Inferring Bivariate Polynomials for Homomorphic Encryption Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Our Results
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Structure of the Paper
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Notations
2.2. Modular Knapsack Problems
2.3. Lattice Reduction: A Tool for Solving Modular Knapsacks
Lattice Reduction-Based Algorithms for Solving (Modular) Knapsacks
| Algorithm 1: Algorithm SV. |
|
| Algorithm 2: Howgrave-Joux Algorithm for Solving Modular Knapsacks. |
|
3. A New Look at Homomorphic Encryption
3.1. Constructing Polynomials Based on Homomorphic Operations
3.2. Defining the Problem
- Bob chooses a polynomial ();
- Alice chooses two numbers () and sends them to Bob;
- Bob computes using the values received from Alice, then sends the result to Alice;
- Given r, Alice attempts to infer P from r;
- If Alice is not successful, then she repeats steps 2 and 3 until she accumulates enough data to guess P.
4. Interpolating Bivariate Polynomials
- Case 1:
- When a is larger than all of P’s coefficients and the number of pairs (n) is equal to , the algorithm always outputs the correct polynomial.
- Case 2:
- When a is less than all of P’s coefficients and the number of pairs (n) is equal to , the algorithm outputs a polynomial (P), although not the correct polynomial.
- Case 3:
- When n is less than , it is possible that some of the values (see Algorithm 3) become negative; thus, the algorithm returns ⊥, since it is clear that the computed polynomial is not correct.
| Algorithm 3: Tries to compute a polynomial P such that . |
 |
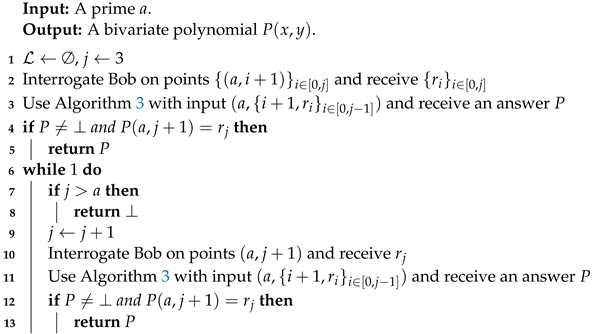
| Algorithm 4: Probes Bob until it finds the correct P. |
 |
5. Lattice-Based Approaches for Reconstructing Bivariate Polynomials
| Algorithm 5: Tries to compute a polynomial P such that . |
 |
6. Implementation
6.1. Performance Analysis
6.2. Recommendations
7. Conclusions
Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dertouzos, M.L.; Rivest, R.L.; Adleman, L. On Data Banks and Privacy Homomorphisms. In Foundations of Secure Computation; Academia Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978; pp. 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Rivest, R.L.; Shamir, A.; Adleman, L. A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 1978, 21, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, C. A Fully Homomorphic Encryption Scheme. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk, M.; Gentry, C.; Halevi, S.; Vaikuntanathan, V. Fully Homomorphic Encryption over the Integers. In Proceedings of the EUROCRYPT’10; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6110, pp. 24–43. [Google Scholar]
- Brakerski, Z.; Gentry, C.; Vaikuntanathan, V. Fully Homomorphic Encryption without Bootstrapping. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Paper 2011/277. 2011. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2011/277.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Fan, J.; Vercauteren, F. Somewhat Practical Fully Homomorphic Encryption. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Paper 2012/144. 2012. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2012/144.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Brakerski, Z. Fully Homomorphic Encryption without Modulus Switching from Classical GapSVP. In Proceedings of the CRYPTO’12; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7417, pp. 868–886. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, J.W.; Lauter, K.E.; Loftus, J.; Naehrig, M. Improved Security for a Ring-Based Fully Homomorphic Encryption Scheme. In Proceedings of the IMACC’13; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 8308, pp. 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, C.; Sahai, A.; Waters, B. Homomorphic Encryption from Learning with Errors: Conceptually-Simpler, Asymptotically-Faster, Attribute-Based. In Proceedings of the CRYPTO’13; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 8042, pp. 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Brakerski, Z.; Vaikuntanathan, V. Lattice-Based FHE as Secure as PKE. In Proceedings of the ITCS’14; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Carpov, S.; Chillotti, I.; Gama, N.; Georgieva, M.; Izabachene, M. TFHE: Fast Fully Homomorphic Encryption Library. 2016. Available online: https://tfhe.github.io/tfhe (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Cheon, J.H.; Kim, A.; Kim, M.; Song, Y.S. Homomorphic Encryption for Arithmetic of Approximate Numbers. In Proceedings of the ASIACRYPT’17; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 10624, pp. 409–437. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Micciancio, D. On the Security of Homomorphic Encryption on Approximate Numbers. In Proceedings of the EUROCRYPT’21; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 12696, pp. 648–677. [Google Scholar]
