Abstract
The Number Theoretic Transform (NTT) has been widely used to speed up polynomial multiplication in lattice-based post-quantum algorithms. All NTT operands use modular arithmetic, especially modular multiplication, which significantly influences NTT hardware implementation efficiency. Until now, most hardware implementations used Digital Signal Processing (DSP) to multiply two integers and optimally perform modulo computations from the multiplication product. This paper presents a customized Lattice-DSP (L-DSP) for modular multiplication based on the Karatsuba algorithm, Vedic multiplier, and modular reduction methods. The proposed L-DSP performs both integer multiplication and modular reduction simultaneously for lattice-based cryptography. As a result, the speed and area efficiency of the L-DSPs are 283 MHz for 77 SLICEs, 272 MHz for 87 SLICEs, and 256 MHz for 101 SLICEs with the parameters q of 3329, 7681, and 12,289, respectively. In addition, the multiplier in the Inverse-NTT (INTT) calculation is also eliminated, reducing the size of the Butterfly Unit (BU) in CRYSTAL-Kyber to about 104 SLICEs, equivalent to a conventional multiplication in the other studies. Based on the proposed DSP, a Point-Wise Matrix Multiplication (PWMM) architecture for CRYSTAL-Kyber is designed on a hardware footprint equivalent to 386 SLICEs. Furthermore, this research is the first DSP designed for lattice-based Post-quantum Cryptography (PQC) modular multiplication.
1. Introduction
In 2016, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) initiated the PQC standardization process. This project aims to develop, deploy, and standardize new post-quantum cryptosystems before any large-scale quantum computers come into being. In July 2022, NIST announced the results of the third round with four candidates to be standardized for Public Key Encryption (PKE) and Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) [1]. Most are Lattice-Based Cryptographic (LBC) algorithms, CRYSTAL-Kyber [2], and CRYSTAL-Dilithium/FALCON [3,4], respectively.
Lattice-based cryptographic constructions are primarily based on solving the Learning-With-Error (LWE) and its variants problem (CRYSTAL-Kyber, Dilithium) or NTRU lattices (FALCON). Implementing the LBC cryptosystem requires performing polynomial multiplication, the most hardware-intensive operation. There are two ways to do polynomial multiplication: the Schoolbook polynomial multiplication and the multiplication based on NTT. Schoolbook multiplication is inefficient for polynomial multiplication because it has a complexity. NTT is the special Discrete Fourier Transform case over a finite field. NTT-based multiplication enhances polynomial multiplication, reducing complexity to quasi-linear complexity . In order to improve the efficiency of the LBC cryptosystem, NTT optimization is necessary. Furthermore, all NTT operations are modulo operations on prime q, including modular addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Performing modular multiplication is a highly intricate task that demands significant hardware resources. Thus, improving modular multiplication can enhance the performance of NTT/INTT and the entire cryptosystem. The optimization problem of modulo computations for multiplication has garnered significant attention in hardware implementations of LBC post-quantum cryptography research.
The accelerator proposals for NTT/INTT are mainly focused on optimizing modulo calculations from the product of multiplying two integers. Montgomery [5] and Barrett [6] are two commonly used constant-time modular reduction algorithms. The Montgomery method has received less attention as it needs to be done in the “Montgomery domain”. On the other hand, the Barret method is more efficient and is used more frequently in LBC cryptosystems [7]. Barrett reduction utilizes pre-computed values to approximate the division by the modulus. The modular multiplication based on the Barret method requires three multiplications, one for the two input coefficients and two for the constants. A variation of the Barret algorithm in [8], called Shift-Add-Multiply-Subtract-Subtract (SAMS2), replaces constant multipliers with simple bit shifts, additions, and subtractions, which are less expensive than multiplication and division operands. Studies [9,10,11] have applied the SAMS2 method for parameters q = 7681 and 12,289.
In the study [12], Plantard introduced a novel constant-time modular reduction algorithm. Like the Montgomery and Barrett algorithms, Plantard multiplication utilizes pre-computed values and requires three multiplications for modular multiplication. But, when performing NTT/INTT with pre-computed twiddle factors, the number of Plantard multiplications can be reduced by one. In another study [13], J. Huang et al. enhanced the Plantard method to accommodate signed integers as input and narrowed the range of the modulus q to .
Another effective method for reducing modulus in the LBC system is to utilize the characteristic property of prime number q [14,15]. This approach enables modular calculations through lightweight operations, including bit-wise, addition, and subtraction. An alternative and more straightforward method for high-order bits modulus q is using the look-up tables, as demonstrated in [16].
In a different research study [17], Longa et al. proposed a method called K-RED, which utilizes a special format of NTT-applicable primes, . This method primarily includes multiplying by a small coefficient (k) and subtracting, resulting in significantly lower computational costs than other methods. The product input is reduced to the signed integer . In study [18], Bisheh-Niasar et al. based on the K-RED method and introduced the -RED method by applying K-RED twice for CRYSTAL-Kyber. Furthermore, the cumulative coefficients, , can be eliminated by merging into the twiddle factor in NTT/INTT processes. In particular, in study [19], Li et al. used the property of the modulo q calculation, which helps to apply the K-RED method to the Point-Wise-Multiplication (PWM) process. Additionally, the multiplication by a factor of has been removed in the INTT process.
Nevertheless, as far as we know, studies presently focus on optimizing from the input multiplication. This study aims to design a DSP for modular multiplication by developing a multiplication unit for two integer inputs and utilizing advanced modular reduction techniques. In particular, the Karatsuba algorithm is used to subdivide the size of multiplication by half. Partial multiplications are performed using the Vertical and Crosswise algorithm, which speeds up computation. The results of the multiplications are reduced to bit-widths following the K-RED method’s condition using the pre-computed look-up table. Finally, the K-RED method is applied to calculate the result of the modulo operation, .
