Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of 12 Months of Combined Exercise Training during Hemodialysis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—Study Protocol of the Dialysis Training Therapy (DiaTT) Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design and Methods
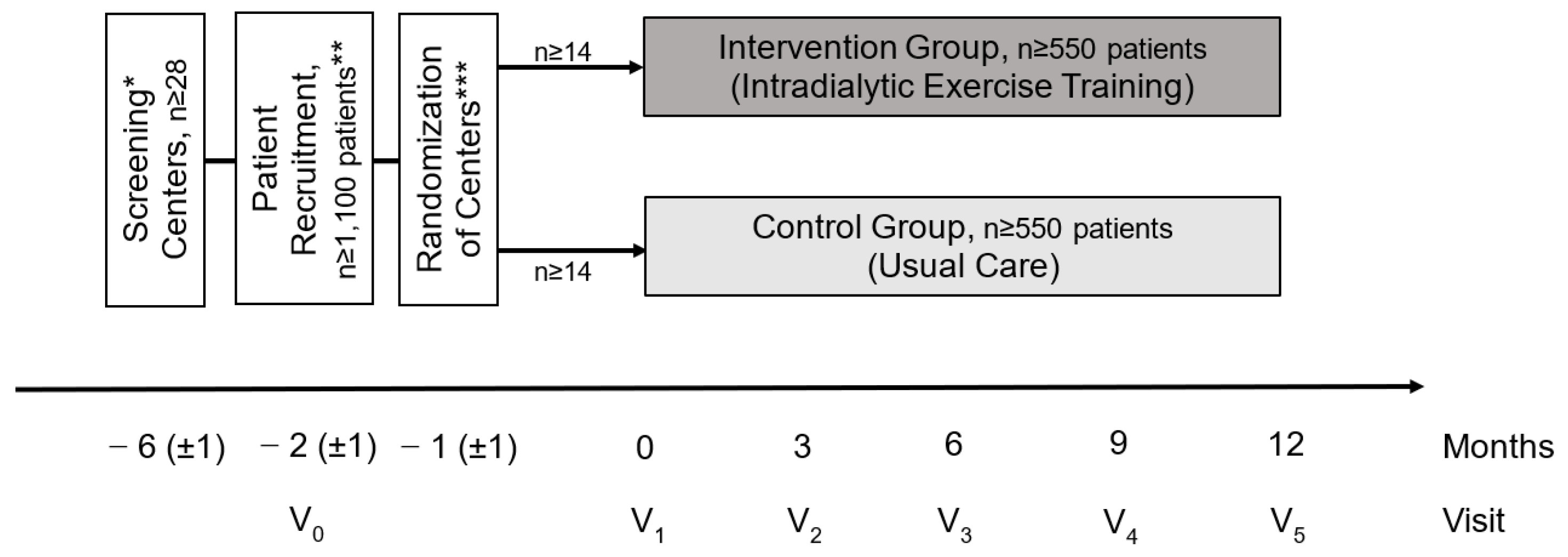
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Center Eligibility
2.3. Cluster Randomization of Centers
2.4. Study Population
3. Procedure
3.1. Intervention and Usual Care Groups
3.1.1. Usual Care
3.1.2. Intervention Group (IG)
Aerobic Training
Resistance Training
Health Literacy Counseling
3.2. Visit Schedule
3.3. Risk-Benefit Assessment
3.4. Adverse Events and Serious Adverse Events
3.5. Study Staff
3.6. Data Handling and Data Management
3.7. Statistical Planning and Analysis
3.7.1. Sample Size Calculation
3.7.2. Definition of Populations Included in the Analysis
3.7.3. Primary Endpoint
3.7.4. Secondary Endpoints for Effectiveness
3.7.5. Health Economics
4. Expected Results/Discussion
4.1. Intervention Program
4.2. Clinical Endpoints
4.3. Safety
4.4. Health Economics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Registration Details
References
- Zelle, D.M.; Klaassen, G.; van Adrichem, E.; Bakker, S.J.; Corpeleijn, E.; Navis, G. Physical inactivity: A risk factor and target for intervention in renal care. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Peel, N.M.; Krosch, M.; Hubbard, R.E. Frailty and chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 68, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jassal, S.V.; Karaboyas, A.; Comment, L.A.; Bieber, B.A.; Morgenstern, H.; Sen, A.; Gillespie, B.W.; De Sequera, P.; Marshall, M.R.; Fukuhara, S.; et al. Functional Dependence and Mortality in the International Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2016, 67, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tentori, F.; Elder, S.J.; Thumma, J.; Pisoni, R.L.; Bommer, J.; Fissell, R.B.; Fukuhara, S.; Jadoul, M.; Keen, M.L.; Saran, R.; et al. Physical exercise among participants in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS): Correlates and associated outcomes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2010, 25, 3050–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Helal, L.; Dipp, T.; Soares, D.; Soldatelli, Â.; Mills, A.L.; Paz, C.; Tenório, M.C.C.; Motta, M.T.; Barcellos, F.C.; et al. Intradialytic training in patients with end-stage renal disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials assessing the effects of five different training interventions. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, M.J.; Bennett, P.N.; Fraser, S.F.; Warmington, S.A. Exercise interventions for improving objective physical function in patients with end-stage kidney disease on dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F856–F872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.N.; Fraser, S.; Barnard, R.; Haines, T.; Ockerby, C.; Street, M.; Wang, W.C.; Daly, R. Effects of an intradialytic resistance training programme on physical function: A prospective stepped-wedge randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2016, 31, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogataj, Š.; Pajek, M.; Pajek, J.; Buturović Ponikvar, J.; Paravlic, A. Exercise-Based Interventions in Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anding, K.; Bar, T.; Trojniak-Hennig, J.; Kuchinke, S.; Krause, R.; Rost, J.M.; Halle, M. A structured exercise programme during haemodialysis for patients with chronic kidney disease: Clinical benefit and long-term adherence. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, T. Let’s programme exercise during haemodialysis (intradialytic exercise) into the care plan for patients, regardless of age. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1357–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, D.S.; Graham-Brown, M.P.; Young, H.M.; Greenwood, S.A.; Burton, J.O. There is nothing more deceptive than an obvious fact: More evidence for the prescription of exercise during haemodialysis (intradialytic exercise) is still required. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howden, E.J.; Coombes, J.S.; Isbel, N.M. The role of exercise training in the management of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, C.M.; Whellan, D.J.; Lee, K.L.; Keteyian, S.J.; Cooper, L.S.; Ellis, S.J.; Leifer, E.S.; Kraus, W.E.; Kitzman, D.W.; Blumenthal, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of exercise training in patients with chronic heart failure: HF-ACTION randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, R.R.; Bolin, P.; Brancati, F.L.; Bray, G.A.; Clark, J.M.; Coday, M.; Crow, R.S.; Curtis, J.M.; Egan, C.M.; Espeland, M.A.; et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Segura-Ortí, E.; Martínez-Olmos, F.J. Test-retest reliability and minimal detectable change scores for sit-to-stand-to-sit tests, the six-minute walk test, the one-leg heel-rise test, and handgrip strength in people undergoing hemodialysis. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, S.; Hoebel, J. Gesundheitskompetenz von Erwachsenen in Deutschland. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2015, 58, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrig, G.; Polidori, M.C.; Rascher, K.; Schaller, M.; Benzing, T.; von Gersdorff, G. Burden of multimorbidity and outcome in ambulatory geriatric hemodialysis patients: Report from the QiN registry in Germany. Z. Fur Gerontol. Und Geriatr. 2018, 51, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.M.; Gerhardus, A.; von Gersdorff, G.D.; Baldamus, C.A.; Schaller, M.; Barth, C.; Scheibler, F. Preferences of patients undergoing hemodialysis—Results from a questionnaire-based study with 4518 patients. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2015, 9, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurella Tamura, M.; Covinsky, K.E.; Chertow, G.M.; Yaffe, K.; Landefeld, C.S.; McCulloch, C.E. Functional Status of Elderly Adults before and after Initiation of Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, J. Frailty and mortality among patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, K.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, J. Intradialytic exercise in hemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ou, S. Efficacy and safety of intradialytic exercise in haemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e020633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, Y.C.; Yeh, M.L.; Liu, Y.M. Effects of intradialytic exercise on the physical function, depression and quality of life for haemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Clin. Nurs. 2017, 26, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Shur, N.F.; Smith, A.C. “Exercise as medicine” in chronic kidney disease. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manfredini, F.; Mallamaci, F.; D’Arrigo, G.; Baggetta, R.; Bolignano, D.; Torino, C.; Lamberti, N.; Bertoli, S.; Ciurlino, D.; Rocca-Rey, L.; et al. Exercise in Patients on Dialysis: A Multicenter, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, N.A.; Williams, A.D.; Levinger, I.; Selig, S.; Howden, E.; Coombes, J.S.; Fassett, R.G. Exercise & Sports Science Australia (ESSA) position statement on exercise and chronic kidney disease. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2013, 16, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Young, H.M.L.; March, D.S.; Graham-Brown, M.P.M.; Jones, A.W.; Curtis, F.; Grantham, C.S.; Churchward, D.R.; Highton, P.; Smith, A.C.; Singh, S.J.; et al. Effects of intradialytic cycling exercise on exercise capacity, quality of life, physical function and cardiovascular measures in adult haemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2018, 33, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segura-Orti, E. Exercise in haemodyalisis patients: A literature systematic review. Nefrol. Publ. Off. Soc. Esp. Nefrol. 2010, 30, 236–246. [Google Scholar]
