Neonatal Screening in Europe Revisited: An ISNS Perspective on the Current State and Developments Since 2010
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scope of the Survey
2.2. Data Collection
3. Results and Discussion
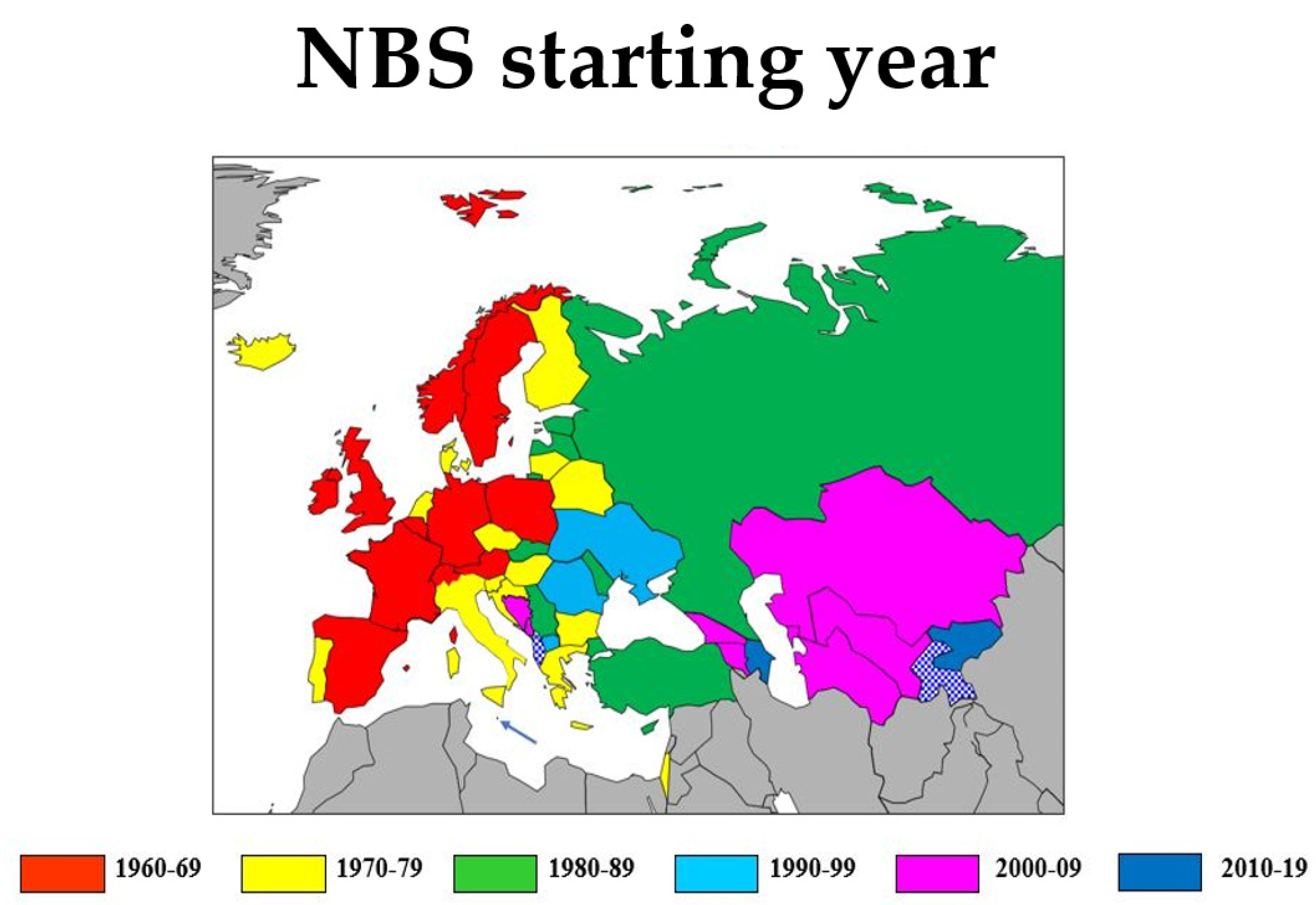
3.1. NBS Infrastructure
3.1.1. Number of Screening Laboratories and Average Annual Workload
3.1.2. Coverage
3.1.3. Screening Information, Parental Consent and Consent for Sample Storage
3.1.4. Sample Logistics
3.1.5. Analysis
3.1.6. Storage of DBS Cards
3.1.7. Reporting of Screening Results
3.2. Panel of Screened Conditions
3.3. Short-Term Programme Developments
3.4. Future Perspectives
3.4.1. Methodological Developments
3.4.2. Logistical Developments
3.4.3. Process and Effect Evaluation
3.4.4. Closer Collaboration Concerning the Organisation of NBS across Europe
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3HMG | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria |
| 3MCC | 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency/3-Methylglutacon aciduria/2-methyl-3-OH-butyric aciduria |
| AAD | Disorders of amino acid metabolism |
| x-ALD | x-Adrenoleukodystrophy |
| ARG | Argininemia |
| ASA | Argininosuccinic aciduria |
| BIO | Biotinidase deficiency |
| BKT | Beta-ketothiolase deficiency |
| CACT | Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase deficiency |
| CAH | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| CF | Cystic fibrosis |
| CFTR | cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| CH | (primary) Congenital hypothyroidism |
| CIT1 | Citrullinaemia type I |
| CIT2 | Citrullinaemia type II |
| CPT1 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase deficiency type I |
| CPT2 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase type II-/Carnitine acylcarnitine transporter deficiency |
| CUD | Carnitine uptake defect |
| E-HOD | European Registry and Network for Homocystinurias and Methylation Defects |
| E-IMD | European Registry and Network for Intoxication type Metabolic Diseases |
| ESID | European Society for Immunodeficiencies |
| EUNENBS | European Network of Experts on Newborn Screening |
| EURORDIS | European Organisation for Rare Diseases |
| FAOD | Disorders of fatty acid metabolism |
| G6PD | Glucose-6-phophate dehydrogenase deficiency |
| GA1 | Glutaric acidaemia type I |
| GA2 | Glutaric acidaemia type II or multiple acyl coA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| GAL | Classical galactosaemia |
| GALK | Galactose kinase deficiency |
| HCY | Homocystinuria (CBS deficiency) |
| HCSD | Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency |
| Hemo | Haemoglobinopathies |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| IPOPI | International Patient Organization for Primary Immunodeficiencies |
| IVA | Isovaleric acidaemia (IVA)/2-Methylbutyrylglycinuria |
| LCHAD | Long-chain L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency/Trifunctional protein deficiency |
| LSD | Lysosomal storage disorder |
| M | Miscellaneous disorders |
| MAT I/III | Methionine adenosyl transferase I/III deficiency |
| MCAD | Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| MCD | Multiple carboxylase deficiency |
| MMA | Methylmalonic acidaemia |
| MSUD | Maple Syrup Urine Disease |
| NBS | Neonatal (Newborn) Screening |
| NGS | Next generation sequencing |
| OA | Disorders of organic acid metabolism |
| PA | Propionic acidaemia |
| PKU/HPA | Phenylketonuria/Hyperphenylalaninaemia |
| RMD | Remethylation disorders (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, methylcobalamine deficiencies) |
| SCD | Sickle cell disease/thalassemia |
| SCID | Severe Combined Immunodeficiencies |
