Effects of Sampling Design on Population Abundance Estimation of Ichthyoplankton in Coastal Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. ‘True’ Values Based on Ordinary Kriging Interpolation
2.3. Sampling Designs
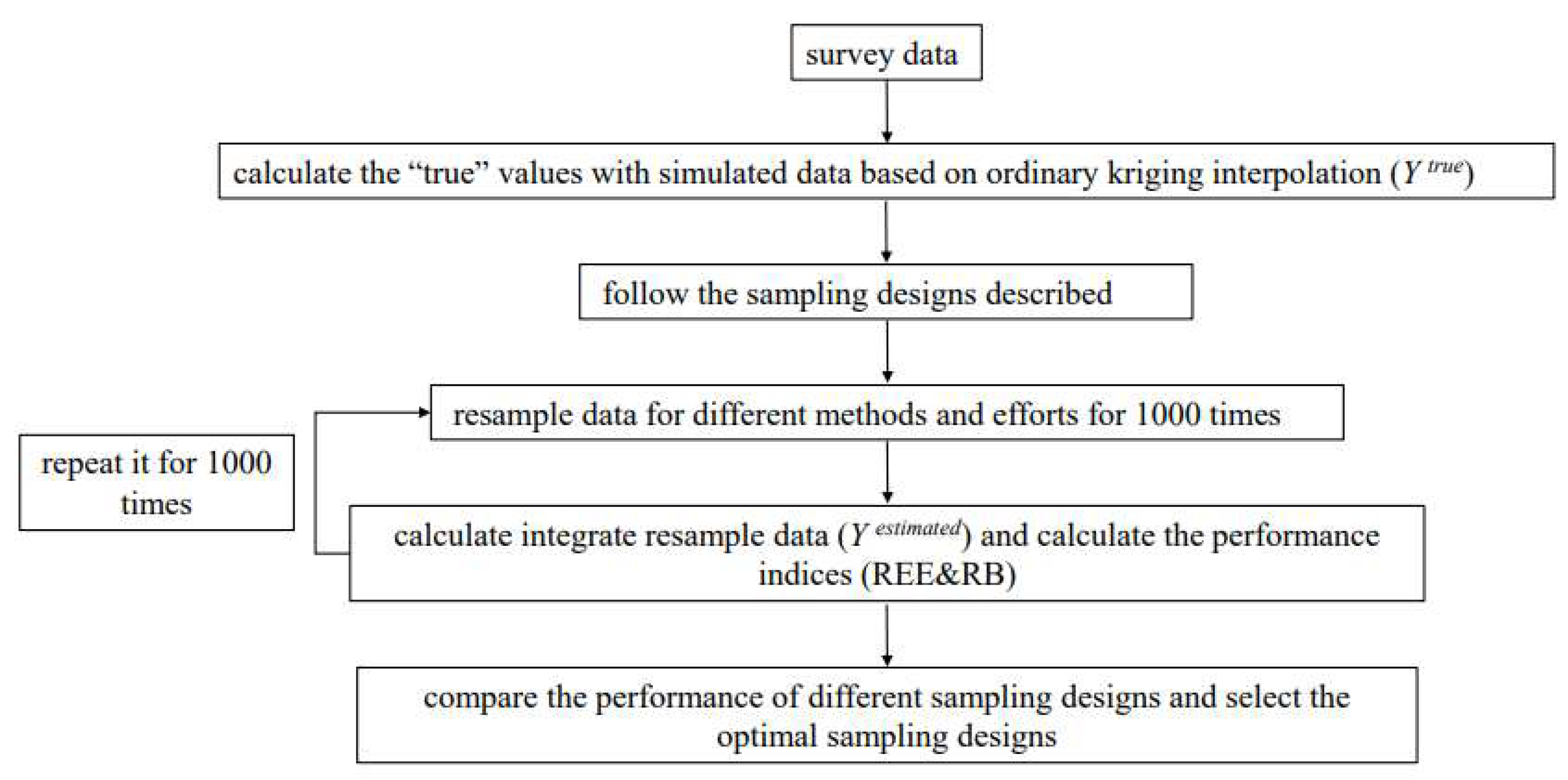
2.4. Simulation Procedure
2.5. Measures for Evaluating Performance
3. Results
3.1. “True” Value of Spatiotemporal Distribution
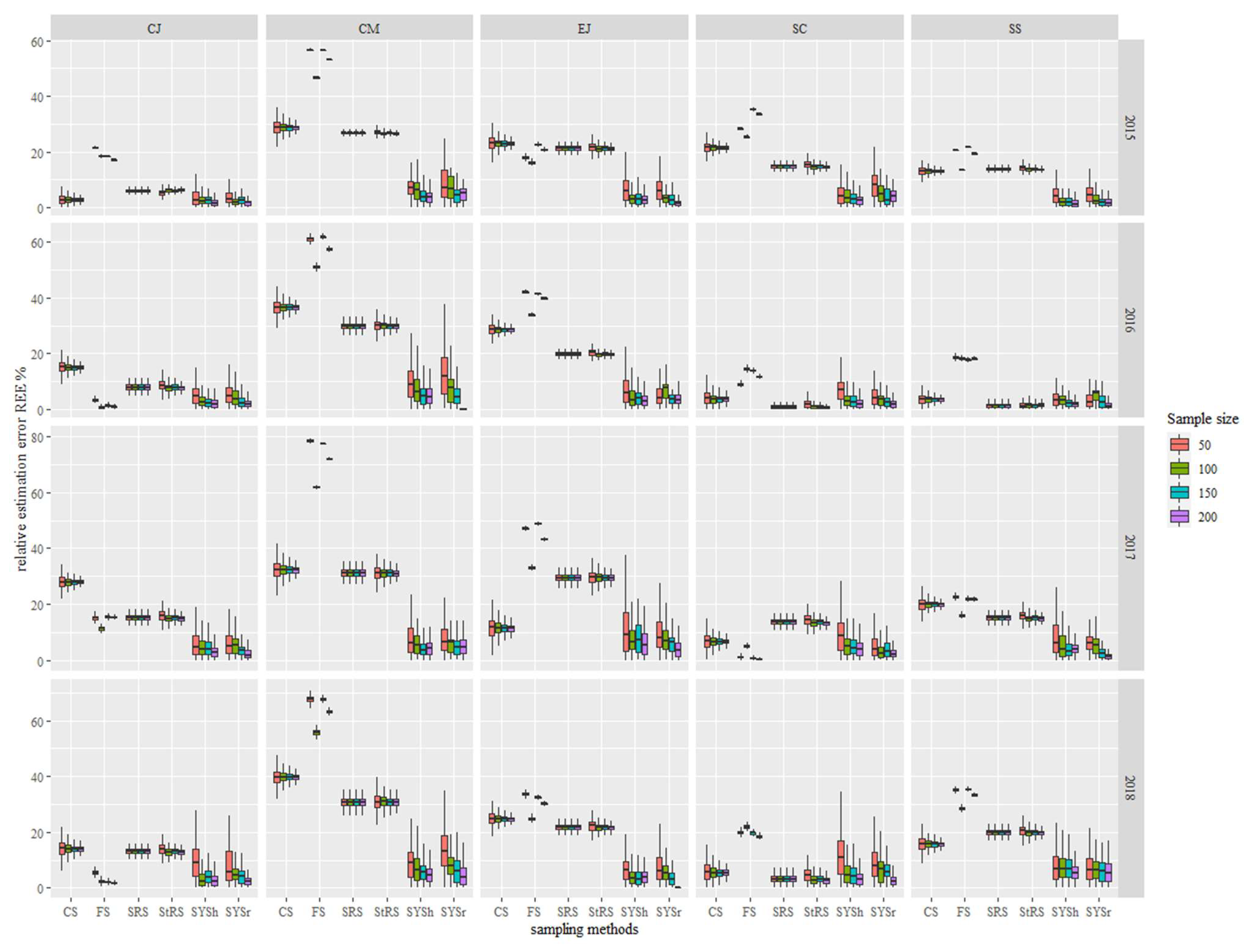
3.2. Comparison of REE
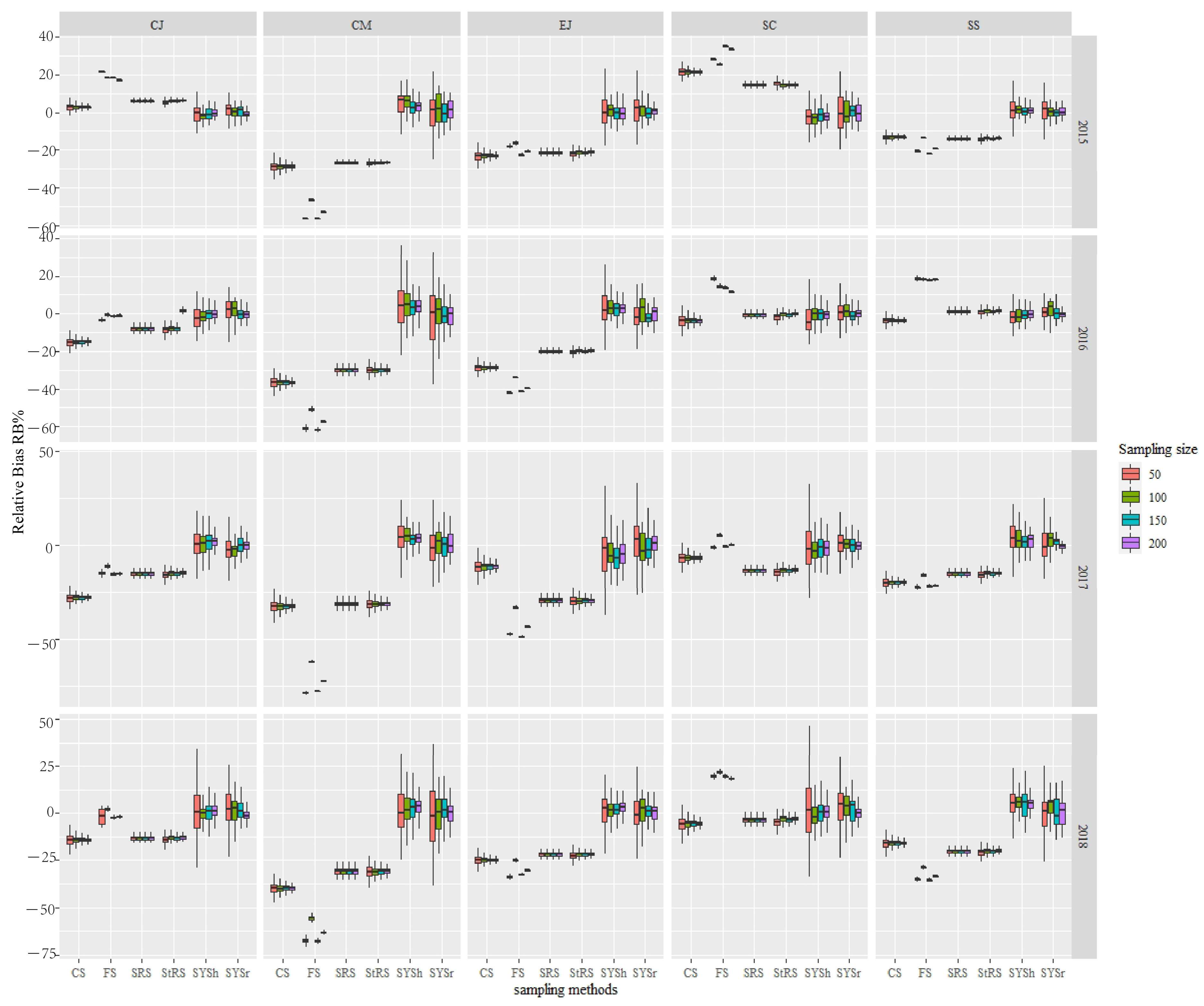
3.3. Comparison of RB
3.4. Comprehensive Comparison of Different Sampling Designs for Multiple Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 18–322. [Google Scholar]
- Rago, P.J. Fishery independent sampling: Survey techniques and data analyses. FAO Fish. Technical. 2005, 474, 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Bazigos, G.; Kavadas, S. Optimal sampling designs for large-scale fishery sample surveys in Greece. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2007, 8, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.E.; Powell, E.N. Influence of adaptive stations in a transect-based sampling design for a multispecies fish survey. Fish. Res. 2007, 86, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jiao, Y.; Su, Z.; Reid, K. Performance comparison of traditional sampling designs and adaptive sampling designs for fishery-independent surveys: A simulation study. Fish. Res. 2012, 113, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wan, R. Optimization of stratification scheme for a fishery-independent survey with multiple objectives. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Y. Evaluation of alternative stratifications for a stratified random fishery-independent survey. Fish. Res. 2018, 207, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tian, S.; Gao, C.; Richard, K.; Zhao, J. Evaluation of sampling designs for different fishery groups in the Yangtze River estuary, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 38, 10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.M.; Vieira, J.P.; Winemiller, K.O. Effects of 1997–1998 El Niño on the dynamics of the shallow-water fish assemblage of the Patos Lagoon Estuary (Brazil). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbaniha, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Lopez-Lopez, L.; Javidpour, J.; Primo, A.L.; Owfi, F.; Sommer, U. Habitat association of larval fish assemblages in the northern Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. 2015, 97, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marina, B.; Svetlana, K.; Francesco, F. The long-term ichthyoplankton abundance summer trends in the coastal waters of the Black Sea under conditions of hydrometeorological changes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 258, 107450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.E.; Richardson, S.L. Standard Techniques for Pelagic Fish Egg and Larval Surveys. FAO Fish. Tech. Pap. 1997, 175, 6–113. [Google Scholar]
- Stratoudakis, Y.; Bernal, M.; Ganias, K.; Uriarte, A. The daily egg production method: Recent advances, current applications and future challenges. Fish Fish. 2006, 7, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerchon, J.; Morov, A.R.; Tagar, A.; Rubin-Blum, M.; Tikochinski, Y.; Berenshtein, I.; Rilov, G.; Stern, N. Marine top secrets: Ichthyoplankton in surface water uncover hidden knowledge on fish diversity and distribution. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 282, 108226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, M.R. Field Investigations of the Early Life Stages of Marine Fish. In Advances in Marine Biology; Academic Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1992; pp. 10–169. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, M.; Beaugrand, G.; Hays, G.C.; Koslow, J.A.; Richardson, A.J. Multi-decadal oceanic ecological datasets and their application in marine policy and management. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, B. Fishery Stock Assessment; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 261–262. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.I.; Lee, J.B. Stock assessment and management implications of horse mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) in Korean waters, based on the relationships between recruitment and the ocean environment. Prog. Oceanogr. 2001, 49, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, C.; Konishi, Y.; Mori, K.E.N. Distribution of jack mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) larvae and juveniles in the East China Sea, with special reference to the larval transport by the Kuroshio Current. Fish. Oceanogr. 2006, 15, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, P.; Helbig, J.A. Sampling variability of ichthyoplankton surveys—Exploring the roles of scale and resolution on uncertainty. Fish. Res. 2012, 117–118, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbia, G.; Lafratta, G. Anisotropic spatial sampling designs for urban pollution. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2002, 51, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. Evaluating the approaches of habitat suitability modelling for whitespotted conger (Conger myriaster). Fish. Res. 2017, 195, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadima, E.; Caramelo, A.; Afonso-Dias, M.; Tandstad, M.; Leiva-Moreno, J. Sampling methods applied to fisheries science: A manual. In FAO Fisheries Technical Paper; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2005; Volume 434, Available online: https://agris.fao.org/search/en/records/65dde2400f3e94b9e5c6baf8 (accessed on 17 April 2021).
