Diet Composition of Twaite Shad, Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803), During the Spawning Migration to the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
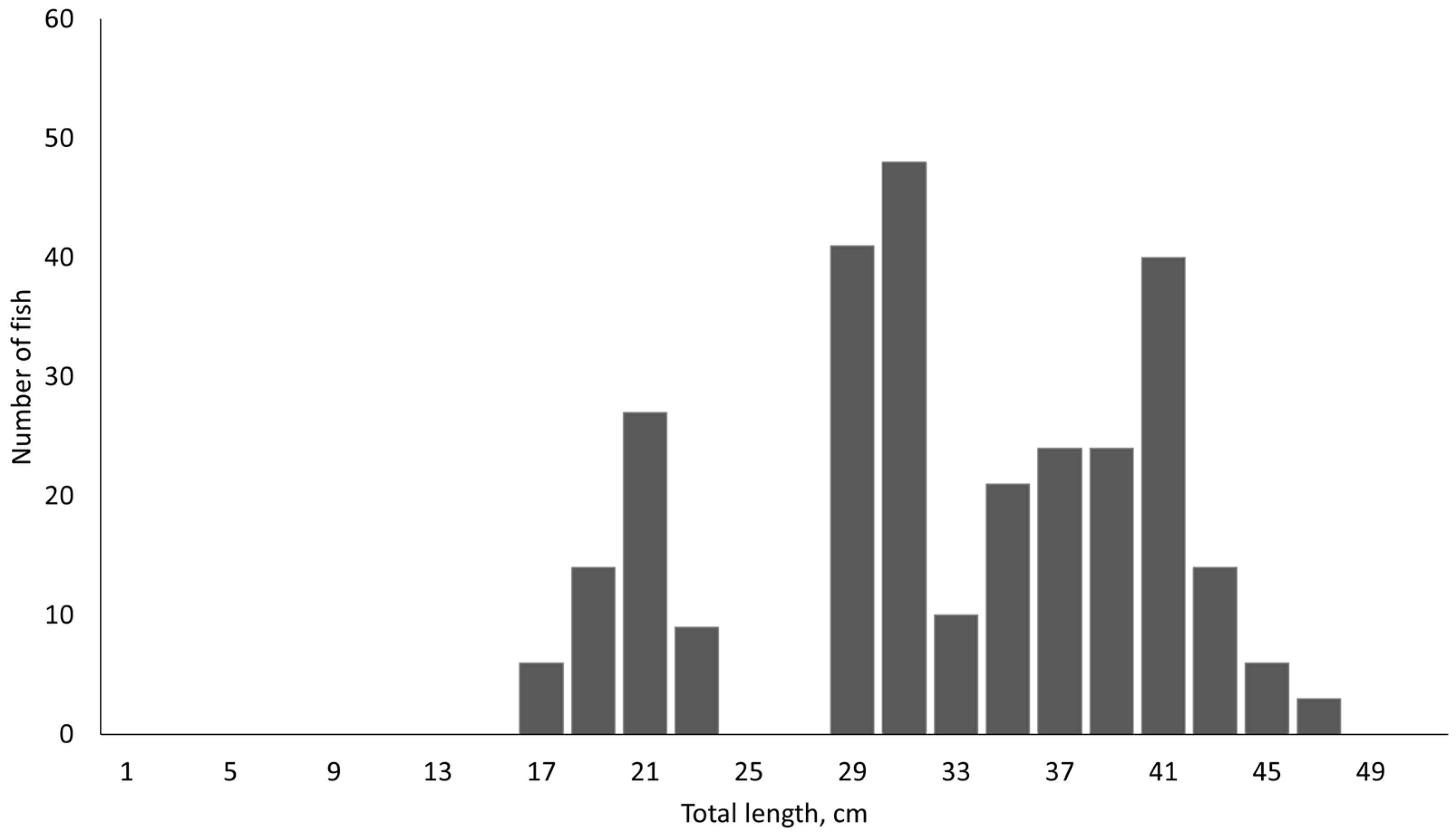
2.1. Sampling Site and Fish Samples
2.2. Sampling Matrix and Preparation
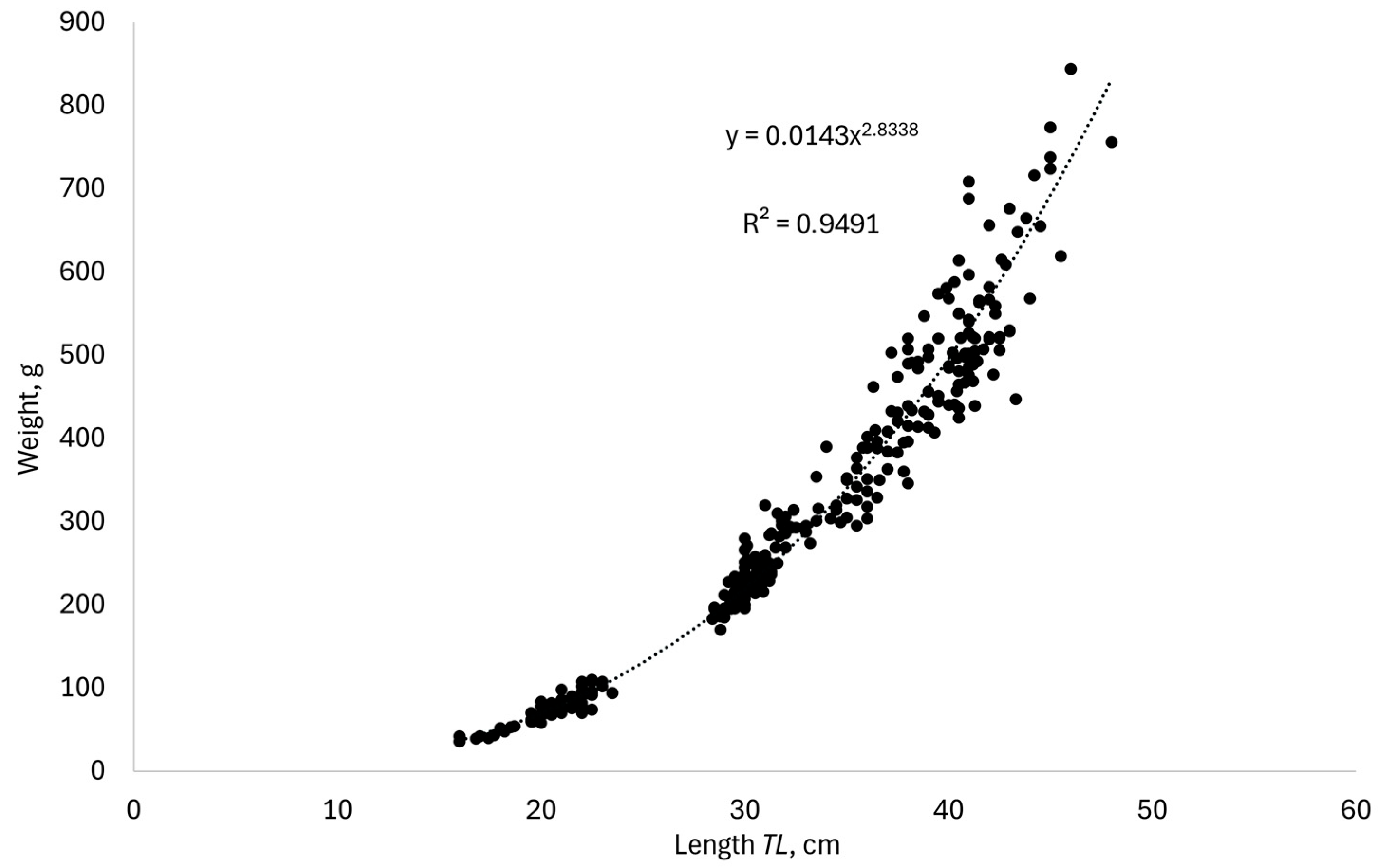
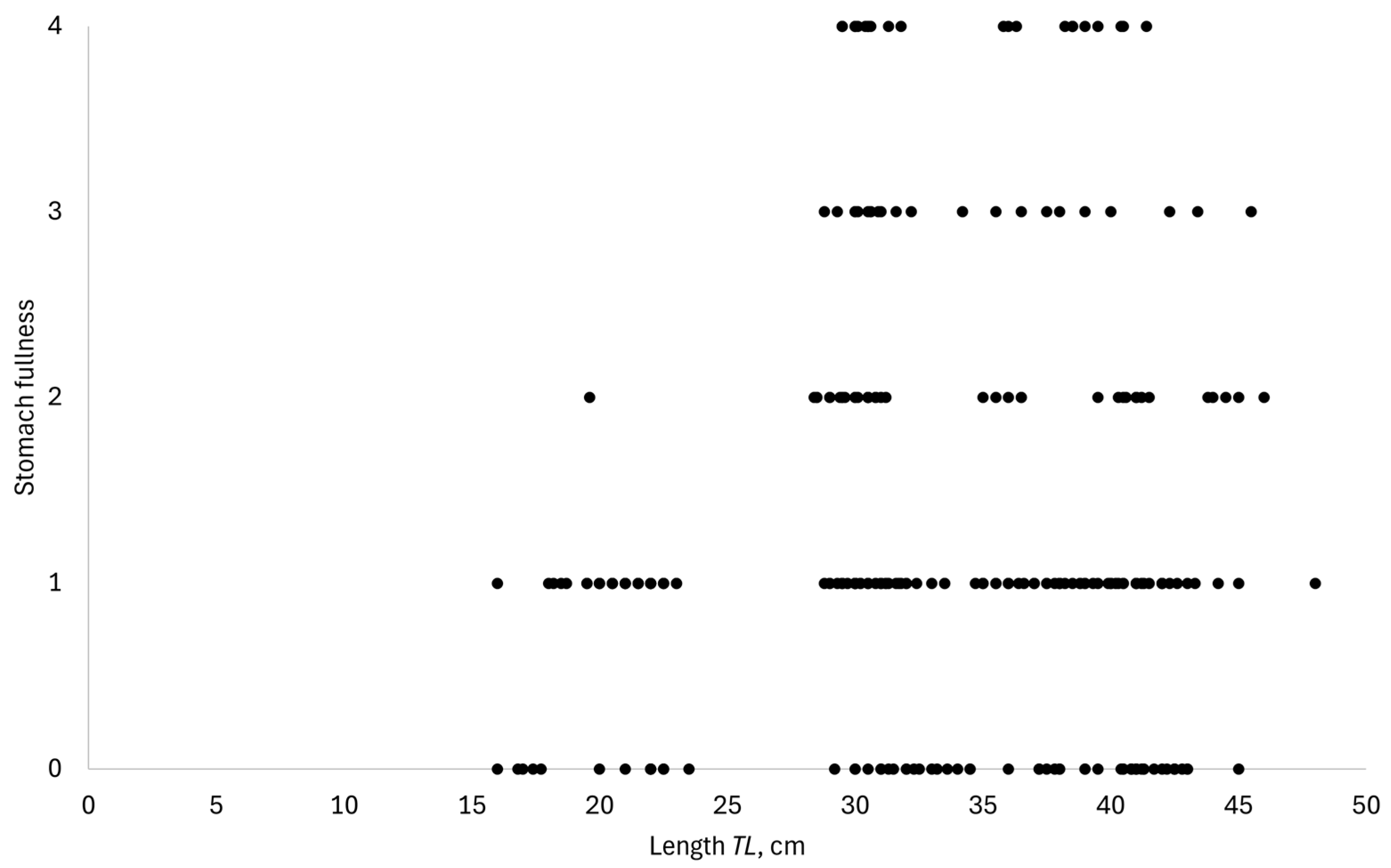
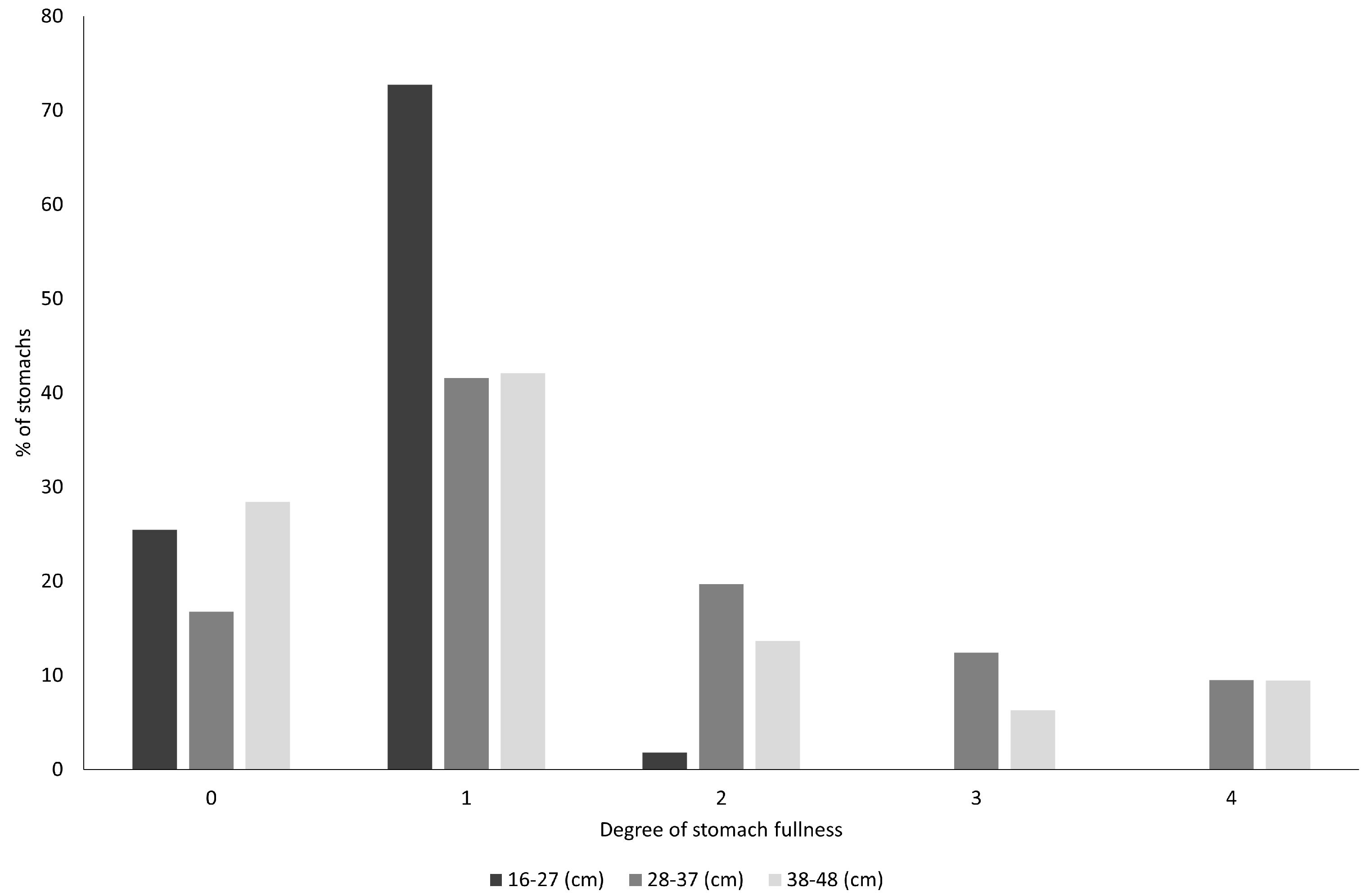
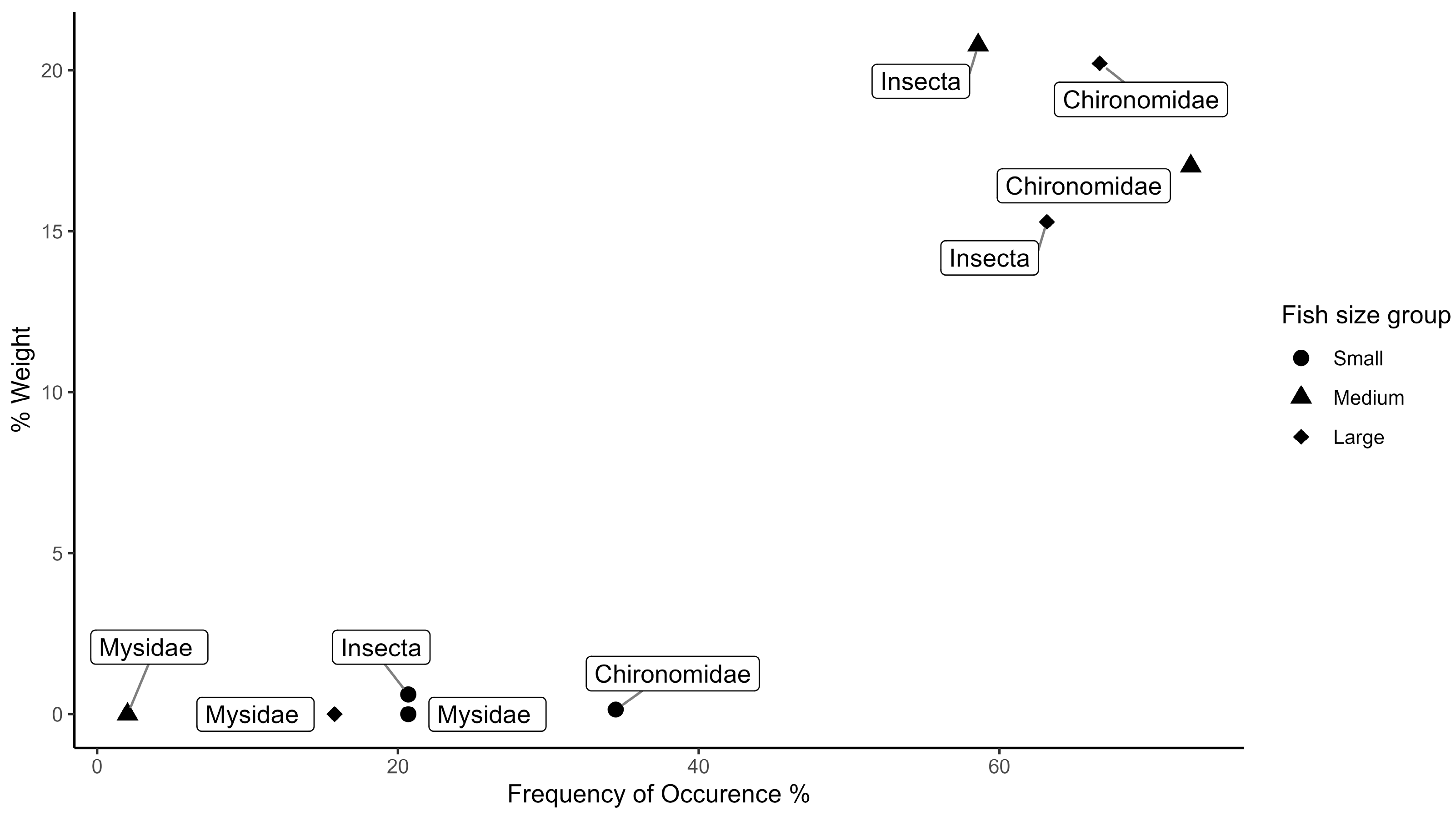
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCA | Stomach Content Analysis |
Appendix A
| Prey Category | Family | Developmental Stage | Ai (%) | Fi (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Medium | Large | Small | Medium | Large | |||
| Aquatic invertebrates | ||||||||
| Anomopoda | Daphniidae | Adult | 7.06 | 9.89 | 12.48 | 6.67 | 9.68 | 7.19 |
| Moinidae | Adult | 0.00 | 1.51 | 1.90 | 0.00 | 1.38 | 1.56 | |
| Bosminidae | Adult | 23.53 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 13.33 | 0.40 | 0.31 | |
| Chydoridae | Adult | 3.53 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 2.22 | 0.00 | 0.63 | |
| Ctenopoda | Sididae | Adult | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.78 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 1.25 |
| Unidentified | Adult | 0.00 | 1.16 | 2.16 | 0.00 | 1.58 | 3.13 | |
| Calanoida | Acartiidae | Adult | 2.35 | 0.61 | 1.31 | 2.22 | 0.99 | 2.19 |
| Unidentified | Adult | 3.53 | 1.87 | 1.50 | 2.22 | 2.17 | 2.19 | |
| Amphipoda | Gammaridae | Adult | 2.35 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 4.44 | 0.99 | 1.25 |
| Unidentified | Adult | 4.71 | 2.17 | 4.51 | 4.44 | 2.17 | 3.75 | |
| Unidentified | Larvae | 11.76 | 1.06 | 0.85 | 8.89 | 2.37 | 2.19 | |
| Mysida | Mysidae | Adult | 7.06 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 13.33 | 0.40 | 2.19 |
| Cyclopoida | Cyclopida | Adult | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 0.94 |
| Mollusca | Valvatidae | Adult | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.78 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.94 |
| Plecoptera | Unidentified | Nymph | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 0.63 |
| Coleoptera | Unidentified | Larvae | 4.71 | 3.08 | 3.53 | 6.67 | 6.32 | 6.56 |
| Unidentified | Adult | 3.53 | 4.59 | 4.38 | 2.22 | 7.51 | 6.88 | |
| Diptera | Chironomidae | Larvae | 1.18 | 14.33 | 11.96 | 2.22 | 12.65 | 9.38 |
| Chironomidae | Pupae | 12.94 | 15.69 | 11.96 | 20.00 | 10.08 | 7.81 | |
