Transcriptomic Responses of Gonadal Development to Photoperiod Regulation in Amur Minnow (Phoxinus lagowskii)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. RNA Isolation and RNA-Seq Library Preparation
2.5. De Novo Assembly and Gene Annotation
2.6. Expression Analysis
2.7. Differential Gene Expression and Enrichment Analysis
2.8. qRT-PCR Validation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
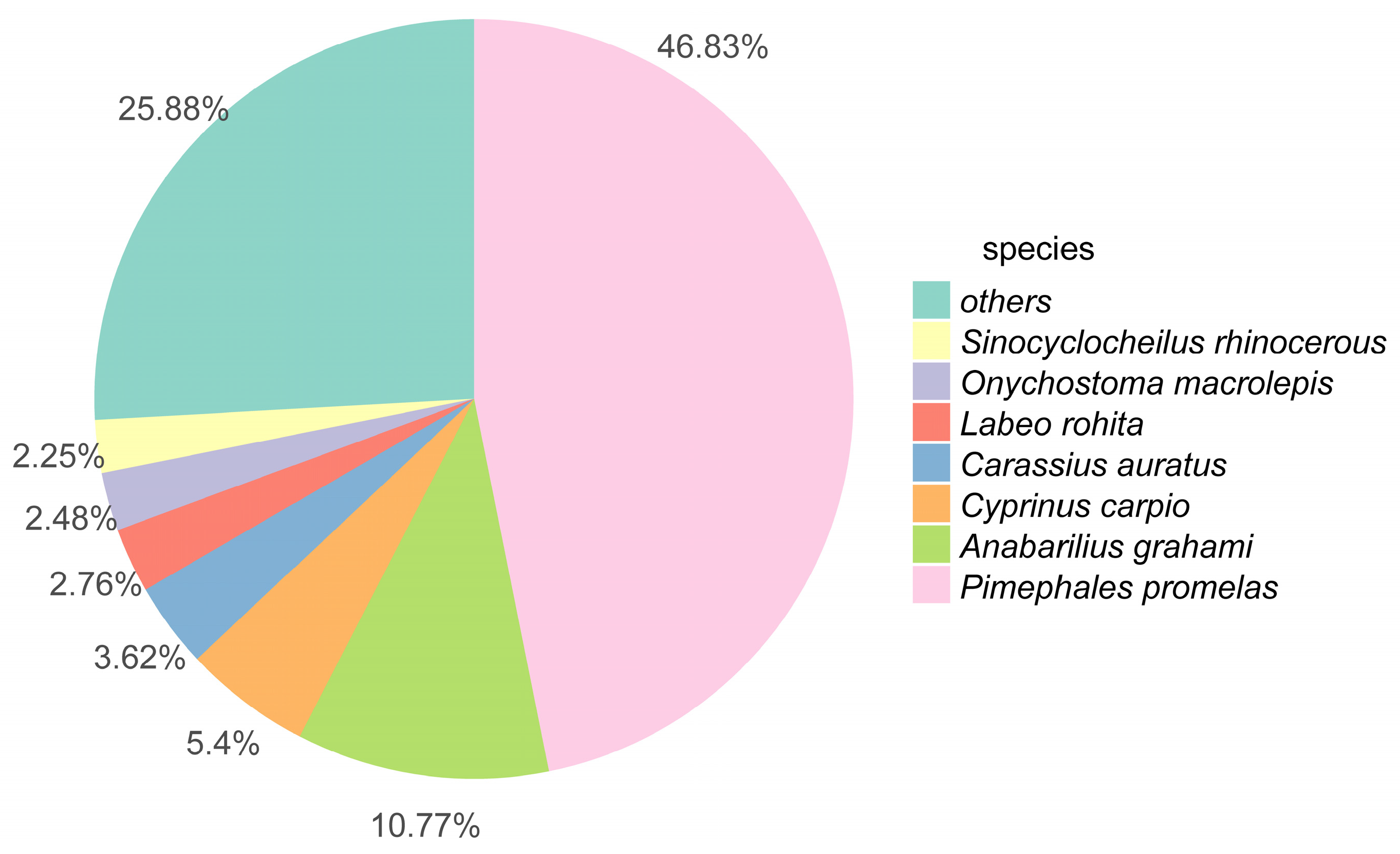
3.1. Transcriptome Sequence Assessment and Annotation
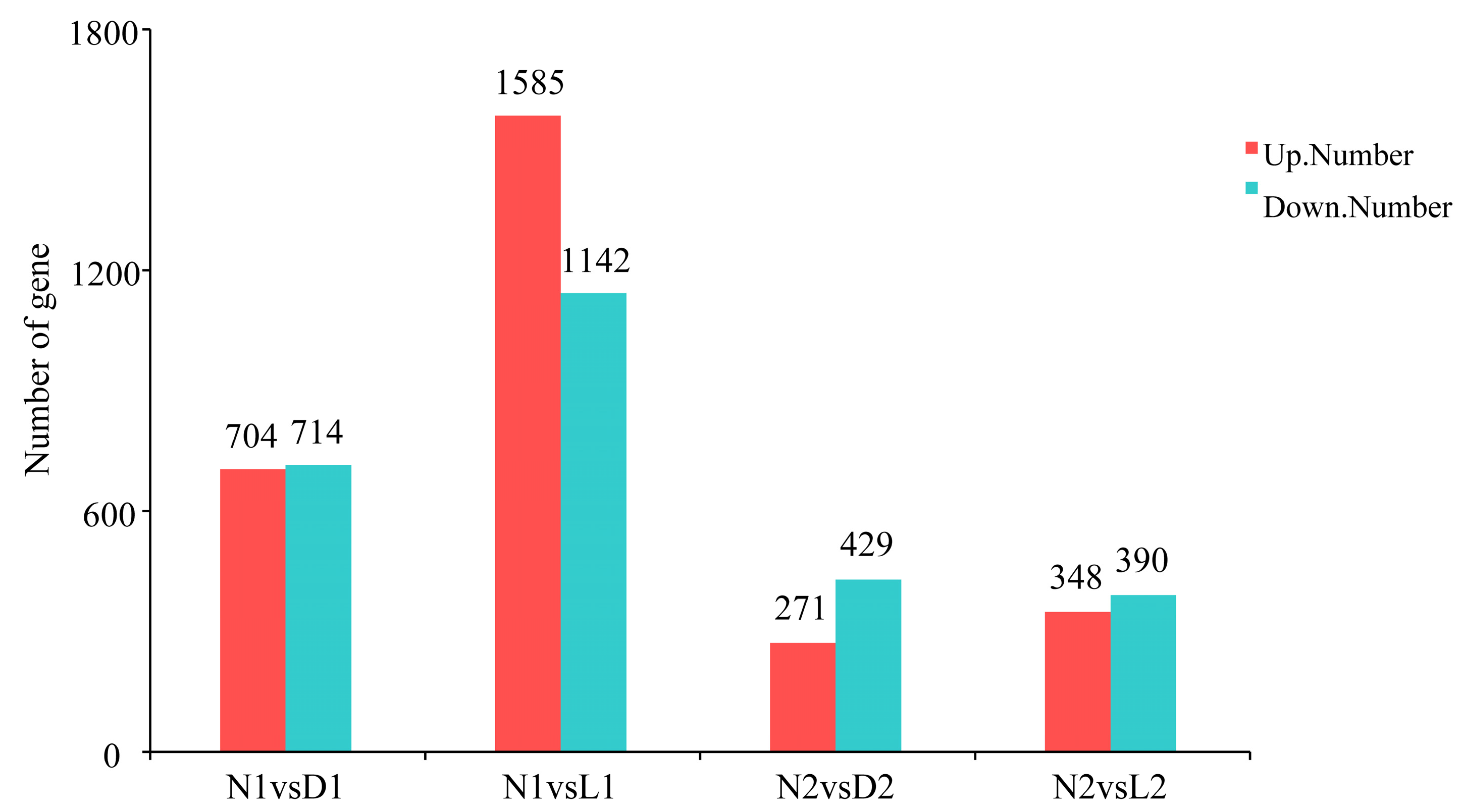
3.2. Differential Expression Analysis
3.3. GO Functional Classification of Differentially Expressed Genes
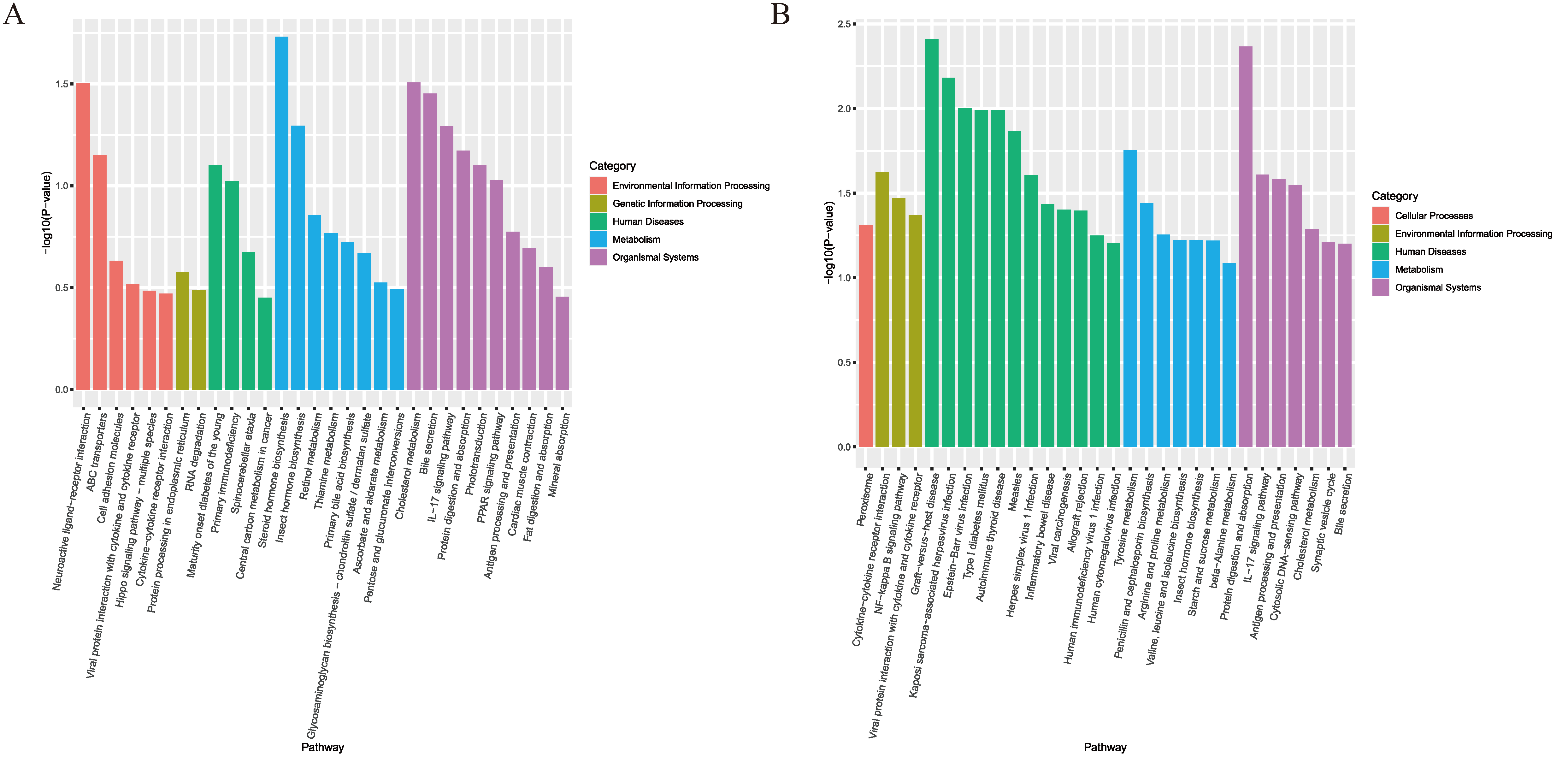
3.4. Significant Enrichment Analysis of KEGG Pathway
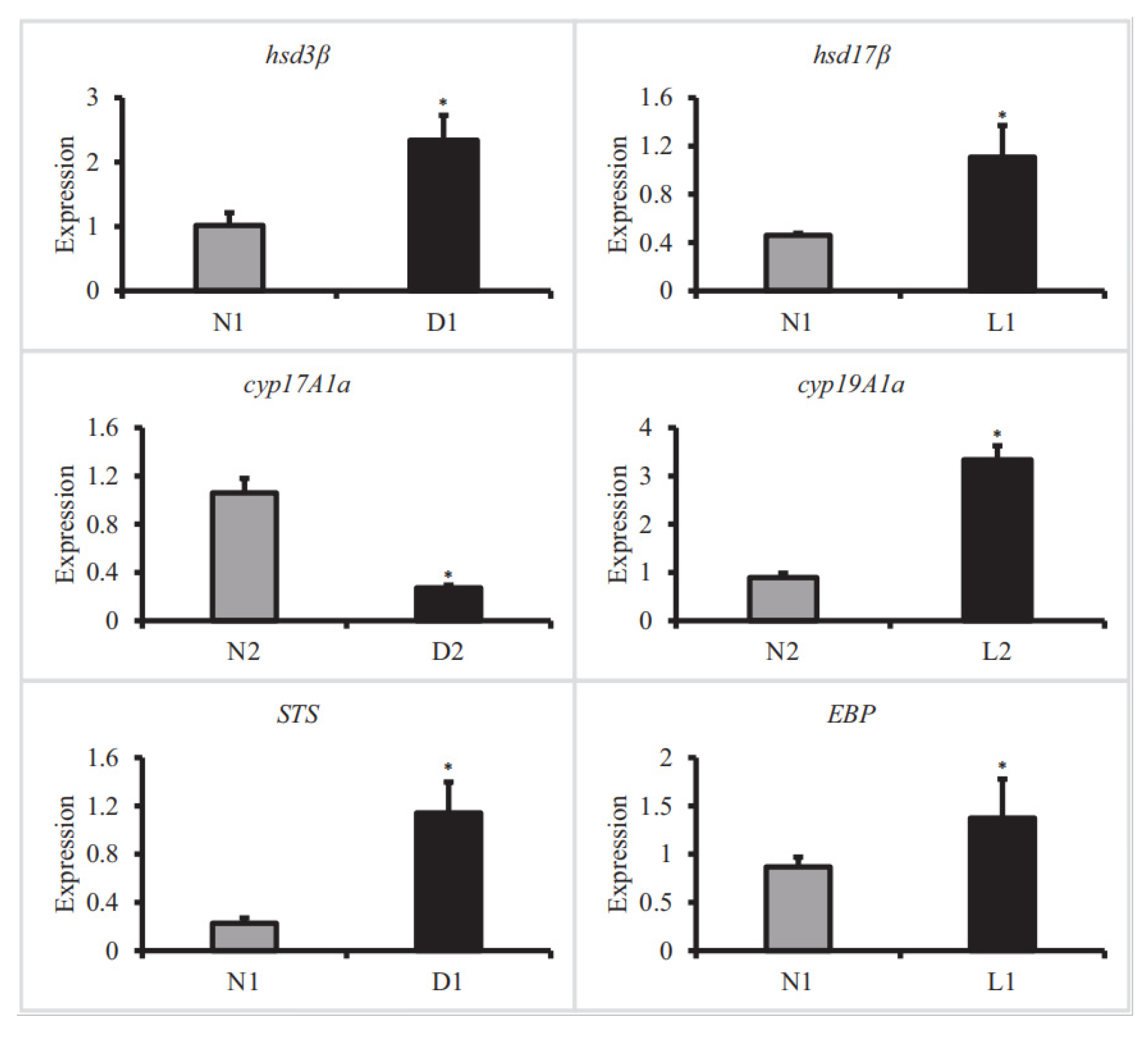
3.5. qRT-PCR Verification
4. Discussion
4.1. Male Responses to Photoperiod
4.2. Female Responses to Photoperiod
4.3. Aquaculture Applications of Photoperiod Regulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adolfi, M.C.; Depincé, A.; Wen, M.; Pan, Q.; Herpin, A. Development of Ovaries and Sex Change in Fish: Bringing Potential into Action. Sex. Dev. 2023, 17, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Teletchea, F.; Kestemont, P.; Milla, S.; Fontaine, P. Photothermal control of the reproductive cycle in temperate fishes. Rev. Aquac. 2010, 2, 209–222. [Google Scholar]
- Imamura, S.; Hur, S.P.; Takeuchi, Y.; Badruzzaman, M.; Mahardini, A.; Rizky, D.; Takemura, A. Effect of short- and long-term melatonin treatments on the reproductive activity of the tropical damselfish Chrysiptera cyanea. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuzawa, K.; Furukawa, K.; Aida, K.; Hanyu, I. Effects of photoperiod and temperature on gonadal maturation, and plasma steroid and gonadotropin levels in a cyprinid fish, the honmoroko Gnathopogon caerulescens. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1989, 75, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.Q.; Dung, H.T.N.; Arukwe, A. Photoperiod manipulation in the induced breeding of the rabbit fish (Siganus guttatus). Tạp Chí Khoa Học Công Nghệ Thủy Sản Trường Đại Học Nha Trang 2018, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Closs, L.E.; Royan, M.R.; Sayyari, A.; Mayer, I.; Weltzien, F.