The major contributions of this paper are as follows:
- Proposes the first specialized DSP that performs modular multiplication for the CRYSTAL-Kyber PQC algorithm, called Kyber-DSP (K-DSP).The K-DSP performs the multiplication of two input integers and modular reduction for the prime q = 3329. The architecture reaches a high frequency of 283 MHz, and the area is only 77 SLICEs, equivalent to 77% of a typical DSP. This result completely outperforms traditional methods of modular multiplication that rely on DSP.
- The proposed Lattice-DSP (L-DSP) configuration optimizes the BU in NTT/INTT.In addition to saving on hardware resources, using the proposed L-DSP also eliminates the multiplication in the INTT process. As a result, the BU architecture requires minimal hardware resources. Choosing the architecture for NTT accelerators based on Decimation-In-Time (DIT), Decimation-In-Frequency (DIF), or both has become more flexible and easier. In CRYSTAL-Kyber, the BU architecture reaches a high frequency of 283 MHz while occupying an area equivalent to one DSP.
- Designs a K-DSP-based PWMM architecture designed for CRYSTAL-Kyber.PWM calculation in CRYSTAL-Kyber is more complicated than other LBC algorithms, requiring at least four multiplications for two PWM results. This study introduces a specific PWM structure for CRYSTAL-Kyber that uses K-DSP. Furthermore, the cumulative computation of matrix multiplication is combined with PWM while maintaining the same hardware cost for all three Kyber security levels (1, 3, and 5). The architecture that implements PWMM on the NTT domain includes PWM and Point-Wise Addition (PWA). The proposed PWMM operating frequency reaches 275 MHz with a hardware area of 386 SLICEs, equivalent to closely 4 DSPs.
- Extended with L-DSP design for prime numbers q = 7681 and 12,289.The proposed DSP design method is ideal for NTT-friendly algorithms with a prime factor . By applying this design to the case where q = 7681 and 12,889, it has been proven that the method still allows for a high operating frequency of 272 MHz and 256 MHz while using 87 SLICEs and 101 SLICEs of hardware resources.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the theoretical background of LBC, specifically the CRYSTAL-Kyber algorithm, and describes the NTT-based polynomial multiplication. Section 3 discusses in more detail the existing implementation studies for modular reduction. Section 4 presents the implementation of a DSP design for modular multiplication and builds upon the BU and PWMM architectures. Section 5 compares the performance of the proposed DSP and the designs built on it with the state-of-the-art reference implementations of Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). Finally, in Section 6, the conclusion of the paper is presented.
2. The Background
In this section, the CRYSTAL-Kyber algorithm is selected as the research basis for the improvement proposals applicable to other LBC algorithms. From a hardware implementation perspective, CRYSTAL-Kyber is designed to do all the polynomial multiplication using NTT. Also, the parameter set of CRYSTAL-Kyber is the smallest with , and PWM operation requires more difficult hardware complexity.
Unlike other LBCs, FALCON is very complex in hardware implementation due to having to perform polynomial multiplication on complex and integer number domains [20]. Fortunately, verification of FALCON is simple and high-performing. This crucial advantage led NIST to select FALCON for standardization with Dilithium after the third-round finalist. Thus, Kyber’s improvements to polynomial multiplication over the integer domain can be applied to enhance FALCON’s verification performance.
2.1. CRYSTAL-Kyber
CRYSTAL-Kyber is built based on the hardness of the Module-LWE problem. Kyber employs a two-stage construction for achieving an INDistinguishability under a Chosen-Ciphertext Attack (IND-CCA) secure Key-Encapsulation Mechanism (KEM). First, an IND-Chosen Plaintext Attack (CPA)-secure public-key encryption scheme is built called Kyber.CPA. Then, the Fujisaki-Okamoto transform is applied to build the CCA-secure KEM.
Kyber operates on with module rank k = 2, 3, and 4, providing security levels 1, 3, and 5 for Kyber512, Kyber768, and Kyber1024, respectively. In the first round of NIST [21], the prime q was chosen as 7681 and satisfying , where N = 256 is the degree of the modular polynomial. In the second round of the NIST competition [22], the Kyber team reduced the q value from 7681 to 3329 as research [23] showed that this value of q also supports very fast NTT-based polynomial multiplication. Simultaneously, q = 3329 also requires a smaller noise range while maintaining the same level of security as Kyber(v01). Table 1 lists the parameters of Kyber(v03), where and are the parameters of the central binomial distribution.

Table 1.
Parameter sets for CRYSTAL-Kyber (v03).
2.2. NTT-Based Polynomial Multiplication
The NTT-based multiplication is commonly used for LBCs. It involves transforming polynomials from coefficient representation to the NTT domain, performing pointwise operations, and then returning the result to the integer domain using the INTT transformation. Using NTT, the multiplication of two integer polynomials with N terms can be performed with a low computational cost of . Especially, the prime q must be chosen with condition to avoid zero-padding when performing NTT-based multiplication, which is also known as Negative-Wrap Convolution (NWC) [24]. For the prime q = 3329 of Kyber(v02/03), the field contains primitive N-th roots of unity but not primitive 2N-th roots. Thus, the NTT of polynomial is a vector of 128 degree-1 polynomials with two coefficients each and is defined as,
where coefficients are defined as,
with is the 256-th root of unity in and i = 0, …, 127 is a 7-bit unsigned integer represented in binary form as . is the bit reversal of i, where . As a result, a 256-term polynomial in Kyber is divided into two 128-term polynomials by parity, and NTT is applied to each one. After NTT, the PWM of the two components f and g of , denoted by , is performed by conducting 128 multiplications of linear polynomials modulo . Specifically,
where is defined as,
Finally, the point-wise multiplications in Kyber are defined as,
3. Related Works
LBC operations are performed on the ring , where q is a prime number and N is a power-of-two. Modular multiplication is the most time-consuming operand in NTT and can be expressed as follows:
Several classical algorithms are available to enhance the efficiency of modular reduction, such as Montgomery reduction and Barret reduction. The Montgomery method is infrequently used due to the resource consumption of conversions into and out of the “Montgomery domain” [25,26]. In contrast, the Barret method is widely adopted and has many improved variants. The basic idea behind Barret’s algorithm is to pre-compute the inverse of modulus q and use simple bit shifting and multiplication instead of costly division. Algorithm 1 utilizes Barrett reduction to compute the product of two integers modulo q.