| Odonata | Unidentified | Nymph | 0.00 | 3.28 | 2.81 | 0.00 | 2.77 | 2.81 |
| Insecta (unknown Order) | Unidentified | Emerging | 0.00 | 3.83 | 4.31 | 0.00 | 3.16 | 4.06 |
| Unidentified | Larval | 0.00 | 6.00 | 3.92 | 0.00 | 4.94 | 3.44 | |
| Unidentified | Pupae | 4.71 | 3.94 | 3.20 | 2.22 | 4.94 | 4.06 | |
| Terrestrial invertebrates | ||||||||
| Odonata | Unidentified | Adult | 0.00 | 4.09 | 3.92 | 0.00 | 2.96 | 4.06 |
| Diptera | Chironomidae | Adult | 0.00 | 10.39 | 9.54 | 0.00 | 8.50 | 6.88 |
| Trichoptera | Unidentified | Adult | 3.53 | 1.31 | 2.35 | 2.22 | 1.98 | 4.38 |
| Ephemeroptera | Unidentified | Adult | 0.00 | 4.14 | 3.66 | 0.00 | 4.35 | 3.44 |
| Insecta | Unidentified | 0.00 | 4.24 | 3.79 | 0.00 | 3.75 | 3.75 | |
| Other prey items | ||||||||
| Unidentified | 22.41 | 2.67 | 2.88 | |||||
| Osmeridae | Osmeridae | 1.18 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 2.22 | 0.20 | 0.63 | |
| Cyprinidae | Cyprinidae | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.31 | |
| Eggs | 2.35 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 2.22 | 1.38 | 1.56 | ||
| Plant material | 0 | 6.96 | 4.89 | |||||
References
- Kulbicki, M.; Bozec, Y.; Labrosse, P.; Letourneur, Y.; Mou-Tham, G.; Wantiez, L. Diet composition of carnivorous fishes from coral reef lagoons of New Caledonia. Aquat. Living Resour. 2005, 18, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.C.; Jesus, K.F.; Souza, C.C.A.; Amorim, A.F. Identificação do conteúdo estomacal de perciformes e carcharhiniformes: Contribuição ao cruzeiro cientifico no Sudeste e Sul do Brasil (Dez/2009). Rev. Ceciliana 2011, 3, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gandini, C.V.; Boratto, I.A.; Fagundes, D.C.; Pompeu, P.S. Estudo da alimentação dos peixes no rio grande à jusante da usina hidrelétrica de Itutinga, Minas Gerais, Brasil. Série Zool. 2012, 102, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.V.; Vasconcelos-Filho, J.E.; Lira, A.S.; Soares, A.; Eduardo, L.N.; Pas-sarone, R.; Le-Loc’h, F.; Lucena-Frédou, F. Trophic ecology and ecomorphology of the Shorthead Drum, Larimus breviceps (Acan-thuriformes: Sciaenidae), from the Northeastern Brazil. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.A.; Damasceno, D.N.F.; Almeida, R.G.; Chellappa, S. Biologia alimentar do mussum, Synbranchus marmoratus (Bloch, 1795) (Osteichthyes: Synbranchidae) no Açude Marechal Dutra localizado no Semi-árido Brasileiro. Biota Amaz. 2011, 1, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.L.; Semmar, N.; Cartes, J.E.; Tuset, V.M.; Lombarte, A.; Ballestera, E.L.; Vaz-dos-Santos, A.M. Methods for trophic ecology assessment in fishes: A critical review of stomach analyses. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2019, 28, 71–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertoni, E.F.; Palma-Silva, C.; Esteves, F.A. Natural diet of three species of shrimp in a tropical coastal lagoon. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2003, 46, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprahamian, M.; Baglinière, J.-L.; Sabatie, M.; Alexandrino, P.; Thiel, R.; Aprahamian, C. Biology, status and conservation of the anadromous twaite shad Alosa fallax fallax (Lacépède, 1803). Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 2003, 35, 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2010.4. 2010. Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 27 December 2010).
- Volk, J.; Bekkevold, D.; Loeschke, V. Weak population differentiation in northern European populations of the endangered anadromous clupeid Alosa fallax. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71 (Suppl. C), 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.J.P. Clupeidae. In Fishes of the North-Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean; Whitehead, P.J.P., Bauchot, M.-L., Hureu, J.-C., Nielsen, J., Tortonose, E., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1986; Volume I, pp. 271–272. [Google Scholar]
- Taverny, C.; Elie, P. Régime alimentaire de la grande alose Alosa alosa (Linné, 1766) et de l’alose feinte Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803) dans le Golfe de Gascogne [Feeding habits of allis shad Alosa alosa (Linné, 1766) and twaite shad Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803) in the Bay of Biscay]. Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic 2001, 362–363, 837–852, (In French with English Summary). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, C.A.; Almeida, P.R.; Moreira, F.; Costa, J.L.; Costa, M.J. Diet of the twaite shad Alosa fallax (Lacépède) (Clupeidae) in the River Tagus estuary, Portugal. J. Fish Biol. 1992, 41, 1049–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.J.P. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid Fishes of the World (Suborder Clupeoidei). An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of the Herrings, Sardines, Pilchards, Sprats, Shads, Anchovies and Wolf-Herrings. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/1):1-303. In Alosa Fallax. FishBase; Froese, R., Pauly, D., Eds.; Worldwide Web Electronic Publication: Cambridge, MA, USA; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985; Available online: https://www.fishbase.org/search.php?region=europe (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Golani, D.; Ozturk, B.; Basusta, N. Fishes of the Eastern Mediterranean. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2007, 59, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, P.S.; Hatton-Ellis, T.W. Ecology of the Allis and Twaite Shad. In Conserving Natura 2000 Rivers Ecology Series No. 3; English Nature: Peterborough, UK, 2003; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Nachon, D.J.; Sanchez-Hernandez, J.S.; Vieira-Lanero, R.; Cobo, F. Feeding of Twaite Shad, Alosa fallax (Lacepede, 1803), during the upstream spawning migration in the River Ulla (NW Spain). Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 64, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankus, S. Spawning Migration and Population Condition of Twaite Shad (Alosa fallax, Lacépède 1803) in Lithuania. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2009, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Repečka, R. Changes in biological indices and abundance of salmon, sea trout, smelt, vimba and twaite shad in the coastal zone of the Baltic Sea and Curonian Lagoon at the beginning of spawning migration. Acta Zool. Litu. 2003, 13, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, R.; Riel, P.; Neumann, R.; Winkler, H.M.; Böttcher, U.; Gröhsler, T. Return of twaite shad Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803) to the Southern Baltic Sea and the transitional area between the Baltic and North Seas. Hydrobiologia 2008, 602, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprahamian, M.W. The diet of juvenile and adult twaite shad Alosa fallax fallax (Lacépède) from the rivers Severn and Wye (Britain). Hydrobiologia 1989, 179, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, J.; Kennedy, M. Notes on some Irish estuarine and inshore fishes. Ir. Fish. Investig. 