Impact of Ocean Acidification on the Intestinal Microflora of Sinonovacula constricta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Diversity Analysis and Functional Prediction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
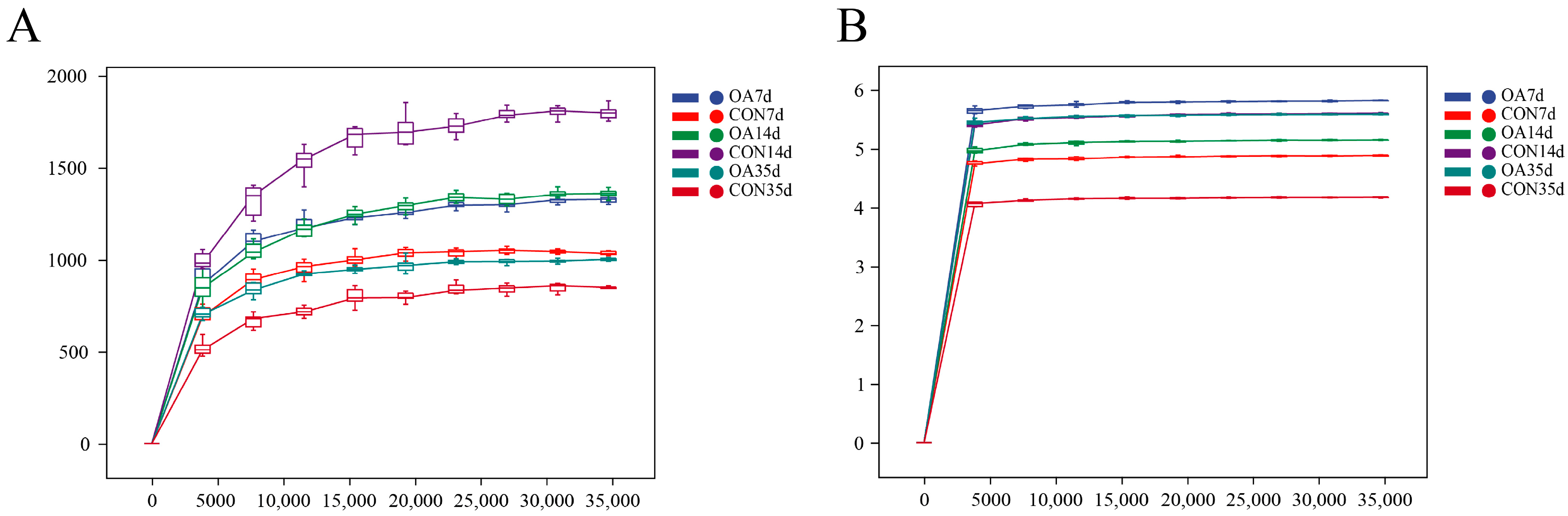
3.1. Characteristics of Sequencing Data
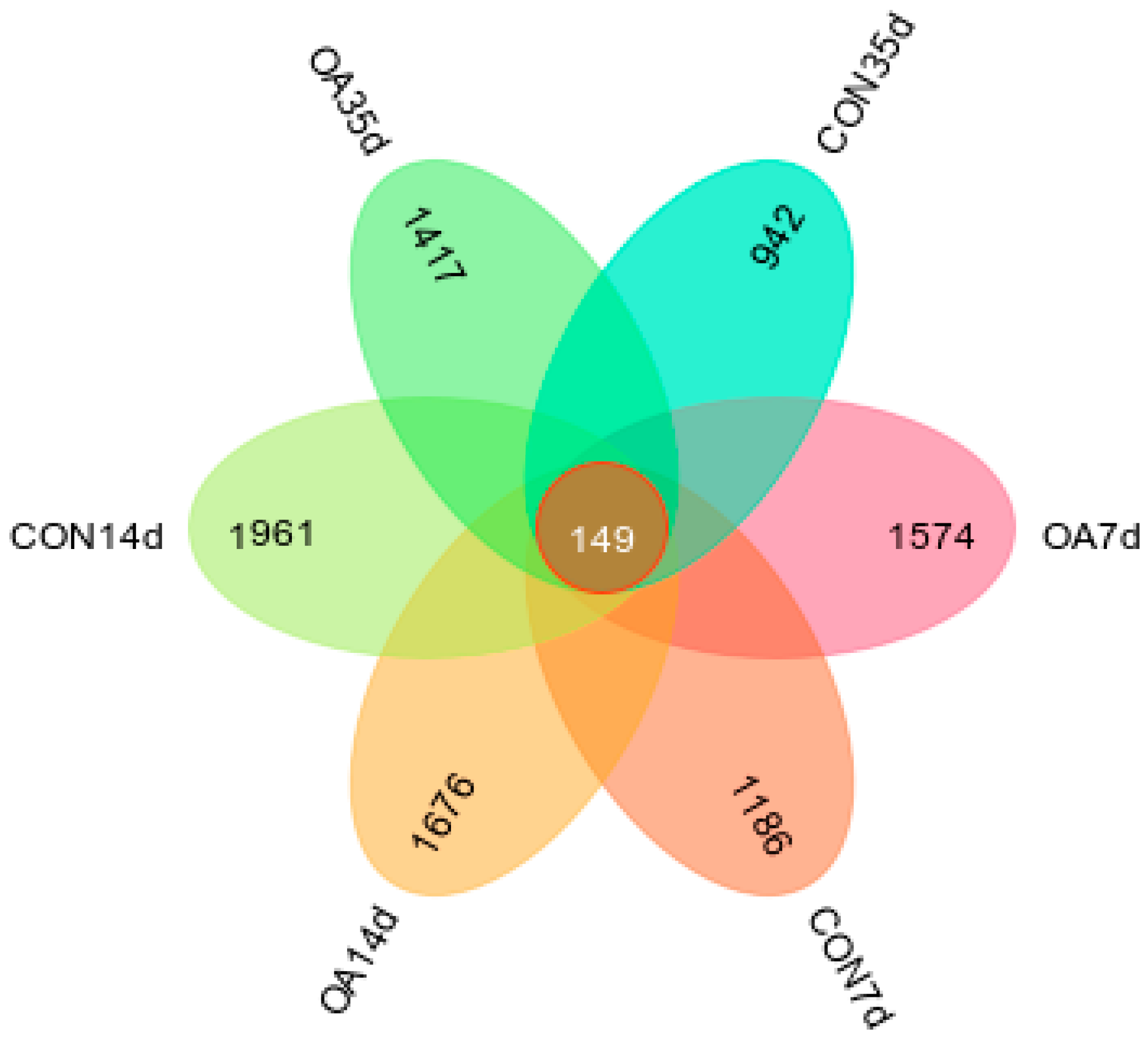
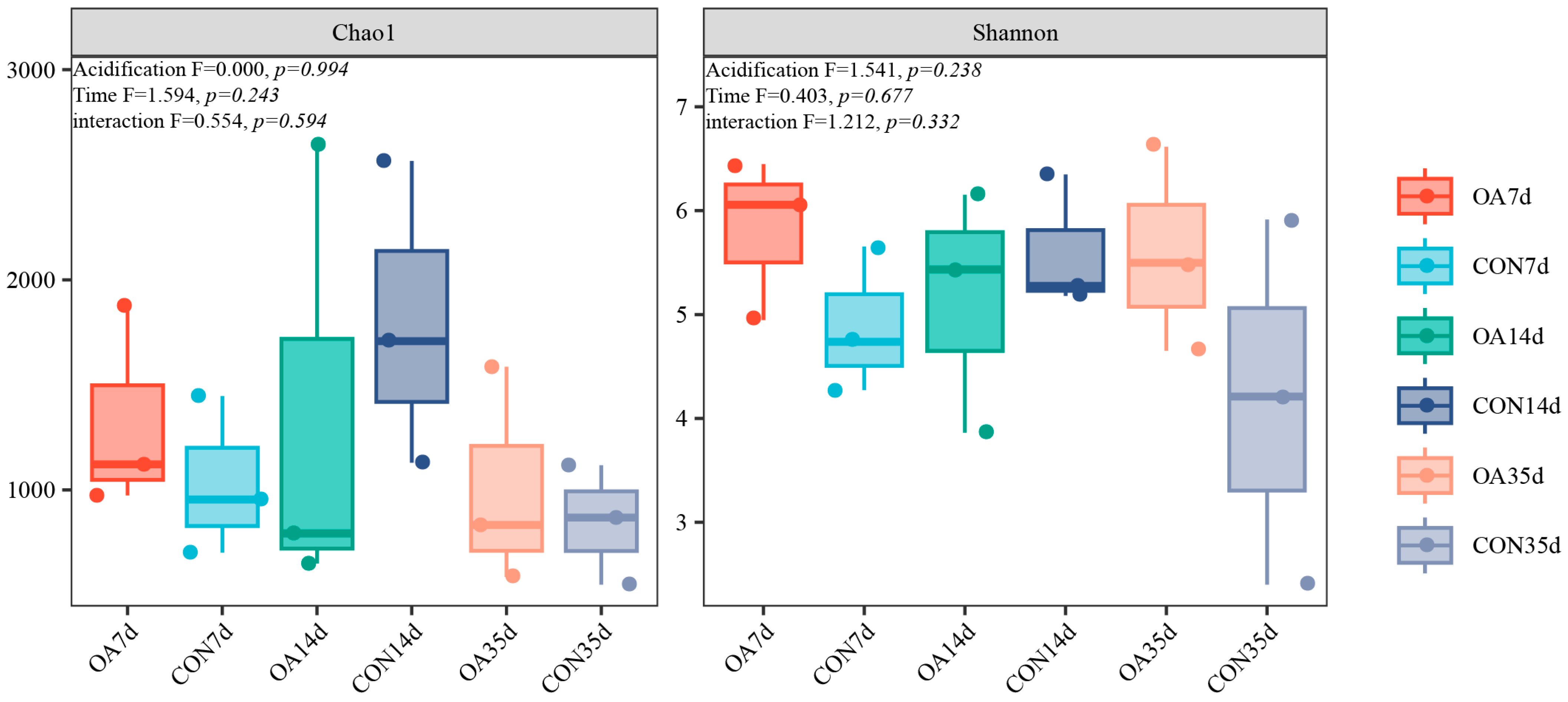
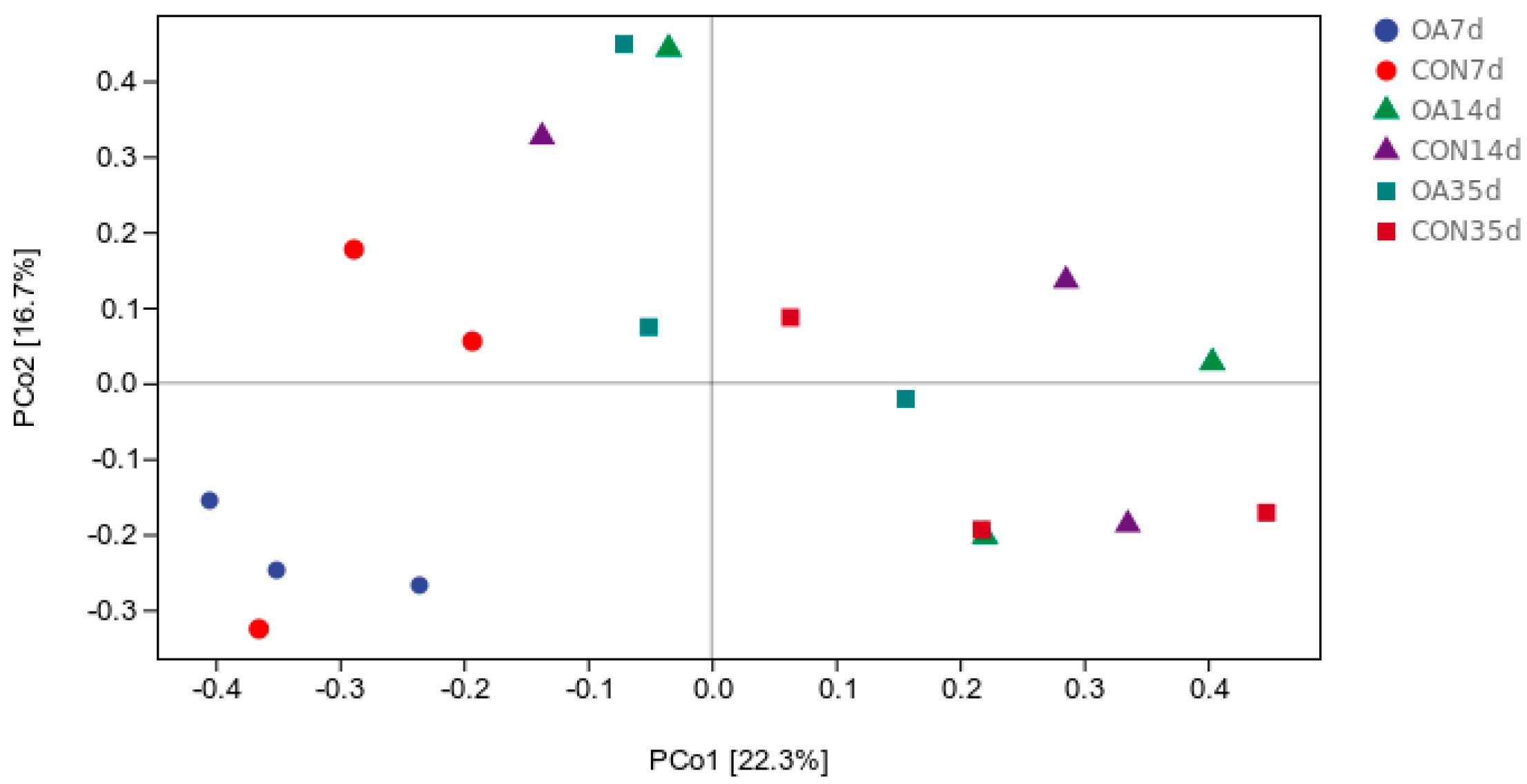
3.2. Diversity and Community Structure of Intestinal Microflora
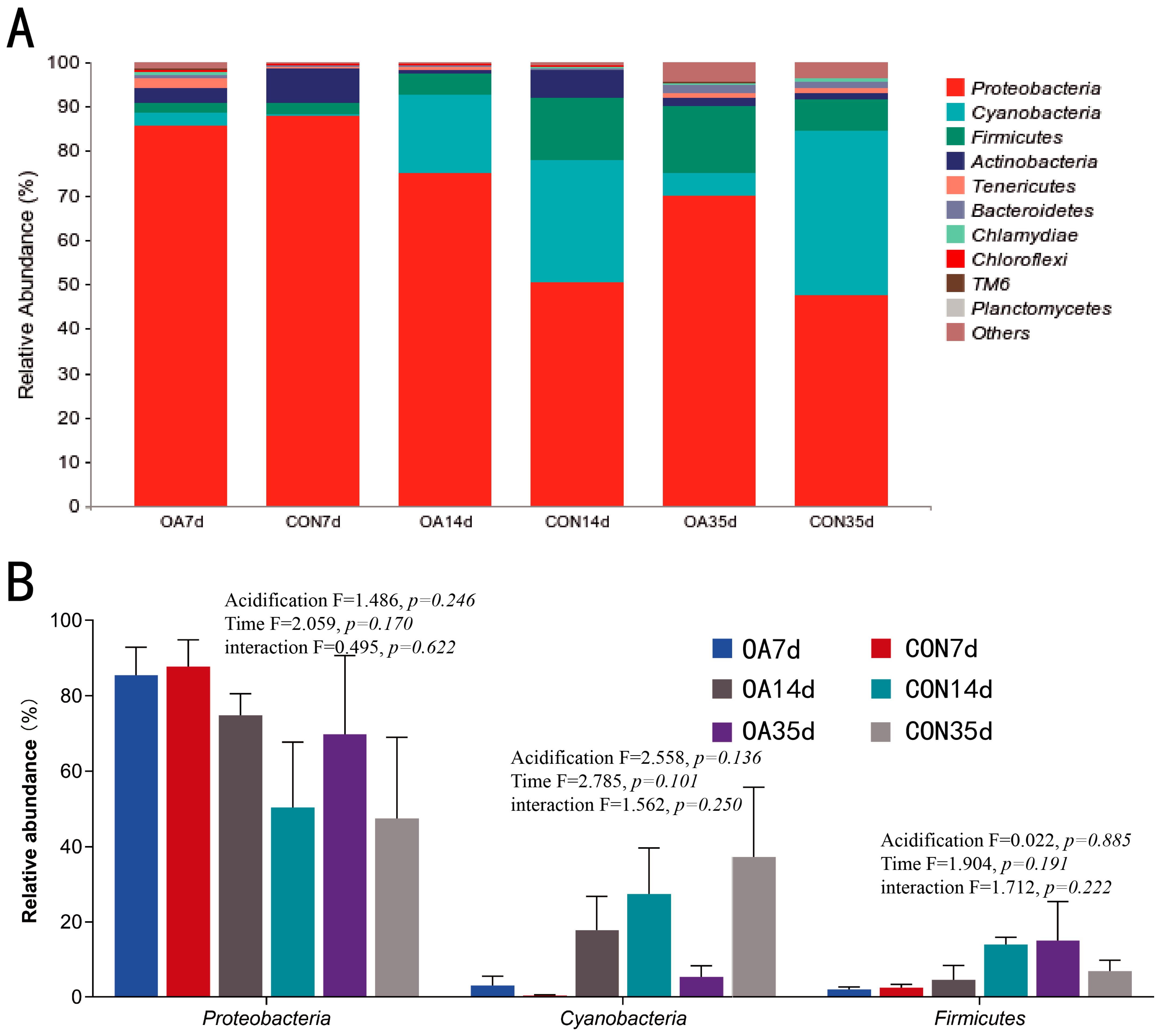
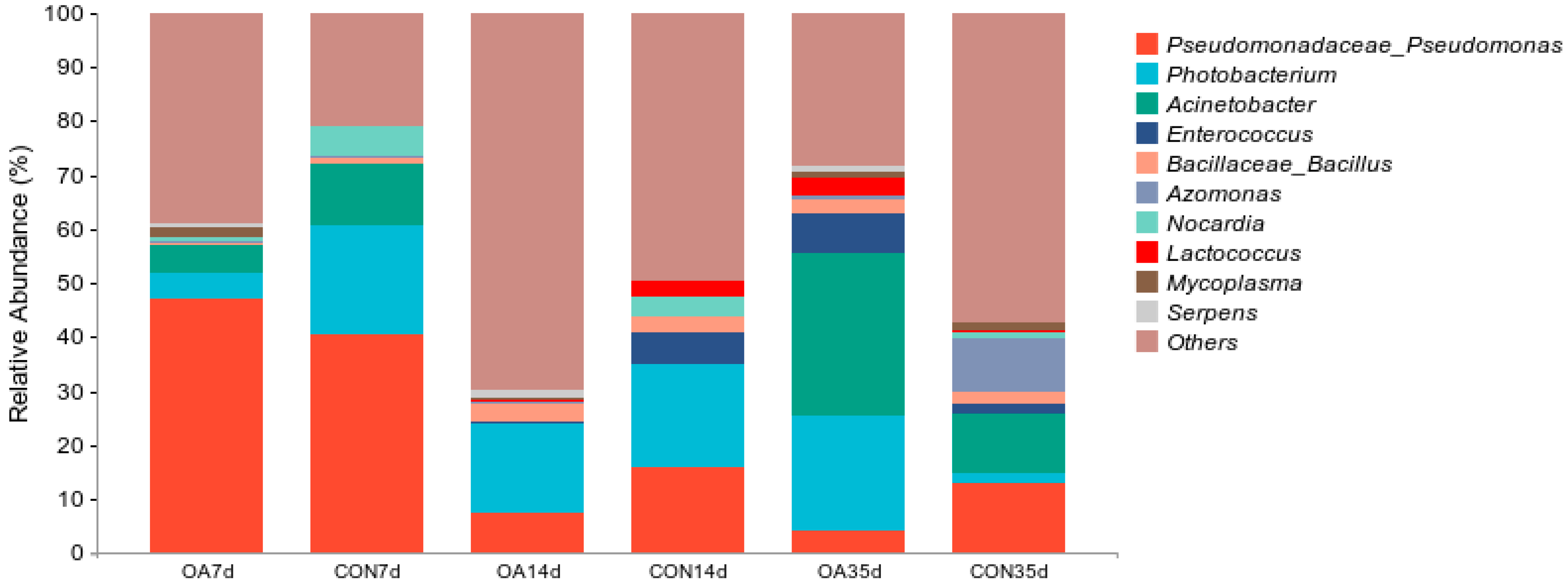
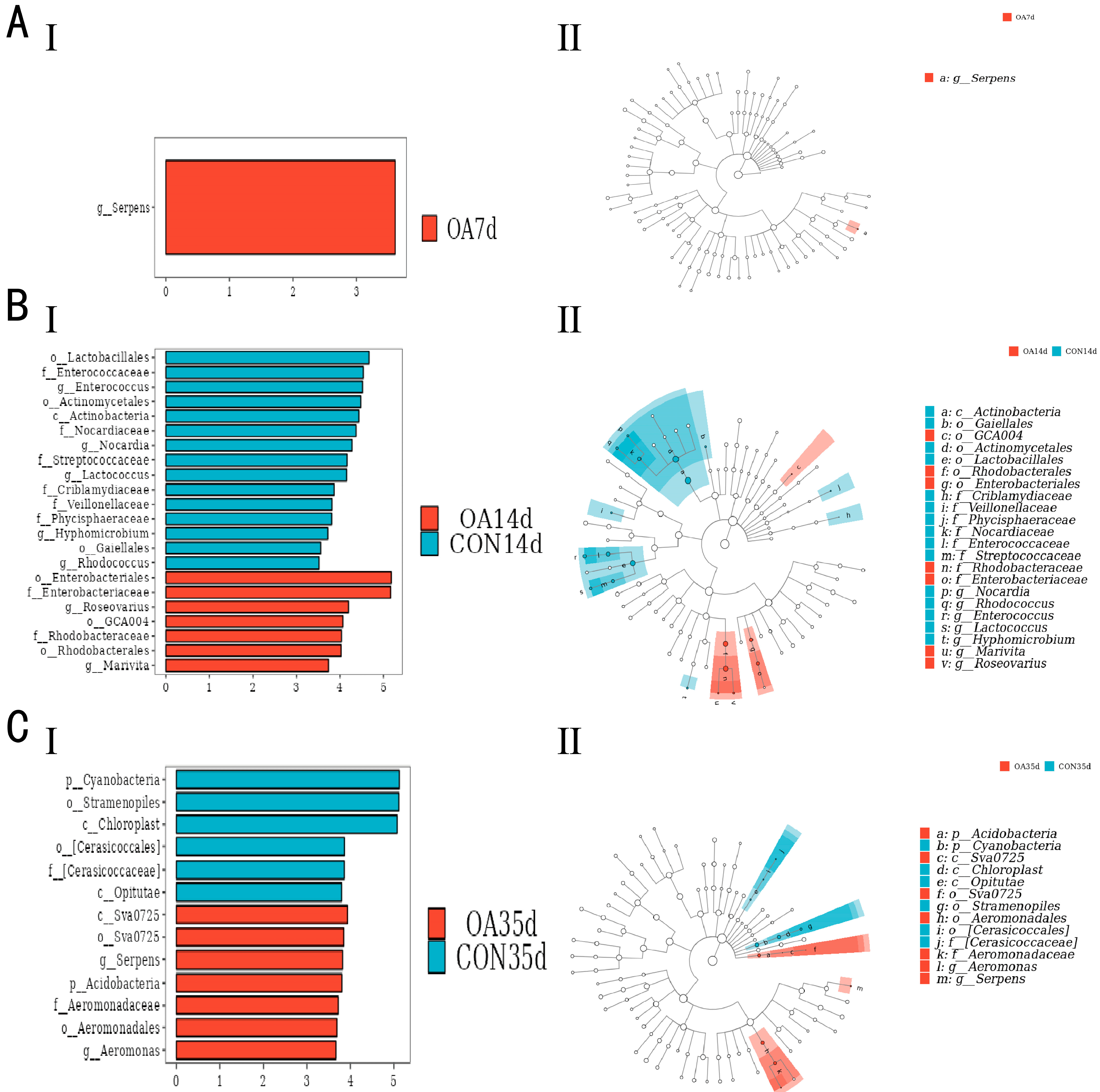
3.3. Species Composition of Intestinal Microflora
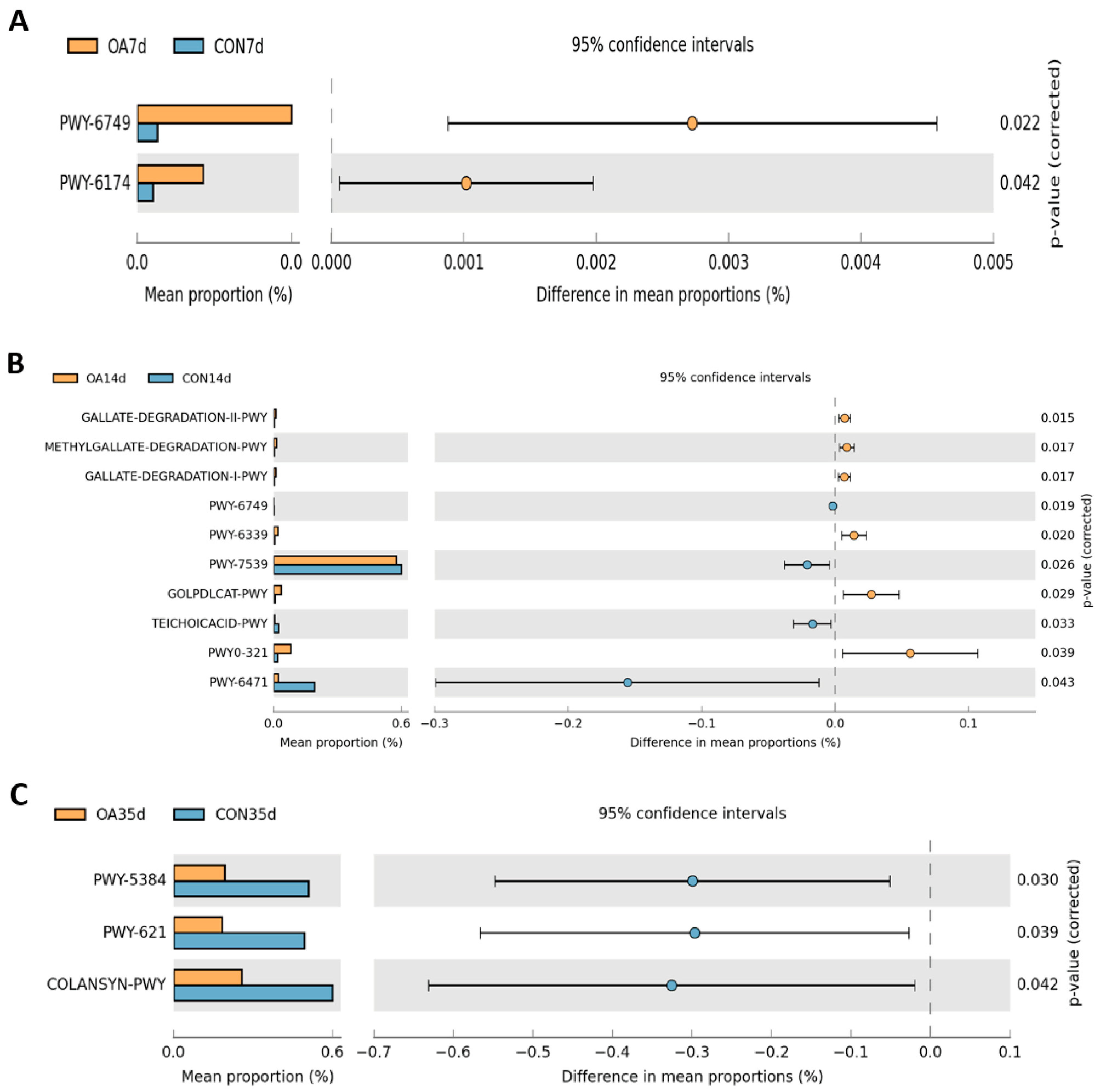
3.4. Functional Prediction of Intestinal Microflora
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity and Community Structure of Intestinal Microflora
4.2. Species Composition of Intestinal Microflora
4.3. Functional Prediction of Intestinal Microflora
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OA | Ocean Acidification |
| OA7d | 7-day group under ocean acidification stress |
| CON7d | Control 7-day group |
| OA14d | 14-day group under ocean acidification stress |
| CON14d | Control 14-day group |
| OA35d | 35-day group under ocean acidification stress |
| CON35d | Control 35-day group |
References
- Meron, D.; Atias, E.; Kruh, L.I.; Elifantz, H.; Minz, D.; Fine, M.; Banin, E. The impact of reduced pH on the microbial community of the coral Acropora eurystoma. ISME J. 2011, 5, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Han, S.; Fu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Impact of ocean acidification on the intestinal microflora of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, X. Bacterial community in Sinonovacula constricta intestine and its relationship with culture environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2022, 106, 5211–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah Khan, F.; Shang, Y.; Chang, X.; Kong, H.; Zuberi, A.; Fang, J.K.H.; Liu, W.