| Algorithm 1 Modular Multiplication by Barret Reduction [7] |
|
In LBC algorithms, the q value is fixed, allowing pre-computation of k, r, and . Barrett-based modular multiplication commonly employs DSPs for multiplying input coefficients and the constant , while multiplying by q is efficiently achieved using bitwise shifts and additions. In study [27], Dang et al. applied a variation of Barret reduction in [28] to select parameter values (, ) and design a single-constant-multiplier for multiplying by the constant . LBC schemes based on NTT implementation using signed integers can eliminate modular addition at each butterfly unit [25,29,30]. The optimized Barrett reduction algorithm for signed integer inputs has been further enhanced by study [31] to narrow its output range to . This improvement effectively limits the growth of coefficients after each butterfly unit, resulting in better performance. The SAMS2 method simplifies multiplication by bit shifting, addition, and subtraction [8,9,10,11]. This significantly reduces the hardware architecture but increases latency due to multiple subtractions. A look-up table can be used to speed up, but it is inefficient in terms of area.
Huang et al. enhanced the Plantard algorithm for a larger range of inputs and a smaller range of outputs [13]. The improved Plantard method saves one multiplication compared to the latest Montgomery and Barrett methods. However, the drawback of this method is that it still requires three multiplications when calculating the PWM and necessitates doubling the width of the pre-computed intermediate twiddle factors.
Several methods have been proposed for modular reduction to optimize the area and speed of NTT accelerator with specific q parameter. Study [14] utilized the form of to replace multiplications in Barret reduction with bit shifts, addition, and subtraction operations. Aikata et al. implemented this technique for the Kyber q = 3329 case [32]. Some recent studies involve calculating the modulus q of higher-order bits in the product of multiplying two 12-bit integers, . In studies [15,33], the property is used to gradually reduce the higher-order bits to an arithmetic combination of the smaller bit arrays. Similarly, in study [34], the bit width of the multiplication product is reduced from 24 to 15, and then apply Barret algorithm. This method is useful in reducing the multiplication size during Barret reduction. Additionally, a different format of , is used to propose a modulus reduction algorithm for Kyber [35]. This algorithm divides the product c into two corresponding parts, , and replaces the large modulus q with the smaller modulus . A simpler and more efficient alternative is introduced in [16]. Zhang et al. used the pre-computed look-up table to store the calculations of , , and . The higher-order bits are used as the input address of the look-up tables, and the outputs are the corresponding modular operations. Finally, the modulo operation of the product is calculated by adding the four numbers on the ring .
Another new modular reduction approach, K-RED, is proposed in study [17]. The K-RED method utilizes the characteristics of Proth numbers represented as where k is a small number, m is a natural number. This approach presents two functions: K-RED and KRED-2X, which take any integer c and return an integer d such that and , respectively. The K-RED method performs one multiplication with a constant factor of k and one subtraction, as described in Algorithm 2. Multiplying by k is achieved with bit shifting and addition, significantly reducing computational costs compared to other methods. However, to correct the reduction results, the output of K-RED must be multiplied by the factor . Bisheh-Niasar et al. in [18] followed this scheme and proposed -RED, by applying K-RED twice in CRYSTAL-Kyber with constant k = 13 and m = 8. The multiplication by can be combined with the pre-computed twiddle factor in NTT/INTT for faster computation with fewer hardware resources. In study [36], Ni et al. segmented the product into two parts. The look-up table method is employed for the bits exceeding 20, while the remaining portion underwent the K-RED technique. This method is simple but requires one more adder. The -RED is extended to -RED for different NTT parameters, where is the number of loops, and t is the bit-length of input coefficients [37]. However, K-RED is not appropriate for PWM calculations with random multipliers. Fortunately, this drawback can be resolved by using the property of , as demonstrated in study [19]. Li et al. applied the K-RED method with modifications in input value and output calculations. In particular, the input product c is multiplied by two, and the subtraction in K-RED is changed sign. Therefore, the output is calculated as,
with (13,256) and for the case of Kyber, the Equation (9) is equivalent to . During the INTT process, multiplying by is considered post-processing. As a result, K-RED can be applied to PWM processes, eliminating the need for post-processing in Kyber by using this method.
| Algorithm 2 K-RED Modular Reduction Algorithm [17] |
|
4. Proposed Hardware Design
The modular reduction of LBCs typically begins with the DSP-based multiplication product, but small multiplication widths can result in suboptimal area usage. As a result, in this section, we present a K-DSP architecture as the basis for implementing BUs in NTT/INTT processes. Further, we propose a PWMM unit for Kyber using the K-DSP and extend the L-DSP design method to other LBC cases with q = 7681 and 12,289.
4.1. K-DSP
The K-DSP performs modular multiplication of two 12-bit coefficients, and , to produce a 12-bit result on the ring . The proposed architecture of K-DSP is shown in Figure 1 with three computational stages. In the initial stage, we employ the Karatsuba algorithm to partition a 12-bit multiplication operation into three discrete components: two 6-bit multiplications and one 7-bit multiplication, respectively , , and . Subsequently, the summation of these partial products is calculated using the look-up table method. As a result of this procedure, the bit-width of the product is reduced from 24 bits to 20 bits. Finally, the K-RED method is utilized to ascertain the modulus q of the 20-bit product.