-A.; Baker, D.M.; Fontaine, R.H. Impact of light pollution at night on male reproductive success in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Gao, D.; Lu, J.; Sun, X. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals the Sexual Dimorphism of Gene Expression Patterns during Gonad Differentiation in the Half-Smooth Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizky, D.; Mahardini, A.; Byun, J.; Takemura, A. Molecular cloning of insulin-like growth factor 3 (igf3) and its expression in the tissues of a female damselfish, Chrysiptera cyanea, in relation to seasonal and food-manipulated reproduction. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 295, 113479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Yin, J.S.; Du, J.; Geng, L.W.; Bai, Q.L.; Xu, W. Analysis of some nutritional components and evaluation of muscle protein of Phoxinus lagowskii Dybowskii. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2013, 35, 406–407+410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Li, B.M.; Jiang, Y.S.; Meng, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Su, X.; Jiang, Z.Q. Study on Individual Fecundity of Phoxinus lagowskii in Taizi River of Benxi City. J. Yangtze Univ. 2013, 10, 28–32+6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.N.; Li, J.; Jin, G.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, J.W.; Yang, P.M.; Jiang, X.H. Artificial Propagation of Fat Minnow Phoxinus lagowskii Dybowski. Fish Sci. 2013, 32, 672–675. [Google Scholar]
- Rad, F.; Bozaoğlu, S.; Gözükara, S.E.; Karahan, A.; Kurt, G. Effects of different long-day photoperiods on somatic growth and gonadal development in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Aquaculture 2006, 255, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Oliver, C.; Brun, C.; Juarez-Martinez, A.B.; Tarabay, Y.; Kadlec, J.; de Massy, B. Mouse REC114 is essential for meiotic DNA double-strand break formation and forms a complex with MEI4. Life Sci. Alliance 2018, 1, e201800259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, J.G.; Zhao, J.; Brundell, E.; Daneholt, B.; Höög, C. The murine SCP3 gene is required for synaptonemal complex assembly, chromosome synapsis, and male fertility. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saram, P.D.; Wilkinson, C.; Murdoch, J. Role of outer dense fiber of sperm tails 2-like (ODF2L) protein in ciliation in mammalian cells and in zebrafish. Cilia 2015, 4 (Suppl. S1), P32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, F.F.; Mönnich, M.; Czirr, E.; Hollemann, T.; Hoyer-Fender, S. Outer dense fibre protein 2 (ODF2) is a self-interacting centrosomal protein with affinity for microtubules. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 4643–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Lü, Z.L. Outer dense fiber 2 and sperm function: Progress in studies. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 2017, 23, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Arukwe, A. Steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein and cholesterol side-chain cleavage (P450scc)-regulated steroidogenesis as an organ-specific molecular and cellular target for endocrine disrupting chemicals in fish. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2008, 24, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Miao, Y.; Cai, J.; Song, L.; Wei, J.; Chakraborty, T.; Wu, L.; Wang, D.; et al. The role of StAR2 gene in testicular differentiation and spermatogenesis in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 214, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, W.; Chen, S. Identification and Expression Pattern of cyp26b1 Gene in Gonad of the Chinese Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Animals 2022, 12, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Hao, S.L.; Yang, W.X. How does retinoic acid (RA) signaling pathway regulate spermatogenesis? Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.M.; Zhong, G.; Hogarth, C.; Huang, W.; Topping, T.; LaFrance, J.; Palau, L.; Czuba, L.C.; Griswold, M.; Ghiaur, G.; et al. Knockout of Cyp26a1 and Cyp26b1 during postnatal life causes reduced lifespan, dermatitis, splenomegaly, and systemic inflammation in mice. Faseb J. 2020, 34, 15788–15804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, G.; Li, H.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Petkovich, M. Apoptotic extinction of germ cells in testes of Cyp26b1 knockout mice. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4560–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damdimopoulou, P.; Chiang, C.; Flaws, J.A. Retinoic acid signaling in ovarian folliculogenesis and steroidogenesis. Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 87, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubzens, E.; Young, G.; Bobe, J.; Cerdà, J. Oogenesis in teleosts: How eggs are formed. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Ahn, J.; Suh, Y.; Ziouzenkova, O.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K. Retinol Binding Protein 7 Promotes Adipogenesis in vitro and Regulates Expression of Genes Involved in Retinol Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 876031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseyev, G.; Chen, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Wu, B.X.; Ma, J.X. RPE65 is the isomerohydrolase in the retinoid visual cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12413–12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; Li, F.; Zheng, Z.; Chai, R.; Hou, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, G. Oogenesis, vitellogenin-mediated ovarian degeneration and immune response in the annual fish Nothobranchius guentheri. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 66, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Tan, J.T.; Emelyanov, A.; Korzh, V.; Gong, Z. Hepatic and extrahepatic expression of vitellogenin genes in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Gene 2005, 356, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Guo, C.; Wang, D. Expression and localization of vitellogenin genes (VTG) and receptor (VGR) in the gonad development of silver pomfret Pampus argenteus. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 1575–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Jo, H.; Kim, D.K.; Kwak, I.S. Environmental Pollutants Impair Transcriptional Regulation of the Vitellogenin Gene in the Burrowing Mud Crab (Macrophthalmus japonicus). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.M. Effects of 17 beta-estradiol injection and red-spectrum light on eyestalk hormones and vitellogenesis of the ornamental cleaner shrimp Lysmata amboinensis (De Man, 1888) (Decapoda: Caridea: Lysmatidae). J. Crustac. Biol. 2020, 40, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wathuliyadde, N.; Willmore, K.E.; Kelly, G.M. Bone Mineralization Regulation: Using Zebrafish as a Model to Study ANKH-associated Mineralization Disorders. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, P.M.; Renfro, J.L.; Power, D.M.; Canario, A.V. The parathyroid hormone family of peptides: Structure, tissue distribution, regulation, and potential functional roles in calcium and phosphate balance in fish. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R679–R696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Duan, C. Stanniocalcin 1a regulates organismal calcium balance and survival by suppressing Trpv6 expression and inhibiting IGF signaling in zebrafish. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1276348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.W.; Pisarska, M.D.; Hsueh, A.J. Identification of a stanniocalcin paralog, stanniocalcin-2, in fish and the paracrine actions of stanniocalcin-2 in the mammalian ovary. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Takeuchi, K.; Csaki, L.S.; Reue, K. Lipin-1 phosphatidic phosphatase activity modulates phosphatidate levels to promote peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) gene expression during adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3485–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.M.; Li, L.O.; Wu, P.C.; Koves, T.R.; Ilkayeva, O.; Stevens, R.D.; Watkins, S.M.; Muoio, D.M.; Coleman, R.A. Adipose acyl-CoA synthetase-1 directs fatty acids toward beta-oxidation and is required for cold thermogenesis. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughey, C.C.; Crawford, P.A. Pyruvate Carboxylase Wields a Double-Edged Metabolic Sword. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1236–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yánez, A.J.; Nualart, F.; Droppelmann, C.; Bertinat, R.; Brito, M.; Concha, I.I.; Slebe, J.C. Broad expression of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase provide evidence for gluconeogenesis in human tissues other than liver and kidney. J. Cell Physiol. 