| SCAD | Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| SMA | Spinal muscular atrophy |
| TFP | Trifunctional protein deficiency |
| TYR1 | Tyrosinaemia type 1 |
| TYR2 | Tyrosinaemia type 2 |
| UDP | UDP-galactose-4-epimerase deficiency |
| UK | United Kingdom |
| VLCAD | Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
References
- Woolf, L.I.; Adams, J. The Early History of PKU. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Følling, I.A. Über Ausscheidung von phenylbrenztraubensäure in den harn als stoffwechselanomalie in verbindung mit imbezillität. Hoppe Seyler´s Z. Physiol. Chem. 1934, 227, 169–181. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centerwall, W.R. Phenylketonuria. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1957, 165, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxova, R. Lionel Sharples Penrose, 1898–1972: A personal memoir in celebration of the centenary of his birth. Genetics 1998, 150, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, R.; Susi, A. A simple phenylalanine method for detecting phenylketonuria in large populations of newborn infants. Pediatrics 1963, 32, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dussault, J.H.; Laberge, C. Thyroxine (T4) determination by radioimmunological method in dried blood eluate: New diagnostic method of neonatal hypothyroidism? Union Med. Can. 1973, 102, 2062–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Millington, D.S.; Kodo, N.; Norwood, D.L.; Roe, C.R. Tandem mass spectrometry: A new method for acylcarnitine profiling with potential for neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1990, 13, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, M.S.; Ozand, P.T.; Harrison, M.E.; Watkins, P.J.F.; Evans, S.; Baillie, P.T.A. Electrospray tandem mass spectrometry in the diagnosis of organic acidemias. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1994, 8, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Lindner, M.; Kohlmüller, D.; Olgemöller, K.; Mayatepek, E.; Hoffmann, G.F. Expanded newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry: Results, outcome, and implications. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Jungner, Y.G. Principles and practice of mass screening for disease. Bull. WHO 1968, 65, 281–393. [Google Scholar]
- International Society for Neonatal Screening—Region Europe. Available online: https://www.isns-neoscreening.org/isns-regions/region-europe/ (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Wikipedia. List of European Countries by Population. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_European_countries_by_population (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- World Bank Data. Birth Rate. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/sp.dyn.cbrt.in (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Burgard, P.; Cornel, M.C.; Di Filippo, F.; Heage, G.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Lindner, M.; Loeber, J.G.; Rigter, T.; Rupp, K.; Taruscio, D.; et al. Short Executive Summary of the Report on the Practices of Newborn Screening for Rare Disorders in Member States of the European Union, Candidate and Potential Candidate, and EFTA Countries; International Society for Neonatal Screening: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2011; Available online: http://www.isns-neoscreening.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Summary20111018.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Cornel, M.C.; Rigter, T.; Weinreich, S.S.; Burgard, P.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Lindner, M.; Loeber, J.G.; Rupp, K.; Taruscio, D.; Vittozzi, L. Newborn screening in Europe; expert opinion document. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeber, J.G. European union should actively stimulate and harmonise neonatal screening initiatives. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2018, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeber, J.G. Neonatal screening in Europe; situation in 2004. J. Inherhit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeber, J.G.; Burgard, P.; Cornel, M.C.; Rigter, T.; Weinreich, S.S.; Rupp, K.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Vittozzi, L. Newborn screening programmes in Europe; arguments and efforts regarding harmonization. Part 1—From blood spot to screening result. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2012, 35, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgard, P.; Rupp, K.; Lindner, M.; Haege, G.; Rigter, T.; Weinreich, S.S.; Loeber, J.G.; Taruscio, D.; Vittozzi, L.; Cornel, M.C.; et al. Newborn screening programmes in Europe; arguments and efforts regarding harmonization. Part 2—From screening laboratory results to treatment, follow-up and quality assurance. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2012, 35, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therrell, B.L.; Padilla, C.D.; Loeber, J.G.; Kneisser, I.; Saadallah, A.; Borrajo, G.J.; Adams, J. Current status of newborn screening worldwide: 2015. Semin. Perinatol. 2015, 39, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groselj, U.; Tansek, M.Z.; Smon, A.; Angelkova, N.; Anton, D.; Baric, I.; Djordjevic, M.; Grimci, L.; Ivanova, M.; Kadam, A.; et al. Newborn screening in southeastern Europe. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 113, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscher, A. Unpublished work. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Estrella, J.; Wilcken, B.; Carpenter, K.; Bhattacharya, K.; Tchan, M.; Wiley, V. Expanded newborn screening in New South Wales: Missed cases. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boneh, A.; Andresen, B.S.; Gregersen, N.; Ibrahim, M.; Tzanakos, N.; Peters, H.; Yaplito-Lee, J.; Pitt, J. VLCAD deficiency: Pitfalls in newborn screening and confirmation of diagnosis by mutation analysis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2006, 88, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymik, I.; Liebig, M.; Mueller, M.; Wendel, U.; Mayatepek, E.; Strauss, A.W.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Spiekerkoetter, U. Pitfalls of neonatal screening for very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency using tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pediatrics 2006, 149, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangeraas, T.; Sæves, I.; Klingenberg, C.; Jørgensen, J.; Kristensen, E.; Gunnarsdottir, G.; Hansen, E.; Strand, J.; Lundman, E.; Ferdinandusse, S.; et al. Performance of expanded newborn screening in Norway supported by post-analytical bioinformatics tools and rapid second-tier dna analyses. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijt, W.J.; Schielen, P.C.; Özer, Y.; Bijsterveld, K.; Van der Sluijs, F.H.; Derks, T.G.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R. Instability of acylcarnitines in stored dried blood spots: The impact on retrospective analysis of biomarkers for inborn errors of metabolism. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) 2016. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32016R0679 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Lanting, C.I.; Van Tijn, D.A.; Loeber, J.G.; Vulsma, T.; de Vijlder, J.J.; Verkerk, P.H. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the use of the thyroxine/thyroxine-binding globulin ratio to detect congenital hypothyroidism of thyroidal and central origin in a neonatal screening program. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroek, K.; Heijboer, A.C.; Bouva, M.J.; Van der Ploeg, C.P.B.; Heijnen, M.-L.A.; Weijman, G.; Bosch, A.M.; De Jonge, R.; Schielen, P.C.J.I.; Van Trotsenburg, A.S.P.; et al. Critical evaluation of the newborn screening for congenital hypothyroidism in the Netherlands. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boemer, F.; Caberg, J.-H.; Dideberg, V.; Dardenne, D.; Bours, V.; Hiligsmann, M.; Dangouloff, T.; Servais, L. Newborn screening for SMA in Southern Belgium. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vill, K.; Köbel, H.; Schwartz, O.; Blaschek, A.; Olgemöller, B.; Harms, E.; Burggraf, S.; Röschinger, W.; Dumer, J.; Gläser, D.; et al. One year of newborn screening for SMA. Results of a German pilot project. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 6, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlina, A.B.; Polo, G.; Salviati, L.; Duro, G.; Zizzo, C.; Dardis, A.; Bembi, B.; Cazzorla, C.; Rubert, L.; Zordan, R.; et al. Newborn screening for lysosomal storage disorders by tandem mass spectrometry in North East Italy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLIR—Collaborative Laboratory Integrated Reports. Available online: https://clir.mayo.edu/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- McHugh, D.; Cameron, C.A.; Abdenur, J.E.; Abdulrahman, M.; Adair, O.; Al Nuaimi, S.A.; Ahlman, H.; Allen, J.J.; Antonozzi, I.; Archer, S.; et al. Clinical validation of cutoff target ranges in newborn screening of metabolic disorders by tandem mass spec-trometry: A worldwide collaborative project. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 230–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, G.; Currier, R.; McHugh, D.M.; Gavrilov, D.; Magera, M.J.; Matern, D.; Oglesbee, D.; Raymond, K.; Rinaldo, P.; Smith, E.H.; et al. Enhanced interpretation of newborn screening results without analyte cutoff values. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerg, M.M.M.; Stoway, S.D.; Hart, J.; Mott, L.; Peck, D.S.; Nett, S.L.; Eckerman, J.S.; Lacey, J.M.; Turgeon, C.T.; Gavrilov, D.; et al. Precision newborn screening for lysosomal disorders. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörensen, L.; Von Döbeln, U.; Åhlman, H.; Ohlsson, A.; Engvall, M.; Naess, K.; Backman-Johansson, C.; Nordqvist, Y.; Wedell, A.; Zetterström, R.H. Expanded screening of one million Swedish babies with R4S and CLIR for post-analytical evaluation of data. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundman, E.; Gaup, H.J.; Bakkeheim, E.; Olafsdottir, E.J.; Rootwelt, T.; Storrøsten, O.T.; Pettersen, R.D. Implementation of newborn screening for cystic fibrosis in Norway. Results from the first three years. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2016, 15, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severin, F.; Borry, P.; Cornel, M.C.; Daniels, N.; Fellmann, F.; Hodgson, S.V.; Howard, H.C.; John, J.; Kääriäinen, H.; Kayserili, H.; et al. Points to consider for prioritizing clinical genetic testing services: A European consensus process oriented at accountability for reasonableness. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Society for Neonatal Screening. Databank Disorders. Available online: https://membership.isns-neoscreening.org/disorders/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- International Society for Neonatal Screening. Guidelines. Available online: https://www.isns-neoscreening.org/isns-general-guidelines-for-neonatal-screening/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