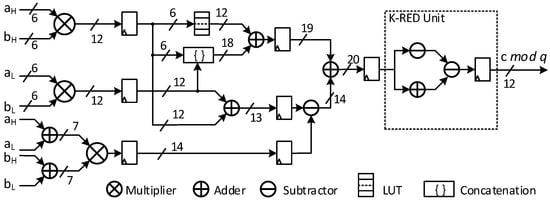
Figure 1.
The proposed architecture of K-DSP.
The choice of multiplier design significantly impacts the speed and area of the proposed DSP. This study selects the Vedic multiplier based on the Vertical and Crosswise technique for designing 6-bit and 7-bit multipliers due to its shorter critical path than the conventional array multipliers [38]. Vedic multipliers are performed in parallel, and the partial products are added together by two or three levels of the adder [39]. Figure 2 shows the 3-bit multiplier architecture of two numbers and . The architecture comprises nine AND gates, three full adders, and three half adders.
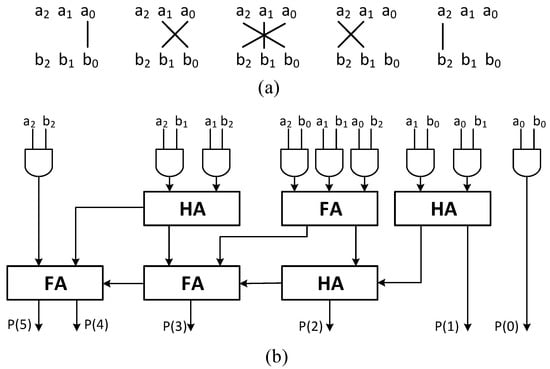
Figure 2.
(a) 3-bit multiplication by Vertically and Crosswise technique. (b) Architecture block diagram for 3-bit Vedic multiplier.
Figure 3 depicts the proposed 6-bit multiplier architecture based on four 3-bit multipliers and three 6-bit adder units. The adder unit used is the carry save adder to perform the additions in parallel, improving speed efficiency [40]. A 4-bit Vedic multiplier is also designed. In the K-DSP architecture, the 3-bit and 4-bit Vedic multipliers are used as the base multipliers for building up the 6-bit and 7-bit multipliers.
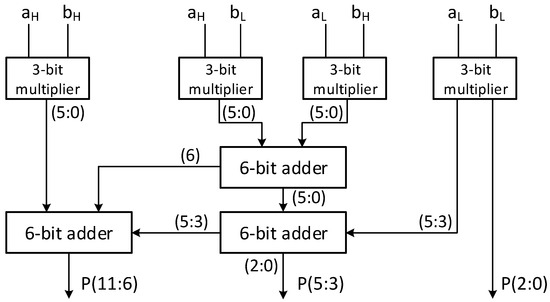
Figure 3.
The architecture of 6-bit Vedic multiplier.
According to the Karatsuba algorithm, multiplication is done in three steps: , , and , then subtract and from the result of to get the product. A look-up table is designed to compute the operation [23:18] ·, with the input address being the [23:18] bits of the product . The final product is then reduced modular to a bit width of 20 bits.
The prime parameter in Kyber is , where the factor values are k = 13 and m = 8. The elimination of accumulation is handled differently by implementing K-DSP in each BU or PWM unit. Consequently, the K-RED-based modular reduction part can be regarded as a specialized sub-module, which will be further discussed in the following sub-sections.
4.2. Butterfly Unit
The NWC technique is utilized in NTT/INTT to avoid doubling the size of the multiplication polynomial. To compute in the ring with NWC, polynomials and must be scaled by a factor before applying NTT (refered to as pre-processing). Subsequently, polynomial product is scaled by a factor after INTT (referred to as post-processing), and is the 2N-th primitive root of the unity. Two methods for calculating the NTT are DIT and DIF, corresponding to the Cooley-Tukey (CT) [41], and Gentleman-Sande (GS) butterfly configurations [42]. Given a pair of coefficients and twiddle factor , the CT and GS butterfly calculations produce the results of and , as depicted in Figure 4a,b.
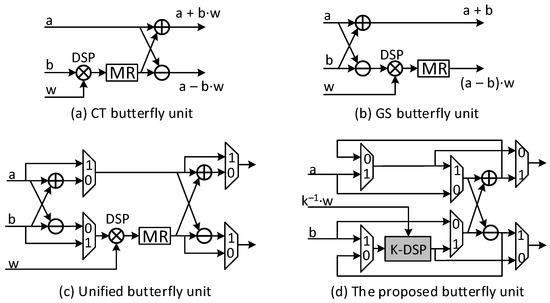
Figure 4.
The configurations of butterfly unit.
In studies [43,44], the multipliers can be merged with NTT and INTT processes. These methods involve separate butterfly operations: CT for NTT with and GS for INTT with . The unified-BU architecture has been proposed for the simultaneous computation of GS and CT in the study [14], as shown in Figure 4c. In the GS calculation, the factor can be pre-computed with the twiddle factor for the operation. With the operation , in study [45], Zhang et al. proposed replacing the multiplication by after INTT with the multiplication by in each butterfly operand, respectively . The hardware architecture for multiplier in is achieved simply by implementing .
Butterfly operations are all modular arithmetic. The specific configuration choice among CT, GS, or both depends on the design of the NTT accelerator. The iterative NTT architecture uses unified BU for butterfly operations in all stages, such as NTT, INTT, and PWM with the Kyber case. The latency of iterative NTT increases with the number of butterfly cores and becomes more complex when handling high-order polynomials. On the other hand, the NTT pipeline architecture allows for flexibility in selecting BU configurations and butterfly cores proportional to the number of NTT stages [11,46,47]. In all cases, modular multiplication is consistently the most hardware-intensive operation and represents the critical delay path.