- Koufaki, P.; Mercer, T.H.; Naish, P.F. Effects of exercise training on aerobic and functional capacity of end-stage renal disease patients. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2002, 22, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; He, Q.; Yin, X.; He, Q.; Cao, S.; Ying, G. Effect of individualized exercise during maintenance haemodialysis on exercise capacity and health-related quality of life in patients with uraemia. J. Int. Med Res. 2014, 42, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.; Klarenbach, S.; Molzahn, A.; Lloyd, A.; Gabrys, I.; Haykowsky, M.; Tonelli, M. Randomised factorial mixed method pilot study of aerobic and resistance exercise in haemodialysis patients: DIALY-SIZE! BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiwe, S.; Jacobson, S.H. Exercise training in adults with CKD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2014, 64, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, C.; Schick-Makaroff, K.; MacRae, J.M.; Tan, M.; Thompson, S. The role of exercise in improving patient-reported outcomes in individuals on dialysis: A scoping review. Semin. Dial. 2019, 32, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Culler, S.D.; Kutner, N.G. Costs and effectiveness of cardiac rehabilitation for dialysis patients following coronary bypass. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Screening Visit 0 | Baseline Visit 1 | Visit 2 | Visit 3 | Visit 4 | Visit 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month (+/−2 weeks) | −2 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 |
| Informed consent | X | |||||
| Inclusion and exclusion criteria | X | |||||
| Randomization | X | |||||
| Physician’s confirmation | X | |||||
| Medical history | X | X | ||||
| Laboratory test (blood sampling) | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Medication | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Dialysis parameters | X | X | X | X | X | |
| SAE/AE | X | |||||
| Physical functioning tests | ||||||
| STS60 | X | X | X | X | X | |
| TUG | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 6MWT | X | X | X | X | X | |
| GST | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Ergometry # | X | X | ||||
| Weekly training sessions | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Health literacy questionnaire | ||||||
| HLS-EU-Q16 | X | X | ||||
| Quality of Life/ Frailty questionnaire | ||||||
| SF-36 | X | X | X | X | ||
| MPI | X | X | X | X | ||
| Health economics (costs) | ||||||
| Medication | X | X | ||||
| Hospitalisation | X | X | ||||
| Mode of transportation | X | X | ||||
| Therapeutic remedies | X | X | ||||
| Medical assistance tools | X | X | ||||
| Nursing | X | X | ||||
| Sick leave from work-place | X | X | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Gersdorff, G.; von Korn, P.; Duvinage, A.; Ihorst, G.; Josef, A.; Kaufmann, M.; Baer, T.; Fellerhoff, T.; Fuhrmann, I.; Koesel, E.; et al. Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of 12 Months of Combined Exercise Training during Hemodialysis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—Study Protocol of the Dialysis Training Therapy (DiaTT) Trial. Methods Protoc. 2021, 4, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps4030060
von Gersdorff G, von Korn P, Duvinage A, Ihorst G, Josef A, Kaufmann M, Baer T, Fellerhoff T, Fuhrmann I, Koesel E, et al. Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of 12 Months of Combined Exercise Training during Hemodialysis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—Study Protocol of the Dialysis Training Therapy (DiaTT) Trial. Methods and Protocols. 2021; 4(3):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps4030060
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Gersdorff, Gero, Pia von Korn, André Duvinage, Gabriele Ihorst, Anika Josef, Margit Kaufmann, Thomas Baer, Tim Fellerhoff, Iris Fuhrmann, Elisa Koesel, and et al. 2021. "Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of 12 Months of Combined Exercise Training during Hemodialysis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—Study Protocol of the Dialysis Training Therapy (DiaTT) Trial" Methods and Protocols 4, no. 3: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps4030060
APA Stylevon Gersdorff, G., von Korn, P., Duvinage, A., Ihorst, G., Josef, A., Kaufmann, M., Baer, T., Fellerhoff, T., Fuhrmann, I., Koesel, E., Zeissler, S., Bobka, L., Heinrich, M., Schindler, A., Weber, R., Breuer, C., Meyer, A. M., Polidori, M. C., Dinges, S. M. T., ... Halle, M. (2021). Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of 12 Months of Combined Exercise Training during Hemodialysis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—Study Protocol of the Dialysis Training Therapy (DiaTT) Trial. Methods and Protocols, 4(3), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps4030060