| Country | Approx. Population 2020 (Million) 1 | Approx. Number of Infants | Number Screening Laboratories | Average Number Samples Per Lab.2 | Interval Birth-Sampling (hrs) | Interval Sampling-Analysis (Days) | % Infants Screened | Information to Parents Available? | Consent Participation? | Consent Storage? | Length Storage (yrs) | Normal Results Reported to Parents? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania (no screening) | 3.0 | 36,000 | n.a.3 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a | n.a | n.a | n.a. |
| Austria | 8.8 | 87,000 | 1 | 87,000 | 36–72 | 1–3 | >99.5 | yes | no | no | 10 | no |
| Armenia | 3.1 | 36,000 | 2 4 | 36,000 | 48–96 | 1–5 | 99.8 | yes | yes | no | I ndef. | no |
| Azerbaijan | 9.7 | 170,000 | 1 | 35,000 | 48–72 | 3–5 | 30 | yes | no | no | n.d. | n.d. |
| Belarus | 9.8 | 108,000 | 1 | 108,000 | 72–120 | 1–5 | n.d. | yes | no | no | 5 | n.d. |
| Belgium | 10.5 | 117,000 | 4 | 30,000 | 48–120 | 2 | 99.8 | yes | no | no | 5 | no |
| Bosnia-Herzegovina | 3.3 | 28,000 | 3 4 | 9000 | 48–96 | 1–7 | 96 | no | no | no | 10 | no |
| Bulgaria | 7.4 | 61,000 | 2 4 | 61,000 | 72–120 | 5–10 | n.d. | no | yes/no | no | 20 | n.d. |
| Croatia | 4.2 | 36,200 | 1 | 36,200 | 48–72 | 3–5 | 100 | yes | no | no | 5 | no |
| Cyprus 5 | 1.1 | 9500 | 1 | 9500 | 48–168 | 5–10 | >99.9 | yes | yes | no | 2 | no |
| Czech Republic | 10.6 | 113,000 | 4 4 | 56,000 | 48–72 | 2.5 | 100 | yes | yes | no | 5 | no |
| Denmark | 5.6 | 63,000 | 1 | 63,000 | 48–72 | 1–2 | 99.1 | yes | yes | yes | indef. | online |
| Estonia | 1.3 | 13,500 | 1 | 13,500 | 48–72 | 2–5 | 99.55 | yes | yes | no | >25 | no |
| Finland | 5.5 | 45,000 | 1 4 | 45,000 | 48–120 | 1–5 | 99 | yes | yes | no | varies | online |
| France | 67 | 760,000 | 16 | 47,000 | 48–72 | 2–3 | 99.96 | yes | yes 6 | no | 1 | no |
| Georgia | 3.7 | 48,500 | 1 | 48,500 | 48–72 | 14–15 | 100 | yes | no | no | 15 | no |
| Germany | 80 | 787,000 | 11 | 71,000 | 36–72 | 2–3 | 100 | yes | yes | yes | <1 | no |
| Greece | 10.5 | 80,000 | 1 | 89,000 | 48–72 | 6–8 | 100 | yes | no | no | 2 | no |
| Hungary | 10 | 90,000 | 2 | 50,000 | 48–72 | 3–4 * | 99.99 | yes | no | no | indef. | no |
| Iceland | 0.35 | 4500 | 1 | 4500 | 48–72 | 3–5 | 100 | yes | yes | yes | indef. | online |
| Ireland | 4.9 | 59,700 | 1 | 59,700 | 72–120 | 1–2 | >99.5 | yes | yes | yes | 10 | no |
| Israel | 9.2 | 194,000 | 1 | 194,000 | 36–72 | 1–3 | 99.8 | yes | no | no | 5 | online |
| Italy | 60.5 | 434,000 | 15 | 28,900 | 48–72 | 1–4 | 96.7 | yes | no | no | 2–10 | no |
| Kazakhstan | 18.7 | 402,000 | 21 | 20,000 | 24–72 | 1–2 | 96.5 | yes | yes | no | 3 | no |
| Kosovo | 1.8 | 25,000 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a | n.a | n.a | n.a. |
| Kyrgyzstan | 7.0 | 160,000 | 1 | 32,000 | 48–72 | 3–5 | 30 | yes | no | no | n.d. | n.d. |
| Latvia | 1.9 | 20,800 | 1 | 20,000 | 48–72 | 5–7 | 98.5 | yes | yes | no | 7 | online |
| Lithuania | 2.8 | 24,600 | 1 | 24,600 | 48–96 | 2–9 | 99.6 | yes | yes | no | 20 | no |
| Luxembourg | 0.6 | 7200 | 1 | 7200 | 48–72 | 4 | >99 | yes | yes | no | indef. | no |
| Malta | 0.48 | 4400 | 2 4 | 4400 | 72–120 | 5 | 99.7 | yes | yes | no | indef. | no |
| Moldova | 3.5 | 37,400 | 1 | 37,400 | >48 | 30 | 92.3 | yes | yes | no | 0 | n.d. |
| Montenegro | 0.62 | 7200 | 1 | 7200 | 24–72 | 1–3 | 100 | no | no | no | 0.5 | no |
| Netherlands | 17.8 | 168,500 | 5 | 34,000 | 72–96 | 1–3 | 99.3 | yes | yes | yes | 5 | |
| North Macedonia | 2.1 | 20,000 | 1 | 20,000 | 32–72 | 3 | >98 | yes | no | yes | 3 | no |
| Norway | 5.3 | 55,500 | 1 | 55,500 | 48–72 | 1–3 | >99 | yes | yes | yes | indef. | no |
| Poland | 38.4 | 373,000 | 6 | 62,000 | 48–96 | 3 | 99.8 | yes | yes | yes | 5 | online |
