Automated Classical Cipher Emulation Attacks via Unified Unsupervised Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Works
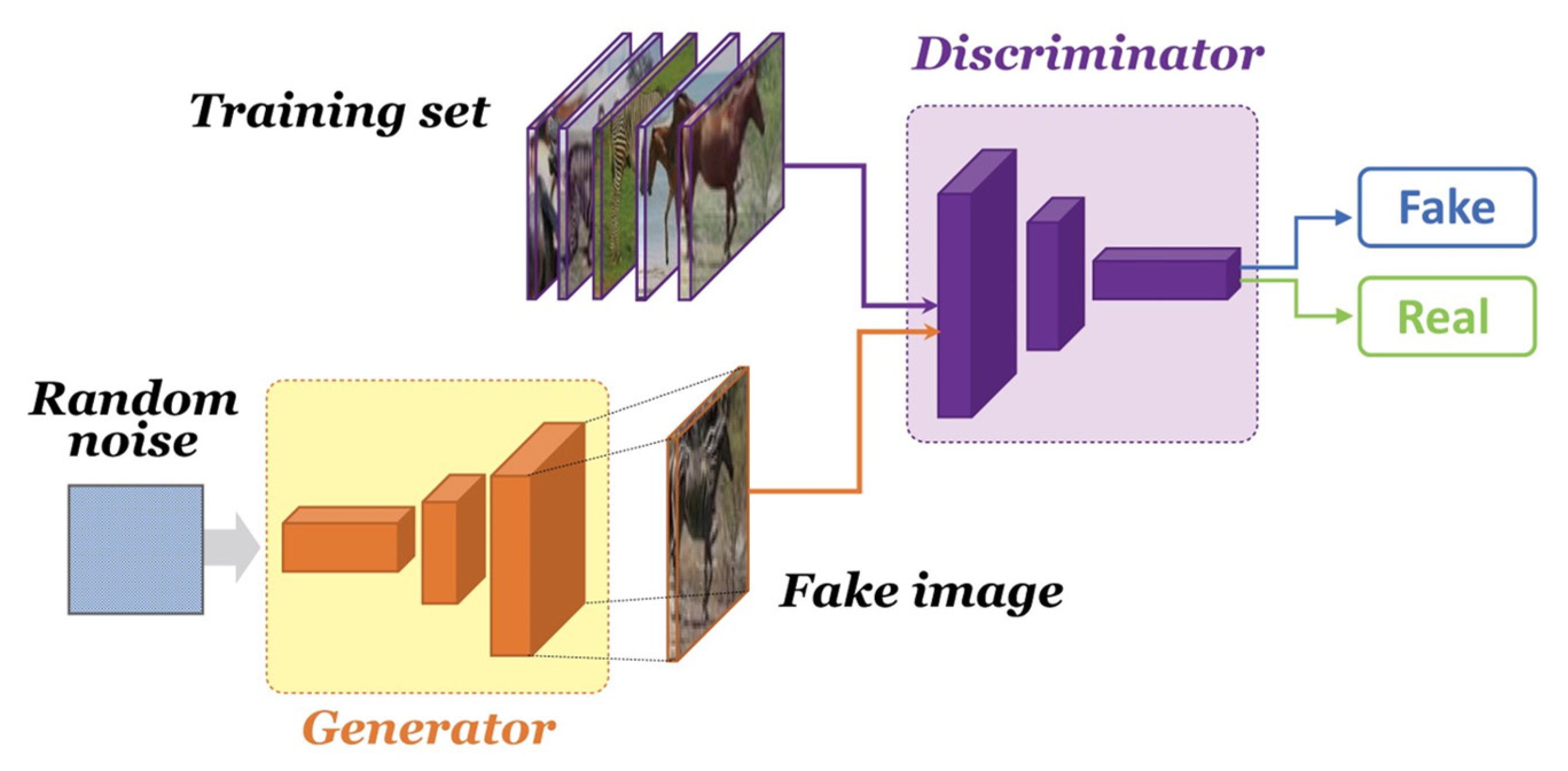
2.1. Generative Adversarial Networks
2.2. Classical Substitution Ciphers
2.3. AI-Based Cryptanalysis
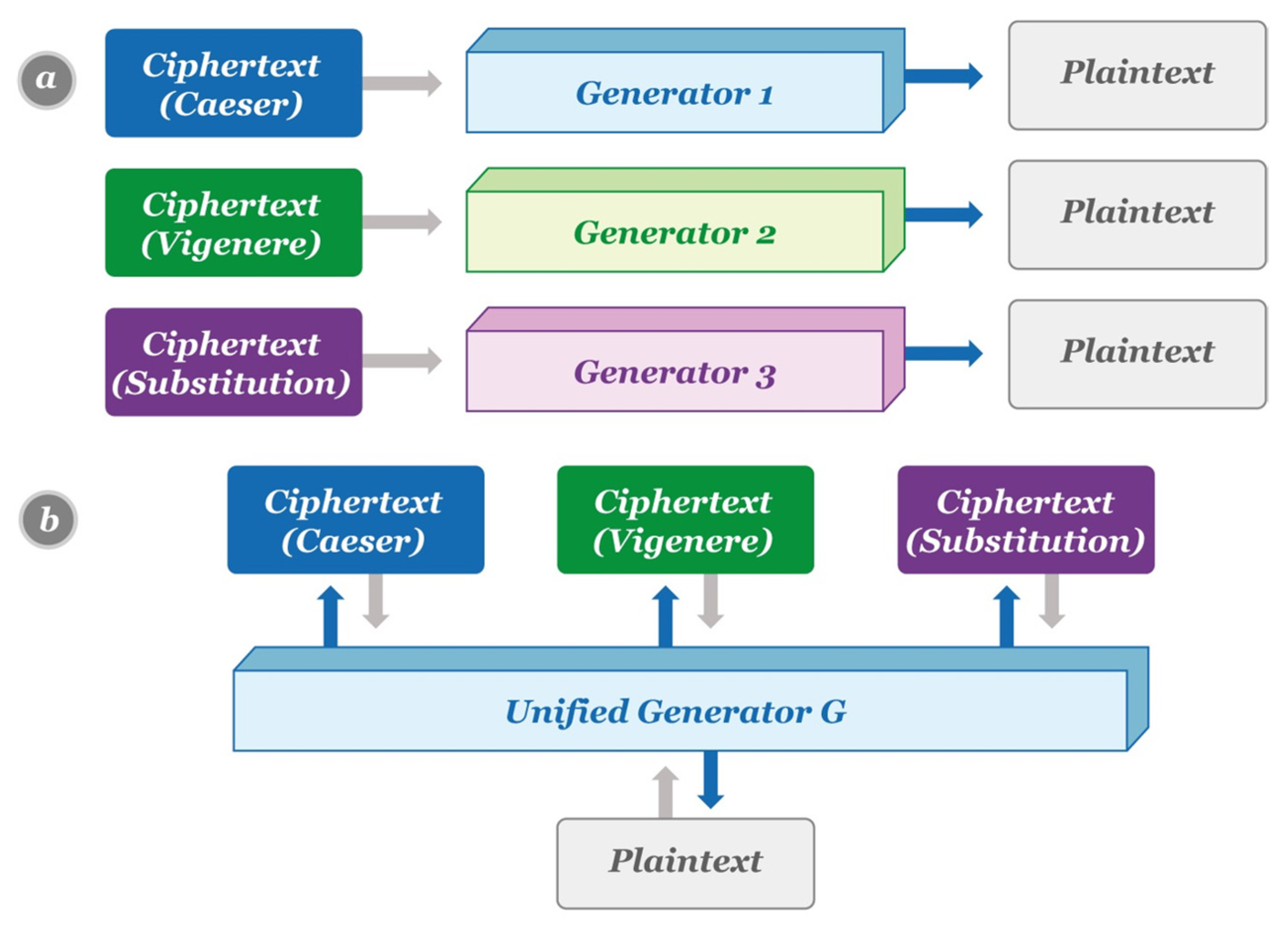
3. Overview of the Proposed UC−GAN Cryptanalysis Model
Network Architecture
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. System Equipment
4.3. Default Hyperparameter
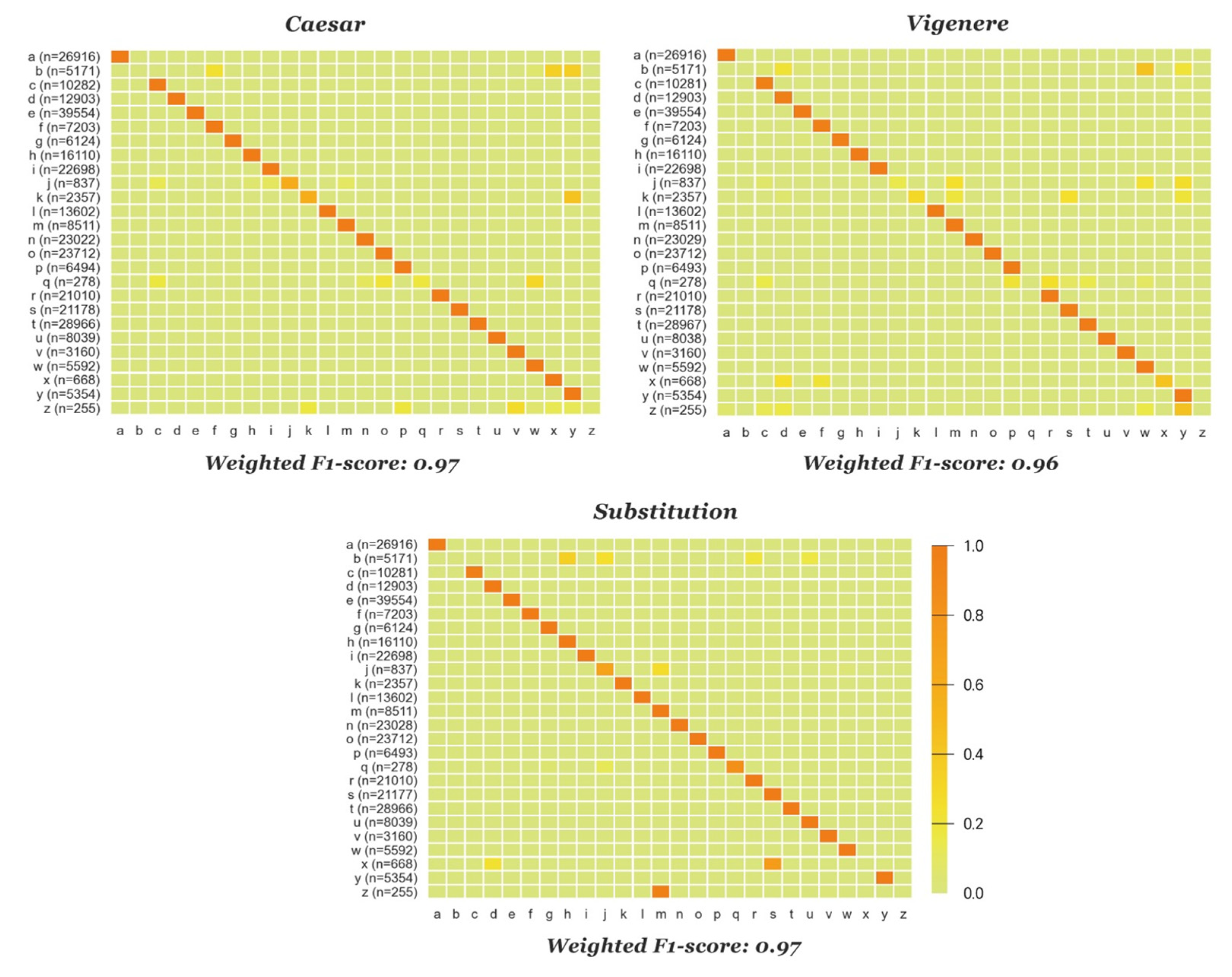
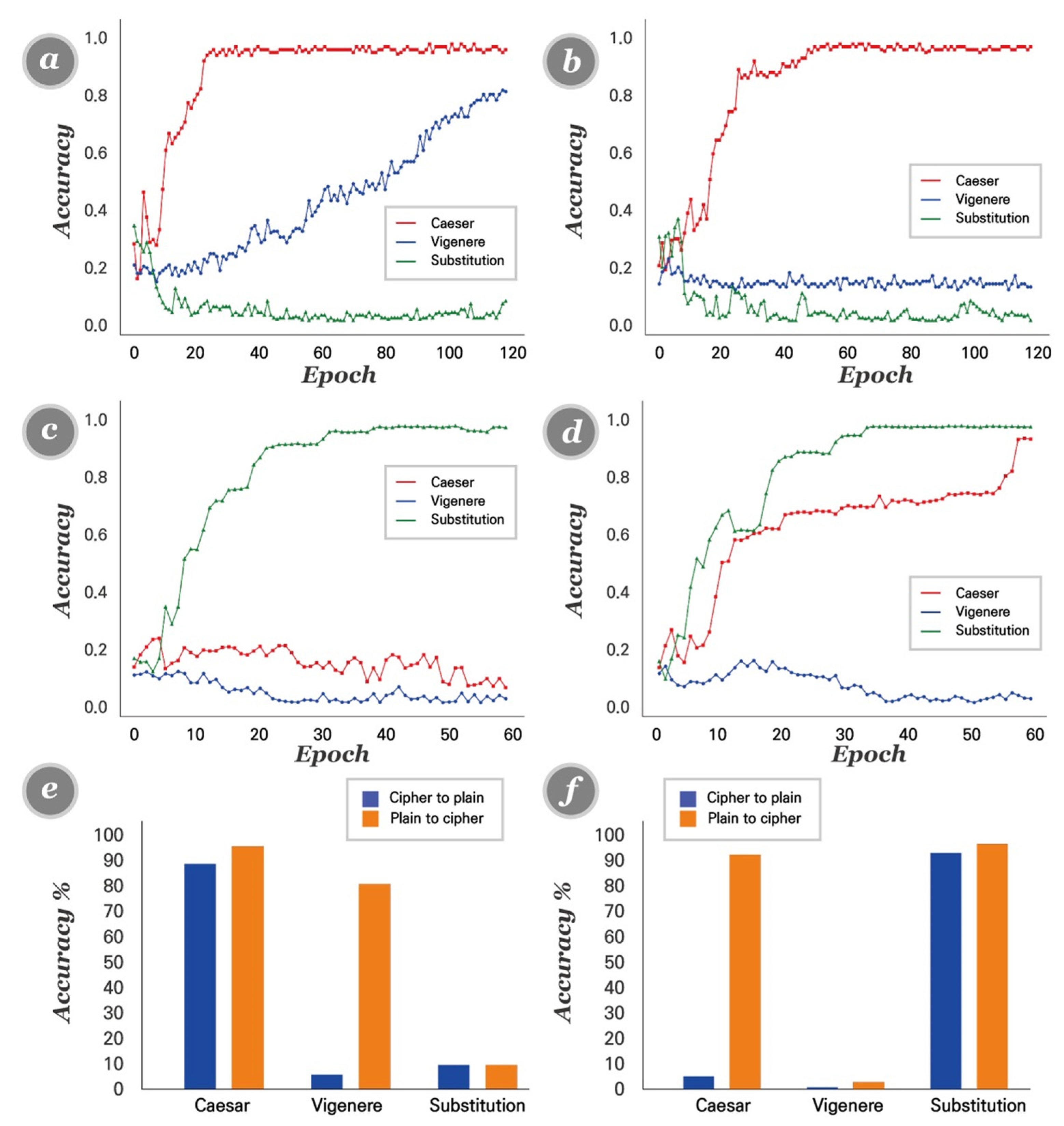
4.4. Cipher Emulation Results
4.5. Computational Complexity and Memory Usage
4.6. Model Result with Various Hyperparameters
4.7. Model Comparison
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Courtois, N.T.; Oprisanu, M.-B.; Schmeh, K. Linear cryptanalysis and block cipher design in East Germany in the 1970s. Cryptologia 2019, 43, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabi, M. A survey on symmetric and asymmetric cryptography algorithms in information security. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. (IJSRP) 2019, 9, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Gao, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Erkan, U.; Tang, X. Aea-NCS: An audio encryption algorithm based on a nested chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 165, 112770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wu, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Tang, X. EFR-CSTP: Encryption for face recognition based on the chaos and semi-tensor product theory. Inf. Sci. 2023, 621, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, E.; Kim, H.; Jeong, O.; Moon, I. A novel dynamic attack on classical ciphers using an