In this study, a BU tailored for Kyber is implemented. This architecture employs K-DSP and comprises one modular addition, one subtraction, and one multiplication. The resulting output is controlled by mux units, allowing the BU to operate in either CT or GS mode, as depicted in Figure 4d. The classical K-RED method is applied for the modular reduction part of K-DSP. The accumulated k = 13 is removed when the inverse is merged into the twiddle factor . Additionally, the multiplication by for the GS calculation is eliminated, as performed at the PWM stage (further details are provided in the subsequent section). BUs utilize K-DSP units, helping reduce the size and improving the efficiency of parallel or pipeline architectures when multiple BUs are used.
4.3. Point-Wise Matrix Multiplication Unit
Calculating the ciphertext is the most intricate operation in Kyber, with , , and are vector polynomials, and is matrix polynomial. The specific mathematical expression for the PWMM is shown in Equation (10) for case module rank k = 2.
The PWMM requires two point-wise operations: PWM and PWA. In Kyber, a 256-term polynomial is performed NTT process using two 128-point NTT, one for the even part () and one for the odd part (). Thus, the PWM on Kyber is multiplying polynomials of the form . In study [48], Xing et al. proposed using the Karatsuba method to reduce the number of point-wise multiplications required to calculate from five to four, as follows:
The previous section mentioned that the K-RED method can be customized to change the output value. To remove the post-processing of the INTT stage, the output values of the PWM calculation should be and , which can be achieved by applying the property characteristic. The PWM architecture for Kyber is detailed in Figure 5. Initially, the calculations , , and all use K-DSPs without K-RED unit, resulting in bit widths 20. The calculation of is performed using modular addition, modular subtraction, and bit shifting. Subsequently, the K-RED unit is utilized to get the result. For the calculation, the PWM is utilized with K-RED to provide the result in the ring . The accumulated factor k is eliminated from the PWM with pre-computed factor . Finally, K-RED is used again to determine the result.
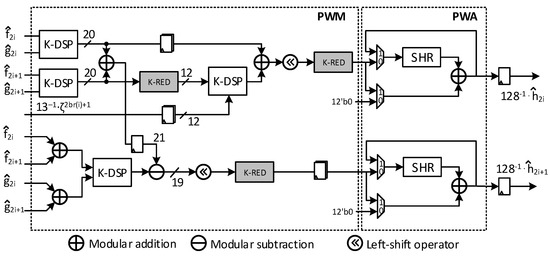
Figure 5.
The proposed architecture of PWMM unit in Kyber implementation.
For PWA calculation, the architecture in Figure 5 shows an efficient and simple way to perform PWA using a shift register SHR with feedback and modular addition. During the initial calculation stage, the SHR takes in the output of PWM and adds value . In the following step, the SHR takes in the result of the previous addition and performs another addition with the outcome of the PWM . This architecture requires no hardware cost changes when implementing different security levels of Kyber, k = 2, 3, and 4, respectively.
4.4. L-DSPs
NTT-based polynomial multiplication is a highly utilized and efficient method for implementing LBC systems, offering quasi-linear complexity of . To quickly calculate NTT using NWC, a prime number q is carefully chosen to meet the condition . This guarantees the existence of the N-th and -th primitive roots of unity (denoted as and ) in the ring . Consequently, the parameters for the LBC algorithms require a relatively large value for N and a relatively small modulus q in form , where and is considered small integer.
This study focuses on analyzing and proposing the DSP for commonly used parameter sets of LBC algorithms, as in Table 2 (referred to as L-DSP). The Kyber team has adopted the parameter pair since round 2 of the NIST competition. It is chosen to address increased bandwidth requirements resulting from removing public key compression. The advantage of using q = 3329 is that NTT-based polynomial multiplication can be performed quickly, leading to smaller noise. One drawback to this parameter set is that PWM calculation is not directly possible.

Table 2.
Parameter sets of LBC algorithms.
Alternatively, is the smallest parameter pair that fully supports fast NTT computation while ensuring high security and the ability to perform direct PWM calculations. Due to this advantage, many current hardware implementations have adopted the prime q = 7681 to optimize their systems [11,46,49]. The remaining set 12,289) is utilized in the latest version of FALCON, where the polynomial degree N can vary depending on the desired security level of the system.
The primary operations that use DSP for modular multiplication are butterfly and PWM. In the BFU architecture, a coefficient is multiplied by a pre-computed twiddle factor (). The accumulated k can be merged to as . The value of N does not impact the K-RED architecture in L-DSP in the case of FALCON. Algorithm 3 outlines the steps for implementing L-DSP for butterfly computation in a comprehensive and detailed manner.
| Algorithm 3 L-DSP for Butterfly Unit |
|
In the PWM operation, one crucial step involves multiplying the output by the value to eliminate post-processing in the INTT. Notably, as the polynomial degree N changes, the value of N consistently satisfies the condition , which ensures that the output can be computed directly as,
with and . The Equation (13) is equivalent to . Additionally, since z is a power of two, it can be easily multiplied by bit-shifting the input of the K-RED part. Algorithm 4 provides a detailed outline of the L-DSP implementation for PWM operation.
For multiplying coefficients with larger bit-width, it is possible to create an efficient multiplier design using 3-bit and 4-bit Vedic multiplier circuits as the basic building blocks.
| Algorithm 4 L-DSP for PWM Unit |
|
5. Implementation Results
This study introduces and applies the proposed modular multiplication L-DSPs in BFU and PWMM units of the NTT-based accelerator in the LBC cryptosystem. These architectures are synthesized and place-and-routed using the Xilinx Vivado 2021.2 suite. The widely used Xilinx Artix-7 FPGA platform (part number XC7A100tfgg676-3) is selected to ensure a fair comparison with state-of-the-art hardware implementations. We introduce the hardware efficiency () for a comparative analysis with previous works. A higher value is desirable and can be calculated as follows,
The study [47] showed a normal DSP with an equivalent conversion rate of 100 SLICEs or 400 LUTs. We use this ratio for area comparison with other studies.