- A Curated List of Amazing Homomorphic Encryption Libraries, Software and Resources. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/jonaschn/awesome-he (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Williams, E.A. Driven by Privacy, Homomorphic Encryption Is Changing the Way We Do Business. 2021. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2021/05/19/driven-by-privacy-homomorphic-encryption-is-changing-the-way-we-do-business/?sh=60d688004cbf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Jackson, A. 20 Use Cases of Homomorphic Encryption Every CISO Must Know. 2023. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/20-use-cases-homomorphic-encryption-every-ciso-must-know-jackson-/ (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Bos, J.W.; Lauter, K.; Naehrig, M. Private Predictive Analysis on Encrypted Medical Data. J. Biomed. Inform. 2014, 50, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Xu, C.; Lu, R. PPDP: An Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Disease Prediction Scheme in Cloud-Based e-Healthcare System. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 79, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjal, K.; Bhatia, R. A Systematic Review of Homomorphic Encryption and its Contributions in Healthcare Industry. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayday, E. Cryptographic Solutions for Genomic Privacy. In Proceedings of the FC 2016; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9604, pp. 328–341. [Google Scholar]
- Graepel, T.; Lauter, K.; Naehrig, M. ML Confidential: Machine Learning on Encrypted Data. In Proceedings of the ICISC 2012; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7839, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Cheon, J.H.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, K. Privacy-Preserving Computations of Predictive Medical Models with Minimax Approximation and Non-Adjacent Form. In Proceedings of the FC 2017; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 10323, pp. 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Marcolla, C.; Sucasas, V.; Manzano, M.; Bassoli, R.; Fitzek, F.H.; Aaraj, N. Survey on Fully Homomorphic Encryption, Theory, and Applications. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 1572–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derler, D.; Ramacher, S.; Slamanig, D. Homomorphic Proxy Re-Authenticators and Applications to Verifiable Multi-User Data Aggregation. In Proceedings of the FC 2017; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 10322, pp. 124–142. [Google Scholar]
- Diallo, M.H.; August, M.; Hallman, R.; Kline, M.; Au, H.; Beach, V. CallForFire: A Mission-Critical Cloud-Based Application Built Using the Nomad Framework. In Proceedings of the FC 2016; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9604, pp. 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Doröz, Y.; Çetin, G.S.; Sunar, B. On-the-fly Homomorphic Batching/Unbatching. In Proceedings of the FC 2016; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9604, pp. 288–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid, D.; Kincaid, D.R.; Cheney, E.W. Numerical Analysis: Mathematics of Scientific Computing; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias, J.C.; Odlyzko, A.M. Solving Low-Density Subset Sum Problems. J. ACM 1985, 32, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coster, M.J.; Joux, A.; LaMacchia, B.A.; Odlyzko, A.M.; Schnorr, C.P.; Stern, J. Improved Low-Density Subset Sum Algorithms. Comput. Complex. 1992, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howgrave-Graham, N.; Joux, A. New Generic Algorithms for Hard Knapsacks. In Proceedings of the EUROCRYPT’10; Gilbert, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 235–256. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.; Coron, J.S.; Joux, A. Improved Generic Algorithms for Hard Knapsacks. In Proceedings of the EUROCRYPT’11; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 364–385. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Stehlé, D. An LLL Algorithm with Quadratic Complexity. SIAM J. Comput. 2009, 39, 874–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, P.; Espitau, T.; Fouque, P.A. Towards Faster Polynomial-Time Lattice Reduction. In Proceedings of the CRYPTO’21; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 12826, pp. 760–790. [Google Scholar]