2003, 197, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Carrasco, M.; Harrison, L.; Jennions, M.D.; Head, M.L. Combined effects of rearing and testing temperatures on sperm traits. J. Evol. Biol. 2020, 33, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Cao, Z. Recruitment of IRAK to the interleukin 1 receptor complex requires interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12829–12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesche, H.; Korherr, C.; Kracht, M.; Falk, W.; Resch, K.; Martin, M.U. The interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) is essential for IL-1-induced activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) and stress-activated protein kinases (SAP kinases). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7727–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Target Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CGGTATCCATGAGACCACCT | CTTCTGCATCCTGTCAGCAA |
| 3β-Hsd | TACCACATCACGAACGACGA | AGCCACAGAAGCAGAGATAACAC |
| 17β-Hsd | AGGTCACTTTGGCAGATGGG | GGACACTTCTCGGATGGTATTCA |
| 19A1a-Cyp | ACATTCTCAACTTACTGCGGTG | ATACTGTCTGCCAGGTGTCAAA |
| 17 A1a -Cyp | GCCTCACAGAGCCATACGAAAC | CAGCAGATAAGCCGTGAATAGAA |
| STS | GTGACCATTTCCCCCCTGAT | CTGCGAGATGCTCCTCCTTT |
| EBP | GCCACGCAACCTGTCTATTC | TAACCTTCTCCCTCCGCTAA |
| Transcript | Unigene | |
|---|---|---|
| Total Length (bp) | 626,836,460 | 180,623,777 |
| Sequence Number | 486,908 | 191,205 |
| Max. Length (bp) | 28,486 | 28,486 |
| Mean Length (bp) | 1287.38 | 944.66 |
| N50 (bp) | 2249 | 1372 |
| N50 Sequence No. | 75,160 | 29,436 |
| N90 (bp) | 486 | 394 |
| N90 Sequence No. | 322,523 | 138,570 |
| GC% | 42.4 | 40.64 |
| Sample | Up/Down | p-Value | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1vsN1 | up | 0.029474453 | 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type |
| 0.000291249 | 3beta-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase/decarboxylase | ||
| 0.000999736 | 3-beta-hydroxysteroid-Delta (8), Delta (7)-isomerase | ||
| 0.000722967 | synaptonemal complex protein | ||
| 0.000003104 | synaptonemal complex protein 3 | ||
| 0.002363752 | meiotic nuclear division protein 1 homolog | ||
| 0.007767200 | meiotic recombination protein REC114 | ||
| 0.013167094 | outer dense fiber protein 2 | ||