Table 3 shows the proposed K-DSP architecture for modular multiplication on CRYSTAL-Kyber, showcasing its speed and area. K-DSP can perform integer multiplication and modular reduction and operates at a frequency of 283 MHz, occupying an area of only 77 SLICEs, equivalent to 77% of a DPS. It is worth noting that all other studies listed in the comparison table use DSP for coefficient multiplication. The implementation results of the K-RED method are better than other methods when performing modular reduction. Notably, in study [36], by combining the K-RED and LUT methods, the operating frequency reached 300 MHz with an equivalent area of 50 (+400) LUTs. In [46], heavy multiplications are efficiently replaced with compact bit-wise operations and additions/subtractions based on an optimized Barrett algorithm. The hardware results achieved an operating frequency of 265 MHz and occupied an equivalent area of 81 (+400) LUTs. Study [33] utilizes a bit-reduce method that is complex and hardware costly. These results demonstrate that the proposed K-DSP architecture has further optimized modular multiplication, with significantly improved performance metrics of , , , , , and compared to studies [18,33,36,46,48,50], respectively.

Table 3.
Comparison of the proposed modular multiplication DSP for Kyber with other approaches.
The results of the K-DSP-based BU implementation for Kyber are displayed in Table 4. The proposed BU architecture comprises one K-DSP, an adder, and a subtractor for CT and GS butterfly operations. The operating frequency of this architecture reaches 283 MHz and takes an area of 104 SLICEs, slightly equal to one DSP. The conventional unified BU architecture uses two DSPs to perform distinct multiplications, adders, and subtractors for CT and GS calculations. The studies [33,48] used this architecture and recorded low operation frequency and high hardware resources of 159 MHz for 774 (+800) LUTs and 161 MHz for 647 (+800) LUTs, respectively. Other studies have built a reduced architecture using only one DSP for multiplication. With the downsized BU architecture, the study [46] has an operating frequency of 265 MHz and consumes 186 (+400) LUTs. It is important to mention that multiplication can impact speed and area. In study [51], a standard implementation of Kyber’s reference code, modular multiplication consumed more DSPs due to applying both the Barret and Montgomery algorithms. The proposed BU architecture based on K-DSP significantly improves the index compared to the research studies [18,27,33,46,48,50]. The improvement is , , , , , and times, respectively.

Table 4.
Implementation results of the proposed BU for CRYSTAL-Kyber and comparison with previous studies.
Table 5 shows the effectiveness of the DSP design method for core operations modular multiplication and butterfly in the NTT accelerator of the LBC cryptosystem. We have developed L-DSPs and BUs architectures for prime q values in , specifically for 3329, 7681, and 12,289. When using L-DSPs, the operating frequencies for q = 3329, 7681, and 12,289 are 283 MHz, 272 MHz, and 256 MHz, respectively. The hardware resources needed for L-DSPs are less than or equal to one DSP, which results in a percentage of the area used of 77%, 87%, and 101% DSP, respectively. On the other hand, using BUs results in hardware resource improvements of 104%, 120%, and 136% DSP for the same q values, respectively. The operating frequencies for BUs are 283 MHz, 260 MHz, and 250 MHz, respectively. All L-DSPs and BUs architectures have less than 400 LUTs hardware resources, equivalent to one DSP.

Table 5.
Implementation results of the proposed L-DSPs and BU for typical cases of prime q in LBC cryptosystem.
The results of implementing the PWMM architecture in Kyber are presented in Table 6. Other studies utilize BRAM [46] or FIFO [47] to temporarily store the accumulation results, leading to further hardware resource consumption for the PWA operation. In order to optimize the NTT accelerator pipelines, our architecture is designed to handle both PWM and PWA operations. Two different architectures, namely one-PWMM and two-PWMM, are designed and achieve the highest operating frequency of 275 MHz with cycles and an area of 128 Clks/1123 LUTs and 64 Clks/2297 LUTs. To be more precise, the hardware resources take fewer SLICEs than the conversion value of 4 and 8 DSPs, which are equivalent to 386 and 797 SLICEs, respectively. In studies [34,35,36], the PWM execution is performed using a shared hardware architecture with BUs. The highest operating frequencies are achieved in studies [35,36], reaching 300 MHz and 303 MHz, respectively. This is primarily due to the use of efficient modular reduction modules. In study [46], an architecture for two-PWM calculation was proposed on Kyber, using 8 DSPs for the multiplications. The operating frequency of this architecture reaches 265 MHz and consumes hardware resources of 749 (+3200) LUTs respectively. Our architecture significantly reduces hardware resources and improves efficiency. The proposed PWMM design reduces ATP(area time product) by 33.8%, 47.8%, 67.3%, and 71.2% compared to [34,35,36,46], respectively.

Table 6.
Implementation results of the proposed PWMM unit for CRYSTAL-Kyber.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we present a method for designing compact and efficient specialized hardware implementations for modular multiplication in LBC systems. Using the proposed approach, we have designed and implemented core architectures within NTT accelerators for polynomial multiplication. The optimization of the BU architecture is performed to completely eliminate the need for post-processing in INTT. Consequently, the BU architecture, when simultaneously executing NTT and INTT, has a footprint equivalent to that of a conventional BU architecture. Additionally, we propose a hardware design for implementing PWMM for the Kyber algorithm. The proposed architecture can perform both PWM and PWA calculations for all security levels without requiring additional temporary memory, such as RAM or FIFO buffers.
