A Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of Optic Nerve Axon Regeneration Lipidomes Using the Xenopus laevis as a Model System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MetaboAnalyst 6.0
2.2. LipidOne 2.3
2.3. Metabolomics Workbench
2.4. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Data Integrity Check and Filtration
3.2. Data Normalization
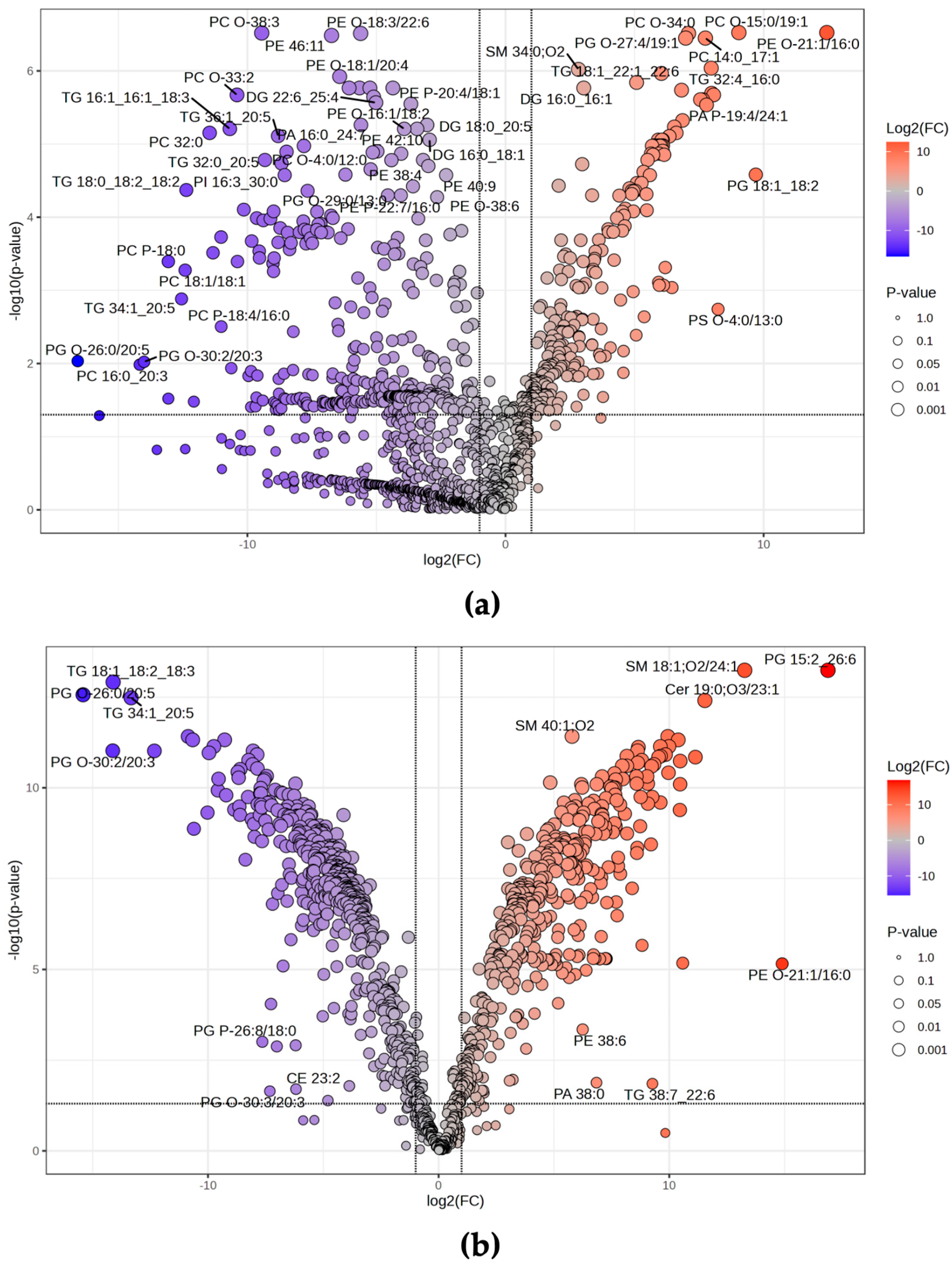
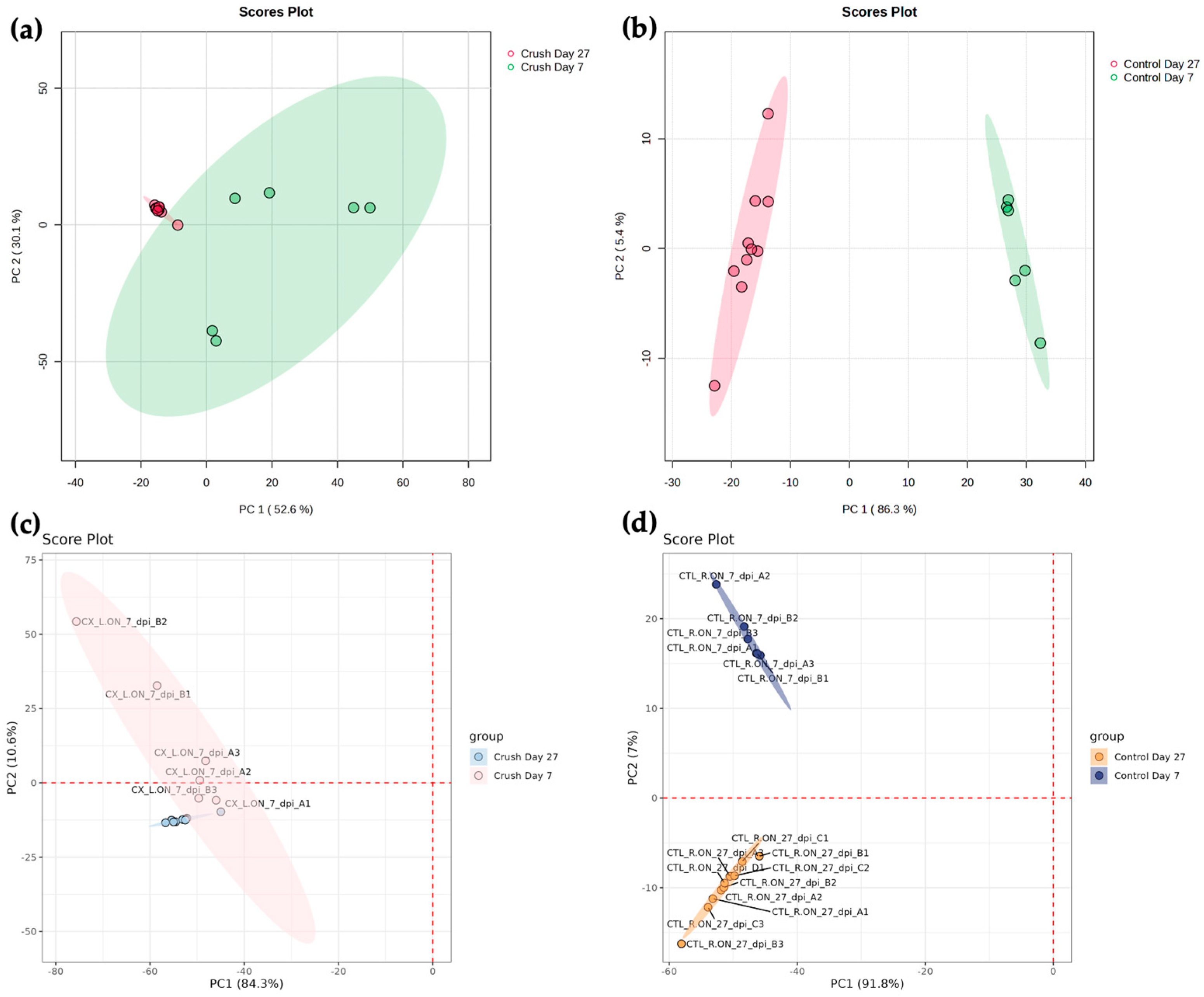
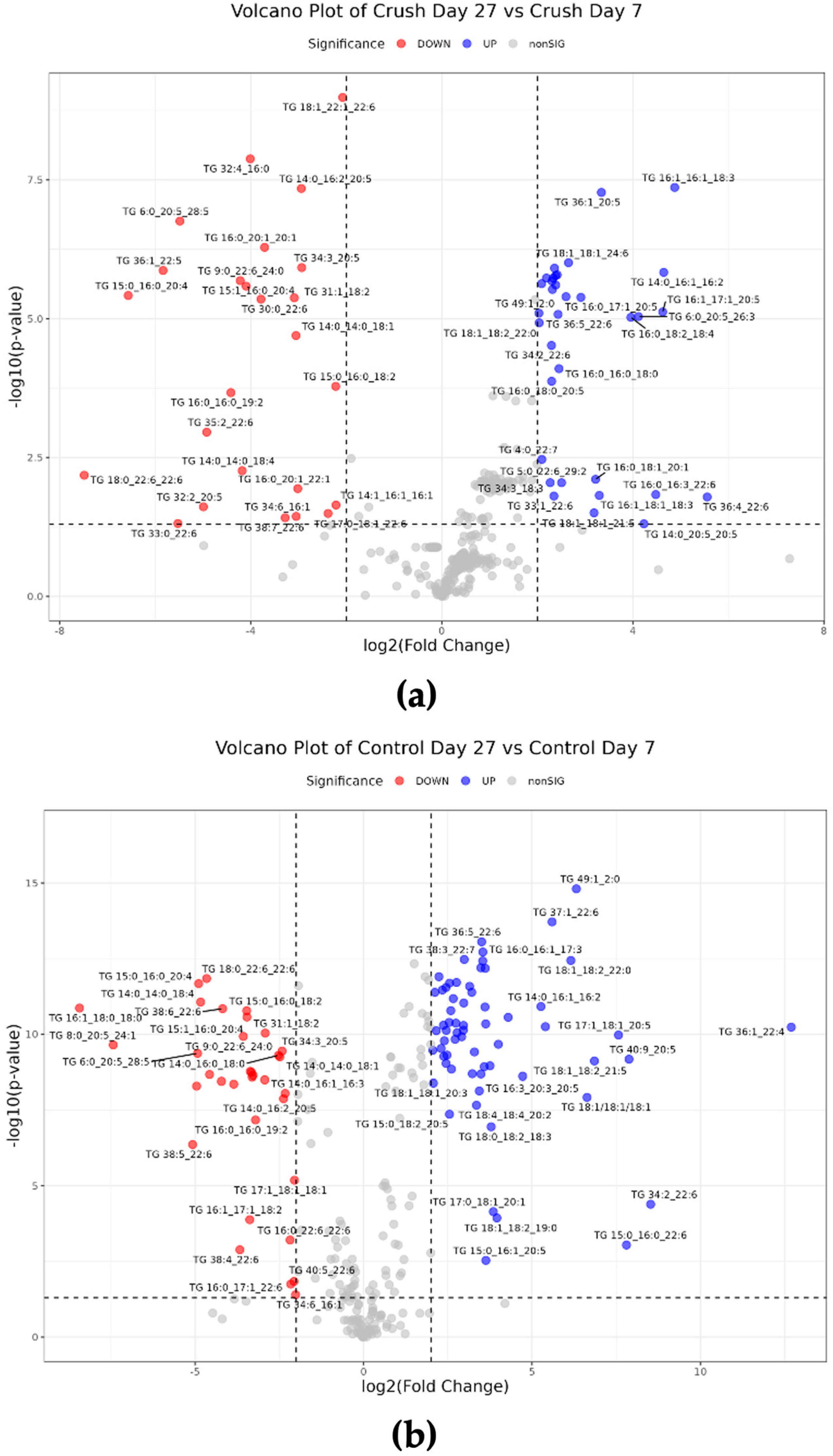
3.3. Statistical Analysis

4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| PL | Phospholipid |
| LC/MS | Liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| FAQs | Frequently asked questions |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| DRCC | Data Repository and Coordinating Center |
| .txt | Tab-delimited text file |
| .csv | Comma-separated values file |
| LSI | Lipidomic Standards Initiative |
| RefMet | A Reference List of Metabolite Names |
| ng/mL | Nanograms per milliliter |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbors |
| LoD | Limit of detection |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| QC | Quality control |
| IQR | Interquantile range |
| MAD | Median absolute deviation |
| ONC | Optic nerve crush |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance |
| R2 | Proportion of variance explained by each principal component |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PG | Phosphatidylglycerol |
| CE | Cholesteryl ester |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| HexCer | Hexosylceramide |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| Cer | Ceramide |
| LSM | Lysosphingomyelin |
| DG | Diacylglycerol |
| LPC | Lysophosphatidylcholine |
| PA | Phosphatidic acid |
| PC-O | Phosphatidylcholine with an alkyl ether-linked fatty acid |
| PC-P | Phosphatidylcholine with an alkenyl ether-linked fatty acid |
| PE-O | Phosphatidylethanolamine with an alkyl ether-linked fatty acid |
| PE-P | Phosphatidylethanolamine with an alkenyl ether-linked fatty acid |
References
