Preactivation Crosslinking—An Efficient Method for the Oriented Immobilization of Antibodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Buffers
2.3. Equipment
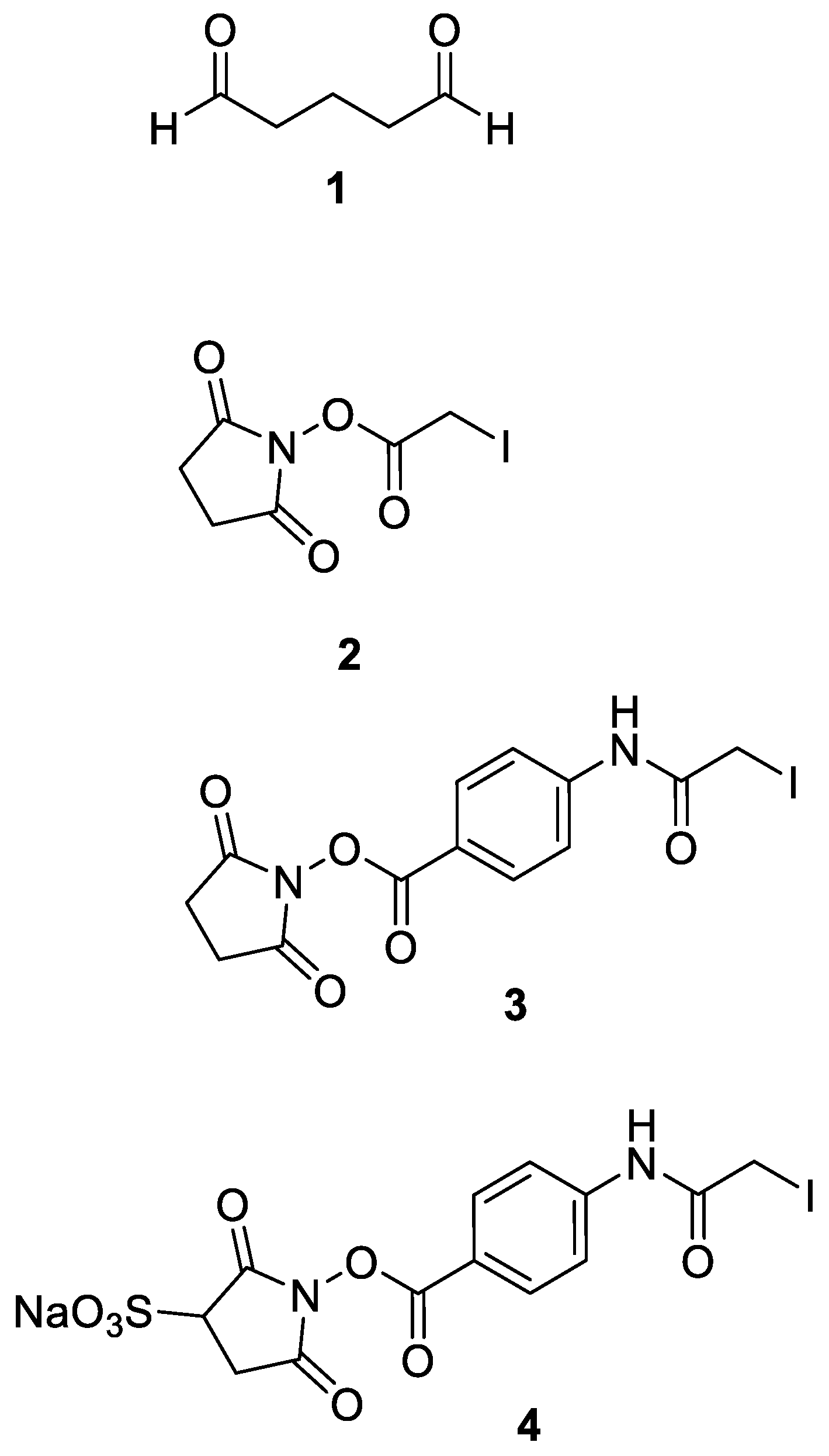
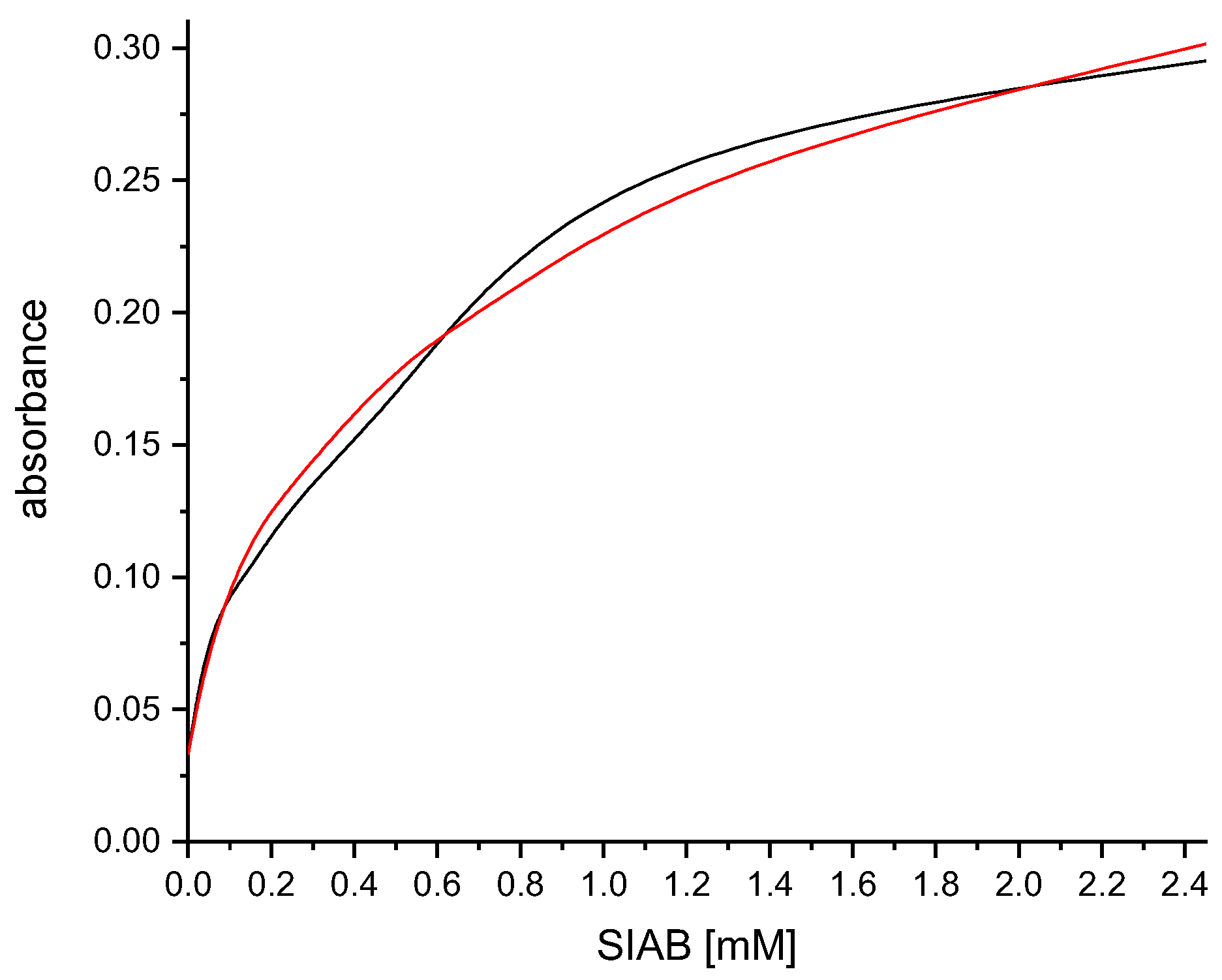
2.4. Crosslinking Protocol with SIAB or Sulfo-SIAB
2.5. Crosslinking Protocol with Glutaraldehyde
2.6. Comparison of Crosslinking Protocols
3. Results
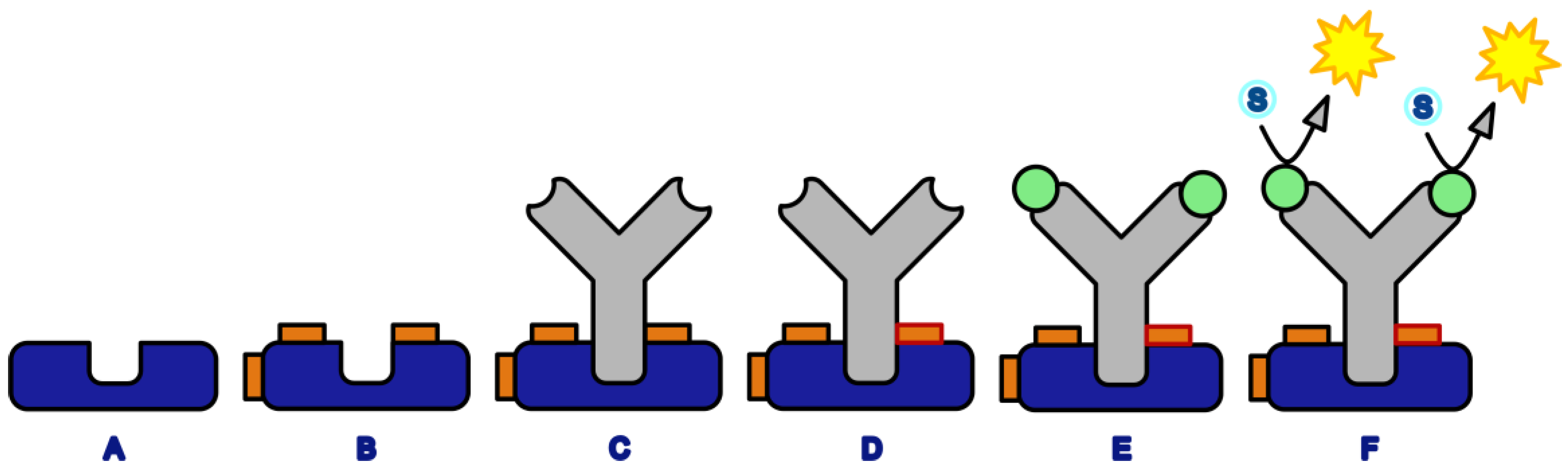
3.1. Crosslinking Assay Based on Protein G–Mouse IgG Interaction
3.2. Crosslinker Screening
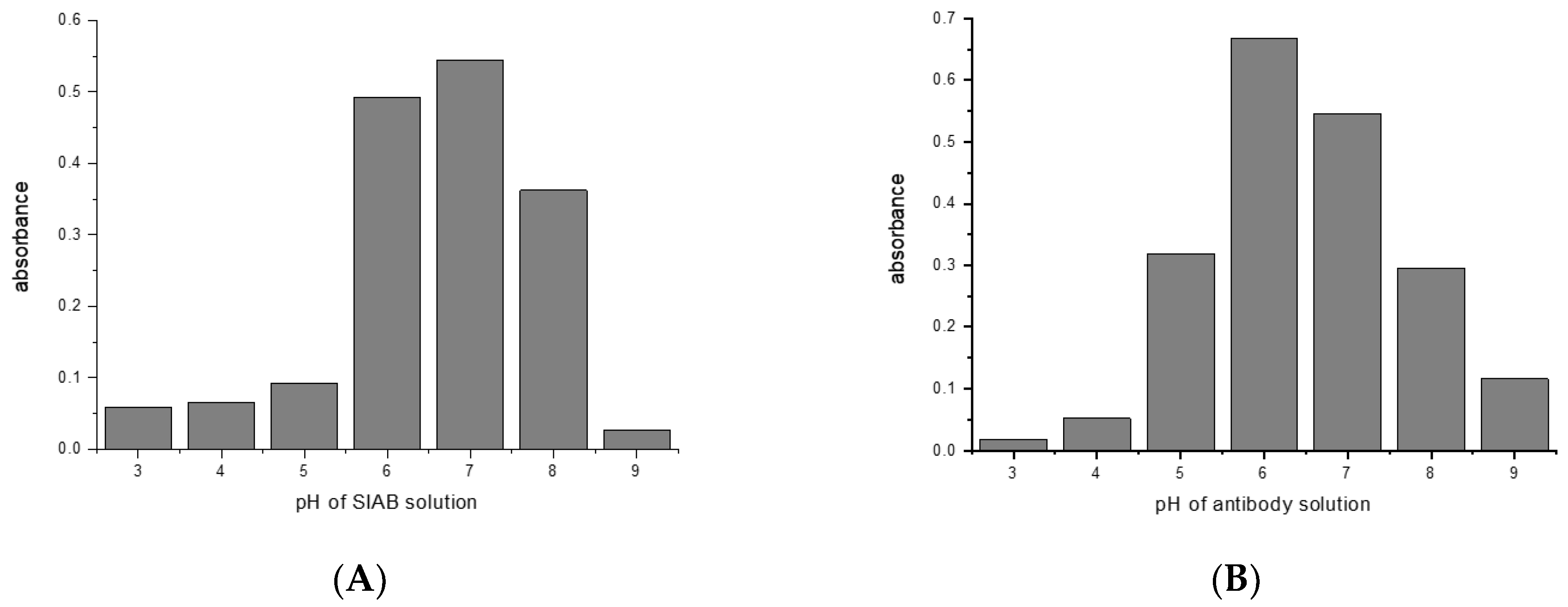
3.3. Influence of pH on the Crosslinking of Protein G with Murine IgG1
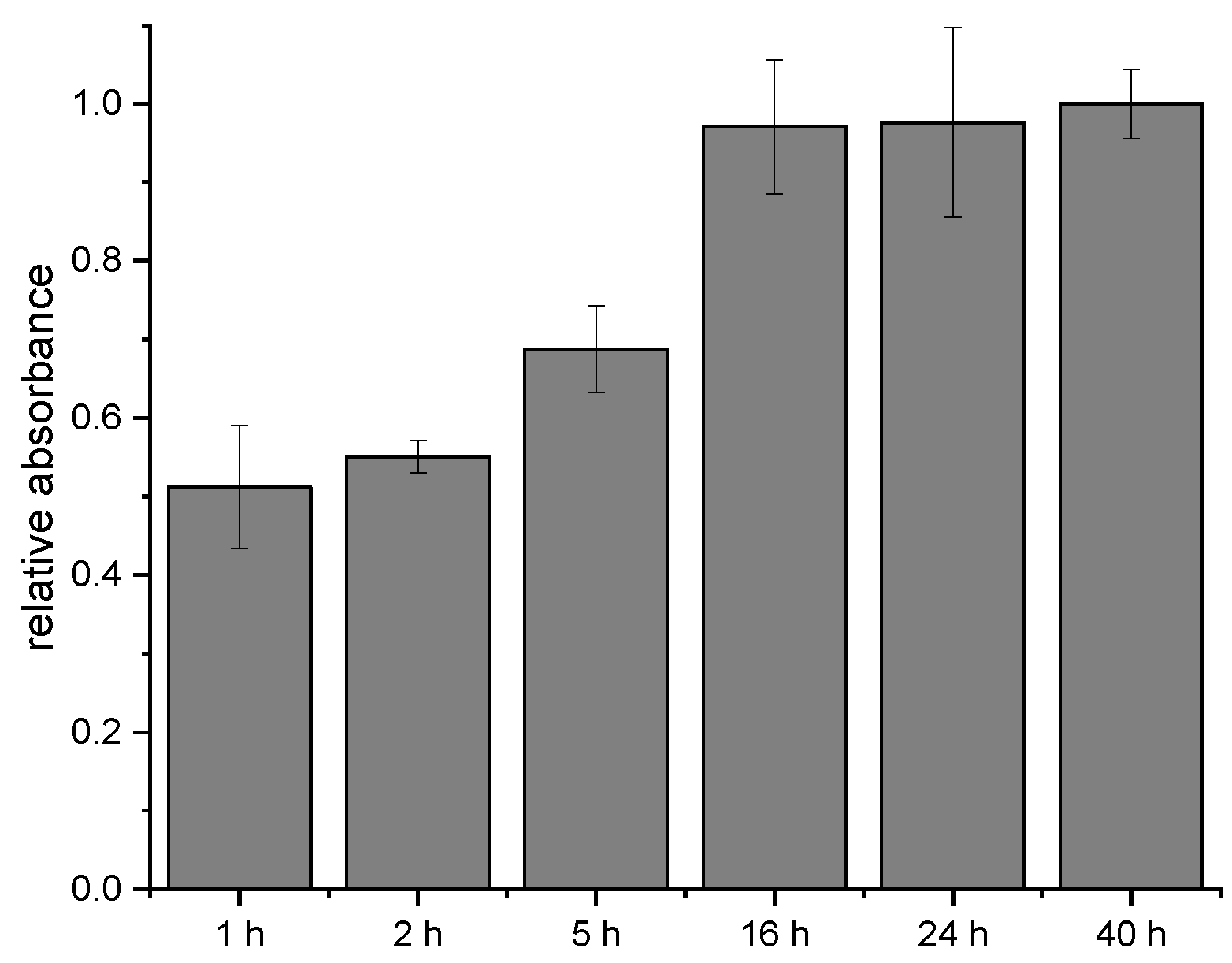
3.4. Incubation Time of SIAB-Activated Protein G with Mouse IgG1
3.5. Influence of Solvents on the Crosslinking Process
3.6. Crosslinking Yield of the Protein A/G IgG System
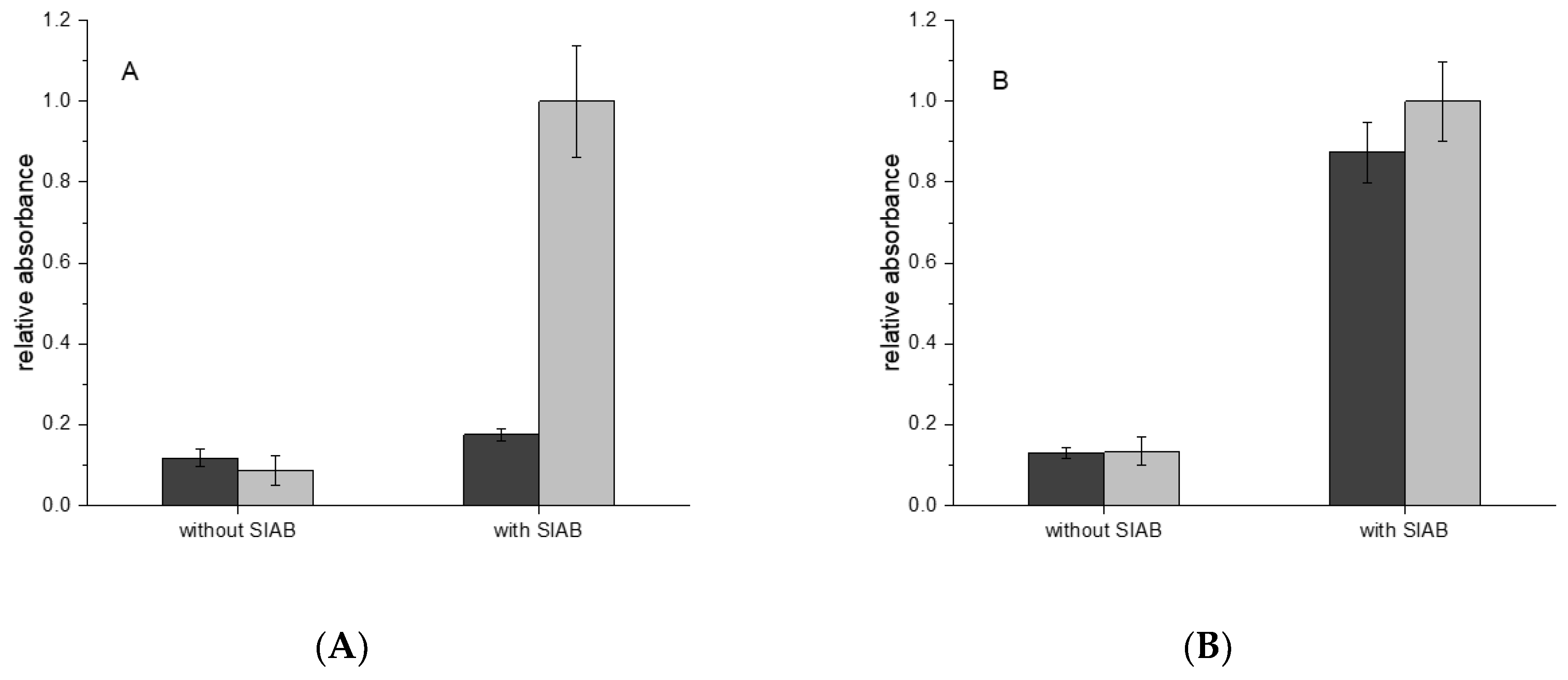
3.7. Comparison of the Efficiency of the Traditional and the Novel Immobilization Method
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raj, J.; Herzog, G.; Manning, M.; Volcke, C.; MacCraith, B.D.; Ballantyne, S.; Thompson, M.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Surface immobilisation of antibody on cyclic olefin copolymer for sandwich immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2654–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiening, M.; Niessner, R.; Weller, M.G. Microplate-based screening methods for the efficient development of sandwich immunoassays. Analyst 2005, 130, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.S.; Kim, N. Thiolated salmonella antibody immobilization onto the gold surface of piezoelectric quartz crystal. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Donner, B.; Edelstein, R.; Breslin, K.; Bhatia, S.K.; Ligler, F.S. Antibody immobilization using heterobifunctional crosslinkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1997, 12, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Shriverlake, L.C.; Prior, K.J.; Georger, J.H.; Calvert, J.M.; Bredehorst, R.; Ligler, F.S. Use of thiol-terminal silanes and heterobifunctional crosslinkers for immobilization of antibodies on silica surfaces. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 178, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danczyk, R.; Krieder, B.; North, A.; Webster, T.; HogenEsch, H.; Rundell, A. Comparison of antibody functionality using different immobilization methods. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 84, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaraviciute, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Site-directed antibody immobilization techniques for immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusnezow, W.; Jacob, A.; Walijew, A.; Diehl, F.; Hoheisel, J.D. Antibody microarrays: An evaluation of production parameters. Proteomics 2003, 3, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, P.; Wilson, D.S.; Do, D.; Tran, H.; Venkatasubbaiah, M.; Quincy, D.; Heidecker, B.; Poindexter, K.; Tolani, N.; Phelan, M.; et al. Optimizing antibody immobilization strategies for the construction of protein microarrays. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 312, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, A.; Wildling, L.; Kamruzzahan, A.S.M.; Rankl, C.; Wruss, J.; Hahn, C.D.; Holzl, M.; Zhu, R.; Kienberger, F.; Blaas, D.; et al. A new, simple method for linking of antibodies to atomic force microscopy tips. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubova, V.; Brynda, E.; Karasova, L.; Skvor, J.; Homola, J.; Dostalek, J.; Tobiska, P.; Rosicky, J. Detection of foodborne pathogens using surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 74, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K.; Dixit, C.K.; MacCraith, B.D.; O'Kennedy, R. Effect of antibody immobilization strategies on the analytical performance of a surface plasmon resonance-based immunoassay. Analyst 2011, 136, 4431–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.G. Immunochromatographic techniques—A critical review. Fresen. J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 366, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisnevitch, M.; Firer, M.A. The solid phase in affinity chromatography: Strategies for antibody attachment. J. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 2001, 49, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Popp, R.; Borchers, C.H. Affinity-mass spectrometric technologies for quantitative proteomics in biological fluids. Trac Trend Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.W.; Krone, J.R.; Bieber, A.L.; Williams, P. Mass-spectrometric immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, M.M.L.; Steen, K.W.; Hagen, L.; Slupphaug, G. Antibody cross-linking and target elution protocols used for immunoprecipitation significantly modulate signal-to noise ratio in downstream 2D-page analysis. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, M.; Mateo, C.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Preparation of inert magnetic nano-particles for the directed immobilization of antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Rusling, J.F.; Dixit, C.K. Site-selective orientated immobilization of antibodies and conjugates for immunodiagnostics development. Methods 2017, 116, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, K.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Control of protein immobilization: Coupling immobilization and site-directed mutagenesis to improve biocatalyst or biosensor performance. Enzyme Microb. Tech. 2011, 48, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Smyth, M.R.; OKennedy, R. Oriented immobilization of antibodies and its applications in immunoassays and immunosensors. Analyst 1996, 121, R29–R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.V.; Anderson, K.W.; Bachas, L.G. Oriented immobilization of proteins. Mikrochim. Acta 1998, 128, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Zhou, X.D.; Hobley, J.; Su, X.D. Comparative study of random and oriented antibody immobilization as measured by dual polarization interferometry and surface plasnnon resonance spectroscopy. Langmuir 2012, 28, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goding, J.W. Use of staphylococcal protein-a as an immunological reagent. J. Immunol. Methods 1978, 20, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, G.; Mandenius, C.F. Orientation and capturing of antibody affinity ligands: Applications to surface plasmon resonance