Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Newborn Screening of SCID, SMA, and XLA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dried Blood Spot Samples
2.2. Contrived and Control Dried Blood Spot Samples
2.3. Punching and DNA Extraction
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. Testing of Newborn DBS Samples
2.6. Run and Sample Acceptance Criteria
2.7. TREC and KREC Copy Number Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Presumed normal Newborn Samples
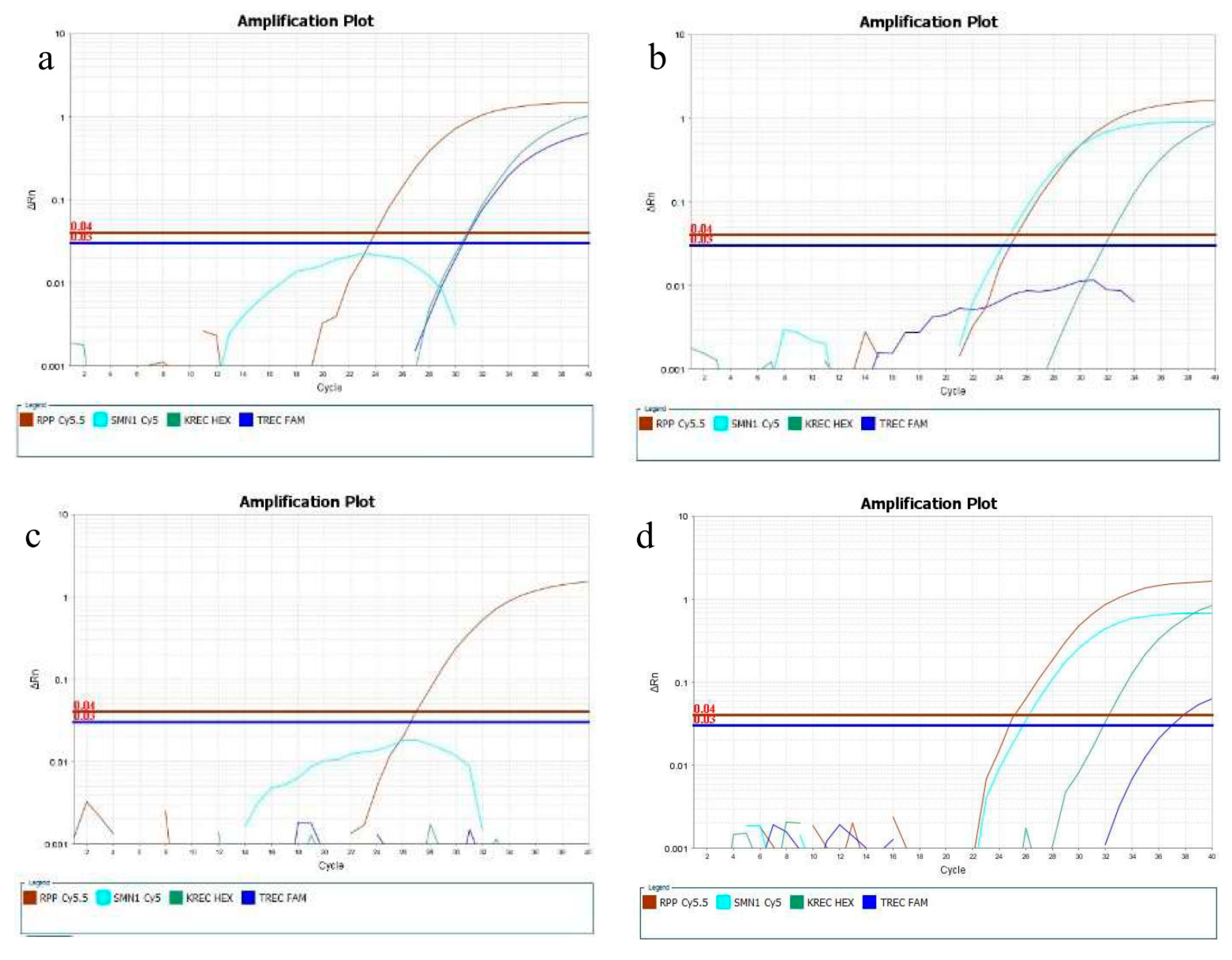
3.2. Reference, Contrived, and Confirmed Positive Samples
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazarin, G.A.; Haque, I.S.; Nazareth, S.; Iori, K.; Patterson, A.S.; Jacobson, J.L.; Marshall, J.R.; Seltzer, W.K.; Patrizio, P.; Evans, E.A.; et al. An empirical estimate of carrier frequencies for 400+ causal Mendelian variants: Results from an ethnically diverse clinical sample of 23,453 individuals. Genet. Med. 2013, 15, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Connolly, A.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Kirschner, J.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Saito, K.; Servais, L.; Tizzano, E.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, J.R.; Al-Zaidy, S.; Shell, R.; Arnold, W.D.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Prior, T.W.; Lowes, L.; Alfano, L.; Berry, K.; Church, K.; et al. Single-Dose Gene-Replacement Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, L.P.; Alfano, L.N.; Arnold, W.D.; Shell, R.; Prior, T.W.; McColly, M.; Lehman, K.J.; Church, K.; Sproule, D.M.; Nagendran, S.; et al. Impact of Age and Motor Function in a Phase 1/2A Study of Infants with SMA Type 1 Receiving Single-Dose Gene Replacement Therapy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 98, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Medical Genetics Newborn Screening Expert Group. Newborn Screening: Towards a Uniform Screening Panel and System. Genet. Med. 2006, 117, S296–S307. [Google Scholar]