- Alves, M.A.; Lamichhane, S.; Dickens, A.; McGlinchey, A.; Ribeiro, H.C.; Sen, P.; Wei, F.; Hyotylainen, T.; Oresic, M. Systems biology approaches to study lipidomes in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, A. Understanding the physiological mechanisms and therapeutic targets of diseases: Lipidomics strategies. Life Sci. 2025, 363, 123411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Han, X. Lipidomics: Techniques, Applications, and Outcomes Related to Biomedical Sciences. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, K.H. Plasma membrane expansion: A neuron’s Herculean task. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, S.D.; Neag, E.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Glycerophospholipid Analysis of Optic Nerve Regeneration Models Indicate Potential Membrane Order Changes Associated with the Lipidomic Shifts. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 39, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabanzadeh, A.P.; Charish, J.; Tassew, N.G.; Farhani, N.; Feng, J.; Qin, X.; Sugita, S.; Mothe, A.J.; Walchli, T.; Koeberle, P.D.; et al. Cholesterol synthesis inhibition promotes axonal regeneration in the injured central nervous system. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 150, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Lu, N.; Siniossoglou, S.; Yao, Z.; Liu, K. Rewiring Neuronal Glycerolipid Metabolism Determines the Extent of Axon Regeneration. Neuron 2020, 105, 276–292.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zullig, T.; Trotzmuller, M.; Kofeler, H.C. Lipidomics from sample preparation to data analysis: A primer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, R.; Ishikawa, M. Precise and global identification of phospholipid molecular species by an Orbitrap mass spectrometer and automated search engine Lipid Search. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4229–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Satoh, A.; Mori, Y.; Uchino, H.; Okahashi, N.; Yamada, Y.; Tada, I.; Bonini, P.; et al. A lipidome atlas in MS-DIAL 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Wolk, M.; Jukes, G.; Mendivelso Espinosa, K.; Ahrends, R.; Aimo, L.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Andrews, S.; Andrews, R.; Bridge, A.; et al. Guiding the choice of informatics software and tools for lipidomics research applications. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiaghi, A.; Ferrario, M.; Masseroli, M. Analysis of metabolomic data: Tools, current strategies and future challenges for omics data integration. Brief Bioinform. 