A Rapid and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS-Method for the Separation and Quantification of Branched-Chain Amino Acids from Dried Blood Samples of Patients with Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
Abstract
: Newborn screening for MSUD is a special challenge since patients with MSUD can metabolically decompensate rapidly without adequate treatment within the first two weeks of life. However, the screening method does not detect the actual marker metabolite (alloisoleucine) specifically, but only as part of the group of the other isobaric amino acids leucine, isoleucine and hydroxyproline. We describe a sensitive and rapid second-tier UPLC-MS/MS method to determine branched-chain amino acids from the initial extraction of the screening sample. Quantification is based on a seven-point calibration curve. Reference ranges (mean ± SD in µmol/L) were determined from 179 normal, not pre-selected samples from the newborn screening: leucine: 72 ± 27; isoleucine: 37 ± 19; valine: 98 ± 46; hydroxyproline: 23 ± 13. The concentration of alloisoleucine was below the detection limit in about 55% of the cases, and the highest concentration was 1.9 µmol/L. In all 30 retrospectively studied screening samples from patients with confirmed MSUD the concentration of alloisoleucine was significantly increased. In 238 samples with false-positive newborn screening due to a significant increase in the combined concentration of leucine + isoleucine + alloisoleucine + hydroxyproline (400 to >4000 µmol/L), alloisoleucine was below 6.5 µmol/L (n = 57) or not detectable (n = 181). The application of this assay markedly reduces the false-positive rate and the associated anxiety and costs. It is also suitable for routinely monitoring blood spots of patients with MSUD.1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSUD | Maple Syrup Urine Disease |
| UPLC | Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| MS/MS | Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| NBS | Newborn Screening |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| TPN | Total Parenteral Nutrition |
| FP | False Positive |