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, M.; et al. Effects of Ocean Acidification, Hypoxia, and Warming on the Gut Microbiota of the Thick Shell Mussel Mytilus coruscus Through 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 736338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chair, R.K.P.; Kingdom, M.R.A.U.; Argentina, V.R.B.; Kingdom, J.B.U.; Belgium, J.P.V.Y. Synthesis Report IPCC AR5; Synthesis Report IPCC AR5; IPCC: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira, K.; Wickett, M.E. Oceanography: Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 2003, 425, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Lan, X.; Bock, C.; Shang, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of ocean acidification and warming on apoptosis and immune response in the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Fish Shellfish. Immun. 2025, 158, 110134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lv, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Sui, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of Ocean Acidification and Microplastics on Microflora Community Composition in the Digestive Tract of the Thick Shell Mussel Mytilus coruscus Through 16S RNA Gene Sequencing. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 107, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishery Administration Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Station. China Fishery Statistics Yearbook 2023; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, J.; Casties, I.; Pansch, C.; Körtzinger, A.; Melzner, F. Food availability outweighs ocean acidification effects in juvenile Mytilus edulis: Laboratory and field experiments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 19, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Zhao, L.; Yan, X. Seawater acidification affects the physiological energetics and spawning capacity of the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum during gonadal maturation. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 2016, 196, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Gloeckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Khan, F.U.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of feed satiation on energy metabolism in the mussel Mytilus coruscus under ocean acidification and warming and possible hormonal regulation. Aquaculture 2025, 604, 742440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Li, Y.; Liang, S.; Guo, Y. Impact of ocean acidification on the physiology of digestive gland of razor clams Sinonovacula constricta. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1010350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Amenyogbe, E.; Chen, G. Effects of hypoxia stress on the intestinal microflora of juvenile of cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, M.; Dong, Z.; Duan, H.; Mao, S.; Feng, S.; Li, W.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; et al. Fecal DNA isolation and degradation in clam Cyclina sinensis: Noninvasive DNA isolation for conservation and genetic assessment. BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.J.; Barnes, A.C. Bacterial diversity of the digestive gland of Sydney rock oysters, Saccostrea glomerata infected with the paramyxean parasite, Marteilia sydneyi. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Huang, W.; Sokolova, I.; Chang, X.; Chen, D.; Wei, S.; Khan, F.U.; Hu, M.; et al. Ocean acidificationf affects the bioenergetics of marine mussels as revealed by high-coverage quantitative metabolomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stechele, B.; Lavaud, R. Including ocean acidification effects on biocalcification through dynamic energy budget modelling. Ecol. Model. 2024, 496, 110816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokmer, A.; Wegner, K.M. Hemolymph microbiome of Pacific oysters in response to temperature, temperature stress and infection. ISME J. 2015, 9, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Leung, J.Y.S.; Wang, T.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Ocean acidification disrupts the energy balance and impairs the health of mussels (Mytilus coruscus) by weakening their trophic interactions with microalgae and intestinal microbiome. Environ. Res. 2025, 276, 121493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Han, W.; Cheng, W.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Yan, B.; Gao, H.; Hu, G. Impact of Ocean Acidification on the Gut Histopathology and Intestinal Microflora of Exopalaemon carinicauda. Animals 2023, 13, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, W.; Shao, A.; Liang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J. Characterization of Gut Microbiome in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in Response to Thermal Stress. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, X.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, C. Effects of ocean acidification on intestinal homeostasis and organismal performance in a marine bivalve: From microbial shifts to physiological suppression. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 222, 118704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceicao, M.V.R.; Costa, S.S.; Schaan, A.P.