- Smith, S.J.; Tremblay, M.J. Fishery-independent trap surveys of lobsters (Homarus americanus): Design considerations. Fish. Res. 2003, 62, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y. Optimization of sampling effort for a fishery-independent survey with multiple goals. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Cao, J.; Tian, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S. Evaluating sampling designs for demersal fish communities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J.; Zhou, X. A comparative study of different sampling designs in fish community estimation. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Y. Impacts of sampling design on the abundance estimation of Portunus trituberculatus using crab pots. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 39, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Y. Impacts of the sampling design on the abundance index estimation of Portunus trituberculatus using bottom trawl. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, R.W.; Holland, J.S. Benthic infaunal variability on a transect in the Gulf of Mexico. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 1980, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, S.D.; Dauer, D.M. Macrobenthic communities of the lower Chesapeake Bay. IV. Bay-wide transects and the inner continental shelf. Benthic Stud. Low. Chesap. Bay 1984, 68, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, W.A. Environmental surveys over time. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 1999, 4, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.L.; Quist, M.C.; Schill, D.J. Creel survey sampling designs for estimating effort in short-duration chinook salmon fisheries. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2013, 33, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Gao, L.; Yu, L.; Duan, X.; Zhu, F.; Tian, H.; Chen, D.; Liu, M. Catch Efficiency of Multi-Mesh Trammel Nets for Sampling Freshwater Fishes. Fishes 2023, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, F.J.; Carassou, L.; Muffelman, S.; Powers, S.P.; Graham, W.M. Comparison of two plankton net mesh sizes for ichthyoplankton collection in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Fish. Res. 2011, 108, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslow, J.A.; Wright, M. Ichthyoplankton sampling design to monitor marine fish populations and communities. Mar. Policy 2016, 68, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Cai, Y. Ichthyoplankton species composition and distribution in Hangzhou Bay in summer during 2004~2010. