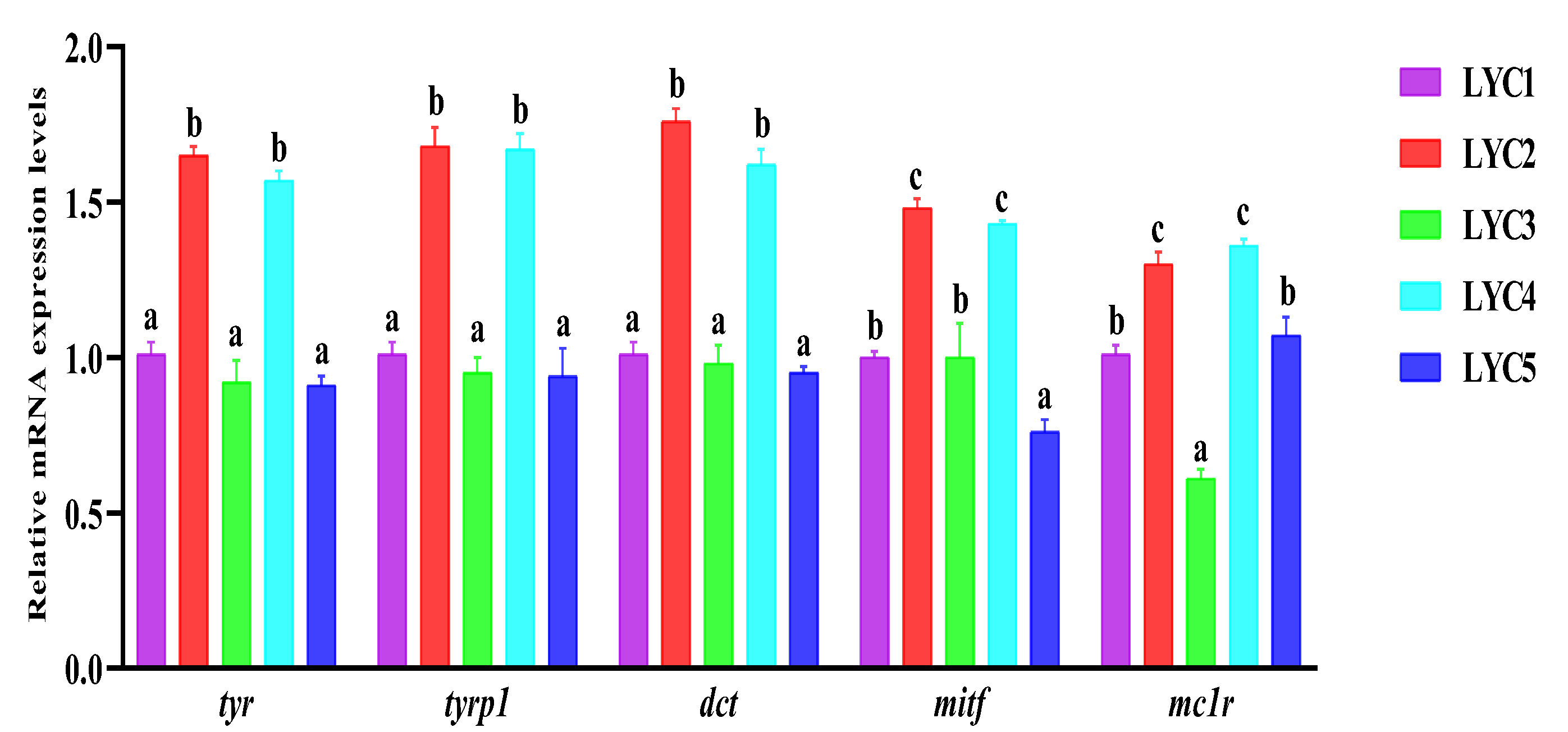
3.9. The Neural Crest Regulation of mRNA Expression in the Skin
3.10. The mRNA Expression of Back Skin Melanin Synthesis
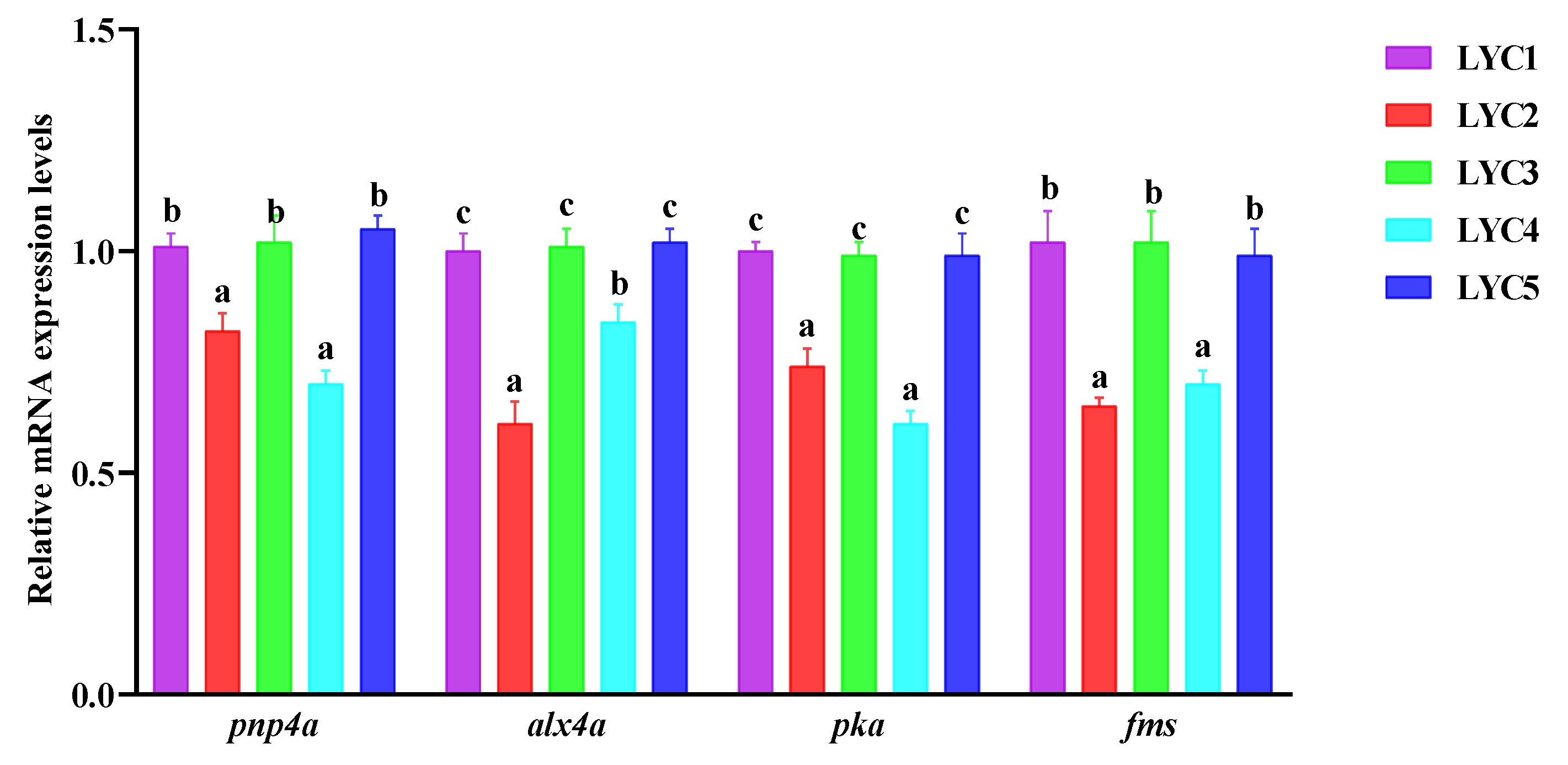
3.11. The mRNA Expression of Iridocytes and Yellow Pigment Cells Related to Genes in the Abdomen Skin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Su, Y.; Hong, W. Aquaculture of the large yellow croaker. In Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 2018, pp. 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Lin, H.; Wu, L.; Zhuang, X.; Ma, J.; Kang, B.; Ding, S. Resource status and effect of long-term stock enhancement of large yellow croaker in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 743836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisheries Administration of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Areas; National Fisheries Technology Extension Center; China Society of Fisheries. Fishery Statistical Yearbook 2024; Chinese Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Ke, H.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liang, P. Physicochemical, flavor, and microbial dynamic changes of cured large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) roe. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Guo, Q.; Liu, A. Prevention of quality characteristic decline in freeze-thawed cultured large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) using flammulina velutipes polysaccharide. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.Q.; Sun, M.; Xie, B.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Evaluating performance of data-limited management procedures in an ecosystem perspective: A case study for Larimichthys crocea (Sciaenidae) in the Min River Estuary, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, J.; Tong, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Ding, S. Resource assessment of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea based on eDNA analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 890756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Jiang, L.; Song, W.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yan, X. Skeletal muscle features of different populations in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea): From an epigenetic point of view. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1403861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Xie, Q.; Wei, F.; Wu, X.; Xu, W.; Zhan, W.; Liu, F.; Guo, D.; Niu, B.L.; Lou, B. Development and identification of a sex-specific molecular marker in Dai-qu stock large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, R.; Xie, X.; Yin, F. Characteristics and risk assessment of cryptocaryoniasis in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) at different densities in industrialized aquaculture. Aquaculture 2024, 582, 740501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, F.; Wang, C. Fish image recognition method based on multi-layer feature fusion convolutional network. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Lu, G.; Yin, H.; Wang, L.; Atuganile, M.; Dong, Z. Fish pigmentation and coloration: Molecular mechanisms and aquaculture perspectives. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2395–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.H.; Aspengren, S.; Wallin, M. Rapid color change in fish and amphibians-function, regulation, and emerging applications. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, S.; Du, Z. Observation of body color formation and pigment cells in grey-black and golden Paramisgumus dabryanus. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parichy, D.M. Evolution of pigment cells and patterns: Recent insights from teleost fishes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2021, 69, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subkhankulova, T.; Camargo Sosa, K.; Uroshlev, L.A.; Nikaido, M.; Shriever, N.; Kasianov, A.S.; Kelsh, R.N. Zebrafish pigment cells develop directly from persistent highly multipotent progenitors. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Feng, Q.; Cheng, L.; Teng, R.; Wei, L.; Yuan, D. Thyroid hormone regulates both melanin and non-melanin pigmentation in Sinibrama taeniatus via three types of chromophores. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1482306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakoudi, S.A.; Chatzi, D.; Dermitzakis, I.; Gargani, S.; Manthou, M.E.; Meditskou, S.; Theotokis, P. Genetic identity of neural crest cell differentiation in tissue and organ development. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2024, 29, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, G.G.; Bronner-Fraser, M.E. Neural crest cell differentiation. In Development, Regeneration and Plasticity of the Autonomic Nervous System; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2024; Volume 2024, pp. 95–137. [Google Scholar]
- Fadeev, A.; Mendoza-Garcia, P.; Irion, U.; Guan, J.; Pfeifer, K.; Wiessner, S.; Palmer, R.H. ALKALs are in vivo ligands for ALK family receptor tyrosine kinases in the neural crest and derived cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, E.S.; Cheng, Q.; Reshetnyak, A.V.; Schlessinger, J.; Nicoli, S. Alk and Ltk ligands are essential for iridophore development in zebrafish mediated by the receptor tyrosine kinase Ltk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12027–12032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petratou, K.; Subkhankulova, T.; Lister, J.A.; Rocco, A.; Schwetlick, H.; Kelsh, R.N. A systems biology approach uncovers the core gene regulatory network governing iridophore fate choice from the neural crest. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, 1007402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.A.; Arduini, B.L.; Berghmans, S.; George, R.E.; Kanki, J.P.; Henion, P.D.; Look, A.T. Zebrafish foxd3 is selectively required for neural crest specification, migration and survival. Dev. Biol. 2006, 292, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Wang, I.J. Heat-shock-induced tyrosinase gene ablation with CRISPR in Zebrafish. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Mou, Y.; Gong, H.; Chen, H.; Xiao, H. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in senescence and age-related diseases. Gerontology 2021, 67, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, S.; Crespo, D.; Schulz, R.W.; Ge, W.; Rotllant, J.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Rocha, A. Role of the melanocortin system in gonadal steroidogenesis of zebrafish. Animals 2022, 12, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Janpoom, S.; Prasertlux, S.; Rongmung, P.; Ittarat, W.; Ratdee, O.; Klinbunga, S. Identification of pigmentation genes in skin, muscle and tail of a Thai-flag variety of Siamese fighting fish Betta splendens. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2024, 50, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouife, M.; Ban, Z.; Yue, X.; Jiang, J.; Xie, J. Molecular characterization, gene expression and functional analysis of goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) macrophage colony stimulating factor 2. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1235370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Balasundaram, C.; Heo, M.S. Fish health aspects in grouper aquaculture. Aquaculture 2011, 320, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, A.K.; Kumari, U.; Mittal, S.; Mittal, A.K. Comparative analysis of innate immune parameters of the skin mucous secretions from certain freshwater teleosts, inhabiting different ecological niches. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanahuja, I.; Fernández-Alacid, L.; Ordóñez-Grande, B.; Sánchez-Nuño, S.; Ramos, A.; Araujo, R.M.; Ibarz, A. Comparison of several non-specific skin mucus immune defenses in three piscine species of aquaculture interest. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, B.H.; Suhartono, E.; Yunita, R.; Biyatmoko, D. Epidermal mucus as a potential biological matrix for fish health analysis. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Kong, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ji, W.; Xu, Z. Response of immunoglobulin M in gut mucosal immunity of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1037517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Mo, Z.; Li, Y. Study on the characterization of grouper (Epinephelus coioides) immunoglobulin T and its positive cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 118, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, H.; Kong, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.; Shi, S. Response of acid and alkaline phosphatase activities to copper exposure and recovery in freshwater fish Carassius auratus gibelio var. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Aida, K. Effects of steroid hormones on immunoglobulin M (IgM) in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1999, 20, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemapoojavalli, G.; Bragadeeswaran, S. Evaluating the antioxidant activity of epidermal mucus extract in marine fishes Anguilla anguilla and Brachirus orientalis. Int. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 2, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ceballos-Francisco, D.; Guardiola, F.A.; Huang, D.; Esteban, M.Á. Skin wound healing in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) fed diets supplemented with arginine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldsine, P.; Abeyta, C.; Andrews, W.H. AOAC International methods committee guidelines for validation of qualitative and quantitative food microbiological official methods of analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2002, 85, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCleary, B.V.; Sloane, N.; Draga, A.; Lazewska, I. Measurement of total dietary fiber using AOAC Method 2009.01 (AACC International Approved Method 32-45.01): Evaluation and updates. Cereal Chem. 2013, 90, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliney, D.H. Radiometric quantities and units used in photobiology and photochemistry: Recommendations of the Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (International Commission on Illumination). Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocho, A.; Chen, B.; Ladanyi, M.; Pan, Q. Validation of the 2−ΔΔCt calculation as an alternate method of data analysis for quantitative PCR of BCR-ABL P210 transcripts. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2006, 15, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, T.M.G.; Coppolino, C.; Arena, P.; Aichouni, A.; Cerrato, A.; Capriotti, A.L.; Mondello, L. Circular economy in the Food Chain: Retrieval and characterization of antimicrobial peptides from Fish Waste hydrolysates. Food Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 178–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvi, B.; Pourmozaffar, S.; Alibeygi, T. The role of live food in reproduction and rearing of marine ornamental fish. J. Ornam. Aquat. 2024, 11, 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- Seidgar, M.; Abbaspour, A.A.; Nahali, S. A review on the use of live feeds in marine ornamental fish culture. J. Ornam. Aquat. 2024, 11, 63–85. [Google Scholar]
- Petrellis, N. Measurement of fish morphological features through image processing and deep learning techniques. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoraki, M.; Ferrándiz, P.M.; Vardali, S.C.; Kontodimas, D.C.; Kotzamanis, Y.P.; Gasco, L.; Antonopoulou, E. A comparative study on the effect of fish meal substitution with three different insect meals on growth, body composition and metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Guo, H.Y.; Liu, B.S.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, K.C.; Zhang, D.C. Analysis of morphological differences in five large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) populations. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2024, 76, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Xu, D. Production of neomale and neofemale large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) and establishment of all-female populations. Aquaculture 2024, 590, 741010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, D.M.; Zaccone, G.; Alesci, A.; Kuciel, M.; Hussein, M.T.; Sayed, R.K. Main components of fish immunity: An overview of the fish immune system. Fishes 2023, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, D.; Singh, M.B.; Verma, P.; Pathak, A.; Kanaujiya, S. Fish skin mucus and its importance in fish and humans. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2023, 42, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; He, M.; Tang, P.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D. Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharide promotes the health of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) by promoting hemocyte phagocytosis, protecting hepatopancreas and enhancing intestinal barrier function. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 146, 109405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, I.; Fernández-Montero, Á.; Ding, Y.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins of teleost fish: A decade of advances. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 121, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Ruíz, C.; Esteban, M.Á. Wound-induced changes in antioxidant enzyme activities in skin mucus and in gene expression in the skin of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fishes 2021, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koner, D.; Banerjee, B.; Kumari, A.; Lanong, A.S.; Snaitang, R.; Saha, N. Molecular characterization of superoxide dismutase and catalase genes, and the induction of antioxidant genes under the zinc oxide nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress in air-breathing magur catfish (Clarias magur). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1909–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.S.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Effects of bioactive substances from turmeric on growth, skin mucosal immunity and antioxidant factors in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Mai, K. Proteomics analysis of skin coloration of large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea fed different dietary carotenoids. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.T.; El-Feky, M.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Sallam, A.E. Synergism of dietary co-supplementation with lutein and bile salts improved the growth performance, carotenoid content, antioxidant capacity, lipid metabolism, and lipase activity of the marbled spinefoot rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. Animals 2020, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilisza, N.; Jusadi, D.; Zairin, J.M.; Artika, I.M.; Priyo, U.N.B.; Kadarini, T.; Suprayudi, M.A. Digestibility, growth and pigmentation of astaxanthin, canthaxanthin or lutein diets in Lake Kurumoi rainbowfish, Melanotaenia parva (Allen) cultured species. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 5517–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukohwo, O.M.; Ejiro, O.P. Luteolin co-treatment abates polystyrene microplastics (PSMPs) induced spermatotoxicity and dysgonadogenesis in rats via up-regulation of gonadotropin, enhanced spermatogenesis, downregulation of caspases, and oxido-inflammation. J. Chem. Health Risks 2024, 14, 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, L.; Ran, X.; Li, S.; Wen, C. Investigating the molecular mechanism of purslane-based vitiligo treatment using network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro analyses. Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuffer, S.J.; Cooper, C.D. Zebrafish syndromic albinism models as tools for understanding and treating pigment cell disease in humans. Cancers 2022, 14, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Muccioli, S.; Brillo, V.; Bachmann, M.; Szabò, I.; Leanza, L. Mitochondrial dysfunction interferes with neural crest specification through the FoxD3 transcription factor. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabangu, M.; Cecil, R.; Strohl, L.; Timoshevskaya, N.; Smith, J.J.; Voss, S.R. Leukocyte tyrosine kinase (LTK) is the mendelian determinant of the axolotl melanoid color variant. Genes 2023, 14, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.S.; Chen, Y.; Ge, J.; Wilkening, A.N.; Hou, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Wang, T. Epigenetic dynamics shaping melanophore and iridophore cell fate in zebrafish. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Lu, J. Identification of pigment genes (melanin, carotenoid and pteridine) associated with skin color variant in red tilapia using transcriptome analysis. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Shi, X.; Guo, J.; Lin, K.; Zhu, W.; Fu, J.; Dong, Z. Deep spatiotemporal transcriptome analysis provides new insights into early development of koi carp (Cyprinus carpio var. koi). Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyadai, M.; Takada, H.; Shiraishi, A.; Kimura, T.; Watakabe, I.; Kobayashi, H.; Hashimoto, H. A gene regulatory network combining Pax3/7, Sox10 and Mitf generates diverse pigment cell types in medaka and zebrafish. Development 2023, 150, dev202114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, I.K.; Manuel, J.L.; Roberts, R.A.; Nuckels, R.J.; Herrington, E.R.; MacDonald, E.L.; Parichy, D.M. Evolutionary diversification of pigment pattern in Danio fishes: Differential fms dependence and stripe loss in D. albolineatus. Development 2005, 132, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, L.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.; Pan, X. Identification of Philaster apodigitiformis in aquaculture and functional characterization of its β-PKA gene and expression analysis of infected Poecilia reticulata. Parasitology 2024, 151, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, F.; Renz, A.J.; Fukamachi, S.; Meyer, A. Genetic, comparative genomic, and expression analyses of the Mc1r locus in the polychromatic Midas cichlid fish (Teleostei, Cichlidae Amphilophus sp.) species group. J. Mol. Evol. 2010, 70, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nagao, Y.; Takada, H.; Miyadai, M.; Adachi, T.; Seki, R.; Kamei, Y.; Hashimoto, H. Distinct interactions of Sox5 and Sox10 in fate specification of pigment cells in medaka and zebrafish. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, 1007260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Wei, K.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shi, Z.C.; Liu, L.K.; Li, J.; Ji, W. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of tyr and tyrp1 genes in normal and albino yellow catfish Tachysurus fulvidraco. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 979–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
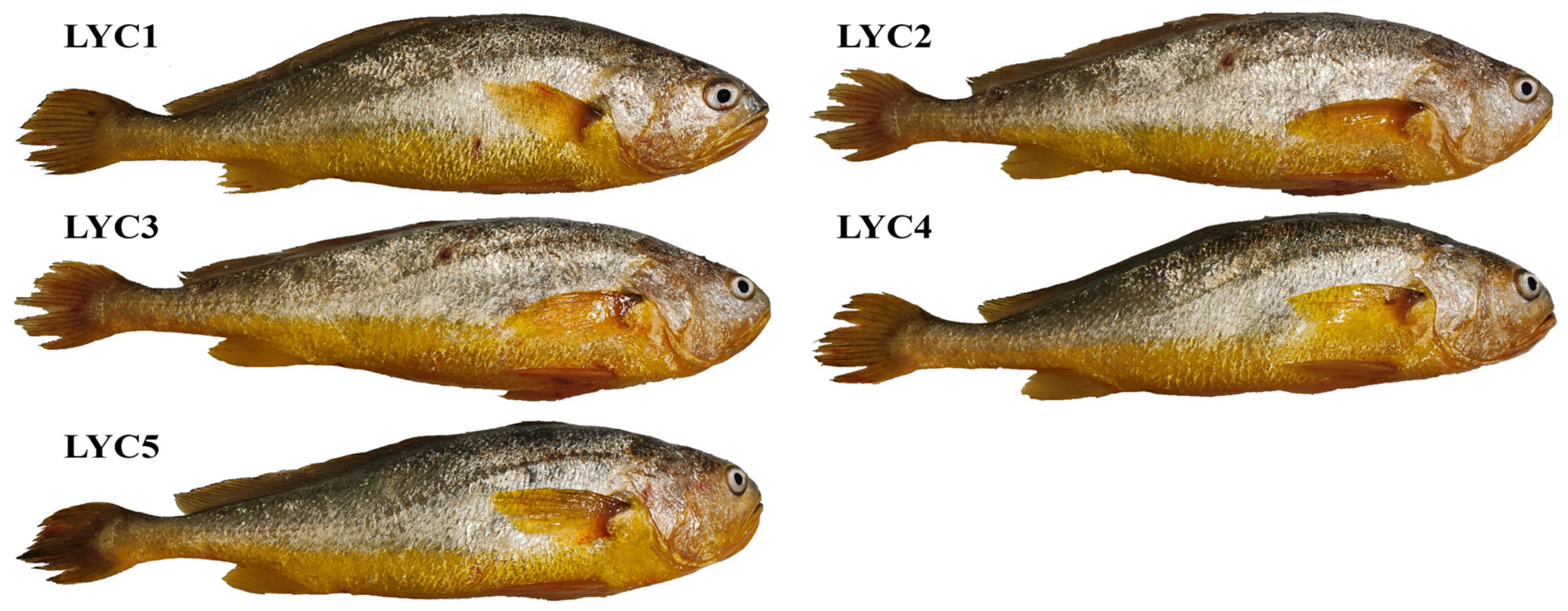
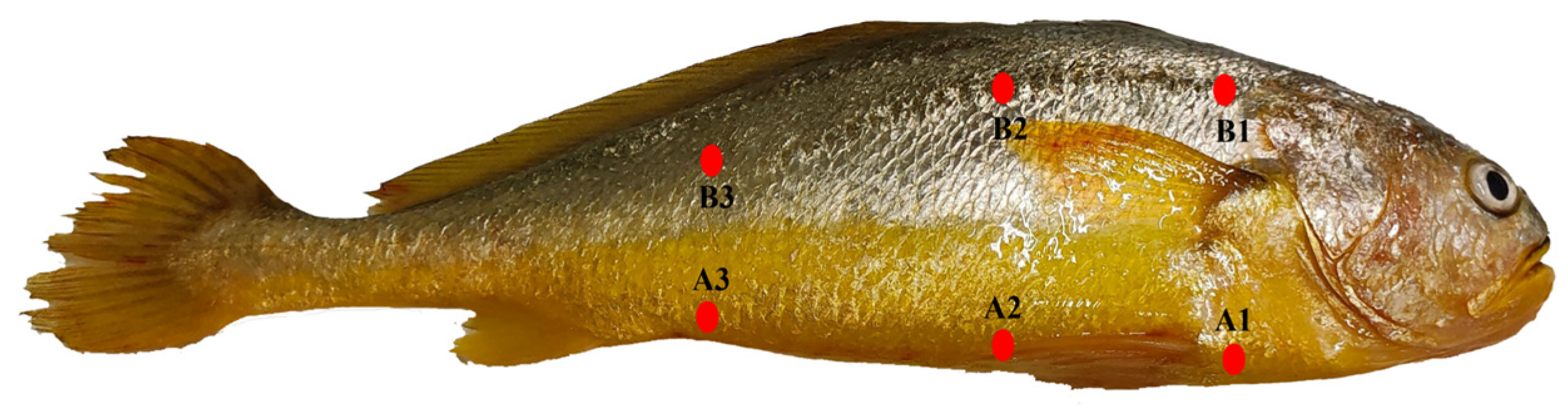
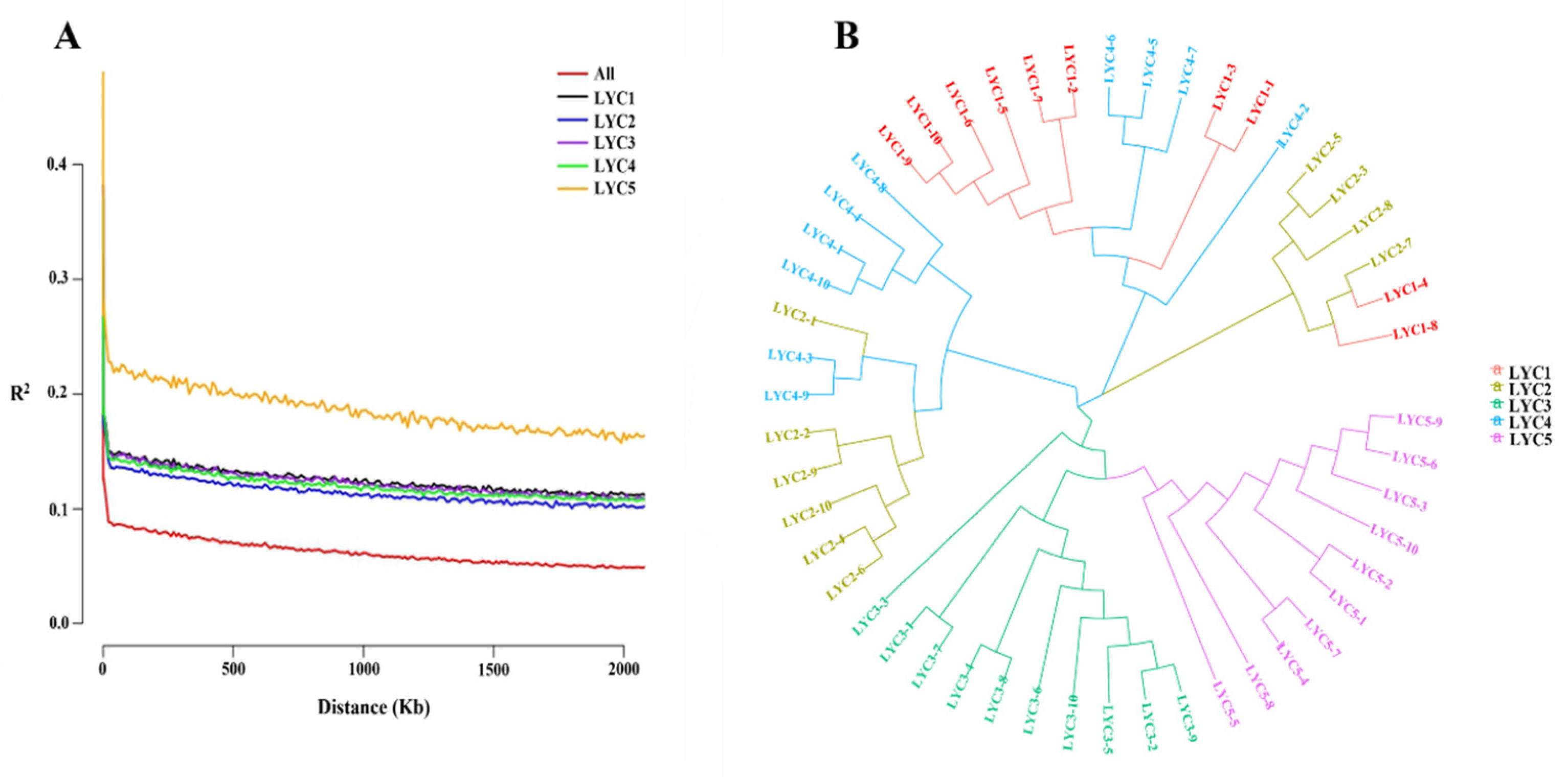
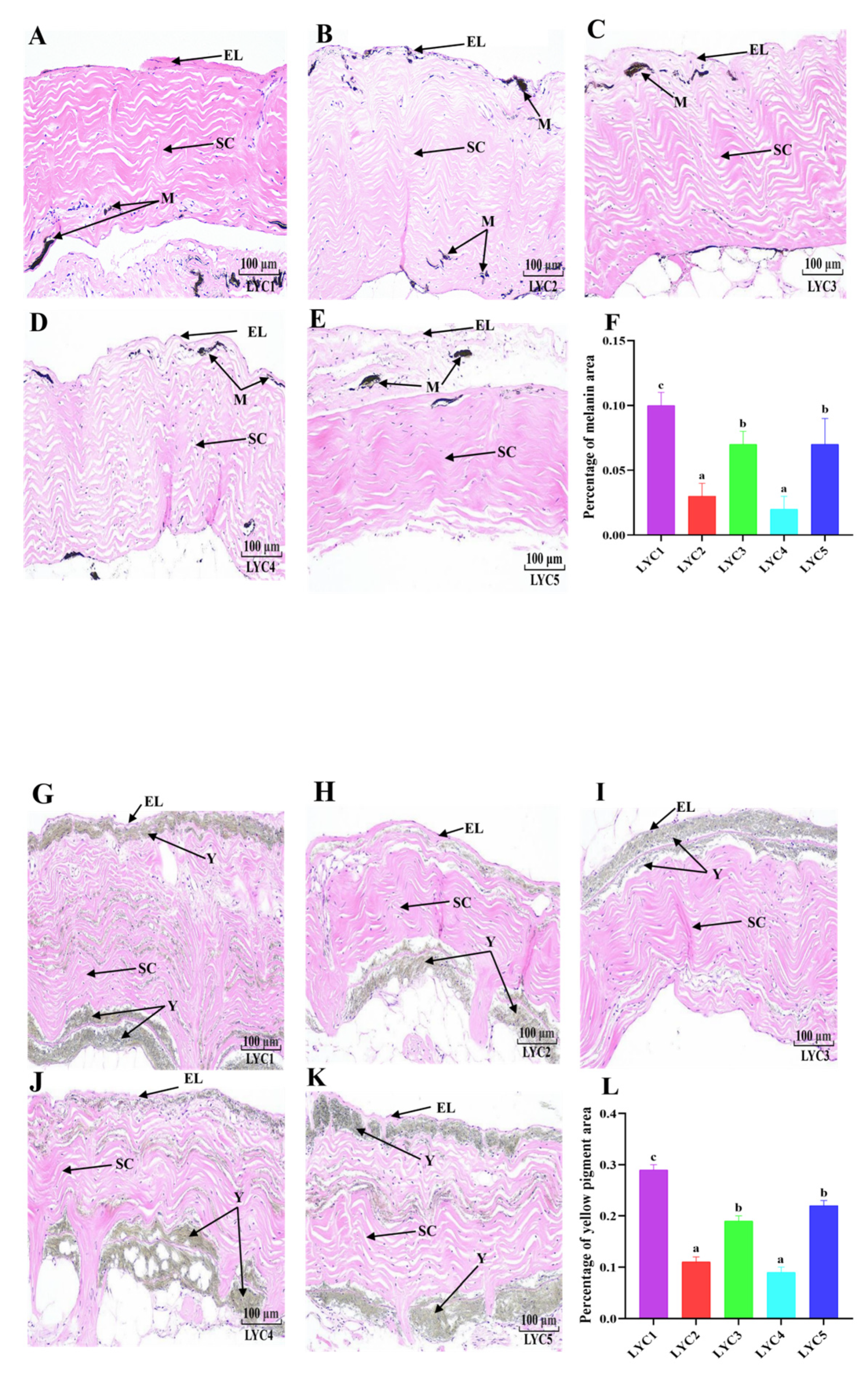
| Items | LYC1 | LYC2 | LYC3 | LYC4 | LYC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large yellow croaker | Wild | Dai-qu population | Yongdai 1 | Min-yuedong population | Fufa 1 |
| Body weight (g) | 343.13 ± 7.21 | 343.60 ± 17.61 | 364.90 ± 14.72 | 355.17 ± 3.58 | 328.27 ± 15.03 |
| Total length | 31.76 ± 0.29 | 32.12 ± 0.55 | 33.96 ± 1.36 | 33.09 ± 0.45 | 32.40 ± 0.66 |
| Tail number | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Time | 15 August 2024 | 13 August 2024 | 13 August 2024 | 17 August 2024 | 17 August 2024 |
| Company | Wenzhou Linbao Feng Aquatic Co. (Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China) | Ningde Jinsheng Aquatic Co. (Ningde, Fujian, China) | Ningde Jinsheng Aquatic Co. (Ningde, Fujian, China) | Fujian Yuhuizhan Agricultural Technology Co. (Ningde, Fujian, China) | Fujian Yuhuizhan Agricultural Technology Co. (Ningde, Fujian, China) |
| Accession No. | Primer | Forward, 5′ to 3′ | Reverse, 5′ to 3′ | Tm (°C) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XM_027274897.1 | alk | GTGCCTGTTCCTCAGCCTCT | CACGGACAAGGAGTCGGAGA | 59.0 | 106 |
| XM_010744505.3 | pka | GTGCCTGTTCCTCAGCCTCT | GGAGAAGAGGAAGGACGAGC | 60.0 | 121 |
| XM_010748017.3 | sox10 | GTGCCTGTTCCTCAGCCTCT | CACGGACAAGGAGTCGGAGA | 59.0 | 156 |
| XM_010737016.3 | pax3 | CCTCTTCTCCTTCCTGCTCG | GGAGAAGAGGAAGGACGAGC | 59.0 | 196 |
| NM_001002102.1 | pnp4a | CTTCTCCTTCCTGCTCCGTGG | CGGTGGTGCGACAAGACAGA | 60.7 | 187 |
| XM_019254989.2 | ltk | GCCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCT | GGTGCGAGAAGACAGACGAC | 59.0 | 190 |
| XM_001340930.8 | alx4a | CCACGCTCTTCTGTCTGCTG | GGGGCTCACTGTTCGGACAT | 60.7 | 112 |
| XM_010730933.3 | foxd3 | CTCCTCACCCACACCGTCAG | GAAGCGGCAGAGGATGGCT | 60.9 | 165 |
| XM_019254738.2 | tyr | CTTCTCCTTCCTGCTCGTGG | CGGTGGTGCGAGAAGACAGA | 59.7 | 149 |
| XM_027279798.1 | fms | GGTCAACCTCCTCTCTGCCA | GGTGCGAGAAGACAGACGAC | 59.6 | 153 |
| XM_010732276.3 | tyrp1 | CACGGACAAGGAGTCGGAGAA | GACGTGGAGCTGGCCGAGGAG | 60.8 | 107 |
| XM_027283126.1 | mitf | GGAGAAGAGGAAGGACGAGCA | TCCCTCTAATCAGCCTCTGGA | 60.2 | 135 |
| XM_010746837.3 | dct | GCCTGTTCCTCAGCCTCTTCT | GGAGAAGAGGAAGGACGAGCA | 60.1 | 122 |
