Abstract
The aim of this study was to observe the outcomes of newborn screening (NBS) in a certain population by using next-generation sequencing (NGS) as a first-tier screening test combined with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). We performed a multicenter study of 29,601 newborns from eight screening centers with NBS via NGS combined with MS/MS. A custom-designed panel targeting the coding region of the 142 genes of 128 inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) was applied as a first-tier screening test, and expanded NBS using MS/MS was executed simultaneously. In total, 52 genes associated with the 38 IEMs screened by MS/MS were analyzed. The NBS performance of these two methods was analyzed and compared respectively. A total of 23 IEMs were diagnosed via NGS combined with MS/MS. The incidence of IEMs was approximately 1 in 1287. Within separate statistical analyses, the positive predictive value (PPV) for MS/MS was 5.29%, and the sensitivity was 91.3%. However, for genetic screening alone, the PPV for NGS was 70.83%, with 73.91% sensitivity. The three most common IEMs were methylmalonic academia (MMA), primary carnitine deficiency (PCD) and phenylketonuria (PKU). The five genes with the most common carrier frequencies were PAH (1:42), PRODH (1:51), MMACHC (1:52), SLC25A13 (1:55) and SLC22A5 (1:63). Our study showed that NBS combined with NGS and MS/MS improves the performance of screening methods, optimizes the process, and provides accurate diagnoses.
1. Introduction
Newborn screening (NBS) for inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) is a successful public health project for detecting life-threatening or long-term health conditions to reduce morbidity and mortality [1]. Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) is a key technique for accessing the NBS program that allows for the rapid detection of many metabolites in dried blood spots (DBS). Measurement of amino acids and acylcarnitines enables the identification of approximately 40 to 50 IEMs a few days after birth. In general, expanded NBS using MS/MS has been widely used worldwide with several advantages, including rapid and convenient procedures, significantly increased detection of IEMs [2], early diagnosis and recognition of death [3] and cost effectiveness [4]. However, the positive predictive value (PPV) is low, and the results may be nonspecific, with additional false positives [5], and poor sensitivity, with additional false negatives [5]. Moreover, when multiple diseases are screened via single-tier analysis of one marker, MS/MS cannot distinguish among different diseases and subtypes, which is not conducive to timely accurate diagnosis and treatment [6].
Second-tier tests, secondary biomarkers, postanalytical tools (R4S and CLIR) [7,8] and random forest (RF) machine learning [9] have been used to improve the performance of NBS via MS/MS. False-positive rates can indeed be reduced, but performance improvements are still limited [10]. Confirmation of a biochemical diagnosis is usually achieved by identifying pathogenic genetic variants; this diagnostic trajectory is often a protracted and lengthy process resulting in delays in diagnosis, and importantly, therapeutic intervention for these rare conditions is also postponed [11].
With advances in next-generation sequencing(NGS) technologies, an increasing number of genetic diseases of unknown cause with nonspecific presentations are best diagnosed by exome sequencing (ES) or NGS [12]. Moreover, evidence demonstrates that ES and NGS are reliable for detecting pathogenic variants in genomic material extracted from DBS [13,14]. Furthermore, confirmatory or second-tier testing using ES/NGS may improve the performance of NBS [15,16]. Newborn genetic screening has also been proven to be successful when using single monogenetic disease or target genetic sequencing panels [17]. Nevertheless, the National Bureau of California (NBSeq) project showed that ES alone was insufficiently sensitive or specific to be a primary screening tool for most NBS IEMs [18]. Thus, we investigated the outcomes of NBS in a certain population via NGS via a multicenter approach in which a gene panel was used for a general newborn population as a first-tier screening test [19] combined with MS/MS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment and Sample Collection
A total of 29,601 newborn born from February 2021 to December 2021 were enrolled from 8 newborn screening centers located in the east, west, south, and north of China, including Shanghai Xinhua Hospital (SH), Chongqing Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital (CQ), Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center (GZ), First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province (YN), Hainan Women and Children’s Medical Center (HN), Jinan Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital (JN), Shijiazhuang Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital (SJZ), and Inner Mongolia Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital (NMG). These centers were selected to represent the nationwide population. DBS samples (at least four 8 × 8 mm pieces) were collected between 3 and 7 days after birth, dried at room temperature, and stored at 4 °C. The amount of DBS in each specimen was tested for genetic NBS and expanded NBS by MS/MS simultaneously. Informed consent was obtained from all participants, and approval was obtained from the institutional review board of each center (XHEC-C-2020-054-1). The project has been registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2100043025) and the National Health Security Information Platform Medical research registration information system (MR-44-21-016154).