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2012, 31, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Y.; Xu, B.; Yu, H.; Ren, Y. Community structure of ichthyoplankton from typical transects in Haizhou Bay and its adjacent waters during spring and summer. J. Fish. Sci. China 2017, 24, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, P.T.; Sugihara, G.; Thompson, A.R.; Semmens, B.X. Identification of shared spatial dynamics in temperature, salinity, and ichthyoplankton community diversity in the California Current System with empirical dynamic modeling. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Wan, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Song, P.; Zhang, F. Sampling designs for monitoring ichthyoplankton in the estuary area: A case study on Coilia mystus in the Yangtze Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 767273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, B.; Holt, K.R.; Peterman, R.M.; Jordan, C.; Larsen, D.P.; Olsen, A.R.; Abdul-Aziz, O.I. Evaluating alternative methods for monitoring and estimating responses of salmon productivity in the North Pacific to future climatic change and other processes: A simulation study. Fish. Res. 2013, 147, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chang, J.H.; Chen, X. An evaluation of an inshore bottom trawl survey design for American lobster (Homarus americanus) using computer simulations. J. N. Atl. Fish. Sci. 2014, 46, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Jiang, Y. Studies on the ecology of eggs and larval of Osteichithyes in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Fish. Res. 1998, 19, 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X. Zooplankton in the coast waters of southern Yellow Sea during winter and spring. Mar. Fish. 2008, 30, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q. Regional Oceanography in China: Fishery Oceanography; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for Oceanographic Survey-Part 6: Marine Biological Survey GB/T 12763. 6-2007; China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, R.; Lu, S. Fish Eggs and Larvae in China Seas, 2nd ed.; Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1985; pp. 18–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Zhang, R. Eggs and Larvae of Fish in the Coastal and Adjacent Waters of China; Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 2017; pp. 45–435. [Google Scholar]
- Schabenberger, O.; Gotway, C. Statistical Methods for Spatial Data Analysis; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 2005; pp. 23–100. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, R.M.; Kuwano, J.; Tachibana, S. A kriging method of interpolation used to map liquefaction potential over alluvial ground. Eng. Geol. 2013, 152, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. A Monte Carlo study on impacts of the size of subsample catch on estimation of fish stock parameters. Fish. Res. 1996, 26, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Schneider, D.; Wroblewski, J. A simulation study of impacts of error structure on modeling stock–recruitment data using generalized linear models. Can. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.-Y.; Seo, Y.I.L. The systematic sampling for inferring the survey indices of Korean groundfish stocks. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sherman, S.; Wilson, C.; Sowles, J. A comparison of two fishery-independent survey programs used to define the population structure of American lobster (Homarus americanus) in the Gulf of Maine. Fish. Bull. 2006, 104, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.J.; Skalski, J.R.; Ianelli, J.N. Optimizing a stratified sampling design when faced with multiple objectives. Ices J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cao, J.; Chang, J.-H.; Wilson, C.; Chen, Y. Evaluation of effectiveness of fixed-station sampling for monitoring American lobster settlement. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2015, 35, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.H.; Palka, D.; Buckland, S.T. Adaptive line transect sampling. Biometrics 2002, 58, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M. Using adaptive line-transect sampling in airborne geophysics studies. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2019, 48, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Lundy, M. Improving the precision of design-based scallop drag surveys using adaptive allocation methods. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, Y. Comparison of sampling effort allocation strategies in a stratified random survey with multiple objectives. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 5, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Yu, H.; Yu, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, J.; Tian, Y. A comprehensive model-based index for identification of larval retention areas: A case study for Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus in the Yellow Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.R.; Hussey, N.E. Movements of a potential fishery resource, porcupine crab (Neolithodes grimaldii) in Northern Davis Strait, Eastern Canadian Arctic. Deep-Sea Res. Pt. I 2019, 154, 103143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Kumar, R. Allocation of Sample in Stratified Sampling using Circular Systematic Sampling. J. Indian Soc. Agric. Stat. 2017, 71, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
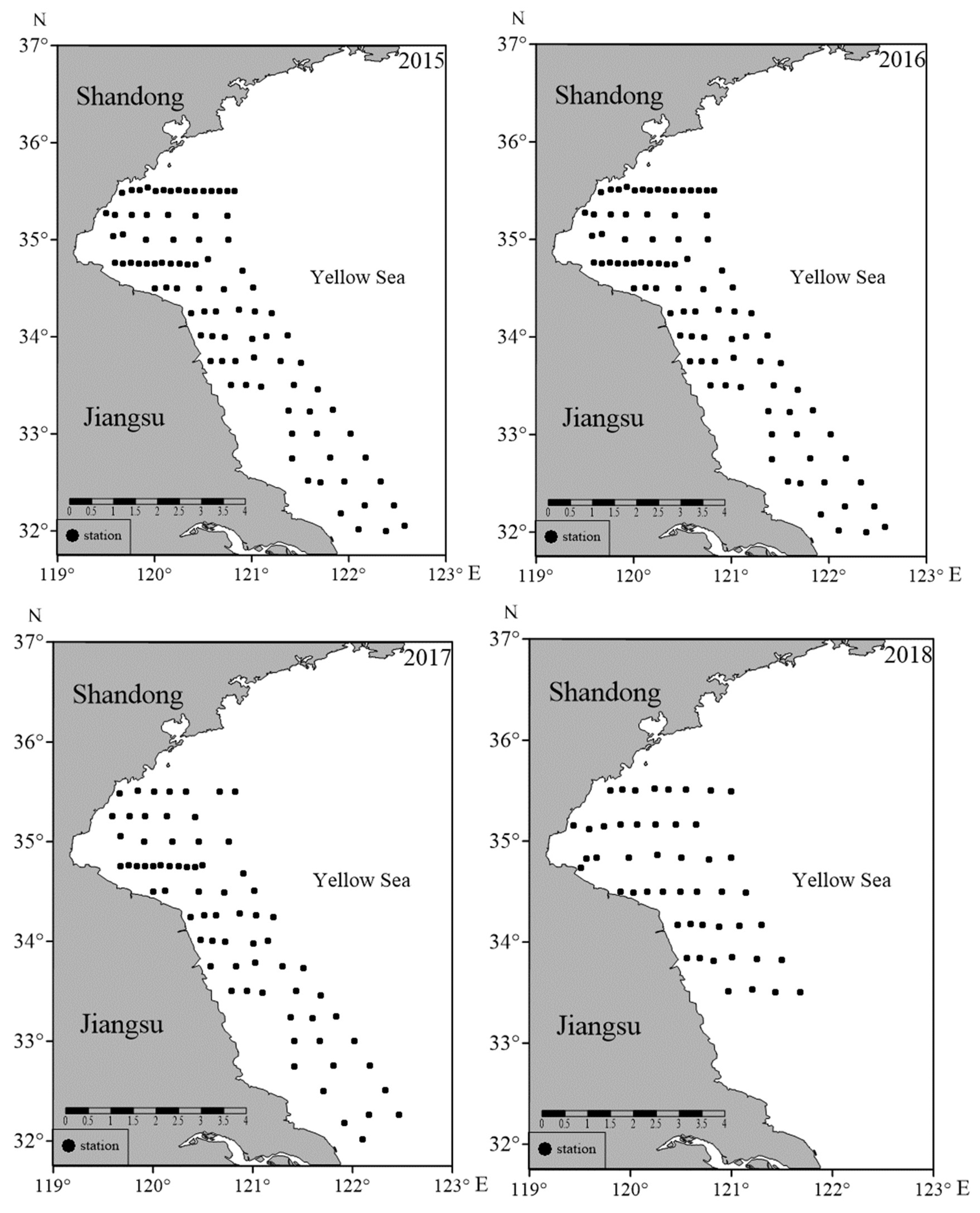
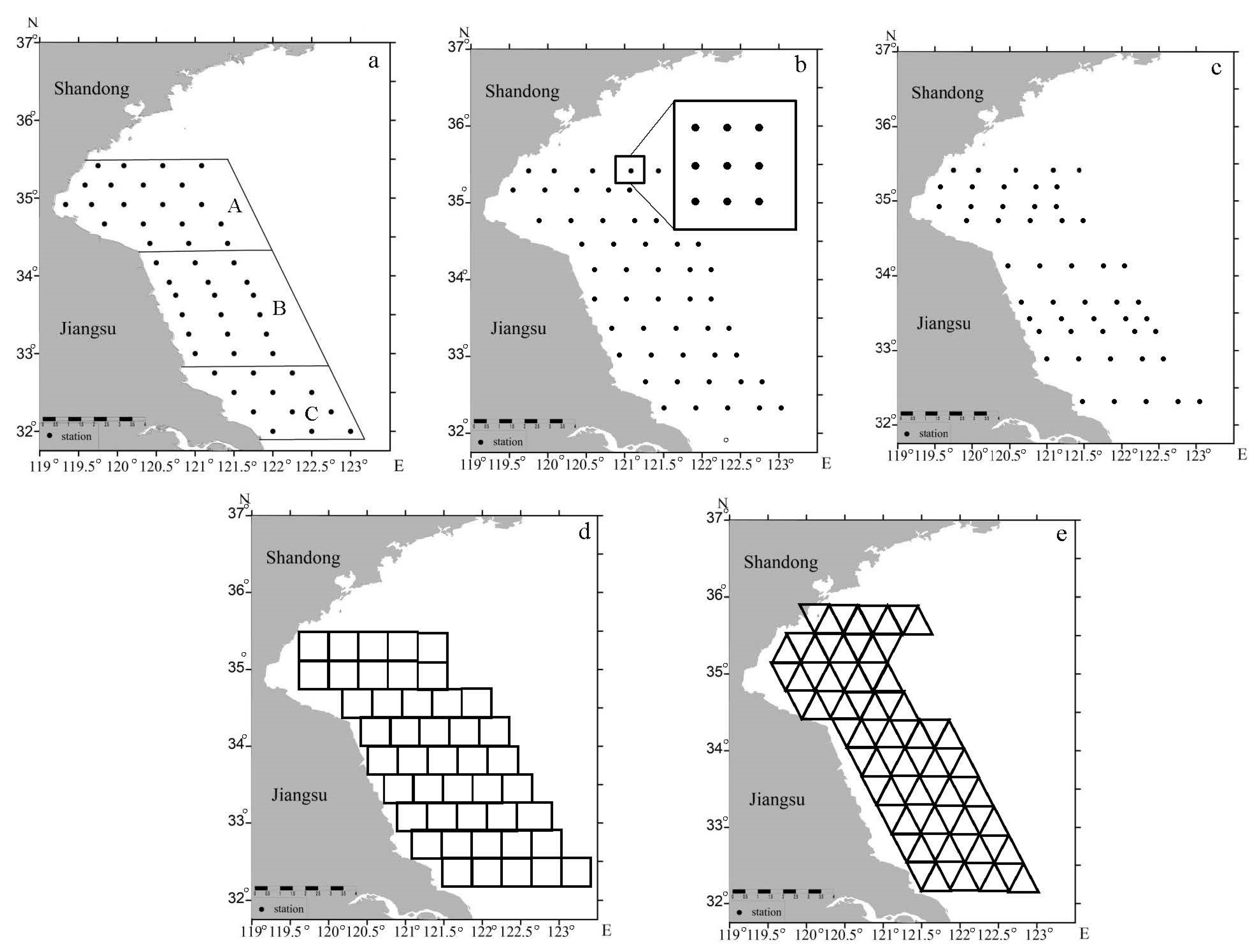

| Stratum | Strata Description | Wh | Nh | nh |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone A | 34.5°~35.75° N, 119.3°~121° E | 0.29 | 50 | 15 |
| 100 | 29 | |||
| 150 | 44 | |||
| 200 | 58 | |||
| Zone B | 33.00°~34.50° N, 121°~122° E | 0.43 | 50 | 21 |