| Portugal | 10.3 | 87,300 | 1 | 87,300 | 48–72 | 1–3 | 99.5 | yes | yes | no | 5 | online |
| Romania 7 | 19.6 | 185,600 | 5 | 31,500 | 48–72 | 18 | 85 | yes | yes | no | 5 | no |
| Russia | 142 | 1,670,000 | 78 4 | 20,000 | 48–72 | 3–5 | 90-92 | yes | yes | no | 3 | n.d. |
| Serbia | 7.0 | 65,000 | 2 | 32,500 | 48–72 | 3–5 | 99 | yes | no | no | 5 | no |
| Slovakia | 5.4 | 57,000 | 1 | 57,000 | 72–96 | 2–3 | 100 | yes | yes | no | indef. | no |
| Slovenia | 2.07 | 20,000 | 1 | 20,000 | 48–72 | 1–2 | >99 | yes | no | no | indef. | no |
| Spain | 46.5 | 372,000 | 15 | 24,800 | 24–72 | 3–10 | 99.2 | yes | yes | yes | 5-indef | |
| Sweden | 10 | 116,000 | 1 | 116,000 | 48–72 | 1–3 | >99.5 | yes | yes | yes | indef. | no |
| Switzerland | 8.1 | 88,000 | 1 | 88,000 | 72–96 | 2 | >99.9 | yes | yes | yes | indef. | no |
| Tajikistan (no screening) | 9.4 | 291,000 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a | n.a | n.a | n.a. |
| Turkey | 84.3 | 1,300,000 | 2 | 650,000 | 48–72* | 1–2 | 97 | yes | yes | yes | 5 | no |
| Turkmenistan | 6.0 | 110,200 | 1 | 35,000 | 48–72 | 3–5 | 30 | yes | no | no | n.d. | n.d. |
| United Kingdom | 66.6 | 760,000 | 16 | 47,500 | 120 | 3–4 | 96.5 | yes | yes | no | >5 | |
| Ukraine | 43.7 | 393,000 | 7 | 56,100 | 48–72 | 3 | n.d. | yes | yes | n.a. | <0.5 | |
| Uzbekistan | 31.3 | 760,600 | 14 | 54,000 | 72–96 | 10. | 95 | yes | yes | n.d. | 1 | n.d. |
| Endocrine Disorders | Amino Acidemias | Organic Acidemias | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH 1 | CAH | CF | PKU | MSUD | HCY | Tyr-1 | Tyr-2 | ASA | Cit.1/2 | ARG | MAT I/III | GA1 | IVA | 3MCC | PA | MMA 3 | BKT | HCSD | 3HMG | MCD | |
| Albania | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Armenia | x 2 | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| Austria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||
| Azerbaijan | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Belarus | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| Belgium | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||
| Bosnia-Her. | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bulgaria | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Croatia | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Cyprus | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| Czech Rep. | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| Denmark | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||
| Estonia | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||
| Finland | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||
| France | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Georgia | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Germany | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||
| Greece | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| Hungary | x | p 1 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Iceland | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Ireland | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||
| Israel | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| Italy | x | p | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Kazakhstan | x | p | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kosovo | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Kyrgyzstan | x | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Latvia | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Lithuania | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Luxembourg | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Malta | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| Moldova | x | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Montenegro | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| Nethelands | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||