2.2. Panel of Screened Disorders
For MS/MS screening, the PE kit nonderivative method (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to assess 38 amino acid disorders/organic acid disorders/fatty acid oxidation disorders (AAs/OAs/FAODs), including 15 amino acid disorders (AAs), 11 organic acid disorders (OAs), and 12 fatty acid oxidation disorders (FAODs). For genetic screening, a custom-designed panel targeting the coding region of the 142 genes (128 diseases) (Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA, USA) was applied. The library was sequenced with a minimum depth of 100× coverage on a genetic sequencer (MGI). An in-house verified variant calling pipeline was used to analyze single nucleotide variants, small insertions and deletions, and copy number variants (CNV) including CNVs involving 2 or more continuous exons in DMD, exon 7 deletion of SMN1, and common CNVs involving HBA1/HBA2/HBB [19]. A total of 52 genes associated with the 38 IEMs were tested by MS/MS and are summarized in Supplemental Table S1.
2.3. Expended NBSs by MS/MS
DBS samples from 29,601 newborns were analyzed via the nonderivative method (Neobase TM) with MS/MS at the newborn screening centers. In total, 11 amino acids, 30 acylcarnitines, free carnitine, and succinylacetone were tested with regard to 38 kinds of IEMs (Supplemental Table S1). Every disease had two or more indicators, including metabolites and ratios. Different newborn screening centers have different reference cutoff values, and a screening-positive result was considered according to the reference cutoff value of each screening center, and the patient was recalled for review.
2.4. NBS by NGS
DBS samples from 29,601 newborns were submitted to the clinical laboratories of the Beijing Genomics Institute for genetic sequencing. Genomic DNA was extracted from DBS using a MagPure Tissue DNA KF Kit (Magen, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China). DNA fragmentation, end repair, and 3′ end tailing were performed using a VAHTS6 Universal Plus Fragmentation Module (Vazyme, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China). A custom-designed panel targeting the coding region of the 142 genes (128 diseases) (Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA, USA) was applied. Consensus about the criteria for variant prioritization and suspicious positive criteria for genetic screening was reached in multicenter studies [19]. A screening-positive result for a gene was defined as a pathogenic (P) or likely pathogenic (LP) variant with a matching inheritance pattern without knowledge of the phenotype and clinical features of the tested individual. Patients with positive results and their families were recalled for confirmatory testing.
2.5. Diagnosis
High-risk infants whose screening was positive by either base-NGS or base-MS/MS screening were referred for confirmatory tests and follow-up. The confirmatory tests varied for different diseases and included blood biochemical tests such as complete blood count, kidney function, liver function, ammonia, lactic acid, homocysteine, and urine organic acids and family inheritance validation, etc. Diagnostic decisions were based on genotype, MS/MS results, and confirmatory tests.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
We present the characteristics of the study participants as a whole and separately by MS/MS and genetic screening. For categorical data, summary data are reported as frequencies and percentages. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 17.0 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Performance of NBS by NGS Combined with MS/MS
Among 29,601 newborns, 23 cases (6 with MMA (5 cblC-MMA, 1 cblA-MMA); 5 with PCD; 3 with PKU; 2 with SCADD; 2 with IBD; 1 with NICCD; 1 with MCAD; 1 with CPTII; 1 with maple syrup urine disease, MSUD; 1 with MADD) of neonatal IEMs involving amino acid, organic acid, or fatty acid metabolism disorders were diagnosed (Table 1). The incidence of IEMs was approximately 1 in 1287 patients.

Table 1.
Incidence and carrier frequencies of inborn errors of metabolism detected by next-generation sequencing combined with tandem mass spectrometry among 29,601 newborns.
As shown in Table 2, the performances of genetic screening and MS/MS screening were compared and analyzed among 29,601 neonates from participating centers.

Table 2.
Comparison of conventional newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry using dried blood spot testing versus next-generation sequencing in a multicenter population of neonates.
3.2. Assessment of NGS as a First-Tier Screening Test
For genetic screening alone and without MS/MS synchronization screening, 24 (0.08%) patients were positive, and 24 (100%) patients were recalled for review. Seventeen IEMs were diagnosed; there were seven false positives. Of these seven patients, three had complex heterozygous variants, one had a homozygous variant in the PAH gene, one had complex heterozygous variation in the PRODH gene, one had complex heterozygous variation in the ACADSB gene, and the last one, who is a male, had a hemizygote variation in the OTC gene with an X-linked disorder. All these variations were P or LP variants and matched the family inheritance pattern when these patients were recalled for confirmatory tests. However, all of them were unaffected based on normal biochemical results (Supplemental Table S3).