2017, 18, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W652–W660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hui, F.; Xu, L.; Viau, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; MacDonald, P.E.; Wishart, D.S.; Li, S.; et al. MetaboAnalyst 6.0: Towards a unified platform for metabolomics data processing, analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W398–W406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackstadt, A.J.; Hess, A.M. Filtering for increased power for microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabed, H.B.R.; Mancini, D.F.; Buratta, S.; Calzoni, E.; Giacomo, D.D.; Emiliani, C.; Martino, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Pellegrino, R.M. LipidOne 2.0: A Web Tool for Discovering Biological Meanings Hidden in Lipidomic Data. Curr. Protoc. 2024, 4, e70009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.M.; Giulietti, M.; Alabed, H.B.R.; Buratta, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Piva, F.; Emiliani, C. LipidOne: User-friendly lipidomic data analysis tool for a deeper interpretation in a systems biology scenario. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1767–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neag, E.; Moceri, I.; Harvey, F.; Udvadia, A.J.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Watson, F.L. Mass spectrometry dataset of LC-MS lipidomics analysis of Xenopus laevis optic nerve. Data Brief 2023, 49, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Azam, K.; Vadivelu, I.; Burant, C.; Edison, A.; Fiehn, O.; Higashi, R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Metabolomics Workbench: An international repository for metabolomics data and metadata, metabolite standards, protocols, tutorials and training, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D463–D470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebisch, G.; Vizcaino, J.A.; Kofeler, H.; Trotzmuller, M.; Griffiths, W.J.; Schmitz, G.; Spener, F.; Wakelam, M.J.O. Shorthand notation for lipid structures derived from mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, P.; Levy, B.D. Resolvins and protectins: Mediating solutions to inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surma, M.A.; Gerl, M.J.; Herzog, R.; Helppi, J.; Simons, K.; Klose, C. Mouse lipidomics reveals inherent flexibility of a mammalian lipidome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klose, C.; Surma, M.A.; Gerl, M.J.; Meyenhofer, F.; Shevchenko, A.; Simons, K. Flexibility of a eukaryotic lipidome--insights from yeast lipidomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Explicit Criterion | |
