High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation of Epigenetic Cytosine Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Resolution of Cytosine Analogs Using C18 Column
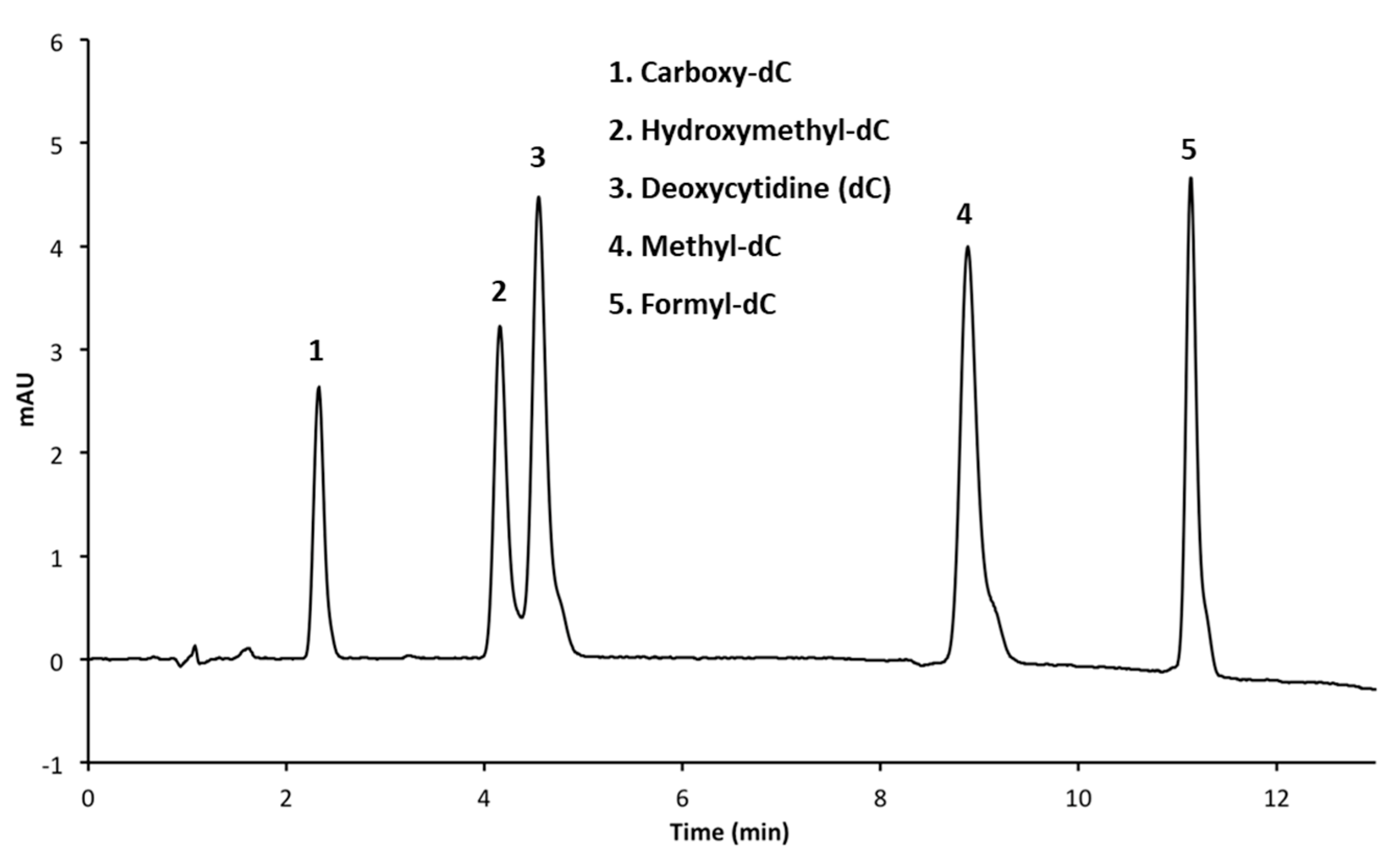
3.2. Resolution of Cytosine Analogs Using Phenyl Hexyl Column
3.2.1. Performing HPLC Runs at a pH of 4.0
3.2.2. Performing HPLC Analysis at a pH of 7.0
3.2.3. Adjusting Methanol Concentration to Improve Resolution
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munzel, M.; Globisch, D.; Carell, T. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, the sixth base of the genome. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 6460–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. The nuclear DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is present in Purkinje neurons and the brain. Science 2009, 324, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.C.; Dong, Q.; Chi, X.F.; Tan, L.; Hu, F.Z. Simultaneous determination of gastrodin and eight nucleosides and nucleobases in Tibet cultured gastrodia elata by HPLC method. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2014, 39, 3798–3802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, K.M.; Bermingham, E.N.; Bassett, S.A.; Treloar, B.P.; Roy, N.C.; Barnett, M.P. Global DNA methylation measurement by HPLC using low amounts of DNA. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, T.; Espina, M.; Montes-Bayon, M.; Sierra, L.M.; Blanco-Gonzalez, E. Anion exchange chromatography for the determination of 5-methyl-2′-Deoxycytidine: Application to cisplatin-sensitive and cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Yuan, J.; Dong, Y.S.; Fu, C.H.; Li, M.T.; Yu, L.J. Optimization of an HPLC method for determining the genomic methylation levels of Taxus cells. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magana, A.A.; Wrobel, K.; Caudillo, Y.A.; Zaina, S.; Lund, G.; Wrobel, K. High-performance liquid chromatography determination of 5-Methyl-2′-Deoxycytidine, 2′-Deoxycytidine, and other deoxynucleosides and nucleosides in DNA digests. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 374, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.L.; Barrientos, E.Y.; Wrobel, K.; Wrobel, K. Selective Derivatization of cytosine and methylcytosine moieties with 2-bromoacetophenone for submicrogram DNA methylation analysis by reversed phase HPLC with spectrofluorimetric detection. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7999–8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gackowski, D.; Zarakowska, E.; Starczak, M.; Modrzejewska, M.; Olinski, R. Tissue-specific differences in DNA modifications (5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-formylcytosine, 5-carboxylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil) and their interrelationships. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriaucionis, S.; Tahiliani, M. Expanding the epigenetic landscape: Novel modifications of cytosine in genomic DNA. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. Mechanisms and functions of TET protein-mediated 5-methylcytosine oxidation. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2436–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wossidlo, M.; Nakamura, T.; Lepikhov, K.; Marques, C.J.; Zakhartchenko, V.; Boiani, M.; Arand, J.; Nakano, T.; Reik, W.; Walter, J. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the mammalian zygote is linked with epigenetic reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarese, F.; Pau, E.C.S.; Stunnenberg, H.G. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine: A new kid on the epigenetic block? Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzov, A.; Tsenkina, Y.; Serio, A.; Dudnakova, T.; Fletcher, J.; Bai, Y.; Chebotareva, T.; Pells, S.; Hannoun, Z.; Sullivan, G.; et al. Lineage-specific distribution of high levels of genomic 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian development. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachman, M.; Uribe-Lewis, S.; Yang, X.; Williams, M.; Murrell, A.; Balasubramanian, S. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is a predominantly stable DNA modification. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahiliani, M.; Koh, K.P.; Shen, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brudno, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Iyer, L.M.; Liu, D.R.; Aravind, L.; et al. Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science 2009, 324, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriukiene, E.; Liutkeviciute, Z.; Klimasauskas, S. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine—The elusive epigenetic mark in mammalian DNA. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6916–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.Y.; DeNizio, J.E.; Kohli, R.M. Quantification of oxidized 5-methylcytosine bases and TET enzyme activity. Methods Enzymol. 2016, 573, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Mo, J.; Lu, M.; Wang, H. Detection of human urinary 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by Stable isotope dilution HPLC-MS/MS analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Globisch, D.; Munzel, M.; Muller, M.; Michalakis, S.; Wagner, M.; Koch, S.; Bruckl, T.; Biel, M.; Carell, T. Tissue distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and search for active demethylation intermediates. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
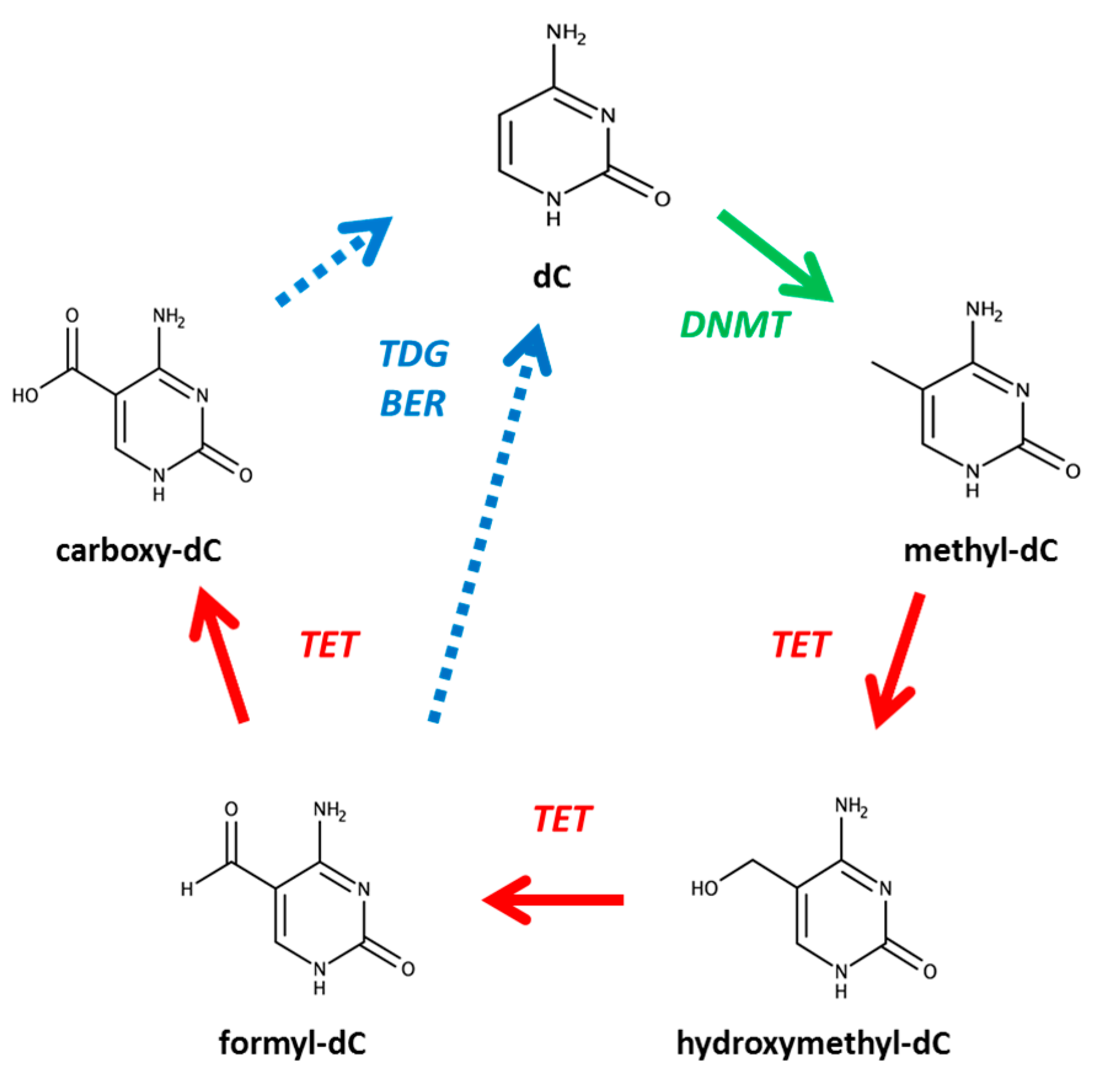
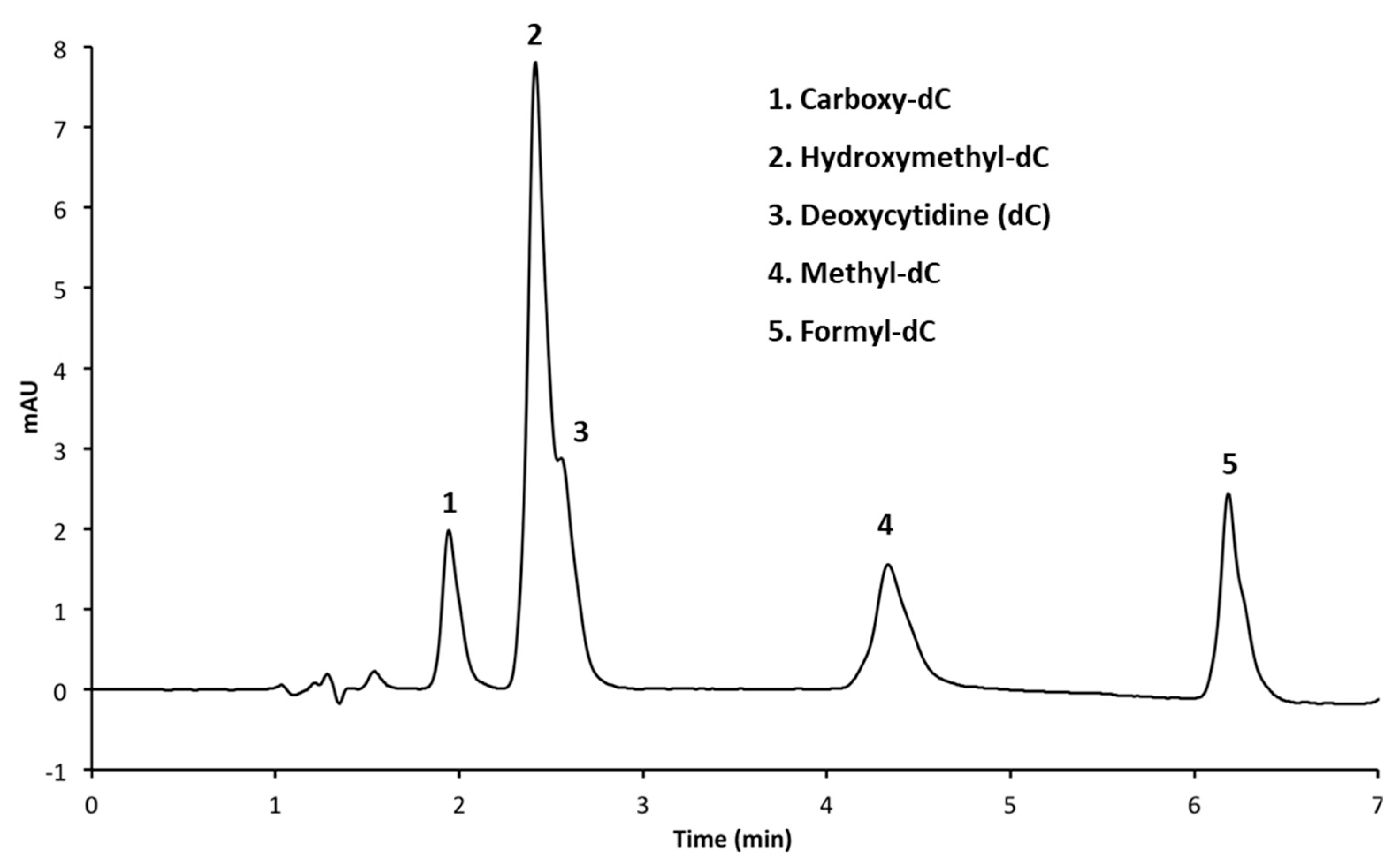
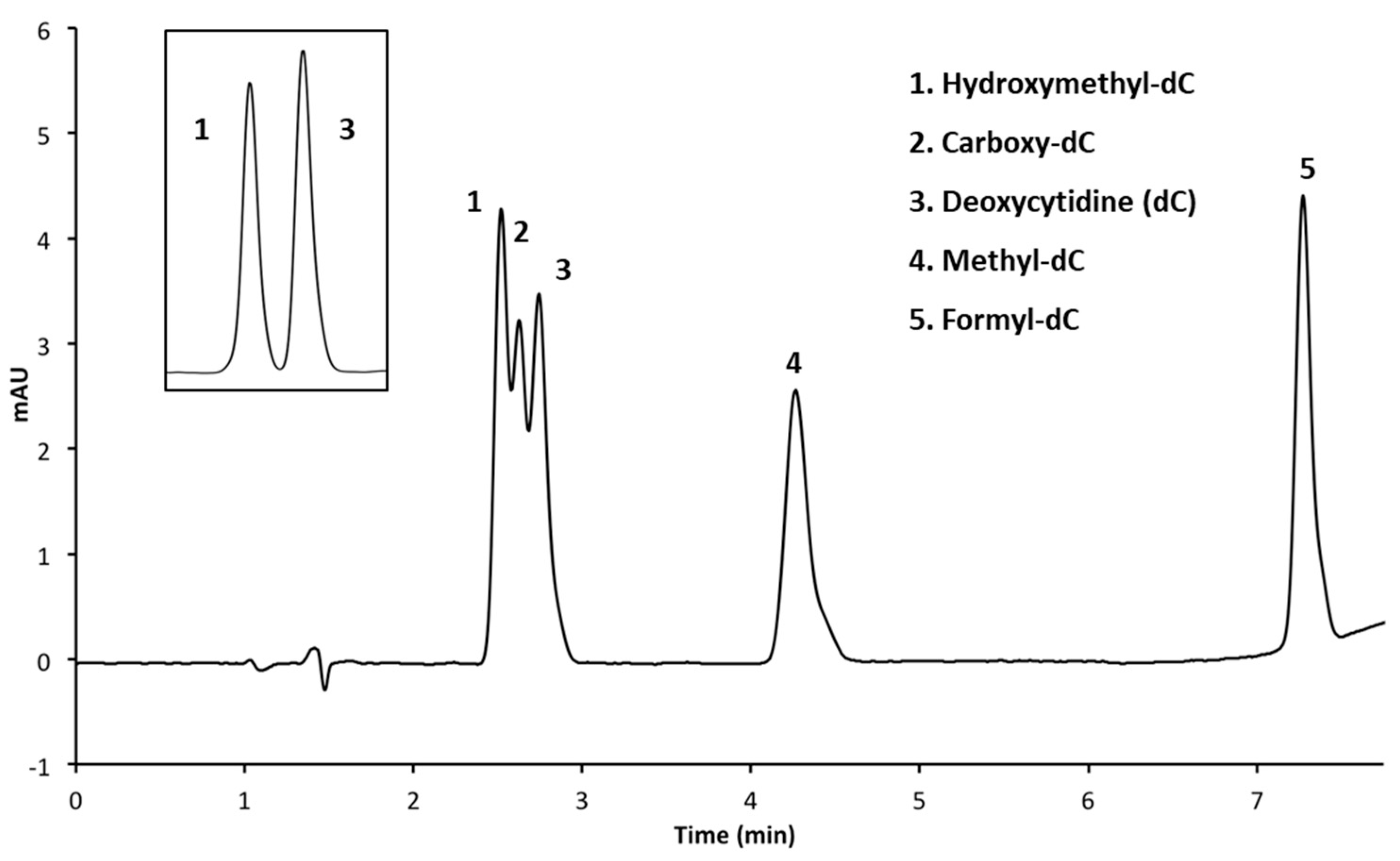
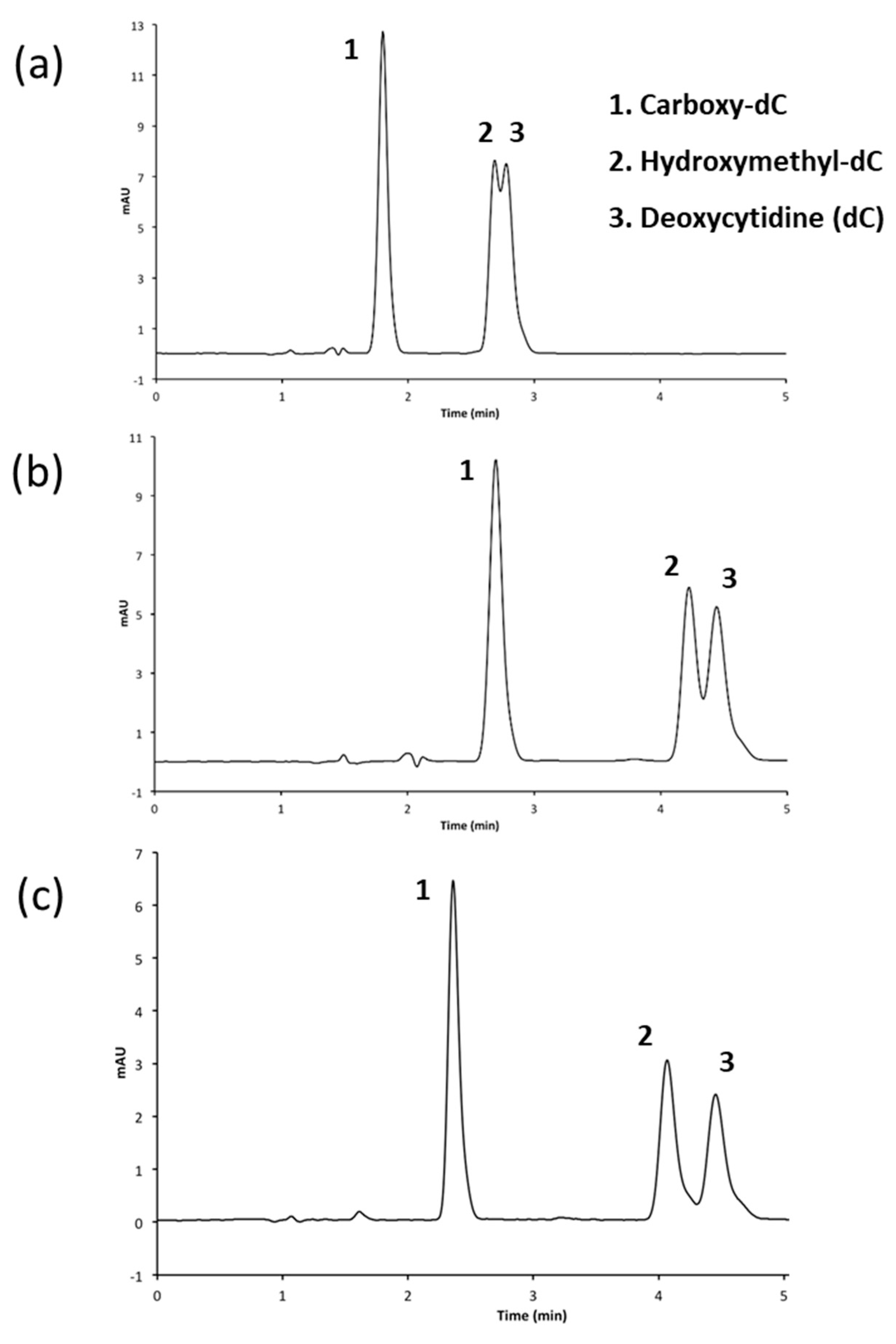
| Figure | Column | Mobile Phases | Elution (%, v/v) | Flow Rate mL/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Agilent C18 (50 × 3 mm, 1.8 μm) | A: CH3OH B: 50 mM NH4H2PO4 (pH 4.0) C: H2O | 3 min 5% A, 15% B 6 min 20% A, 15% B 6.05 min 30% A, 15% B 9 min 30% A, 15% B 9.05 min 5% A, 15% B 13 min 5% A, 15% B | 1.4 |
| 3 | Luna Phenyl Hexyl (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | A: CH3OH B: 50 mM NH4H2PO4 (pH 4.0) C: H2O | 4 min 5% A, 15% B 6 min 20% A, 15% B 6.05 min 30% A, 15% B 9 min 30% A, 15% B 9.05 min 5% A, 15% B | 1.4 |
