Correlation of Genotype-Phenotype of Congenital Hypothyroidism Cohort Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Long-Term Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
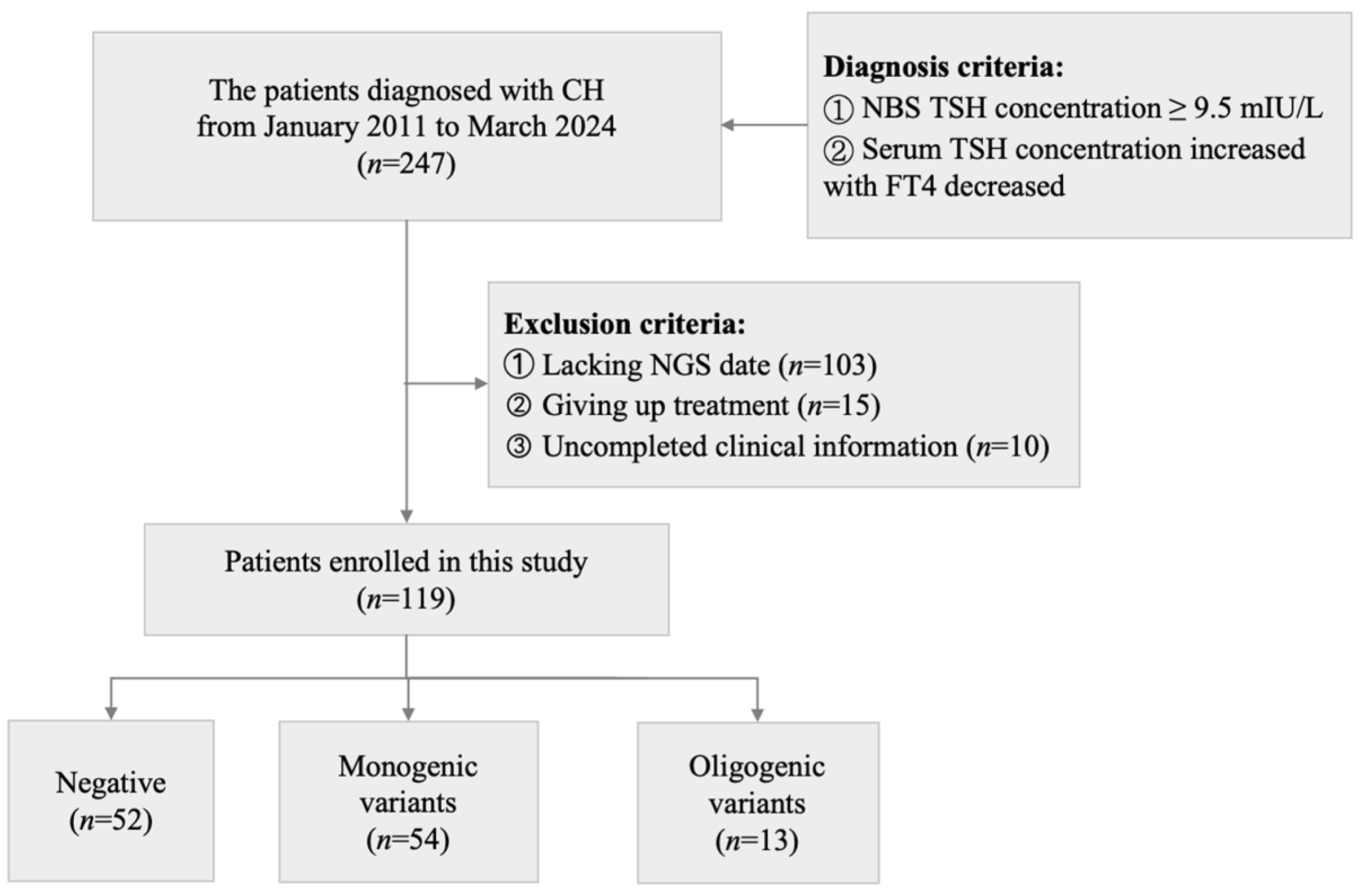
2.2. Participants and Data Collection
2.3. Laboratory Assessments
2.4. Thyroid Ultrasonography Examination
2.5. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing and Variant Annotations
2.6. Classification of Variants in Patients with CH
2.7. Definition of Phenotypic Indicators
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Spectrum of 119 Patients with CH by Next-Generation Sequencing
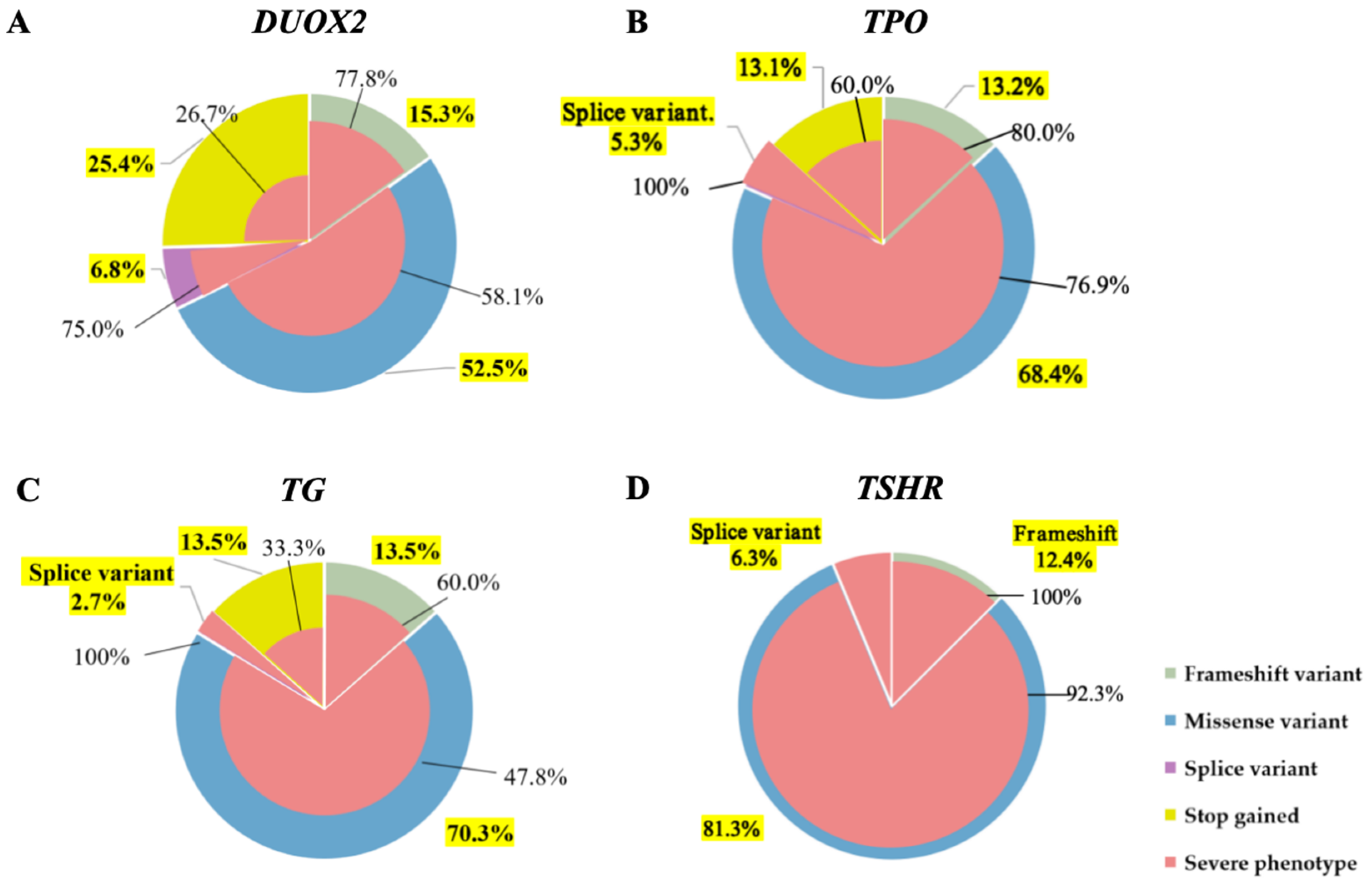
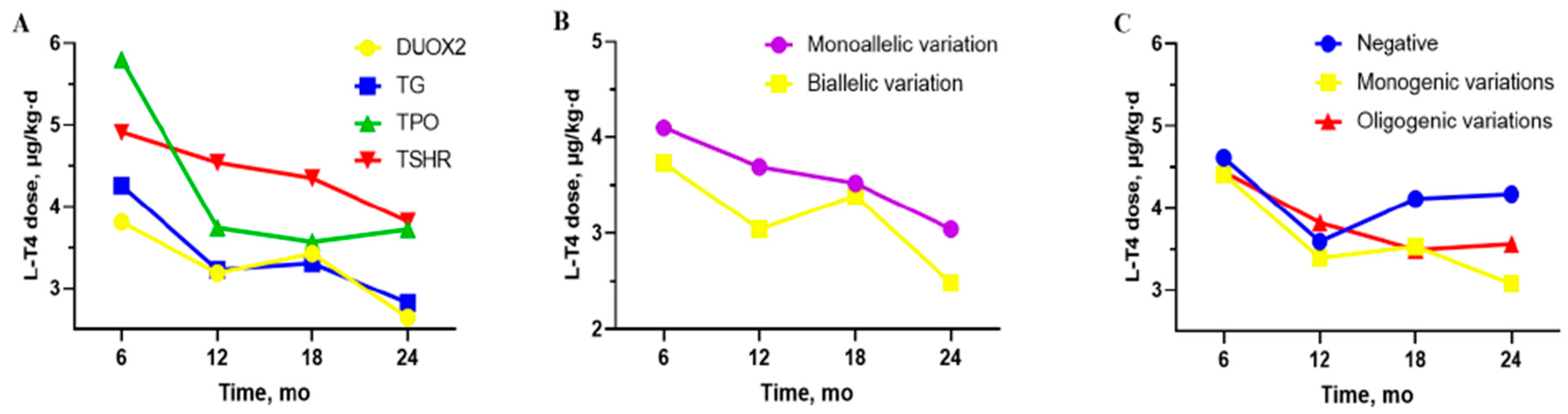
3.2. Relationship Between Different Genes and Clinical Phenotypes
3.3. The Differences Between “DUOX2 Monoallelic Variations” and “DUOX2 Biallelic Variations”
3.4. The Differences Between “Negative”, “Monogenic Variations” and “Oligogenic Variations” Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Trotsenburg, P.; Stoupa, A.; Léger, J.; Rohrer, T.; Peters, C.; Fugazzola, L.; Cassio, A.; Heinrichs, C.; Beauloye, V.; Pohlenz, J.; et al. Congenital Hypothyroidism: A 2020-2021 Consensus Guidelines Update-An ENDO-European Reference Network Initiative Endorsed by the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and the European Society for Endocrinology. Thyroid 2021, 31, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.; van Trotsenburg, A.S.P.; Schoenmakers, N. DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Congenital hypothyroidism: Update and perspectives. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, R297–R317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, C.; Yang, R. Clinical, biochemical characteristics and genotype-phenotype analysis of congenital hypothyroidism diagnosed by newborn screening in China. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 547, 117459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Fagman, H. Development of the thyroid gland. Development 2017, 144, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitropoulos, A.; Molinari, L.; Etter, K.; Torresani, T.; Lang-Muritano, M.; Jenni, O.G.; Largo, R.H.; Latal, B. Children with congenital hypothyroidism: Long-term intellectual outcome after early high-dose treatment. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, S.D.; Van Vliet, G. Prevention of intellectual disability through screening for congenital hypothyroidism: How much and at what level? Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 96, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Tang, C.; Jia, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, W.; Sheng, H.; Feng, Y.; et al. The prevalence, clinical, and molecular characteristics of congenital hypothyroidism caused by DUOX2 mutations: A population-based cohort study in Guangzhou. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Lu, G.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, L.; Yu, B. Targeted next-generation sequencing of thirteen causative genes in Chinese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nakamura, A.; Nakayama, K.; Hishimura, N.; Morikawa, S.; Ishizu, K.; Tajima, T. Targeted next-generation sequencing for congenital hypothyroidism with positive neonatal TSH screening. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, dgaa308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levaillant, L.; Bouhours-Nouet, N.; Illouz, F.; Jager, J.A.; Bachelot, A.; Barat, P.; Baron, S.; Bensignor, C.; De La Perriere, A.B.; Djellas, Y.B.; et al. The severity of congenital hypothyroidism with gland-in-situ predicts molecular yield by targeted next-generation sequencing. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e779–e788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherella, C.E.; Wassner, A.J. Congenital hypothyroidism: Insights into pathogenesis and treatment. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, J.-X.; Yang, C.-Y.; Gao, G.-Q.; Zhu, W.-B.; Han, B.; Zhang, L.-L.; Wan, Y.-Y.; Ye, X.-P.; Ma, Y.-R.; et al. The genetic characteristics of congenital hypothyroidism in China by comprehensive screening of 21 candidate genes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, T.; Gelmini, G.; Paraboschi, E.; Vigone, M.C.; Di Frenna, M.; Marelli, F.; Bonomi, M.; Cassio, A.; Larizza, D.; Moro, M.; et al. A frequent oligogenic involvement in congenital hypothyroidism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Guide of Newborn Screening in China (2010) A/OL. (2010-12-01). Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn (accessed on 20 April 2025). (In Chinese)