Six cases would have been missed but with the results of MS/MS screening and the recall review received positive results. These six cases had MSUD, IBD, PCD, SCADD, MADD, and CPTII, respectively. The PPV of genetic screening was 70.83%, and the sensitivity was 73.91%.
3.3. Assessment of MS-MS as a First-Tier Screening Test
For MS/MS screening alone, 507 (1.71%) patients were positive, and 397 (78.3%) were recalled for review. In total, 21 patients with IEMs were diagnosed without genetic synchronization screening. There were 376 false positives, and all of these patients were recalled for diagnosis or censoring but had normal results.
Two patients were missed but had positive genetic screening results: one with NICCD and another with cblC-MMA. The PPV of MS/MS screening was 5.29%, and the sensitivity was 91.3%.
3.4. Biochemical and Molecular Characteristics of the Diagnosed Patients
Eleven different genes were found among the 23 diagnosed patients, including MMACHC, MMAA, ACAD8, ACADS, ACADM, PAH, SLC22A5, SLC25A13, CPT2, DBT, and ETFA, all exhibited recessive inheritance, involving 34 different variants (Table 3). Among the 23 patients diagnosed by genetic screening combined with MS/MS, 17 (P1–P17) were genetic-screening positive with positive or negative MS/MS results, and 6 (P18–P23) were genetic-screening negative with positive MS/MS results. In one of these six patients, P23, the detected ETFA gene was not included in the gene panel; the others were detected to carry at least one variant of uncertain significance (VUS). Two patients (P5 and P17) were MS/MS-screening negative with positive genetic results. One patient diagnosed with cblC-MMA (P5) was compound heterozygous for two LP missense variants (c.482G>A and c.565C>T) of the MMACHC gene with a normal propionylcarnitine (C3) level but abnormal confirmatory test results during the recall review. Another patient diagnosed with NICCD (P17) was compound heterozygous for two P variants (c.1638_1660dup and c.852_855delTATG) of the SLC25A13 gene with a normal citrulline (Cit) level at the first screening but an increased Cit level at reexamination. Of these six confirmed cases of MMA, four (P2–P5) had normal propionylcarnitine (C3) levels, but three (P2–P4) had true-positive MS/MS results indicating that methionine (Met) was decreased or that its ratio with acetylcarnitine (C3/C2) was increased. Moreover, confirmatory test results showed that methylmalonic acid in urine (27.09–38.06 mmol/mol creatinine) and blood serum homocysteine (31.8–123.9 µmol/L) were increased. Notably, all three of these patients were cblC-deficient and harbored c.80A>G complex heterozygous variants of the MMACHC gene. Of the five confirmed cases of PCD, three carried c.1400C>G complex heterozygous variants, and one had a c.1400C>G homozygous variant of the SLC22A5 gene.

Table 3.
Diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism using next-generation sequencing combined with tandem mass spectrometry.
3.5. Carrier Frequencies and Geographical Distribution of Targeted Genes
The carrier frequencies of variants in 52 genes were calculated (Table S2). The five genes related to the highest variant carrier frequencies in these newborns were PAH (1:42), PRODH (1:51), MMACHC (1:52), SLC25A13 (1:55) and SLC22A5 (1:63). Variants of the PAH and MMACHC genes had higher carriage rates in the northern participating units NMG, JN, and SJZ, which was consistent with the regional distribution of confirmed cases. SLC25A13 and SLC22A5 had higher carriage rates in the southern participating units GZ and HN, which was also consistent with the geographical distribution of confirmed cases. The composition and geographical distribution of the variants of these four genes in the healthy population were determined (Supplemental Figures S1–S4). The top ten variants of these four genes are summarized in Figure 1. These three variants of the PAH gene that were the most common in the healthy population were c.728G>A, c.721C>T, and c.611A>G. The top three variants of the MMACHC gene were c.609G>A, c.658_660delAAG, and c.482G>A. The variants c.852_855delTATG/c.790G>A were found to be SLC25A13 gene hotspots. The variants c.1400C>G and c.51C>G were SLC22A5 gene hotspots. In addition, the genes with a carrier rate greater than 1:550 were MADD (ETFDH), SCADD (ACADS), BH4D (PTS), IBD (ACAD8), MCAD (ACADM), VLCAD (ACADVL), BTD (BTD), 3-MCC (MCCC1, MCCC2), CACT (SLC25A20), CTLN1 (ASS1), PA (PCCB), and HHHS (SLC25A15).