|---|---|
| Data upload | Does the tool support multiple file types and dataset formats? |
| Data processing | Does the tool allow user-defined filters for feature exclusion? |
| Missing value replacement | Does the tool allow replacement of missing values? |
| Data normalization | Does the tool allow user-defined normalization? |
| Data transformation | Does the tool allow user-defined data transformation? |
| Data scaling | Does the tool allow user-defined data scaling? |
| Class-level statistics | Can statistical tests be run directly on lipid classes? |
| Building block-level statistics | Does the tool support analysis of lipid building blocks (such as chain length, unsaturation, odd/even chains)? |
| Univariate statistics | Does the tool support commonly used univariate analyses? |
| Multivariate statistics | Does the tool support commonly used multivariate analyses? |
| Multiple testing correction | Is multiple testing correction (such as FDR) available and documented? |
| Reproducibility support | Is a script or command history available for users to inspect and replicate the exact processing and statistical analyses performed by the tool? |
| Visualization options | Are there customizable options for images generated? Are there options to edit image file type, resolution, and size? |
| Export formats | Can results be exported in .csv format? Can datasets be downloaded after changes are made in the tool (such as normalization or scaling)? |
| MetaboAnalyst 6.0 | LipidOne 2.3 | |
|---|---|---|
| Data upload | Accepts .txt, .csv., compressed, mzTab, XLSX from Metabolon, or directly from Metabolomics Workbench; accepts samples in rows or columns | Accepts .txt and .csv files; accepts samples in columns |
| Data processing | Low-quality, low-variance, and low-repeatability filters are user-defined | None |
| Missing value replacement | User-defined | Automatic replacement of zero/missing values with 1/10th of lowest value of variable |
| Data normalization | User-defined and recalibrated after every feature, sample, and/or group exclusion | Normalization by median automatically performed for PCA |
| Data transformation | User-defined and recalibrated after every feature, sample, and/or group exclusion | None |
| Data scaling | User-defined and recalibrated after every feature, sample, and/or group exclusion | Autoscaling or Pareto scaling options available for select analyses |