- Yao, D.; He, X.; Yang, R.-L.; Jiang, G.-P.; Xu, Y.-H.; Zou, C.-C.; Zhao, Z.-Y. Sonographic measurement of thyroid volumes in healthy Chinese infants aged 0 to 12 months. J. Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Jia, C.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, D. Molecular and clinical characteristics of congenital hypothyroidism in a large cohort study based on comprehensive thyroid transcription factor mutation screening in Henan. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 518, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostopoulou, E.; Miliordos, K.; Spiliotis, B. Genetics of primary congenital hypothyroidism-a review. Hormones 2021, 20, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, A.; Fazzini, C.; Medda, E.; Italian Study Group for Congenital Hypothyroidism. Multiple factors influencing the incidence of congenital hypothyroidism detected by neonatal screening. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2015, 83, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupa, A.; Kariyawasam, D.; Polak, M.; Carré, A. Genetics of congenital hypothyroidism: Modern concepts. Pediatr. Investig. 2022, 6, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-J.; Park, H.-K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Park, H.-D.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-W. DUOX2 mutations are frequently associated with congenital hypothyroidism in the Korean population. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Aoyama, K.; Suzuki, A.; Saitoh, S.; Mizuno, H. Clinical and genetic investigation of 136 Japanese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narumi, S.; Muroya, K.; Asakura, Y.; Aachi, M.; Hasegawa, T. Molecular basis of thyroid dyshormonogenesis: Genetic screening in population-based Japanese patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1838–E1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wu, J.; Ke, S.; Hu, Y.; Fei, A.; Zhen, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhu, K. High prevalence of DUOX2 gene mutations among children with congenital hypothyroidism in central China. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhang, S.; Su, J.; Luo, S.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Qin, H.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Hu, X.; et al. Mutation screening of DUOX2 in Chinese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lu, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Yan, S. Genotypes and phenotypes of congenital goitre and hypothyroidism caused by mutations in dual oxidase 2 genes. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Wu, F.