1967, 3, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Glossary of fish terms. Available online: https://australian.museum/learn/animals/fishes/glossary-of-fish-terms/#s-section (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Pliuraite, V. Species diversity of zooplankton in the Curonian Lagoon in 2001. Acta Zoologica Lituanica 2003, 13, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, A.S. Quantitative characteristics of zooplankton of the Curonian lagoon taken by different sampling methods. Hydrobiol. J. 2011, 47, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). Available online: https://www.itis.gov/ (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- The European Register of Marine Species (ERMS). Available online: https://www.marbef.org/data/erms.php (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- ICES. Identification Leaflets for Plankton. Available online: https://www.ices.dk/Science/publications/Pages/ID_leaflets_plankton.aspx (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- The Great International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Available online: http://www.iczn.org (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach contents analysis: A review of methods and their application. J. Fish Biol. 1980, 17, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesmann, S.; Thiel, R. Feeding of juvenile twaite shad (Alosa fallax Lacepede, 1803) in the Elbe Estuary. Bull. Fr. Peche Piscic. 2001, 362–363, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCepède, B.G.E. Histoire Naturelle des Poisdons; Plassan: Paris, France, 1803; Volume 5, p. 803. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Calif. Fish Game 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, M.J. Predator feeding strategy and prey importance: A new graphical analysis. J. Fish Biol. 1990, 36, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, P.A.; Gabler, H.M.; Staldvik, F.J. A New Approach to Graphical Analysis of Feeding Strategy from Stomach Contents Data—Modification of the Costello (1990) Method. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 48, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M. Stomach contents of adult sea trout caught in six English rivers. J. Fish Biol. 1997, 50, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, D.; O’Maoileidigh, N.; McCarthy, T.K. The biology, ecology and future conservation of twaite shad (Alosa fallax Lace’pede), allis shad (Alosa alosa L.) and killarney shad (Alosa fallax killarnensis Tate Regan) in Ireland. Biol. Environ. Proc. R. Ir. Acad. 2004, 104B, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, P.S.; Lyle, A.A. Ecology of Allis Shad Alosa alosa and Twaite Shad Alosa fallax in the Solway Firth, Scotland. Hydrobiologia 2005, 534, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhan, T.; Akyol, O.; Sever, T.M.; Kara, A. Diet composition of adult twaite shad (Alosa fallax) in the Aegean Sea (Izmir Bay, Turkey). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2012, 92, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacevičius, E. Ilgalaikė perpelės (Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803: Clupeidae)) mitybos ir apsikrėtimo parazitais tyrimai pietryčių Baltijoje ir Kuršių mariose [Investigation of feeding peculiarities and parasites of twaite shad (Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803: Clupeidae)) from Lithuanian coastal zone and the Curonian Lagoon]. Žuvininkystė Litetuvoje 2007, 7, 125–141, (In Lithuanian with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Skora, M.E.; Sapota, M.R.; Skora, K.E.; Pawelec, A. Diet of the twaite shad Alosa fallax (Lacepede, 1803) (Clupeidae) in the Gulf of Gdansk, the Baltic Sea. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2012, 41, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, A.D.; Noble, R.A.A.; Harvey, J.P.; Cowx, I.G. The diets and parasites of larval and 0+ juvenile twaite shad in the lower reaches and estuaries of the rivers Wye, Usk and Towy, UK. Hydrobiologia 2008, 614, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, S.; Schirmer, M. Die Finte (Alosa fallax) wieder in der Weser—Endlich gesicherte Daten [The twaite shad (Alosa fallax) back in the Weser—Finally validated data]. Verh. Ges. Ichthyol. Bd. 2006, 5, 269–283, (In German with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, A. The Fishes of the British Isles and North-West Europe; Macmillan: London, UK, 1969; p. 613. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolsky, G.V. Special Ichthyology; National Science Foundation & Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; p. 538. [Google Scholar]
- Badola, S.P.; Singh, H.R. Food and feeding habits of fishes of the Genera Tor, Puntius and Barilius. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. B Biol. Sci. 1980, 46, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Biology, Fisheries and Conservation Status. In Migratory Fishes of South America; Carolsfeld, J., Harvey, B., Ross, C., Baer, A., Eds.; IDRC, World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; p. 388. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the use of insects in the diet of farmed fish: Past and future. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Biagioni, R.C.; Smith, W.S. Estudo da dieta natural da ictiofauna de um reservatorio centenario, Sao Paulo, Brasil. Iheringia. Ser. Zool. Porto Alegre 2014, 104, 404–412. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, I.D.; Soares, M.O. The seasonal diet of Aequidens tetramerus (Cichlidae) in a small forest stream in the Machado River basin, Rondonia, Brazil. Acta Amaz. 2015, 45, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Neves, M.; Delariva, R.L.; Lazzarini Wolff, L. Diet and ecomorphological relationships of an endemic, species-poor fish assemblage in a stream in the Iguacu National Park. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2015, 13, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severo-Neto, F.; Teresa, F.B.; Froehlich, O. Ecomorphology and diet reflect the spatial segregation between two Siluriformes species inhabiting a stream of the Bodoquena Plateau, in Central Brazil. Iheringia. Ser. Zool. Porto Alegre 2015, 105, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abilhoa, V.; Valduga, M.O.; Frehse, F.A.; Vitule, J.R.S. Use of food resources and resource partitioning among five syntopic species of Hypostomus (Teleostei: Loricariidae) in an Atlantic Forest river in southern Brazil. Zoologia 2016, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, D.C.; Perissinotto, R.; Carrasco, N.K. Temporal and spatial dietary dynamics of the longspine glassy (Ambassis ambassis) in the St. Lucia estuarine system, iSimangaliso Wetland Park. Water SA 2015, 41, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferrareze, M.; Nogueira, M.G.; Casatti, L. Differences in ichthyofauna feeding habits among lateral lagoons and the river channel in a large reservoir. Braz. J. Biol. 2015, 75, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Spataru, P.; Hepher, B.; Halevy, A. The effect of the method of supplementary feed application on the feeding habits of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) with regard to natural food in ponds. Hydrobiologia 1980, 72, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Poleto, S.L.; Venere, P.C. Feeding of juvenile pirarucu (Arapaima gigas, arapaimidae) in their natural environment, lago Quatro Bocas, Araguaina- MT, Brazil. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2005, 3, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhakim, A.; Addo, S.; Lawan, Z.A.; Ebenezer, A. Feeding habits and conditions factor of Oreochromis niloticus in Lake Alau, Northeastern Nigeria. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 3, 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, S.P. Native fish species boosting Brazilian’s aquaculture development. Acta Fish. Aquat. Resour. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, R.M. Food Habits of fishes and larger invertebrates of Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana, an estuarine community. Inst. Mar. Sci. 1958, 5, 353–416. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, J. Feeding behaviour repertoire of the alewives, Alosa pseudoharengus and the ciscoes, Coregonus hoyi and C. artedii. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 1978, 35, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, B.P. The effect of fish predation on the zooplankton of ten Adirondack lakes, with particular reference to the alewife Alosa Pseudoharengus. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1971, 2, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nobili, E.; Gorfine, H.; Jakubavičiūtė, E.; Pūtys, Ž.; Ložys, L. Diet Composition of Twaite Shad, Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803), During the Spawning Migration to the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania). Fishes 2025, 10, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060256
Nobili E, Gorfine H, Jakubavičiūtė E, Pūtys Ž, Ložys L. Diet Composition of Twaite Shad, Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803), During the Spawning Migration to the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania). Fishes. 2025; 10(6):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060256
Chicago/Turabian StyleNobili, Edoardo, Harry Gorfine, Eglė Jakubavičiūtė, Žilvinas Pūtys, and Linas Ložys. 2025. "Diet Composition of Twaite Shad, Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803), During the Spawning Migration to the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania)" Fishes 10, no. 6: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060256
APA StyleNobili, E., Gorfine, H., Jakubavičiūtė, E., Pūtys, Ž., & Ložys, L. (2025). Diet Composition of Twaite Shad, Alosa fallax (Lacépède, 1803), During the Spawning Migration to the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania). Fishes, 10(6), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060256