- American College of Medical Genetics Newborn Screening Expert Group. Naming and Counting Disorders (Conditions) Included in Newborn Screening Panels. Pediatrics 2006, 117, S308–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House Passes AACC Backed Newborn Screening Measure. Available online: https://www.aacc.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Baker, M.W.; Grossman, W.J.; Laessig, R.H.; Hoffman, G.L.; Brokopp, C.D.; Kurtycz, D.F.; Cogley, M.F.; Litsheim, T.J.; Katcher, M.L.; Routes, J.M. Development of a routine newborn screening protocol for severe combined immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Puck, J.M. Development of population-based newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.; Abraham, R.S.; Currier, R.; Brower, A.; Andruszewski, K.; Abbott, J.K.; Baker, M.; Ballow, M.; Bartoshesky, L.E.; Bonagura, V.R.; et al. Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency in 11 screening programs in the United States. JAMA 2014, 312, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borte, S.; Meeths, M.; Liebscher, I.; Krist, K.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Hammarström, L.; von Döbeln, U.; Henter, J.I.; Bryceson, Y.T. Combined newborn screening for familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and severe T- and B-cell immunodeficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourizadeh, M.; Shakerian, L.; Borte, S.; Fazlollahi, M.; Badalzadeh, M.; Houshmand, M.; Alizadeh, Z.; Dalili, H.; Rashidi-Nezhad, A.; Kazemnejad, A.; et al. Newborn screening using TREC/KREC assay for severe T and B cell lymphopenia in Iran. Scand. J. Immunol. 2018, 26, 12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.R.; Hammarström, L. Newborn Screening for Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: History, Current and Future Practice. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, S.Y.; Logan, B.R.; Griffith, L.M.; Buckley, R.H.; Parrott, R.E.; Dvorak, C.C.; Kapoor, N.; Hanson, I.C.; Filipovich, A.H.; Jyonouchi, S.; et al. Transplantation outcomes for severe combined immunodeficiency, 2000–2009. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plebani, A.; Soresina, A.; Rondelli, R.; Amato, G.M.; Azzari, C.; Cardinale, F.; Cazzola, G.; Consolini, R.; De Mattia, D.; Dell’Erba, G.; et al. Clinical, immunological, and molecular analysis in a large cohort of patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia: An Italian multicenter study. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 104, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, T.W.; Snyder, P.J.; Rink, B.D.; Pearl, D.K.; Pyatt, R.E.; Mihal, D.C.; Conlan, T.; Schmalz, B.; Montgomery, L.; Ziegler, K.; et al. Newborn and carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.L.; Lee, F.K.; Yazdanpanah, G.K.; Staropoli, J.F.; Liu, M.; Carulli, J.P.; Sun, C.; Dobrowolski, S.F.; Hannon, W.H.; Vogt, R.F. Newborn blood spot screening test using multiplexed real-time PCR to simultaneously screen for spinal muscular atrophy and severe combined immunodeficiency. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensen, A.; Ochs, C.; Stroux, A.; Wittenbecher, F.; Szyska, M.; Imberti, L.; Fillatreau, S.; Uharek, L.; Arnold, R.; Dörken, B.; et al. Utilization of TREC and KREC quantification for the monitoring of early T- and B-cell neogenesis in adult patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranda, B.; Fan, L.; Soucy, J.F.; Simard, L.; Mitchell, G.A. Spinal muscular atrophy: Clinical validation of a single-tube multiplex real time PCR assay for determination of SMN1 and SMN2 copy numbers. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puck, J.M. Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency and T-cell lymphopenia. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 287, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felipe, B.; Olbrich, P.; Lucenas, J.M.; Delgado-Pecellin, C.; Pavon-Delgado, A.; Marquez, J.; Salamanca, C.; Soler-Palacin, P.; Gonzalez-Granado, L.I.; Antolin, L.F.; et al. Prospective neonatal screening for severe T- and B-lymphocyte deficiencies in Seville. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Mendell, J.R.; Baker, M.; Wiley, V.; Kwon, J.M.; Alfano, L.N.; Connolly, A.M.; Jay, C.; Polari, H.; et al. Progress in treatment and newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy. World J. Pediatr. 2019, 15, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monani, U.R.; Lorson, C.L.; Parsons, D.W.; Prior, T.W.; Androphy, E.J.; Burghes, A.H.; McPherson, J.D. A single nucleotide difference that alters splicing patterns distinguishes the SMA gene SMN1 from the copy gene SMN2. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, Y.H.; Chiang, S.C.; Weng, W.C.; Lee, N.C.; Lin, C.J.; Hsieh, W.S.; Lee, W.T.; Jong, Y.J.; Ko, T.M.; Hwu, W.L. Presymptomatic Diagnosis of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Through Newborn Screening. J. Pediatr. 