| XM_047732415.1 | mc1r | ACCTCCCTCTAATCAGCCCTC | GGAGAAGAGGAAGGACGAGCA | 59.0 | 132 |
| GU584189.1 | β-actin | GACAAGGAGTGCGAGAAGAGGA | GACGTGGAGCTGGCCGAGGAGG | 59.6 | 112 |
| Items | LYC1 | LYC2 | LYC3 | LYC4 | LYC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 75.83 ± 0.94 c | 71.29 ± 0.48 a | 75.24 ± 0.16 c | 72.20 ± 0.18 ab | 74.25 ± 0.50 bc |
| Crude protein (%, dry matter) | 20.42 ± 0.25 b | 16.65 ± 0.16 a | 19.48 ± 0.16 b | 15.71 ± 0.34 a | 16.75 ± 0.25 a |
| Crude lipid (%, dry matter) | 3.60 ± 0.23 a | 7.40 ± 0.28 c | 4.60 ± 0.53 ab | 5.84 ± 0.34 bc | 5.69 ± 0.29 b |
| Crude ash (%, dry matter) | 1.34 ± 0.12 | 1.72 ± 0.12 | 1.39 ± 0.10 | 1.67 ± 0.09 | 1.69 ± 0.11 |
| Items | LYC1 | LYC2 | LYC3 | LYC4 | LYC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA (nmol/mL) | 5.21 ± 0.17 | 6.07 ± 0.38 | 5.24 ± 0.16 | 5.98 ± 0.37 | 5.51 ± 0.27 |
| SOD (U/mL) | 113.37 ± 4.38 b | 70.73 ± 7.48 a | 83.25 ± 1.93 a | 76.82 ± 3.98 a | 104.12 ± 3.86 b |
| CAT (U/mL) | 46.27 ± 3.64 b | 28.42 ± 4.05 a | 32.23 ± 4.02 a | 27.74 ± 0.53 a | 45.64 ± 1.71 b |
| Items | LYC1 | LYC2 | LYC3 | LYC4 | LYC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP (IU/L) | 171.67 ± 7.55 c | 98.85 ± 2.85 a | 138.22 ± 4.25 bc | 77.52 ± 14.25 a | 107.07 ± 6.20 ab |
| ACP (IU/L) | 9.30 ± 0.13 b | 6.74 ± 0.30 a | 8.39 ± 0.30 b | 6.50 ± 0.28 a | 7.25 ± 0.25 a |
| LYS (U/mL) | 4.69 ± 0.26 c | 3.44 ± 0.19 a | 4.60 ± 0.11 bc | 3.60 ± 0.05 a | 3.86 ± 0.28 ab |
| Ig M (μg/mL) | 1251.62 ± 66.11 c | 545.63 ± 73.96 a | 928.33 ± 24.24 b | 576.62 ± 22.78 a | 615.30 ± 81.42 a |
| Ig T (g/L) | 4.71 ± 0.11 d | 1.24 ± 0.15 a | 3.51 ± 0.15 c | 1.44 ± 0.08 a | 1.94 ± 0.06 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, H.; Guo, Q.; Wei, B.; Zhong, J.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, N.; Zheng, S. Comparative Analysis of Different Body Composition, Mucus Biochemical Indices, and Body Color in Five Strains of Larimichthys crocea. Fishes 2025, 10, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070305
Deng H, Guo Q, Wei B, Zhong J, Zheng M, Zheng Y, Lin N, Zheng S. Comparative Analysis of Different Body Composition, Mucus Biochemical Indices, and Body Color in Five Strains of Larimichthys crocea. Fishes. 2025; 10(7):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070305
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Hongjin, Quanyou Guo, Banghong Wei, Jiehui Zhong, Mengyao Zheng, Yao Zheng, Na Lin, and Shengyang Zheng. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Different Body Composition, Mucus Biochemical Indices, and Body Color in Five Strains of Larimichthys crocea" Fishes 10, no. 7: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070305
APA StyleDeng, H., Guo, Q., Wei, B., Zhong, J., Zheng, M., Zheng, Y., Lin, N., & Zheng, S. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Different Body Composition, Mucus Biochemical Indices, and Body Color in Five Strains of Larimichthys crocea. Fishes, 10(7), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070305