| 100 | 43 | |||
| 150 | 64 | |||
| 200 | 86 | |||
| Zone C | 32.00°~33.00° N, 122°~123° E | 0.28 | 50 | 14 |
| 100 | 28 | |||
| 150 | 42 | |||
| 200 | 56 |
| Species | Scientific Name | Year | Average Abundance (ind./100 m3) | Standard Deviation (SD) | Frequency of Occurrence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| red tonguesole | Cynoglossus joyneri | 2015 | 4.26 | 13.21 | 53.33 |
| 2016 | 32.80 | 131.20 | 77.53 | ||
| 2017 | 0.92 | 2.86 | 31.51 | ||
| 2018 | 8.44 | 31.92 | 56.25 | ||
| silver sillago | Sillago sihama | 2015 | 5.15 | 28.17 | 48.89 |
| 2016 | 10.39 | 37.78 | 77.53 | ||
| 2017 | 10.12 | 46.67 | 50.69 | ||
| 2018 | 1.36 | 5.20 | 37.50 | ||
| Commerson’s anchovy | Stolephorus commersonni | 2015 | 12.40 | 44.44 | 45.56 |
| 2016 | 132.04 | 1014.07 | 59.55 | ||
| 2017 | 5.72 | 23.85 | 36.99 | ||
| 2018 | 83.90 | 437.97 | 54.17 | ||
| dragonet | Callionymus·spp. | 2015 | 9.31 | 27.06 | 27.78 |
| 2016 | 3.14 | 11.92 | 25.84 | ||
| 2017 | 9.75 | 33.26 | 30.14 | ||
| 2018 | 10.70 | 51.72 | 31.25 | ||
| Japanese anchovy | Engraulis japonicus | 2015 | 12.31 | 78.46 | 25.56 |
| 2016 | 7.26 | 36.64 | 49.44 | ||
| 2017 | 8.58 | 29.12 | 64.38 | ||
| 2018 | 14.21 | 62.02 | 43.75 |
| Performance Index | Year | SRS | StRS | FS | CS | SYSh | SYSr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 82.90 | 82.89 | 140.83 | 89.38 | 18.64 | 21.31 | |
| 2016 | 60.99 | 60.48 | 129.17 | 87.61 | 21.98 | 21.88 | |
| 2017 | 106.78 | 105.97 | 170.81 | 111.45 | 28.63 | 26.92 | |
| 2018 | 106.63 | 105.85 | 163.12 | 110.09 | 30.58 | 31.29 | |
| 2015 | 82.90 | 82.29 | 143.78 | 89.14 | 12.99 | 14.58 | |
| 2016 | 60.00 | 53.40 | 128.02 | 87.35 | 14.74 | 14.77 | |
| 2017 | 104.19 | 103.15 | 152.55 | 98.13 | 22.36 | 18.04 | |
| 2018 | 88.84 | 87.56 | 147.17 | 99.70 | 21.13 | 20.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Y.; Ji, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xu, B. Effects of Sampling Design on Population Abundance Estimation of Ichthyoplankton in Coastal Waters. Fishes 2025, 10, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10020039
Ma Y, Zhang C, Xue Y, Ji Y, Ren Y, Xu B. Effects of Sampling Design on Population Abundance Estimation of Ichthyoplankton in Coastal Waters. Fishes. 2025; 10(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yihong, Chongliang Zhang, Ying Xue, Yupeng Ji, Yiping Ren, and Binduo Xu. 2025. "Effects of Sampling Design on Population Abundance Estimation of Ichthyoplankton in Coastal Waters" Fishes 10, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10020039
APA StyleMa, Y., Zhang, C., Xue, Y., Ji, Y., Ren, Y., & Xu, B. (2025). Effects of Sampling Design on Population Abundance Estimation of Ichthyoplankton in Coastal Waters. Fishes, 10(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10020039