Furthermore, we have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method by designing it for common prime parameters q, used in various LBC algorithms. FPGA-based implementation results show the outperforming hardware efficiency of the K-DSP, L-DSP, BU, and PWMM architectures compared to existing implementations. The findings of this paper can further optimize NTT accelerators with pipeline or iterative configurations. Therefore, the proposed architectures represent an important step toward designing compact and high-performance post-quantum lattice-based cryptography systems on hardware platforms.
Author Contributions
Supervision, C.-K.P. and T.-T.H.; methodology, T.-H.N.; investigation, T.-H.N.; writing—original draft preparation, T.-H.N.; writing—review and editing, T.-H.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the University of Electro-Communications (UEC) via the Support for External Funds Acquisition by Early Career Scientists program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alagic, G.; Apon, D.; Cooper, D.; Dang, Q.; Dang, T.; Kelsey, J.; Lichtinger, J.; Liu, Y.K.; Miller, C.; Moody, D.; et al. Status Report on the Third Round of the NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Process; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Avanzi, R.; Bos, J.; Ducas, L.; Kiltz, E.; Lepoint, T.; Lyubashevsky, V.; Schanck, J.M.; Schwabe, P.; Seiler, G.; Stehlé, D. CRYSTALS-Kyber: Algorithm Specifications And Supporting Documentation (Version 3.01). January 2021. Available online: https://pq-crystals.org/kyber/data/kyber-specification-round3-20210131.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Bai, S.; Ducas, L.; Kiltz, E.; Lepoint, T.; Lyubashevsky, V.; Schwabe, P.; Seiler, G.; Stehlé, D. CRYSTALS-Dilithium: Algorithm Specifications And Supporting Documentation (Version 3.01). February 2021. Available online: https://pq-crystals.org/dilithium/data/dilithium-specification-round3-20210208.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Fouque, P.-A.; Hoffstein, J.; Kirchner, P.; Lyubashevsky, V.; Pornin, T.; Prest, T.; Ricosset, T.; Seiler, G.; Whyte, W.; Zhang, Z. Falcon: Fast-Fourier Lattice-Based Compact Signatures over NTRU (v1.2). October 2020. Available online: https://falcon-sign.info/falcon.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Montgomery, P.L. Modular Multiplication Without Trial Division. Math. Comput. 1985, 44, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, P. Implementing the Rivest Shamir and Adleman Public Key Encryption Algorithm on a Standard Digital Signal Processor. In Proceedings of the Advances in Crypto (CRYPTO), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 16–20 August 1987; pp. 311–323. [Google Scholar]
- Satriawan, A.; Syafalni, I.; Mareta, R.; Anshori, I.; Shalannanda, W.; Barra, A. Conceptual Review on Number Theoretic Transform and Comprehensive Review on Its Implementations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 70288–70316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Seo, H.; Sinha Roy, S.; Großschädl, J.; Kim, H.; Verbauwhede, I. Efficient Ring-LWE Encryption on 8-Bit AVR Processors. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES), Saint-Malo, France, 13–16 September 2015; pp. 663–682. [Google Scholar]
- Renteria-Mejia, C.P.; Velasco-Medina, J. High-Throughput Ring-LWE Cryptoprocessors. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2017, 25, 2332–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fan, S.; Khalid, A.; Rafferty, C.; O’Neill, M. Optimized Schoolbook Polynomial Multiplication for Compact Lattice-Based Cryptography on FPGA. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2019, 27, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Khalid, A.; O’Neill, M.; Liu, W. Ultra High-Speed Polynomial Multiplications for Lattice-Based Cryptography on FPGAs. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comp. 2022, 10, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar]
- Plantard, T. Efficient Word Size Modular Arithmetic. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comp. 2021, 9, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Cheung, R.C.; Koç, Ç.K.; Chen, D. Improved Plantard Arithmetic for Lattice-based Cryptography. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. (TCHES) 2022, 2022, 614–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, U.; Ukyab, T.S.; Chandrakasan, A.P. Sapphire: A Configurable Crypto-Processor for Post-Quantum Lattice-based Protocols. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. (TCHES) 2019, 2019, 17–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, F.; Mert, A.C.; Öztürk, E.; Savaş, E. A Hardware Accelerator for Polynomial Multiplication Operation of CRYSTALS-KYBER PQC Scheme. In Proceedings of the 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 1020–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Zou, X.; Niu, G.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Q. Towards Efficient Hardware Implementation of NTT for Kyber on FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Longa, P.; Naehrig, M. Speeding up the Number Theoretic Transform for Faster Ideal Lattice-Based Cryptography. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cryptology and Network Security (CANS), Milan, Italy, 14–16 November 2016; pp. 124–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bisheh-Niasar, M.; Azarderakhsh, R.; Mozaffari-Kermani, M. High-Speed NTT-based Polynomial Multiplication Accelerator for Post-Quantum Cryptography. In Proceedings of the IEEE ymposium on Computer Arithmetic (ARITH), Lyngby, Denmark, 14–16 June 2021; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lil, M.; Tian, J.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z. High-Speed and Low-Complexity Modular Reduction Design for CRYSTALS-Kyber. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), Shenzhen, China, 11–13 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Song, J.; Seo, S.C. Accelerating Falcon on ARMv8. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 44446–44460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagic, G.; Alagic, G.; Alperin-Sheriff, J.; Apon, D.; Cooper, D.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.-K.; Miller, C.; Moody, D.; Peralta, R.; et al. Status Report on the First Round of the NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Process; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Alagic, G.; Alperin-Sheriff, J.; Apon, D.; Cooper, D.; Dang, Q.; Kelsey, J.; Liu, Y.-K.; Miller, C.; Moody, D.; Peralta, R.; et al. Status Report on the Second Round of the NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Process; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lyubashevsky, V.; Seiler, G. NTTRU: Truly Fast NTRU Using NTT. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. (TCHES) 2019, 2019, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubashevsky, V.; Micciancio, D.; Peikert, C.; Rosen, A. SWIFFT: A Modest Proposal for FFT Hashing. In Proceedings of the Fast Software Encryption (FSE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 10–13 February 2008; pp. 54–72. [Google Scholar]