| D1vsN1 | up | 0.010584677 | steryl-sulfatase |
| 0.003844435 | IgGFc-binding protein | ||
| 0.011899415 | interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 | ||
| 0.045882465 | interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1-A, partial | ||
| 0.000040235 | interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1-A | ||
| down | 0.045486438 | cytochrome P450 26B1 | |
| 0.025096338 | steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, mitochondrial | ||
| L2vsN2 | up | 0.021603321 | interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1-A |
| 0.041204660 | Vitellogenin | ||
| 0.011875355 | gonad-type aromatase | ||
| 0.006767053 | Stanniocalcin-1 | ||
| 0.020644057 | progressive ankylosis protein homolog B | ||
| 0.029653844 | parathyroid hormone-like hormone a isoform X1 | ||
| down | 0.043634470 | retinoid-binding protein 7 | |
| 0.017177363 | retinoid isomerohydrolase | ||
| 0.032199842 | oocyte zinc finger protein XlCOF15-like | ||
| D2vsN2 | up | 0.007083353 | interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1-A |
| 0.011621115 | phosphatidate phosphatase LPIN1 | ||
| down | 0.014829061 | long-chain-fatty-acid-CoA ligase 1a isoform X2 | |
| 0.015619958 | pyruvate carboxylase, mitochondrial | ||
| 0.045357704 | fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase isozyme 2 isoform X1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Transcriptomic Responses of Gonadal Development to Photoperiod Regulation in Amur Minnow (Phoxinus lagowskii). Fishes 2025, 10, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030137
Zhang M, Li Y. Transcriptomic Responses of Gonadal Development to Photoperiod Regulation in Amur Minnow (Phoxinus lagowskii). Fishes. 2025; 10(3):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mingchao, and Yingdong Li. 2025. "Transcriptomic Responses of Gonadal Development to Photoperiod Regulation in Amur Minnow (Phoxinus lagowskii)" Fishes 10, no. 3: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030137
APA StyleZhang, M., & Li, Y. (2025). Transcriptomic Responses of Gonadal Development to Photoperiod Regulation in Amur Minnow (Phoxinus lagowskii). Fishes, 10(3), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030137