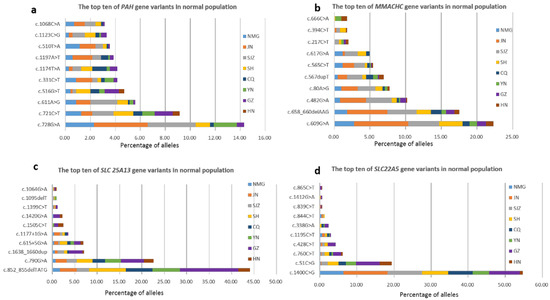
Figure 1.
The top ten of four genes’ variants in normal population and geographical distribution in this multicenter study. (a) The top ten PAH gene variants. (b) The top ten MMACHC gene variants. (c) The top ten SLC 25A13 gene variants. (d) The top ten SLC22A5 gene variants.
4. Discussion
Genetic NBS has been proven to be successful when used to evaluate monogenic diseases in China. In combination, genetic NBS and traditional NBS can complement each other [20]. This is the latest, prospective pilot study of NBS using NGS combined with MS/MS results for IEMs.
Our results showed that genetic screening improved the specificity and sensitivity of MS/MS screening. After MS/MS screening alone and subsequent confirmation via genomic sequencing, the PPV was 5.29%, and the number of false-positive patients was 376. However, for NGS, a first-tier newborn screening test, the PPV reached 70.83%, which means that there were fewer false positives and fewer unnecessary follow-up visits [5]. In this study, although we conducted genetic screening combined with MS/MS screening and recalled both genetic and MS/MS screening positive-patients simultaneously, it seems that the number of false positives in this study did not decrease. However, if combined screening is routine in the future, these MS/MS screening false-positive cases, especially those that are boundary and negative with genetic screening, should not be recalled. The sensitivity ranged from 91.3% to 100%. The two missed patients were MS-MS-screening negative but were revealed by genetic screening to be NICCD and cblC-MMA, the two most common diseases identified during newborn screening in China [21]. Elevated citrulline levels and several citrulline-based ratios are key indices of NICCD screening by MS/MS, but these indices are not very sensitive because citrulline levels might not increase immediately after birth [22,23]. Even at elevated levels, MS/MS could not determine whether the patient had NICCD or type I citrullinemia. The MMA concentration was identified by MS-MS using specific cutoff values for propionylcarnitine (C3) and its ratio with acetylcarnitine (C2). This patient (P5) with cblC-MMA was missed because her C3 level and C3/C2 were normal but with compound heterozygous for two missense variants (c.482G>A/c.565C>T) of the MMACHC gene; the variant c.482G>A is associated with milder disease [24] and late onset [25]. Therefore, these two missing patients were very difficult to avoid by MS/MS. In addition to the patient (P5), three patients (P2–P4) with cblC deficiency had normal C3 levels. However, they were defined as being true-positive cases by MS/MS screening only for high C3/C2 or low Met levels (Table 3). Each screening center may have its own interpretation criteria, and most screening centers will follow the main indicator of C3 increase before considering this ratio. The judgment of negative or positive involves more the interpretation standards of different screening centers. Thus, the combined screening method can optimize processes for rapid diagnosis.
Well-recognized genotype-phenotype correlations are helpful for the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of diseases. All three of the patients harbored the c.80A>G complex heterozygous variant of the MMACHC gene. The variant c.80A>G is reported to be associated with late-onset diffuse lung disease (DLD) [26] and prominent renal complications, and the most frequent renal pathological manifestation is thrombotic microangiopathy [27]. The variant c.80A>G should be considered to indicate disease of the cardiovascular system [25]. Analysis of the composition of the MMACHC gene variants in the healthy population (Supplemental Figure S2) revealed the four most common variants to be c.609G>A, c.658_660delAAG, c.482G>A, and c.80A>G, which is basically consistent with reported data for Chinese patients. The most common c.609G>A variant is reported to likely lead to early-onset cblC disease [28]. However, patients with the c.80A>G and c.609G>A compound heterozygotic variant genotypes had late-onset disease with neuropsychiatric symptoms and pulmonary hypertension [25]. In this study, two patients (P2 and P3) had the same genotype. In addition, the spread of the c.80A>G and c.609G>A variants in Chinese patients has been reported to be caused by a founder effect [29].