| N. Macedonia | x | p | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Norway | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||
| Poland | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||
| Portugal | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Romania | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Russia | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| Serbia | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Slovakia | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Slovenia | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||
| Spain | x | p | x | x | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | x | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | |
| Sweden | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||
| Switzerland | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||
| Tajikistan | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Turkey | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Turkmenistan | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| United Kingdom | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||
| Ukraine | x | x | x | x | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | ||||
| Uzbekistan | x | p | x | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | |||||||
| Total 4 | 47 | 24 + 2 | 25 + 4 | 46 | 22 + 3 | 16 + 3 | 19 + 3 | 10 + 2 | 11 + 3 | 13 + 3 | 12 + 3 | 3 | 24 + 2 | 21 + 3 | 9 + 32 | 18 + 2 | 17 + 3 | 10 + 2 | 6 + 2 | 10 + 1 | 8 + 1 |
| Fatty acid Oxidation Disorders | Miscellaneous | Hemo | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA2 1 | MCAD | LCHAD/TFP | VLCAD | SCAD | CPT1 | CPT2 | CACT | CUD | RMD | GAL | BIOT | UDP | G6PD | xALD | SCID | SMA | SCD | Total 3 | |
| Albania | n.d. 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Armenia | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Austria | x 2 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 26 | |||||||
| Azerbaijan | x | x | 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| Belarus | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Belgium | x | x | x | x | x | p | p | p | 17 + 3 | ||||||||||
| Bosnia-Herzegovina | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Bulgaria | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Croatia | x | x | x | x | 8 | ||||||||||||||
| Cyprus | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Czech Republic | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 18 | ||||||||||
| Denmark | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | 19 + 1 | ||||||||||
| Estonia | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 19 | |||||||||||
| Finland | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | 21 + 1 | |||||||||
| France | x | x | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Georgia | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Germany | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | p | 17 + 2 | |||||||
| Greece | x | x | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Hungary | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 26 + 1 | ||||||||
| Iceland | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | x | 27 + 1 | |||||||
| Ireland | x | x | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Israel | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | x | 19 + 1 | |||||||
| Italy | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | p | p | 31 + 4 | |||