-Y.; Li, X.-S.; Tu, P.-H.; Zhang, C.-X.; Yang, R.-M.; Cui, R.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. TSHR variant screening and phenotype analysis in 367 chinese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Ann. Lab. Med. 2024, 44, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.-J.; Sun, F.; Chen, F.; Fang, Y.; Yan, C.-Y.; Zhang, C.-R.; Ying, Y.-X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.-X.; Wu, F.-Y.; et al. The TPO mutation screening and genotype-phenotype analysis in 230 Chinese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 506, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Liu, S. DUOX2 and DUOXA2 variants confer susceptibility to thyroid dysgenesis and gland-in-situ with congenital hypothyroidism. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.C.; Bikker, H.; Kempers, M.J.; van Trotsenburg, A.P.; Baas, F.; de Vijlder, J.J.; Vulsma, T.; Ris-Stalpers, C. Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, Y.; Nagasaki, K.; Matsui, K.; Mimura, Y.; Mori, A.; Fukami, M.; Takeuchi, Y. Natural course of congenital hypothyroidism by dual oxidase 2 mutations from the neonatal period through puberty. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiaole, L.; Ma, R.; Zhao, D.; Liu, S. Dual oxidase system genes defects in children with congenital hypothyroidism. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzza, M.; Rabbiosi, S.; Vigone, M.C.; Zamproni, I.; Cirello, V.; Maffini, M.A.; Maruca, K.; Schoenmakers, N.; Beccaria, L.; Gallo, F.; et al. The clinical and molecular characterization of patients with dyshormonogenic congenital hypothyroidism reveals specific diagnostic clues for DUOX2 defects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E544–E553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Y.; Heo, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, G.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Lee, B.-H.; Yoo, H.-W. High frequency of DUOX2 mutations in transient or permanent congenital hypothyroidism with eutopic thyroid glands. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2014, 82, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, B. Complicated relationship between genetic mutations and phenotypic characteristics in transient and permanent congenital hypothyroidism: Analysis of pooled literature data. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 6808517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kong, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Ding, G.; Wang, H. Mutational spectrum analysis of seven genes associated with thyroid dyshormonogenesis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 8986475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | DUOX2 (n = 28) | TG (n = 10) | TPO (n = 15) | TSHR (n = 10) | p Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male n (%) | 16 (57.1) | 2 (20.0) | 5 (33.3) | 4 (40.0) | 0.168 |
| Ethnicity n (%) | |||||
| 16 (57.1) b | 2 (20.0) | 1 (6.7) | 1 (10.0) | 0.001 |
| 11 (39.3) c | 8 (80.0) | 13 (86.7) | 8 (80.0) | |
| TSH level at NBS, M (Q1, Q3), mIU/L | 100.0 (79.8, 120.0) | 105.5 (93.1, 147.8) | 172.1 (108.2, 2 21.6) de | 137.5 (98.1, 205.0) | 0.022 |
| TSH level at diagnosis, M (Q1, Q3), mIU/L | 100.0 (83.6, 100.0) | 100.0 (91.2, 100.0) | 100.0 (100.0, 150.0) | 100.0 (100.0, 100.0) | 0.096 |
| FT4 level at diagnosis, M (Q1, Q3), pmol/L | 3.5 (1.7, 6.5) | 3.0 (0.7, 6.9) | 1.64 (0.6, 5.0) | 1.1 (0.2, 4.1) | 0.089 |
| L-T4 dose at 6 mo, mean (SD), μg/kg·d | 3.8 (1.9) | 4.3 (2.0) | 5.8 (2.2) | 4.9 (1.9) | 0.059 |
| L-T4 dose at 12 mo, mean (SD), μg/kg·d | 3.2 (1.2) | 3.2 (1.8) | 3.7 (0.9) | 4.5 (0.7) f | 0.049 |
| L-T4 dose at 18 mo, mean (SD), μg/kg·d | 3.4 (2.2) | 3.3 (1.7) | 3.6 (1.2) | 4.4 (0.6) | 0.458 |
| L-T4 dose at 24 mo, mean (SD), μg/kg·d | 2.6 (1.5) | 2.8 (1.7) | 3.7 (1.4) | 3.8 (1.2) | 0.220 |
| Sever Clinical phenotype n (%) | 11 (39.3) | 3 (30.0) | 12 (80.0) g | 9 (90.0) h | 0.003 |
| Thyroid ultrasound n (%) | 0.017 | ||||
| 1 (3.6) | 2 (20.0) | 1 (6.7) | 4 (40) | |
| 20 (71.4) | 4 (40.0) | 7 (46.7) | 6 (60) | |
| 7 (25.0) | 4 (40.0) | 7 (46.7) | 0 (0) ij | |
| Outcome n (%) | 0.528 | ||||
| 21 (75.0) | 9 (90.0) | 14 (93.3) | 9 (90.0) | |
| 4 (14.3) | 1 (10.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| 3 (10.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (6.7) | 1 (10.0) |
| Case | Sex | Gene | Variation 1 | Variation 2 | TSH Level at NBS, mIU/L | Ultrasound | Clinical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | F | TPO | c.940C > T | c.940C > T | 281 | Normal | PCH |
| NKX2-5 | c.641_642insGCC | ||||||
| DUOX2 | c.2182G > A | ||||||
| 20 | F | TSHR | c.1736C > T | c.1736C > T | 225 | Hypoplasia | PCH |
| DUOX2 | c.1295G > A | ||||||
| 26 | F | SLC26A4 | c.1790T > A | 27 | Hypoplasia | PCH | |
| TSHR | c.154C > A | ||||||
| 27 | M | TSHR | c.394G > C | 178 | Hypoplasia | PCH | |