Although seven patients were defined as having false-positive results in genetic screening (Supplemental Table S3), they met the genetic diagnosis criteria but had biochemically normal or borderline cutoff values and did not have any clinical symptoms. Among the four patients with variants in the PAH gene, one had the c.516G>T homozygous variant, one had the c.516G>T compound heterozygous variant associated with mild PKU [30], one had the c.1068C>A compound heterozygous variant, and one had the c.728G>A compound heterozygous variant; these two variants are clearly associated with classic PKU [31]. One patient with c.1322T>C/c.273+1G>C in the PRODH gene had the same genotypes as the reported patient, with no clinical manifestations observed at 5 years or 7 months [32]. The other patient was a male with suspected OTCD and the c.830 G>A variant in the OTC gene was found in one patient with late-disease onset [33]. X-linked ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD), the most common urea cycle defect [34], is difficult to detect by expanded NBS due to the insensitivity of the citrulline indicator [35]. A patient is defined as positive for genetic screening and negative for MS/MS with a normal citrulline level in the early stage. The onset of OTCD symptoms is extremely variable [36]. Considering the possibility of late onset, long-term attention and follow-up are needed for these patients, which is a major challenge for genetic screening. At the same time, for NGS, the epigenetics of some diseases should also be considered [37]. However, due to the fact that this study is only an NGS sequencing panel of genes, it is limited.
Combined with MS-MS screening, the sensitivity of genetic screening was improved by this approach. In our study, genetic screening alone, without knowledge of the phenotype and clinical features of the tested individuals, was insufficiently sensitive (73.91%) as a first-tier screening test, with a sensitivity lower than that of MS/MS (91.3%). This finding is comparable with the reference sensitivity of 88% for ES compared to 99.0% for MS/MS [18]. Based on biochemical positive results, except for one patient (P23) for whom the genetic method was not used, five genetic screening false-negative cases were considered positive in reanalysis, which elevated the sensitivity to 95.6% (22/23). Moreover, MS-MS screening supplements the deficiencies of genetic screening. The case (P23) with the ETFA gene not included in the gene panel was detected by MS-MS screening and then diagnosed by ES, which emphasizes the importance of genetic selection in genetic screening [20].
Due to the small sample size, the epidemiological incidence rate could not be statistically analyzed. However, according to the healthy population carrying rate and Hardy Weinberg’s law [38], the population disease incidence rate could be estimated. The highest incidence of genetic metabolic disease screening by MS/MS was detected in the HPA population in China [21], which was consistent with the highest carrier frequency of PAH (up to 1/42) in this study. The prevalence of MMA, PCD, and NICCD, which are associated with a high incidence of disease in China [21], was also consistent with the carrier rate. Moreover, we clearly delineated the geographical distribution of diseases and genes. PKU and MMA are the two most common disorders in the northwestern Chinese population [39,40], and PCD is the most common disorder in the southern Chinese population [41,42]. In this study, the carriage rates of PAH, MMACHC, SLC25A13, and SLC22A5 gene variants were consistent with the regional distribution of confirmed cases. Supplemental Table S2 shows that the carrier rate of the SLC25A20 variant was the highest in GZ. GZ accounted for the largest proportion of the hotspots of the c.199-10T>G variant of SLC25A20 in the healthy population (Supplemental Figure S5), which was related to the founder effect [43] and explained by the incidence of CACT being reportedly higher in the Guangdong area than in the other regions [3]. For the same reason, the hotspots PAH and MMACHC in the healthy population were distributed mainly in JN and SJZ, and the hotspots of SLC25A13 and SLC25A5 in the healthy population were distributed mainly in GZ (Figure 1).
In conclusion, NBS-based NGS combined with MS/MS significantly improved the sensitivity and specificity, optimized the process, and provided accurate diagnoses. With general support for genetic screening [44] and the guidance of expert consensuses about the application of NGS in the screening of monogenic diseases [20], it is believed that genetic screening combined with MS/MS can better serve in NBS for IEMs. The cohort of NBS could be implemented for future recommendations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijns10020028/s1. Figure S1: The composition and geographical distribution of PAH gene variants in normal population of this pilot study, Figure S2: The composition and geographical distribution of MMACHC gene variants in normal population of this pilot study, Figure S3: The composition and geographical distribution of SLC25A13 gene variants in normal population of this pilot study, Figure S4: The composition and geographical distribution of SLC22A5 gene variants in normal population of this pilot study, Figure S5:The composition and geographical distribution of SLC25A20 gene variants in normal population of this pilot study, Table S1: The list of 52 genes associated with the 38 IEMs, Table S2: The carrier frequencies of 52 genes, Table S3: Characteristics of 7 unaffected cases for genetic screening.