attention-based LSTM encoder-decoder model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60960–60970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, E.; Kim, H.; Jeong, O.; Kim, N.; Moon, I. A deep bidirectional LSTM-GRU network model for automated ciphertext classification. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 3228–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.-H.; Jia, K.; Gao, S.; Lu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Ma, Y. PCANet: A simple deep learning baseline for image classification? IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 5017–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, E.; Jaferzadeh, K.; Shin, S.; Moon, I. Automated single cardiomyocyte characterization by nucleus extraction from dynamic holographic images using a fully convolutional neural network. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 1501–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomicheva, M.; Sun, S.; Yankovskaya, L.; Blain, F.; Guzmán, F.; Fishel, M.; Aletras, N.; Chaudhary, V.; Specia, L. Unsupervised quality estimation for neural machine translation. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2020, 8, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichotedumrong, W.; Kiya, H. A gan-based image transformation scheme for privacy-preserving deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 28th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Virtual, 18–22 January 2021; pp. 745–749. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, B. Multi-scale adversarial network for underwater image restoration. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 110, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Falco, G.; Viswanathan, A.; Caldera, C.; Shrobe, H. A master attack methodology for an AI-based automated attack planner for smart cities. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48360–48373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.S.; Premchand, P. A Review on Combined Attacks on Security Systems. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 4562, 16252–16278. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Gou, C.; Duan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, F.-Y. Generative adversarial networks: Introduction and outlook. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hwang, U.; Yoo, J.; Yoon, S. How generative adversarial networks and their variants work: An overview. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2019, 52, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdizadehaghdam, S.; Panahi, A.; Krim, H. Sparse generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ding, W.; Sadasivam, R.; Cui, X.; Chen, P. His-GAN: A histogram-based GAN model to improve data generation quality. Neural Netw. 2019, 119, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y. Seqgan: Sequence generative adversarial nets with policy gradient. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Xu, D.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Sebe, N.; Yan, Y. Cycle in cycle generative adversarial networks for keypoint-guided image generation. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 2052–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Pan, Y. Generative adversarial networks: A survey toward private and secure applications. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, I.; Li, B.M.; Osama, M.; Kaiser, L. Unsupervised cipher cracking using discrete gans. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.04883. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Choo, J. Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8789–8797. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.; Xie, X.; Guo, M. Learning graph representation with generative adversarial nets. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2019, 33, 3090–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmotaal, H.; Abdou, A.A.; Omar, A.F.; El-Sebaity, D.M.; Abdelazeem, K. Pix2pix conditional generative adversarial networks for scheimpflug camera color-coded corneal tomography image generation. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welander, P.; Karlsson, S.; Eklund, A. Generative adversarial networks for image-to-image translation on multi-contrast mr images-a comparison of cyclegan and unit. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07777. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Gong, S.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, L. A brief review on cycle generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 7th IIAE International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Image Processing (ICISIP), Taiwan, 5–9 September 2019; pp. 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, T.; Kameoka, H.; Tanaka, K.; Hojo, N. Stargan-vc2: Rethinking conditional methods for stargan-based voice conversion. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.12279. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Uh, Y.; Yoo, J.; Ha, J.-W. Stargan v2: Diverse image synthesis for multiple domains. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8188–8197. [Google Scholar]
- Abd, A.J.; Al-Janabi, S. Classification and identification of classical cipher type using artificial neural networks. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 14, 3549–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Kim, K. Recent advances of neural attacks against block ciphers. In Proceedings of the 2020 Symposium on Cryptography and Information Security (SCIS 2020), Kochi, Japan, 28–31 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gohr, A. Improving attacks on round-reduced speck32/64 using deep learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Cryptology–CRYPTO 2019: 39th Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 18–22 August 2019; pp. 150–179. [Google Scholar]
- Baksi, A.; Baksi, A. Machine learning-assisted differential distinguishers for lightweight ciphers. In Classical and Physical Security of Symmetric Key Cryptographic Algorithms; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 141–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Tan, F.; Qin, Z.; Cao, M.; Choo, K.-K.R.; Qin, Z. DeepKeyGen: A deep learning-based stream cipher generator for medical image encryption and decryption. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 4915–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, K.; Kukreja, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, K.K. Towards deep learning for efficient image encryption. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of theAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Li, Q.; Xie, H.; Lau, R.Y.; Wang, Z.; Paul Smolley, S. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2794–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- CrypTool Portal:Cryptography for everybody. Available online: https://www.cryptool.org/en/ (accessed on 2 September 2022).







| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| 𝔼[x] | Expectation |
| E(x) | Embedding |
| Concatenated embedding and target | |
| L1 norm (mean absolute error) | |
| G | Generator |
| D | Discriminator |
| c | Target domain label |
| c′ | Original domain label |
| Gradient |
| Method | Objectives | Data | Basic Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gomez et al. [23] | Cipher cracking | Shift and Vigenere ciphers | CycleGAN |
| Baek et al. [33] | AI-based attacks review | Block ciphers | Dense, CNN |
| Gohr et al. [34] | Ciphertext distinguisher | Lightweight ciphers (Speck32/64) | Resnet |
| Baksi et al. [35] | Ciphertext distinguisher | Lightweight ciphers (Gimli, Ascon, Knot, and Chaskey) | MLP, CNN, LSTM |
| Sirichotedumrong et al. [10] | Image transformation scheme | CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100 | GAN |
| Ding et al. [36] | Private key generation | Medical images (Stream cipher) | GAN |
| Panwar et al. [37] | End-to-end image encryption survey | - | GAN, Diffusion, CNN |
| Plaintext | Encrypted Sentence | Encryption Method/Key |
|---|---|---|
| eelementaryschoolodequindrewhich hasbeenattendedthisyearbyfourofth ekowalskichildrenincloudingchristine | hhohphqwdubvfkrrorghtxlqguhzklfkkdvehhqd wwhqghgwklvbhduebirxuriwk hnrzdovnlfkloguhqlqforxglqjfkulvwlqh | Caesar/3 shift to the right |
| hiqkpiszdvdyfltuosiktyntgvjckmh nkexhhisgwxjtgiizkmxehewhbjtauskzkipu zeqynmhnlpixhrntfptagmsmflwovxnth | Vigenere/defg | |
| ttstdtfzqknleiggsgrtjxofrktvioeiiqlwttfqzztfr trziolntqkwnygxkgyzitagv qslaoeiosrktfofesgxrofueikolzoft | Substitution/ qwertyuiopasdfghjkzxcvbnm |
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Cori7-7700 |
| GPU | GTX 1080Ti |
| Language | Python |
| Memory | 16 GB |
| System type | 64-bit operating system |
| OS type | Window 10/64 |
| Encryption Method | Original Plaintext | Target Ciphertext | Generated Ciphertext |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caeser | medicalpiratesannuallyyouwillcomeu pwithafrighteningtotalthatswhythef datheamericanmedicalassociationa | phglfdosludwhvdqqxdoobbrxzloofrphx szlwkdiuljkwhqlqjwrwdowkdwvzkbw khigdwkhdphulfdqphglfdodvvrfldwlrqd | phglfdosludwhvdqqxdooxxrxzloofrphxs zlwkdiuljkwhqlqjwrwdowkdwvzkxwkh igdwkhdphulfdqphglfdodvvrfldwlrqd |
| Vigenere | medicalpiratesannuallyyouwillco meupwithafrighteningtotalthatswhyt hefdatheamericanmedicalassociationa | piiofeqvlvfzhwftqyfrocduxanrogtshyu clxmgivnmkxjtlrlzrxfrwlfzvamewljl geynherkumhgqqjjlgfrdwxufmfzlssg | piiofeqvlvfzhwftqyfrosduxanrogtshyucl xmgivnmkxjtlrlzrxfrwlfzvamew ljlgeynherkumhgqqjjlgfrdwxufmfzlssg |
| Substitution | medicalpiratesannuallyyouwillcom eupwithafrighteningtotalthatswhyt hefdatheamericanmedicalassociationa | dtroeqshokqztlqffxqssnngxvosse gdtxhvoziqykouiztfofuzgzqsziqzlvinz ityrqzitqdtkoeqfdtroeqsqllgeoqzogfq | dtroeqshokqztlqffxqssnngxvosseg dtxhvoziqykouiztfofuzgzqsziqzlvinz ityrqzitqdtkoeqfdtroeqsqllgeoqzogfq |