| MRM | Multiple Reaction Monitoring |
| C.I. | Confidence Interval |
References
- Chuang, D.T.; Shih, V.E.; Wynn, R.M. Maple Syrup Urine Disease (Branched-Chain Ketoaciduria). In The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease; Valle, D., Beaudet, A.L., Vogelstein, B., Kinzler, K.W., Antonarakis, S.E., Ballabio, A., Gibson, K.M., Mitchell, G., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: Columbus, OH, USA, 2016; Chapter 87. [Google Scholar]
- Morten, D.H.; Strauss, K.A.; Robinson, D.L.; Puffenberger, E.G.; Kelley, R.I. Diagnosis and treatment of maple syrup urine disease: A study of 36 patients. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 99–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanyan, S.B.; Quadri, S.M.; Dhalla, M.B.; Ozand, P.T. The diagnosis and management of MSUD in Saudi Arabia by using two different methods. Indian J. Pediatr. 1990, 57, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingerhut, R. Recall rate and positive predictive value of MSUD screening is not influenced by hydroxyproline. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 168, 559–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadewaldt, P.; Hammen, H.-W.; Dalle-Feste, C.; Wendel, U. On the mechanism of l-alloisoleucine formation: Studies on a healthy subject and in fibroblasts from normals and patients with maple syrupe urine disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1990, 13, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamer, O.A.; Reimer, M.L.J. On the mechanisms of the formation of l-alloisoleucine and the 2-hydroxy-3-methylvaleric acid stereoisomers from l-isoleucine in maple syrup urine disease patients and in normal humans. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 22141–22147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simon, E.; Fingerhut, R.; Baumkötter, J.; Konstantopoulou, V.; Ratschmann, R.; Wendel, U. Maple syrup urine disease: Favourable effect of early diagnosis by newborn screening on the neonatal course of the disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingerhut, R.; Simon, E.; Maier, E.M.; Hennermann, J.B.; Wendel, U. Maple syrup urine disease: Newborn screening fails to discriminate between classical and variant forms. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1739–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baykal, T.; Karaaslan, I.; Gokcay, G.; Demir, F.; Laleli, Y.; Demirkol, M. Hyperhydroxyprolinaemia detected by newborn screening with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2004, 27, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Marca, G.; Malvagia, S.; Pasquini, E.; Donati, M.A.; Procopio, E.; Zammarchi, E. Hyperhydroxyprolinaemia: A new case diagnosed during neonatal screening with tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oglesbee, D.; Sanders, K.A.; Lacey, J.M.; Magera, M.J.; Casetta, B.; Strauss, K.A.; Tortorelli, S.; Rinaldo, P.; Matern, D. Second-tier test for quantification of alloisoleucine and branched-chain amino acids in dried blood spots to improve newborn screening for maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowell, J.; Pollard, L.; Wood, T. Quantification of branched-chain amino acids in blood spots and plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the diagnosis of maple syrup urine disease. J. Sep. Sci. 2001, 34, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alodaib, A.; Carpenter, K.; Wiley, V.; Sim, K.; Christodoulou, J.; Wilcken, B. An improved ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of alloisoleucine and branched chain amino acids in dried blood samples. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 48, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haymond, M.W.; Ben-Galim, E.; Strobel, K.E. Glucose and alanine metabolism in children with maple syrup urine disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1978, 62, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
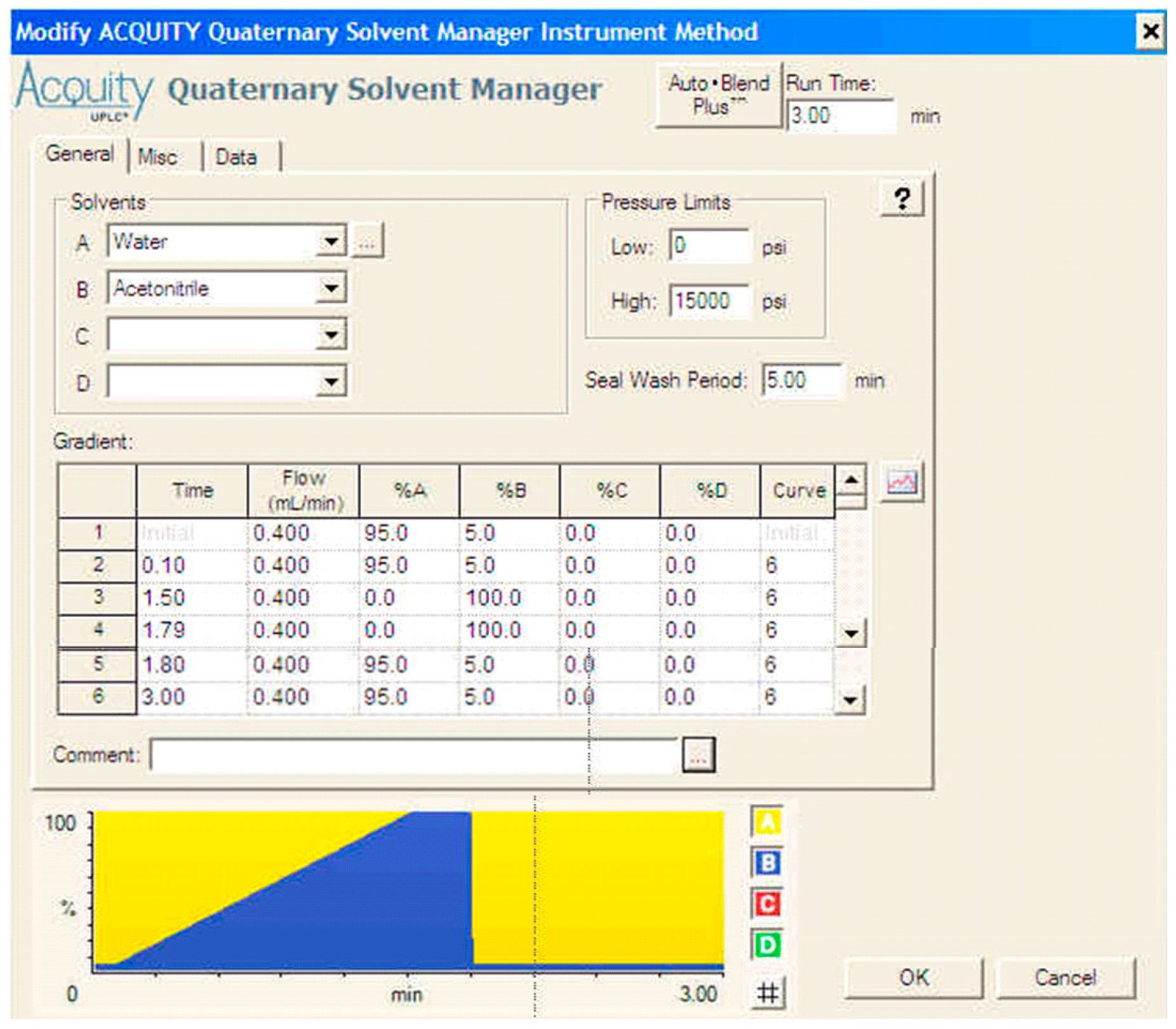
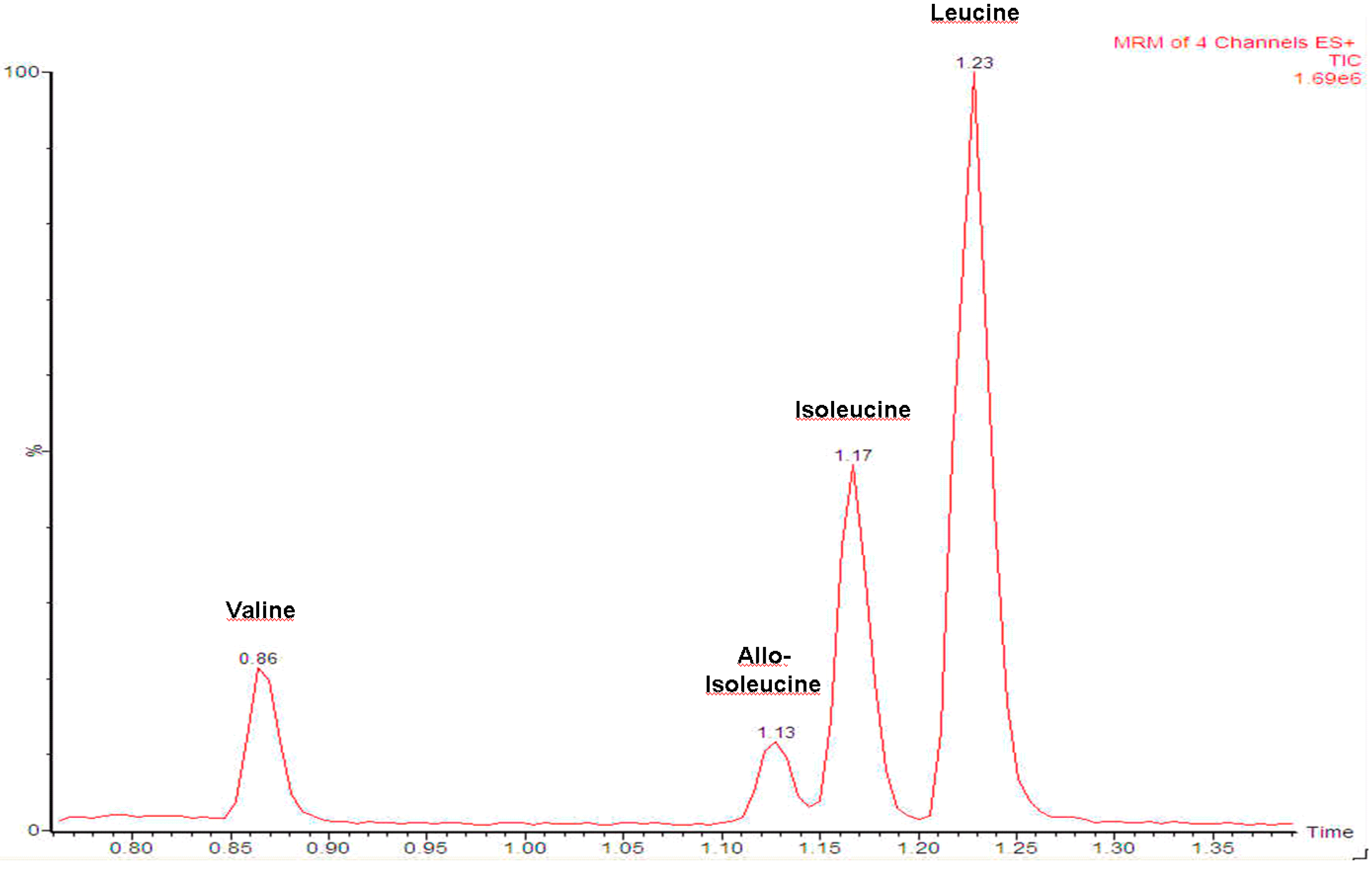

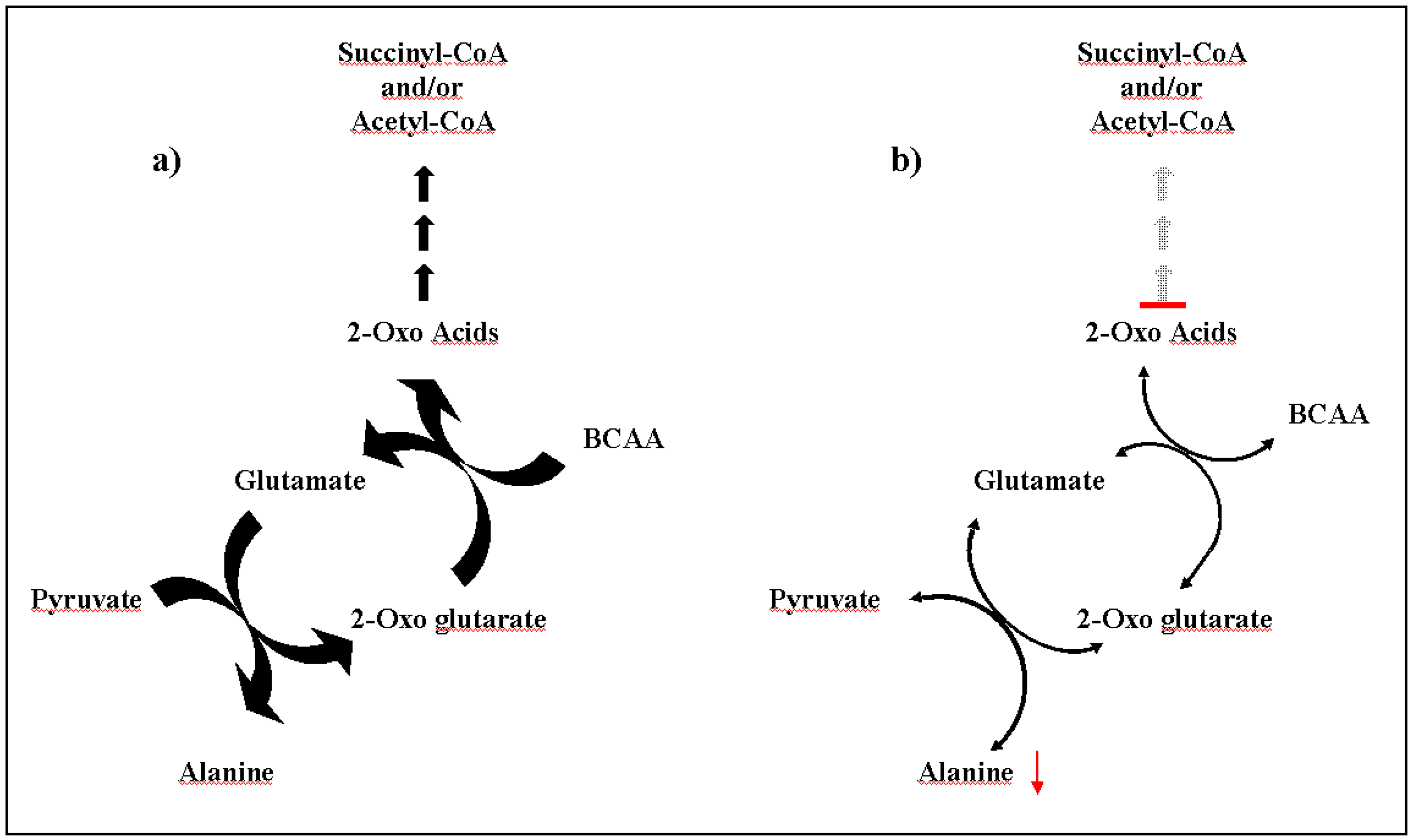
| Compound | Parent [Da] | Daughter [Da] | Dwell Time [s] | Cone Voltage [V] | Collision Energy [eV] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucine * | 132.1 | 86.1 | 0.05 | 22 | 10 |
| 2H3-leucine # | 135.1 | 89.1 | 0.05 | 22 | 10 |
| valine | 118.1 | 72.1 | 0.05 | 22 | 10 |