Author Contributions
Y.H., J.F. and L.H. had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. C.T., L.L., T.C. and Y.L. contributed equally to this work. Conceptualization, Y.H., J.F. and L.H.; data curation, C.T., L.L., T.C. and Y.L; formal analysis, B.Z. (Bo Zhu), Y.Z., Y.Y. and X.L; writing—original draft, C.T., L.L., T.C. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.H., J.F., L.H., H.Z., X.W., B.Z. (Baosheng Zhu), J.M., C.H., B.Z. (Bo Zhu), Y.Z., Y.Y., X.L., C.T., L.L., T.C. and Y.L.; supervision, Y.H., J.F. and L.H.; project administration, Y.H., J.F., L.H., H.Z., X.W., B.Z. (Baosheng Zhu), J.M. and C.H. The manuscript was critically reviewed for important intellectual content by all the authors, and the final version was approved by all the authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Project Plan of the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (202140346), Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou (202201020618), and the Application Technology Research and Development Project of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2020GG0119). We also received support in sequencing from BGI Genomics. The authors confirm their independence from the sponsors; the content of the article has not been influenced by the sponsors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethics approval was obtained from the institutional review board of each center before conducting the study (XHEC-C-2020-054-1).
Informed Consent Statement
Participants or their parents or legal guardian signed consent for study participation after the risks and benefits had been explained. Consent extends to the purposes of the study, the limitations of the tests and the understanding and approval of data storage, data analysis and management.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available to qualified researchers on request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the newborns and their families who participated in the study and all the medical personnel from the eight screening centers. We also thank Chunjing Xu (Tianjin Medical Laboratory, BGI-Tianjin), Chunna Fan (BGI Genomics), Weiwei Jing (Tianjin Medical Laboratory, BGI-Tianjin) and Hui Huang (BGI Genomics) for their assistance in sequencing experiment, data curation and variant interpretation.
Conflicts of Interest
No financial or non-financial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. The funder had no role in the design of the study or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| MMA | Methylmalonic academia |
| cblC-MMA | Methylmalonic academia, Cobalamin C defect |
| cblA-MMA | Methylmalonic acidemia, Cobalamin A defect |
| PCD | Primary carnitine deficiency |
| PKU | Phenylketonuria |
| SCADD | Short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| IBD | Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| NICCD | Citrin deficiency |
| MCAD | Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| CPTII | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency |
| MSUD | Maple syrup urine disease |
| MSUD (type II) | Maple syrup urine disease, type II |
| MADD | Multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| OTCD | Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency |
| SH | Shanghai Xinhua Hospital |
| GZ | Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center |
| JN | Jinan Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital |
| SJZ | Shijiazhuang Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital |
| CQ | Chongqing Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital |
| YN | First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province |
| NMG | Inner Mongolia Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital |
| HN | Hainan Women and Children’s Medical Center |
| P | Pathogenic |
| LP | Likely pathogenic |
| VUS | Variant of uncertain significance or unclassified |
| Het | Heterozygous |
| Hom | Homozygous |
| AR | Autosomal recessive |
| NBS | Newborn screening |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| IEMs | Inborn errors of metabolism |
| MS/MS | Tandem mass spectrometry |
| DBS | Dried blood spots |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
References
- Loeber, J.G.; Platis, D.; Zetterstrom, R.H.; Almashanu, S.; Boemer, F.; Bonham, J.R.; Borde, P.; Brincat, I.; Cheillan, D.; Dekkers, E.; et al. Neonatal Screening in Europe Revisited: An ISNS Perspective on the Current State and Developments Since 2010. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Meli, C.; Raudino, F.; Pittala, A.; Arena, A.; Barone, R.; Giuffrida, F.; Iacobacci, R.; Muccilli, V.; Sorge, G.; et al. Expanded Newborn Screening Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Seven Years of Experience in Eastern Sicily. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2018, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Liu, S.; Wu, M.; Lin, S.; Lin, Y.; Su, L.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y. Clinical and molecular characteristics of carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency: Experience with six patients in Guangdong China. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Zhou, D.; Huang, X.; Dong, H. Newborn screening for inherited metabolic diseases using tandem mass spectrometry in China: Outcome and cost-utility analysis. J. Med. Screen. 2022, 29, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarini, B.A.; Christakis, D.A.; Welch, H.G. State newborn screening in the tandem mass spectrometry era: More tests, more false-positive results. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, E.; Kölker, S.; Gleich, F.; Feyh, P.; Hörster, F.; Haas, D.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Morath, M.; Gramer, G.; Röschinger, W.; et al. Combined Newborn Screening Allows Comprehensive Identification also of Attenuated Phenotypes for Methylmalonic Acidurias and Homocystinuria. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younesi, S.; Yazdani, B.; Taheri Amin, M.M.; Saadati, P.; Jamali, S.; Modarresi, M.H.; Savad, S.; Amidi, S.; Razavi, H.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Incorporation of second-tier tests and secondary biomarkers to improve positive predictive value (PPV) rate in newborn metabolic screening program. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.L.; Marquardt, G.; McHugh, D.M.; Currier, R.J.; Tang, H.; Stoway, S.D.; Rinaldo, P. Postanalytical tools improve performance of newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tang, Y.; Cowan, T.M.; Enns, G.M.; Zhao, H.; Scharfe, C. Reducing False-Positive Results in Newborn Screening Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombrone, D.; Giocaliere, E.; Forni, G.; Malvagia, S.; la Marca, G. Expanded newborn screening by mass spectrometry: New tests, future perspectives. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordaunt, D.; Cox, D.; Fuller, M. Metabolomics to Improve the Diagnostic Efficiency of Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, T.; Wapner, R.J. Genetic testing for unexplained perinatal disorders. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2021, 33, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boemer, F.; Fasquelle, C.; d’Otreppe, S.; Josse, C.; Dideberg, V.; Segers, K.; Guissard, V.; Capraro, V.; Debray, F.G.; Bours, V. A next-generation newborn screening pilot study: NGS on dried blood spots detects causal mutations in patients with inherited metabolic diseases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, J.B.; Lescai, F.; Grove, J.; Baekvad-Hansen, M.; Christiansen, M.; Hagen, C.M.; Maller, J.; Stevens, C.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; et al. High-Quality Exome Sequencing of Whole-Genome Amplified Neonatal Dried Blood Spot DNA. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.M.; Park, K.S.; Kang, Y.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Park, I.; Chae, H.W.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, K.A.; Kim, J.W. A New Integrated Newborn Screening Workflow Can Provide a Shortcut to Differential Diagnosis and Confirmation of Inherited Metabolic Diseases. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.J.; Park, S.; Lee, E.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Park, H.D.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.W. A Population-Based Genomic Study of Inherited Metabolic Diseases Detected Through Newborn Screening. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, D.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, R.; Yang, J.; He, Q.; Zhu, B.; You, Y.; Xiao, R.; et al. Application of a next-generation sequencing (NGS) panel in newborn screening efficiently identifies inborn disorders of neonates. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, A.N.; Gallagher, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Currier, R.J.; Amatuni, G.; Bassaganyas, L.; Chen, F.; Kundu, K.; Kvale, M.; Mooney, S.D.; et al. The role of exome sequencing in newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Fan, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Jin, W.; et al. Genomic Sequencing as a First-Tier Screening Test and Outcomes of Newborn Screening. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2331162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Wang, J.; Xiao, R.; Wu, B.B.; Zou, C.C.; Wu, D.W.; Wang, H.; Zou, H.; Han, L.S.; Yang, L.; et al. Application of next generation sequencing in the screening of monogenic diseases in China, 2021: A consensus among Chinese newborn screening experts. World J. Pediatr. 2022, 18, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.T.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tu, W.J.; Wang, W.P.; Gong, L.M.; Wang, D.W.; Ye, Y.T.; Fang, S.G.; Jing, P.W. Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism in mainland china: 30 years of experience. JIMD Rep. 2012, 6, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamamori, A.; Fujimoto, A.; Okano, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Saheki, T.; Tagami, Y.; Takei, H.; Shigematsu, Y.; Hata, I.; Ozaki, H.; et al. Effects of citrin deficiency in the perinatal period: Feasibility of newborn mass screening for citrin deficiency. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 56, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chengfang, T.; Sichi, L.; Yi, F.; Huifen, M.; Haiping, L.; Jinwen, F.; Lixin, Y.; Guoqing, W.; Li, L.; Yonglan, H. Newborn screening program and blood amino acid profiling in early neonates with citrin deficiency. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2019, 57, 797–801. [Google Scholar]