- Seiler, G. Faster AVX2 Optimized NTT Multiplication for Ring-LWE Lattice Cryptography. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Paper 2018/039. 2018. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/039 (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Chung, C.M.M.; Hwang, V.; Kannwischer, M.J.; Seiler, G.; Shih, C.J.; Yang, B.Y. NTT Multiplication for NTT-unfriendly Rings: New Speed Records for Saber and NTRU on Cortex-M4 and AVX2. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. (TCHES) 2021, 2021, 159–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.B.; Mohajerani, K.; Gaj, K. High-Speed Hardware Architectures and FPGA Benchmarking of CRYSTALS-Kyber, NTRU, and Saber. IEEE Trans. Comp. 2023, 72, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, M.; Vercauteren, F.; Verbauwhede, I. Faster Interleaved Modular Multiplication Based on Barrett and Montgomery Reduction Methods. IEEE Trans. Comp. 2010, 59, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, L.; Kannwischer, M.J.; Schwabe, P. Memory-Efficient High-Speed Implementation of Kyber on Cortex-M4. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Paper 2019/489. 2019. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2019/489 (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Alkim, E.; Alper Bilgin, Y.; Cenk, M.; Gérard, F. Cortex-M4 optimizations for R,M LWE schemes. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. (TCHES) 2020, 2020, 336–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.; Hwang, V.; Kannwischer, M.J.; Sprenkels, A. Faster Kyber and Dilithium on the Cortex-M4. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Paper 2022/112. 2022. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2022/112 (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Aikata, A.; Mert, A.C.; Imran, M.; Pagliarini, S.; Roy, S.S. KaLi: A Crystal for Post-Quantum Security Using Kyber and Dilithium. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, S.; Kong, L. An Efficient Implementation of KYBER. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs (TCAS-II) 2022, 69, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, S. Highly-Efficient Hardware Architecture for CRYSTALS-Kyber with a Novel Conflict-Free Memory Access Pattern. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tian, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z. Reconfigurable and High-Efficiency Polynomial Multiplication Accelerator for CRYSTALS-Kyber. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2023, 42, 2540–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Khalid, A.; Liu, W.; O’Neill, M. Towards a Lightweight CRYSTALS-Kyber in FPGAs: An Ultra-lightweight BRAM-free NTT Core. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 23 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Cheung, R.C.; Huang, K. PipeNTT: A Pipelined Number Theoretic Transform Architecture. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 4068–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, Y.; Madhu, C.; Kaur, P. High Speed Vedic Multiplier Designs—A Review. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Engineering and Computational Sciences (RAECS), Chandigarh, India, 6–8 March 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- James, A.P.; Kumar, D.S.; Ajayan, A. Threshold Logic Computing: Memristive-CMOS Circuits for Fast Fourier Transform and Vedic Multiplication. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2015, 23, 2690–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Song, W.; Lu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, Z. Symmetric-Mapping LUT-Based Method and Architecture for Computing XY-Like Functions. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I Regul. Papers (TCAS-I) 2021, 68, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, J.W.; Tukey, J.W. An Algorithm for the Machine Calculation of Complex Fourier Series. Math. Comput. 1965, 19, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentleman, W.M.; Sande, G. Fast Fourier Transforms: For Fun and Profit. In Proceedings of the Fall Joint Computer Conference (AFIPS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–10 November 1966; pp. 563–578. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.S.; Vercauteren, F.; Mentens, N.; Chen, D.D.; Verbauwhede, I. Compact Ring-LWE Cryptoprocessor. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES), Busan, Republic of Korea, 23–26 September 2014; pp. 371–391. [Google Scholar]
- Pöppelmann, T.; Oder, T.; Güneysu, T. High-Performance Ideal Lattice-Based Cryptography on 8-Bit ATxmega Microcontrollers. In Proceedings of the Progress in Cryptology (LATINCRYPT), Guadalajara, Mexico, 23–26 August 2015; pp. 346–365. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Yin, S.; Wei, S.; Liu, L. Highly efficient architecture of NewHope-NIST on FPGA using low-complexity NTT/INTT. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. (TCHES) 2020, 2020, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong-Ngoc, P.; Lee, H. Configurable Mixed-Radix Number Theoretic Transform Architecture for Lattice-Based Cryptography. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 12732–12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Khalid, A.; O’Neill, M.; Liu, W. HPKA: A High-Performance CRYSTALS-Kyber Accelerator Exploring Efficient Pipelining. IEEE Trans. Comp. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, S. A Compact Hardware Implementation of CCAsecure Key Exchange Mechanism CRYSTALS-Kyber on FPGA. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. (TCHES) 2021, 328–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Wang, C.; O’Neill, M.; Liu, W. Towards CRYSTALS-Kyber: A M-LWE Cryptoprocessor with Area-Time Trade-Off. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Itabashi, Y.; Ueno, R.; Homma, N. Efficient Modular Polynomial Multiplier for NTT Accelerator of Crystals-Kyber. In Proceedings of the Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), Maspalomas, Spain, 31 August–2 September 2022; pp. 528–533. [Google Scholar]
- Nannipieri, P.; Di Matteo, S.; Zulberti, L.; Albicocchi, F.; Saponara, S.; Fanucci, L. A RISC-V Post Quantum Cryptography Instruction Set Extension for Number Theoretic Transform to Speed-Up CRYSTALS Algorithms. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 150798–150808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).