biochips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 158, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, W.L.; Oshannessy, D.J. Site-specific immobilization of antibodies by their oligosaccharide moieties to new hydrazide derivatized solid supports. J. Immunol. Methods 1988, 112, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.W.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.W.; Yoon, J.W.; Cho, H.M.; Chung, B.H. Photoactivable antibody binding protein: Site-selective and covalent coupling of antibody. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanje, S.; Hober, S. In vivo biotinylation and incorporation of a photo-inducible unnatural amino acid to an antibody-binding domain improve site-specific labeling of antibodies. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessela, B.C.C.; Mateo, C.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Vian, A.; Garcia, J.L.; Rivas, G.; Alfonso, C.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. One-step purification, covalent immobilization, and additional stabilization of a thermophilic poly-his-tagged beta-galactosidase from Thermus sp strain T2 by using novel heterofunctional chelate-epoxy sepabeads. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, C.; Grazu, V.; Palomo, J.M.; Lopez-Gallego, F.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Guisan, J.M. Immobilization of enzymes on heterofunctional epoxy supports. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbosa, O.; Torres, R.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Heterofunctional supports in enzyme immobilization: From traditional immobilization protocols to opportunities in tuning enzyme properties. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2433–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Strategies for the one-step immobilization-purification of enzymes as industrial biocatalysts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Lacey, V.K.; Ren, H.Y.; Xu, J.; Burban, D.J.; Jennings, P.A.; Wang, L. Proximity-enabled protein crosslinking through genetically encoding haloalkane unnatural amino acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2190–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Ren, H.Y.; Hu, Y.; Coin, I.; Wei, J.; Cang, H.; Wang, L. Unnatural covalent bond formation inside and between proteins through proximity-enhanced reaction. FASEB J. 2014, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Ren, H.Y.; Hu, Y.S.; Coin, I.; Wei, J.; Cang, H.; Wang, L. Adding an unnatural covalent bond to proteins through proximity-enhanced bioreactivity (vol 10, pg 885, 2013). Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Ren, H.Y.; Hu, Y.S.; Coin, I.; Wei, J.; Cang, H.; Wang, L. Adding an unnatural covalent bond to proteins through proximity-enhanced bioreactivity. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cigler, M.; Muller, T.G.; Horn-Ghetko, D.; von Wrisberg, M.K.; Fottner, M.; Goody, R.S.; Itzen, A.; Muller, M.P.; Lang, K. Proximity-triggered covalent stabilization of low-affinity protein complexes in vitro and in vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15737–15741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Hoppmann, C.; Yang, B.; Wang, L. Using protein-confined proximity to determine chemical reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14832–14835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, J.L.; Kang, M.C.; Choi, S.; Cao, Y.; Wold, E.D.; Sun, S.B.; Smider, V.V.; Schultz, P.G.; Kim, C.H. A genetically encoded aza-michael acceptor for covalent cross-linking of protein-receptor complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8411–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.M.; Shao, S.D.; Schultz, P.G. Protein crosslinking by genetically encoded noncanonical amino acids with reactive aryl carbamate side chains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5096–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.M.; Li, J.; Luo, X.Z.; Schultz, P.G. Genetic incorporation of a reactive isothiocyanate group into proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10065–10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.F.; Tang, J.; Loredo, A.; Chen, Y.D.; Jung, S.Y.; Jain, A.; Gordon, A.; Xiao, H. Proximity-induced site-specific antibody conjugation. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3522–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jeong, J.; Lee, G.