2017, 190, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahnen, E.; Schönling, J.; Rudnik-Schöneborn, S.; Zerres, K.; Wirth, B. Hybrid survival motor neuron genes in patients with autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy: New insights into molecular mechanisms responsible for the disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The Evidence-based Review Group. Evidence-Based Review of Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA): Final Report (v5.2). Prepared for: Maternal and Child Health Bureau. 2018. Available online: https://www.hrsa.gov/sites/default/files/hrsa/advisory-committees/heritable-disorders/reports-recommendations/sma-final-report.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2019).
- Boemer, F.; Caberg, J.H.; Dideberg, V.; Dardenne, D.; Bours, V.; Hiligsmann, M.; Dangouloff, T.; Servais, L. Newborn screening for SMA in Southern Belgium. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borte, S.; von Döbeln, U.; Hammarström, L. Guidelines for newborn screening of primary immunodeficiency diseases. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2013, 20, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, M.; Ohlsson, A.; Borte, S.; Jonsson, S.; Zetterström, R.H.; King, J.; Winiarski, J.; von Döbeln, U.; Hammarström, L. Newborn screening for severe primary immunodeficiency diseases in Sweden-a 2-year pilot TREC and KREC screening study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borte, S.; von Döbeln, U.; Fasth, A.; Wang, N.; Janzi, M.; Winiarski, J.; Sack, U.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; Borte, M.; Hammarström, L. Neonatal screening for severe primary immunodeficiency diseases using high-throughput triplex real-time PCR. Blood 2012, 119, 2552–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstel-Thompson, J.L.; Wilkey, J.F.; Baptiste, J.C.; Navas, J.S.; Pai, S.Y.; Pass, K.A.; Eaton, R.B.; Comeau, A.M. High-throughput multiplexed T-cell-receptor excision circle quantitative PCR assay with internal controls for detection of severe combined immunodeficiency in population-based newborn screening. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EnLite™ Neonatal TREC system. EnLite™ Neonatal TREC Kit 3401-0010. Instructions for Use; PerkinElmer Catalogue: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
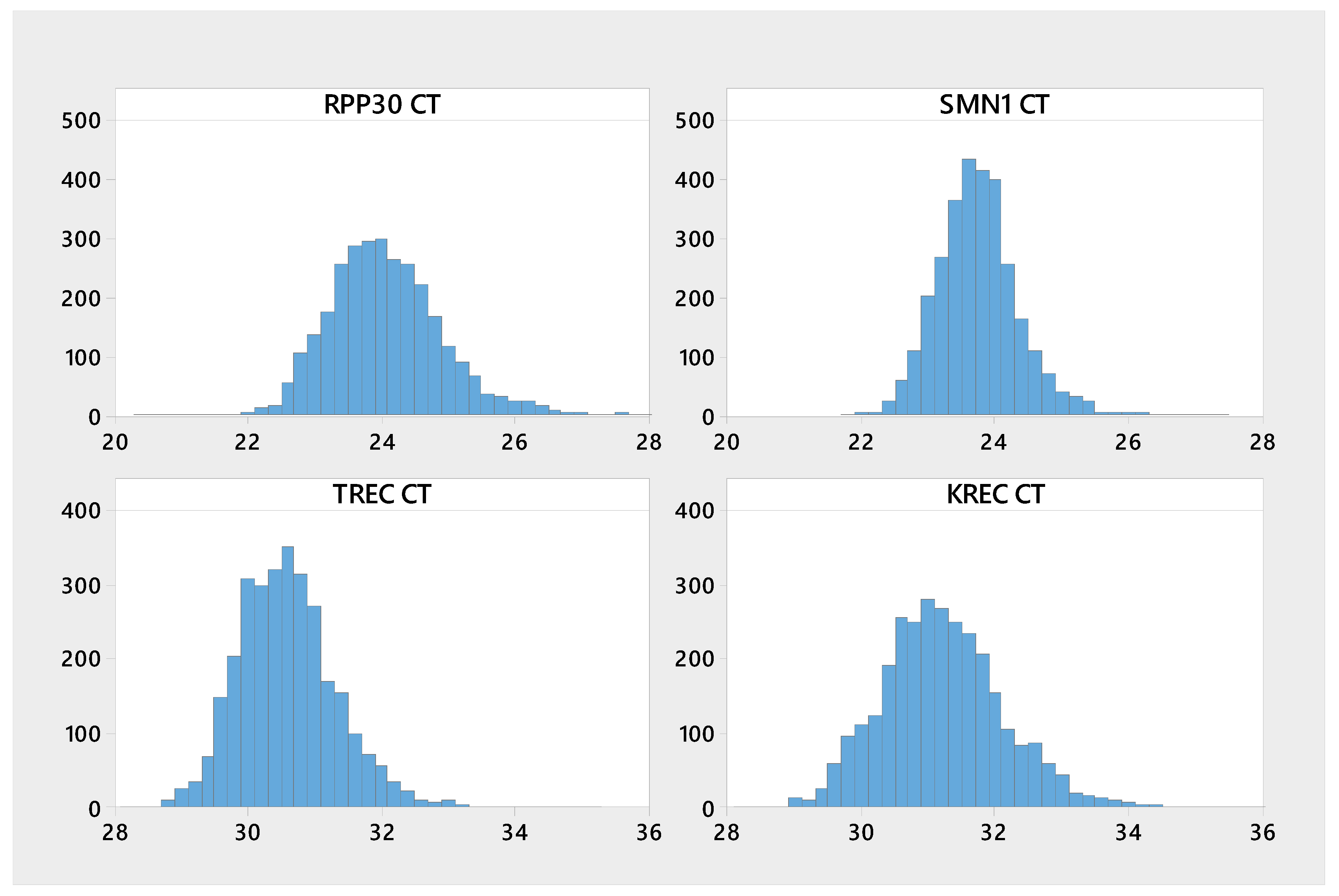
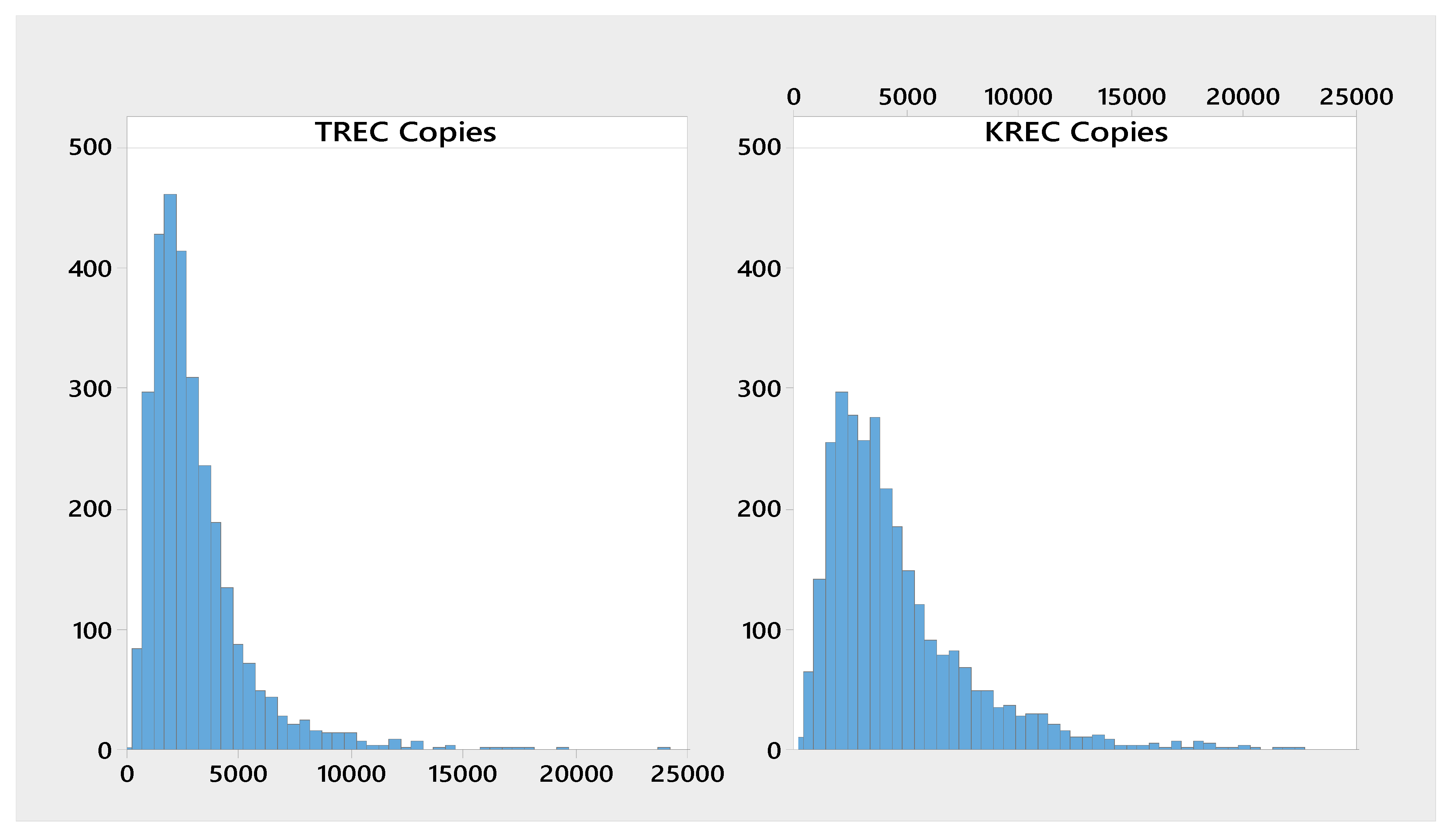