| Class-level statistics | None | Univariate and multivariate analyses |
| Building block-level statistics | None | Univariate analyses |
| Univariate statistics | Fold change, t-test, volcano plot, ANOVA, correlation heatmaps, pattern search, correlation networks | Bar graph, t-test, ANOVA, correlation, volcano plot, biomarker discovery, box plot, ROC analysis, sequence analysis |
| Multivariate statistics | PCA, PLS-DA, sPLS-DA, orthoPLS-DA | PCA, PLS-DA, sPLS-DA, orthoPLS-DA, ROC analysis |
| Multiple testing correction | FDR correction | FDR correction only for select analyses (unavailable for volcano plot) |
| Reproducibility support | R Command history available | None |
| Visualization options | Customization for group colors, significance colors, and feature labels; User-defined image file type, resolution, and size for download | Customization for group colors; only .png file can be downloaded and without specification of resolution or size |
| Export formats | Results can be downloaded in .csv format; datasets can be exported in .csv format | Only select results can be downloaded in .csv format; no option to download datasets |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volante, V.S.; Watson, F.L.; Bhattacharya, S.K. A Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of Optic Nerve Axon Regeneration Lipidomes Using the Xenopus laevis as a Model System. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8050110
Volante VS, Watson FL, Bhattacharya SK. A Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of Optic Nerve Axon Regeneration Lipidomes Using the Xenopus laevis as a Model System. Methods and Protocols. 2025; 8(5):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8050110
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolante, Vernon S., Fiona L. Watson, and Sanjoy K. Bhattacharya. 2025. "A Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of Optic Nerve Axon Regeneration Lipidomes Using the Xenopus laevis as a Model System" Methods and Protocols 8, no. 5: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8050110
APA StyleVolante, V. S., Watson, F. L., & Bhattacharya, S. K. (2025). A Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of Optic Nerve Axon Regeneration Lipidomes Using the Xenopus laevis as a Model System. Methods and Protocols, 8(5), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8050110