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, M.K. Covalent and oriented surface immobilization of antibody using photoactivatable antibody fc-binding protein expressed in escherichia coli. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9503–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klykov, O.; Weller, M.G. Quantification of n-hydroxysuccinimide and n-hydroxysulfosuccinimide by hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC). Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6443–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staros, J.V. N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide active esters: Bis(n-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) esters of two dicarboxylic acids are hydrophilic, membrane-impermeant, protein cross-linkers. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 3950–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkhof, S.; Sinz, A. Chances and pitfalls of chemical cross-linking with amine-reactive n-hydroxysuccinimide esters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, J.; Guo, X.C.; Kast, J. Identification of protein-protein interactions using in vivo cross-linking and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2004, 4, 3845–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 1–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Kyratzis, I. Covalent immobilization of proteins on carbon nanotubes using the cross-linker 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide - a critical assessment. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C.; Bertrand, M.J.; Waldron, K.C. Glutaraldehyde: Behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. Biotechniques 2004, 37, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Gallego, F.; Betancor, L.; Mateo, C.; Hidalgo, A.; Alonso-Morales, N.; Dellamora-Ortiz, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Enzyme stabilization by glutaraldehyde crosslinking of adsorbed proteins on aminated supports. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 119, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Glutaraldehyde in bio-catalysts design: A useful crosslinker and a versatile tool in enzyme immobilization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.M.; Schwaar, T.; Bienwald, F.; Weller, M.G. Predictable peptide conjugation ratios by activation of proteins with succinimidyl iodoacetate (SIA). Methods Protocols 2018, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonebay, A.; Timony, P.E. A new sulfo-SIAB synthesis. Synthetic Commun. 1988, 18, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrameas, S.; Ternynck, T. Cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry 1969, 6, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, F.M.; Knowles, J.R. Glutaraldehyde as a protein cross-linking reagent. J. Mol. Biol. 1968, 37, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Matsumaru, H.; Ooishi, A.; Feng, Y.W.; Odahara, T.; Suto, K.; Honda, S. Optimizing pH response of affinity between protein G and IgG Fc. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12373–12383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerstrom, B.; Bjorck, L. A physicochemical study of protein-g, a molecule with unique immunoglobulin-G-binding properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Langone, J.J. Applications of immobilized protein-A in immunochemical techniques. J. Immunol. Methods 1982, 55, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Instructions—DSS and BS3 crosslinkers. In User Guide 2018, MAN0011240, Pub. Part No. 2160418; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Rockford, IL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.S.; Lee, S.; Poulter, C.D. Regioselective covalent immobilization of recombinant antibody-binding proteins A, G, and L for construction of antibody arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8973–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebacher, J.; Mallick, P.; Zhang, N.; Eddes, J.S.; Aebersold, R.; Gelb, M.H. Protein cross-linking analysis using mass spectrometry, isotope-coded cross-linkers, and integrated computational data processing. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 2270–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinz, A. Chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometry to map three-dimensional protein structures and protein-protein interactions. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2006, 25, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinz, A.; Arlt, C.; Chorev, D.; Sharon, M. Chemical cross-linking and native mass spectrometry: A fruitful combination for structural biology. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 1193–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Crosslinker | Abbr. | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Formaldehyde [47] | FA | - |
| Disuccinimidyl tartrate [48] | DST | - |
| Tris(hydroxymethyl) phosphine | THP | - |
| 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide [49]/N-Hydroxysuccinimide | EDC/NHS | - |
| Bis(sulfosuccinimidyl)suberate [48] | BS3 | + |
| 1,3-Butadiendiepoxide | BDDE | + |
| Glutaraldehyde [50,51,52] | GA | ++ |
| Succinimidyl iodoacetate [53] | SIA | ++ |
| Succinimidyl (4-iodoacetyl)aminobenzoate [48] | SIAB | +++ |
| Sulfosuccinimidyl (4-iodoacetyl)aminobenzoate [48,54] | Sulfo-SIAB | +++ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schroeder, B.; Le Xuan, H.; Völzke, J.L.; Weller, M.G. Preactivation Crosslinking—An Efficient Method for the Oriented Immobilization of Antibodies. Methods Protoc. 2019, 2, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps2020035
Schroeder B, Le Xuan H, Völzke JL, Weller MG. Preactivation Crosslinking—An Efficient Method for the Oriented Immobilization of Antibodies. Methods and Protocols. 2019; 2(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps2020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchroeder, Barbara, Hoa Le Xuan, Jule L. Völzke, and Michael G. Weller. 2019. "Preactivation Crosslinking—An Efficient Method for the Oriented Immobilization of Antibodies" Methods and Protocols 2, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps2020035
APA StyleSchroeder, B., Le Xuan, H., Völzke, J. L., & Weller, M. G. (2019). Preactivation Crosslinking—An Efficient Method for the Oriented Immobilization of Antibodies. Methods and Protocols, 2(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps2020035