| Analyte | n | Mean | Median | SD | CV | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KREC | 3020 | 31.2 | 31.2 | 0.97 | 3.11 | 28.3 | 39.3 |
| RPP30 | 3023 | 24.1 | 24 | 0.88 | 3.66 | 20.4 | 28.4 |
| SMN1 | 3023 | 23.7 | 23.7 | 0.63 | 2.64 | 21.8 | 27.4 |
| TREC | 3022 | 30.6 | 30.5 | 0.76 | 2.48 | 28.2 | 35.1 |
| Analyte | n | Mean | Median | P0.1 | P0.5 | P1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆Ct KREC-RPP30 | 3023 | 4790 | 3590 | 34.8 | 231 | 466 |
| ∆Ct TREC-RPP30 | 3023 | 3220 | 2500 | 218 | 380 | 518 |
| Analyte | n | CT Mean | Median | P 99.9 | P 99.5 | P 99.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMN1 | 3023 | 23.7 | 23.7 | 27.1 | 25.9 | 25.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutierrez-Mateo, C.; Timonen, A.; Vaahtera, K.; Jaakkola, M.; Hougaard, D.M.; Bybjerg-Grauholm, J.; Baekvad-Hansen, M.; Adamsen, D.; Filippov, G.; Dallaire, S.; et al. Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Newborn Screening of SCID, SMA, and XLA. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2019, 5, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns5040039
Gutierrez-Mateo C, Timonen A, Vaahtera K, Jaakkola M, Hougaard DM, Bybjerg-Grauholm J, Baekvad-Hansen M, Adamsen D, Filippov G, Dallaire S, et al. Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Newborn Screening of SCID, SMA, and XLA. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2019; 5(4):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns5040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutierrez-Mateo, Cristina, Anne Timonen, Katja Vaahtera, Markku Jaakkola, David M Hougaard, Jonas Bybjerg-Grauholm, Marie Baekvad-Hansen, Dea Adamsen, Galina Filippov, Stephanie Dallaire, and et al. 2019. "Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Newborn Screening of SCID, SMA, and XLA" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 5, no. 4: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns5040039
APA StyleGutierrez-Mateo, C., Timonen, A., Vaahtera, K., Jaakkola, M., Hougaard, D. M., Bybjerg-Grauholm, J., Baekvad-Hansen, M., Adamsen, D., Filippov, G., Dallaire, S., Goldfarb, D., Schoener, D., & Wu, R. (2019). Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Newborn Screening of SCID, SMA, and XLA. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 5(4), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns5040039