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, A.K.C.; Silva, A.; Gracas, D.A.D.; Schneider, M.P.C.; Barauna, R.A. Amazonia Seasons Have an Influence in the Composition of Bacterial Gut Microbiota of Mangrove Oysters (Crassostrea gasar). Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 602608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.L.; Ward, J.E. Gut Microbiomes of the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and the Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis): Temporal Variation and the Influence of Marine Aggregate-Associated Microbial Communities. Msphere 2019, 4, e00730-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumithra, T.G.; Sharma, K.S.R.; Gangadharan, S.; Suresh, G.; Prasad, V.; Amala, P.V.; Sayooj, P.; Gop, A.P.; Anil, M.K.; Patil, P.K.; et al. Dysbiosis and Restoration Dynamics of the Gut Microbiome Following Therapeutic Exposure to Florfenicol in Snubnose Pompano (Trachinotus blochii) to Aid in Sustainable Aquaculture Production Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 881275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Pathogenic Pathology of Black Body Disease in Farmed Grouper and Analysis of Gut Microbiota Structure Under Drug Intervention. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2017; p. 65. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Chang, L.; Shi, J.; Kong, X.; Li, M.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W.; Bao, Z.; et al. Paralytic shellfish toxins producing dinoflagellates cause dysbacteriosis in scallop gut microbial biofilms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Wu, W.; Fang, W.; Wen, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H. Heat stress-induced mucosal barrier dysfunction is potentially associated with gut microbiota dysbiosis in pigs. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Miao, J.; Pan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, X. Impacts of benzo (a) pyrene exposure on scallop (Chlamys farreri) gut health and gut microbiota composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology—Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.M.; Guan, Y.; Tian, S.Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Short-term Chronic Intermittent Hypobaric Hypoxia Alters Gut Microbiota Composition in Rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2018, 31, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.C.; Tan, B.P.; Dong, X.H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.Q.; Chi, J.Y. Effect of chitosan oligosaccharide and mycotoxin adsorbents on intestinal mucosa structure and gut flora of Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Fish. Sci. China 2018, 25, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.P. Bioactive compound synthetic capacity and ecological significance of marine bacterial genus Pseudoalteromonas. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 220–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wu, P.; Kumar, R.; Wang, H.; Lu, H. Low salinity stress increases the risk of Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection and gut microbiota dysbiosis in Pacific white shrimp. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, M.J.; Actis, L.; Pachon, J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Human infections, factors contributing to pathogenesis and animal models. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 130–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, M.J.; Stone, D.M.; Alderman, D.J. Comparison of conventional and molecular techniques to investigate the intestinal microflora of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2006, 261, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Yao, B.; Ringo, E.; Yoon, I. Effects of dietary Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product (DVAQUA) on growth performance, intestinal autochthonous bacterial community and non-specific immunity of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus ♀ × O. aureus ♂ cultured in cages). Aquaculture 2009, 294, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; He, S.; Yao, B.; Ringo, E. Molecular characterization of the autochthonous microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract of adult yellow grouper (Epinephelus awoara) cultured in cages. Aquaculture 2009, 286, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, G.; Li, W.; Zou, H. Characterization of bacterial community in the stomach of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). World J. Microb. Biot. 2012, 28, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Freire, A.; De Marchi, L.; Freitas, R.; Velo, A.; Babarro, J.M.F.; Cobelo-Garcia, A. Ocean acidification impact on the uptake of trace elements by mussels and their biochemical effects. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 269, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratov, T.A.; Kirsanova, L.A.; Kaparullina, E.N.; Kevbrin, V.V.; Dedysh, S.N. Telmatobacter bradus gen. nov., sp. nov., a cellulolytic facultative anaerobe from subdivision 1 of the Acidobacteria, and emended description of Acidobacterium capsulatum Kishimoto et al. 1991. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Su, Y.; Yu, H.; Ge, X.; Zhang, C. Starvation affects the intestinal microbiota structure and the expression of inflammatory-related genes of the juvenile blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Xiong, K.; Zhang, C.; Fang, J.K.; Song, J.; Tai, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of Ocean Acidification on Molting, Oxidative Stress, and Gut Microbiota in Juvenile Horseshoe Crab Tachypleus tridentatus. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 813582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Fu, Q.; Lian, X.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Comparative characterization of bacterial communities in digestive glands of Crassostrea gigas fed with different microalgal diets. ISJ-Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2020, 17, 51. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Dou, H.; Chai, C.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Guo, Y. Impact of Ocean Acidification on the Intestinal Microflora of Sinonovacula constricta. Fishes 2025, 10, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110571
Wei Y, Dou H, Chai C, Wang T, Liu H, Liang S, Li Y, Liang J, Guo Y. Impact of Ocean Acidification on the Intestinal Microflora of Sinonovacula constricta. Fishes. 2025; 10(11):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110571
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yuan, Hesheng Dou, Chengju Chai, Tingkuan Wang, Huiru Liu, Shuang Liang, Yongren Li, Jian Liang, and Yongjun Guo. 2025. "Impact of Ocean Acidification on the Intestinal Microflora of Sinonovacula constricta" Fishes 10, no. 11: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110571
APA StyleWei, Y., Dou, H., Chai, C., Wang, T., Liu, H., Liang, S., Li, Y., Liang, J., & Guo, Y. (2025). Impact of Ocean Acidification on the Intestinal Microflora of Sinonovacula constricta. Fishes, 10(11), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110571