| Encryption Method | Original Ciphertext | Target Plaintext | Generated Plaintext |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caeser | gdxjkwhuplvvvxvdqdqqylhwkwrpufrq udgzdoovrqrigufrqudgzdoodqgpuvqhoo nhqqhgbzdoowkhpduuldjhzlooehtxlhwo | daughtermisssusanannviethtomrco nradwallsonofdrconradwallandmrsn ellkennedywallthemarriagewillbequietl | daughtermisssusanannviethtomrcon radwallsonofdrconradwallandmrsn ellkennedywallthemarriagewillyequietl |
| Vigenere | rtzykesjsvtjkmroqxtzkiukujjiwmttwljbh xjxdrrgqelkuwfcdwfzkvnromsms sxylfnrlxdzkitrgqftzexgoqtywxtussxy | opushandprodhimintotheperfectionth eveteranmanagersawasathrillingposs ibilitytheoldmanwasalmosttooposs | opushandprodhimintotheperfectio nthepeteranmanagersawasathrillingpo ssiyilitytheoldmanwasalmosttooposs |
| Substitution | hktltfztrzgzitzgvfeqxfeossqlzfou izqlviqzolightrvosswtzityoklzlzthofg wzqofofuqigdtkxsteiqkztkygkzitzg | presentedtothetowncauncillast nightaswhatishopedwillbethefirstste pinobtainingahomerulecharterfortheto | Presentedtothetowncouncillastnightaswh atishopedwillpethefirststepinoptaininga homerulecharterfortheto |
| Parameter | Default Setting | Experiment 1 | Experiment 2 | Experiment 3 | Experiment 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning rate (lr) | 1.8 × 10−4 | 1.8 × 10−4 | 1.8 × 10−4 | 1.8 × 10−4 | 1.8 × 10−4 |
| Batch size (bs) | 32 | 8 | 128 | 32 | 32 |
| Embedding space and | 256 | 256 | 256 | 128 | 512 |
| Lambda for classification loss function () | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Lambda for reconstruction function () | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Emulation Method | Target | Network Model Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pix2Pix | CipherGAN | UC−GAN | ||
| Single cipher To Plain | Caesar to Plain | 99.96 | 99.53 | 99.40 |
| Vigenere to Plain | 99.84 | 99.79 | 98.33 | |
| Substitution to Plain | 99.84 | 99.45 | 98.71 | |
| Plain to Single cipher | Plain to Caesar | 99.95 | 99.44 | 98.37 |
| Plain to Vigenere | 99.84 | 99.79 | 97.72 | |
| Plain to Substitution | 99.84 | 99.45 | 99.82 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, H.; Moon, I. Automated Classical Cipher Emulation Attacks via Unified Unsupervised Generative Adversarial Networks. Cryptography 2023, 7, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7030035
Park S, Kim H, Moon I. Automated Classical Cipher Emulation Attacks via Unified Unsupervised Generative Adversarial Networks. Cryptography. 2023; 7(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7030035
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seonghwan, Hyunil Kim, and Inkyu Moon. 2023. "Automated Classical Cipher Emulation Attacks via Unified Unsupervised Generative Adversarial Networks" Cryptography 7, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7030035
APA StylePark, S., Kim, H., & Moon, I. (2023). Automated Classical Cipher Emulation Attacks via Unified Unsupervised Generative Adversarial Networks. Cryptography, 7(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7030035