| GNAS | c.946G > C | ||||||
| 31 | F | TPO | c.2677G > A | 150 | Normal | PCH | |
| TSHR | c.1349G > A | ||||||
| 38 | F | TG | c.7198A > G | c.7198A > G | 74.3 | Hypoplasia | PCH |
| NKX2-1 | c.1054G > A | ||||||
| 39 | F | TSHR | c.243-1G > C | 92.31 | Normal | PCH | |
| TG | c.4859C > T | ||||||
| 52 | F | DUOX2 | c.3175C > T | 163.7 | Hypoplasia | PCH | |
| TPO | c.256G > A | ||||||
| 60 | M | TSHR | c.1942A > T | c.350T > G | 100 | Normal | PCH |
| DUOX2 | c.835G > A | ||||||
| 63 | M | DUOX2 | c.2654G > T | 105.2 | Enlarged | PCH | |
| PAX8 | c.1046C > A | ||||||
| 66 | M | DUOX2 | c.1588A > T | 192.05 | Enlarged | TCH | |
| DUOXA2 | c.412-412delinsTA | ||||||
| 79 | F | TPO | c.1781G > A | c.1781G > A | 221.61 | NA | PCH |
| TPO | c.1905G > C | c.1905G > C | |||||
| JAG1 | c.574T > C | ||||||
| TSHR | c.154C > T | ||||||
| 114 | F | SLC26A4 | c.1003T > C | 424.91 | Hypoplasia | NA | |
| TPO | c.2306G > A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Neonatal Screening. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Lei, X.; Muhetaer, A.; He, J.; Li, L. Correlation of Genotype-Phenotype of Congenital Hypothyroidism Cohort Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Long-Term Observational Study. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2025, 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11040098
Su Y, Lei X, Muhetaer A, He J, Li L. Correlation of Genotype-Phenotype of Congenital Hypothyroidism Cohort Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Long-Term Observational Study. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2025; 11(4):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11040098
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yajie, Xifeng Lei, Ayijiamali Muhetaer, Jinfeng He, and Long Li. 2025. "Correlation of Genotype-Phenotype of Congenital Hypothyroidism Cohort Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Long-Term Observational Study" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 11, no. 4: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11040098
APA StyleSu, Y., Lei, X., Muhetaer, A., He, J., & Li, L. (2025). Correlation of Genotype-Phenotype of Congenital Hypothyroidism Cohort Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Long-Term Observational Study. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 11(4), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11040098