| Kazakhstan | 2 + 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kosovo | n.d. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kyrgyzstan | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Latvia | x | x | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Lithuania | x | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Luxembourg | x | 5 | |||||||||||||||||
| Malta | x | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Moldova | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Montenegro | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Netherlands | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | p | 20 + 2 | |||||||||
| North Macedonia | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 25 + 1 | |||||||||
| Norway | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 23 | ||||||||||
| Poland | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | x | p | 27 + 2 | |||||||
| Portugal | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 24 | ||||||||||
| Romania | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Russia | x | 6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Serbia | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Slovakia | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | p | 25 + 2 | ||||||||
| Slovenia | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | p | 19 + 1 | ||||||||||
| Spain | p | x | x | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | x | 7 + 26 | |||||
| Sweden | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 25 | |||||||
| Switzerland | x | x | x | x | 10 | ||||||||||||||
| Tajikistan | n.d. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Turkey | x | 5 | |||||||||||||||||
| Turkmenistan | x | x | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| United Kingdom | x | x | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
| Ukraine | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | 4 + 24 | ||||||||
| Uzbekistan | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | 2 + 19 | |||||||||||
| Total 3 | 11 + 2 | 26 + 2 | 20 + 2 | 19 + 3 | + | 17 + 3 | 16 + 3 | 15 + 1 | 15 + 3 | + | 17 + 3 | 13 + 3 | 1 | 3 + 2 | 1 + 3 | 7 + 6 | 0 + 5 | 4 + 3 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loeber, J.G.; Platis, D.; Zetterström, R.H.; Almashanu, S.; Boemer, F.; Bonham, J.R.; Borde, P.; Brincat, I.; Cheillan, D.; Dekkers, E.; et al. Neonatal Screening in Europe Revisited: An ISNS Perspective on the Current State and Developments Since 2010. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010015
Loeber JG, Platis D, Zetterström RH, Almashanu S, Boemer F, Bonham JR, Borde P, Brincat I, Cheillan D, Dekkers E, et al. Neonatal Screening in Europe Revisited: An ISNS Perspective on the Current State and Developments Since 2010. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2021; 7(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoeber, J. Gerard, Dimitris Platis, Rolf H. Zetterström, Shlomo Almashanu, François Boemer, James R. Bonham, Patricia Borde, Ian Brincat, David Cheillan, Eugenie Dekkers, and et al. 2021. "Neonatal Screening in Europe Revisited: An ISNS Perspective on the Current State and Developments Since 2010" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 7, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010015
APA StyleLoeber, J. G., Platis, D., Zetterström, R. H., Almashanu, S., Boemer, F., Bonham, J. R., Borde, P., Brincat, I., Cheillan, D., Dekkers, E., Dimitrov, D., Fingerhut, R., Franzson, L., Groselj, U., Hougaard, D., Knapkova, M., Kocova, M., Kotori, V., Kozich, V., ... Schielen, P. C. J. I. (2021). Neonatal Screening in Europe Revisited: An ISNS Perspective on the Current State and Developments Since 2010. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 7(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010015