| 3 (insert) | Luna Phenyl Hexyl (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | A: CH3OH B: 50 mM NH4H2PO4 (pH 4.0) C: H2O | 8 min 5% A, 15% B 11 min 20% A, 15% B 11.05 min 30% A, 15% B 16 min 30% A, 15% B 16.05 min 5% A, 15% B | 1.4 |
| 4a | Luna Phenyl Hexyl (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | A: CH3OH B: 50 mM NH4H2PO4 (pH 7.0) C: H2O | 8 min 5% A, 15% B 11 min 20% A, 15% B 11.05 min 30% A, 15% B 16 min 30% A, 15% B 16.05 min 5% A, 15% B | 1.4 |
| 4b | Luna Phenyl Hexyl (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | A: CH3OH B: 50 mM NH4H2PO4 (pH 7.0) C: H2O | 8 min 3 % A, 15% B 11 min 20% A, 15% B 11.05 min 30% A, 15% B 16 min 30% A, 15% B 16.05 min 3% A, 15% B | 1.0 |
| 4c | Luna Phenyl Hexyl (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | A: CH3OH B: 50 mM NH4H2PO4 (pH 7.0) C: H2O | 8 min 1% A, 15% B 11 min 20% A, 15% B 11.05 min 30% A, 15% B 16 min 30% A, 15% B 16.05 min 1% A, 15% B | 1.4 |
| Column | Luna Phenyl Hexyl (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile phases | A: Methanol | ||
| B: 50 mM ammonium phosphate (pH of 7.0) | |||
| C: Deionized water | |||
| Gradient elution | Time (min) | %A | %B |
| 0 | 1 | 15 | |
| 6 | 1 | 15 | |
| 14 | 30 | 15 | |
| 16 | 30 | 15 | |
| 16.05 | 100 | 0 | |
| 18 | 100 | 0 | |
| 18.05 | 1 | 15 | |
| 21 | 1 | 15 | |
| Injection volume | 50 μL | ||
| Actual injection | 40 μL | ||
| Flow rate | 1.4 mL·min−1 | ||
| Detection | Diode-Array Dectector 1 A, Signal = 280 nm Reference = 360 nm | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roberts, C.E.; Raner, G.M.; Isaacs, G.D. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation of Epigenetic Cytosine Variants. Methods Protoc. 2018, 1, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020010
Roberts CE, Raner GM, Isaacs GD. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation of Epigenetic Cytosine Variants. Methods and Protocols. 2018; 1(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoberts, Caroline E., Gregory M. Raner, and Gary D. Isaacs. 2018. "High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation of Epigenetic Cytosine Variants" Methods and Protocols 1, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020010
APA StyleRoberts, C. E., Raner, G. M., & Isaacs, G. D. (2018). High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation of Epigenetic Cytosine Variants. Methods and Protocols, 1(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020010