- Koy, H.; Schnorr, C.P. Segment LLL-Reduction of Lattice Bases. In Proceedings of the Cryptography and Lattices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Schnorr, C.P. Fast LLL-type lattice reduction. Inf. Comput. 2006, 204, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Stern, J. Adapting Density Attacks to Low-Weight Knapsacks. In Proceedings of the ASIACRYPT; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3788, pp. 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Micchelli, C.A. Algebraic Aspects of Interpolation. In Proceedings of Symposia in Applied Mathematics; AMS: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 36, pp. 81–102. [Google Scholar]
- Saniee, K. A Simple Expression for Multivariate Lagrange Interpolation. SIAM Undergrad. Res. Online 2008, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garey, M.R.; Johnson, D.S. Computers and Intractability; A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness; W. H. Freeman & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Martello, S.; Toth, P. Knapsack Problems: Algorithms and Computer Implementations; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Merkle, R.; Hellman, M. Hiding Information and Signatures in Trapdoor Knapsacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1978, 24, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccache, D.; Stern, J. A New Public-Key Cryptosystem. In Proceedings of the EUROCRYPT ’97; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 1233, pp. 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Salomaa, A. A Deterministic Algorithm for Modular Knapsack Problems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 1991, 88, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, Y.M.; Joux, A.; Stern, J. The Cryptanalysis of a New Public-Key Cryptosystem Based on Modular Knapsacks. In Proceedings of the CRYPTO’91; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; Volume 576, pp. 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein, J.; Pipher, J.; Silverman, J. An Introduction to Mathematical Cryptography; Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Anzala-Yamajako, A. Review of Algorithmic Cryptanalysis, by Antoine Joux. SIGACT News 2012, 43, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenstra, A.; Lenstra, H.; Lovász, L. Factoring polynomials with rational coefficients. Math. Ann. 1982, 261, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeppel, R.; Shamir, A. A T = O(2n/2), S = O(2n/4) Algorithm for Certain NP-Complete Problems. SIAM J. Comput. 1981, 10, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnorr, C. A Hierarchy of Polynomial Time Lattice Basis Reduction Algorithms. Theor. Comput. Sci. 1987, 53, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- fpLLL. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/fplll/fplll (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Kirchner, P.; Espitau, T.; Fouque, P.A. Fast Reduction of Algebraic Lattices over Cyclotomic Fields. In Proceedings of the CRYPTO’20; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 12171, pp. 155–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, K.; Heninger, N. Fast Practical Lattice Reduction through Iterated Compression. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Paper 2023/237. 2023. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2023/237 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Aho, A.; Sloane, N. Some Doubly Exponential Sequences. Fibonacci Q. 1973, 11, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Sequence A007018. Available online: https://oeis.org/A007018 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, H.R.P.; Bailey, D.H.; Kutler, P. A Polynomial Time, Numerically Stable Integer Relation Algorithm; NASA Technical Report RNR–91–032. 1991. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20020052399 (accessed on 25 May 2023).


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maimuţ, D.; Teşeleanu, G. Inferring Bivariate Polynomials for Homomorphic Encryption Application. Cryptography 2023, 7, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7020031
Maimuţ D, Teşeleanu G. Inferring Bivariate Polynomials for Homomorphic Encryption Application. Cryptography. 2023; 7(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaimuţ, Diana, and George Teşeleanu. 2023. "Inferring Bivariate Polynomials for Homomorphic Encryption Application" Cryptography 7, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7020031
APA StyleMaimuţ, D., & Teşeleanu, G. (2023). Inferring Bivariate Polynomials for Homomorphic Encryption Application. Cryptography, 7(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7020031