- Almannai, M.; Marom, R.; Divin, K.; Scaglia, F.; Sutton, V.R.; Craigen, W.J.; Lee, B.; Burrage, L.C.; Graham, B.H. Milder Clinical and Biochemical Phenotypes Associated with the c.482G>A (p.Arg161Gln) Pathogenic Variant in Cobalamin C Disease: Implications for Management and Screening. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; He, R.; Song, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.; et al. Late-onset cblC defciency around puberty: A retrospective study of the clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, N.; Liu, X.; Meng, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhao, S. Combined methylmalonic acidemia and homocysteinemia presenting predominantly with late-onset diffuse lung disease: A case series of four patients. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, H.; Yao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, X.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, F. Prominent renal complications associated with MMACHC pathogenic variant c.80A > G in Chinese children with cobalamin C deficiency. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1057594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, D.; Cai, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Mutation spectrum of MMACHC in Chinese pediatric patients with cobalamin C disease: A case series and literature review. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 62, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Chiang, S.H.; Lin, S.P.; Han, L.S.; Qi, Y.; Hsiao, K.J.; Liu, T.T. Mutation spectrum of MMACHC in Chinese patients with combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 55, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Li, N.; Jia, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Deng, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, J. Correlation between genotype and the tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenotype in Chinese patients with phenylketonuria. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; He, C.; Li, J.; Tao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, J.; Deng, Y.; et al. Analysis of the genotype-phenotype correlation in patients with phenylketonuria in mainland China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Jia, L.; Gong, M.; Ma, C.; Feng, J. Tandem Mass Spectrometry Screening and Gene Mutation Analysis of Neonatal Hyperprolinemia. J. Int. Reprod. Health/Fam. Plan. 2022, 41, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchman, M.; Morizono, H.; Rajagopal, B.S.; Plante, R.J.; Allewell, N.M. Identification of ‘private’ mutations in patients with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 1997, 20, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Hernández, E.; Aldámiz-Echevarría, L.; Castejón-Ponce, E.; Pedrón-Giner, C.; Couce, M.L.; Serrano-Nieto, J.; Pintos-Morell, G.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Martínez-Pardo, M.; García-Silva, M.T.; et al. Urea cycle disorders in Spain: An observational, cross-sectional and multicentric study of 104 cases. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Han, F.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, H.; Ye, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhan, X.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of 69 Chinese patients with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldovic, L.; Abdikarim, I.; Narain, S.; Tuchman, M.; Morizono, H. Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency: A Mutation Update. J. Genet. Genom. 2015, 42, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, M.A.; Guerrini, R.; Guéant, J.L.; Morrone, A. PRDX1 gene-related epi-cblC disease is a common type of inborn error of cobalamin metabolism with mono- or bi-allelic MMACHC epimutations. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffelman, J.; Weir, B.S. The transitivity of the Hardy–Weinberg law. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2022, 58, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Cai, H.; Li, H.; Ji, Z.; Gu, M. Quantification of Differential Metabolites in Dried Blood Spots Using Second-Tier Testing for SCADD/IBDD Disorders Based on Large-Scale Newborn Screening in a Chinese Population. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 757424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Qiang, R.; Song, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, R.; Yu, W.; Feng, M.; Yang, L.; et al. Spectrum analysis of inborn errors of metabolism for expanded newborn screening in a northwestern Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Chen, D.; Chang, R.; Pan, L.; Yang, J.; Yuan, D.; Huang, L.; Yan, T.; Ning, H.; Wei, J.; et al. Tandem Mass Spectrometry Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism in Newborns and High-Risk Infants in Southern China: Disease Spectrum and Genetic Characteristics in a Chinese Population. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 631688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, W.; Fu, Q. Expanded newborn screening for inherited metabolic disorders and genetic characteristics in a southern Chinese population. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 494, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, F.; Bobo, X.; Qiang, Z.; Shang, Y.; Guoxing, G.; Qi, Y.; Jingsi, L.; Jin, W.; Chuan, L.; Shaoke, C.; et al. Analysis of four carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency cases caused by homozygous mutation of SLC25A20 c.199-10T> G. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2018, 56, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Guan, X.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, P.Y.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, T. Current attitudes and preconceptions on newborn genetic screening in the Chinese reproductive-aged population. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).