| 2H8-valine # | 126.1 | 80.1 | 0.05 | 22 | 10 |
| Samples | n | xle * | Leucine * | Isoleucine * | Allo-Ile * | Valine * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| normal | 179 | 137 ± 36 | 72 ± 27 | 37 ± 19 | n.d.–1.9 | 98 ± 46 |
| MSUD | 30 | 247–3530 | 280–4000 | 79–643 | 10–400 | 157–1206 |
| TPN/FP ‡ | 238 | 300 – >4000 | 400 – >4000 | 107 – >3000 | n.d.–7 | 397 – >3000 |
| CV # | 29 | - | 10.3/10.8 | 7.1/12.9 | 12.2/17.5 | 15.3/15.9 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fingerhut, R.; Röschinger, W.; Heck, M. A Rapid and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS-Method for the Separation and Quantification of Branched-Chain Amino Acids from Dried Blood Samples of Patients with Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD). Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2016, 2, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns2020002
Fingerhut R, Röschinger W, Heck M. A Rapid and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS-Method for the Separation and Quantification of Branched-Chain Amino Acids from Dried Blood Samples of Patients with Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD). International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2016; 2(2):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns2020002
Chicago/Turabian StyleFingerhut, Ralph, Wulf Röschinger, and Markus Heck. 2016. "A Rapid and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS-Method for the Separation and Quantification of Branched-Chain Amino Acids from Dried Blood Samples of Patients with Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 2, no. 2: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns2020002
APA StyleFingerhut, R., Röschinger, W., & Heck, M. (2016). A Rapid and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS-Method for the Separation and Quantification of Branched-Chain Amino Acids from Dried Blood Samples of Patients with Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD). International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 2(2), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns2020002







