Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Score (Pi-Rads) and Glutathione S-Transferase P1 Methylation Status (Gst-P1) in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Patients With Borderline PSA Values
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and Methods
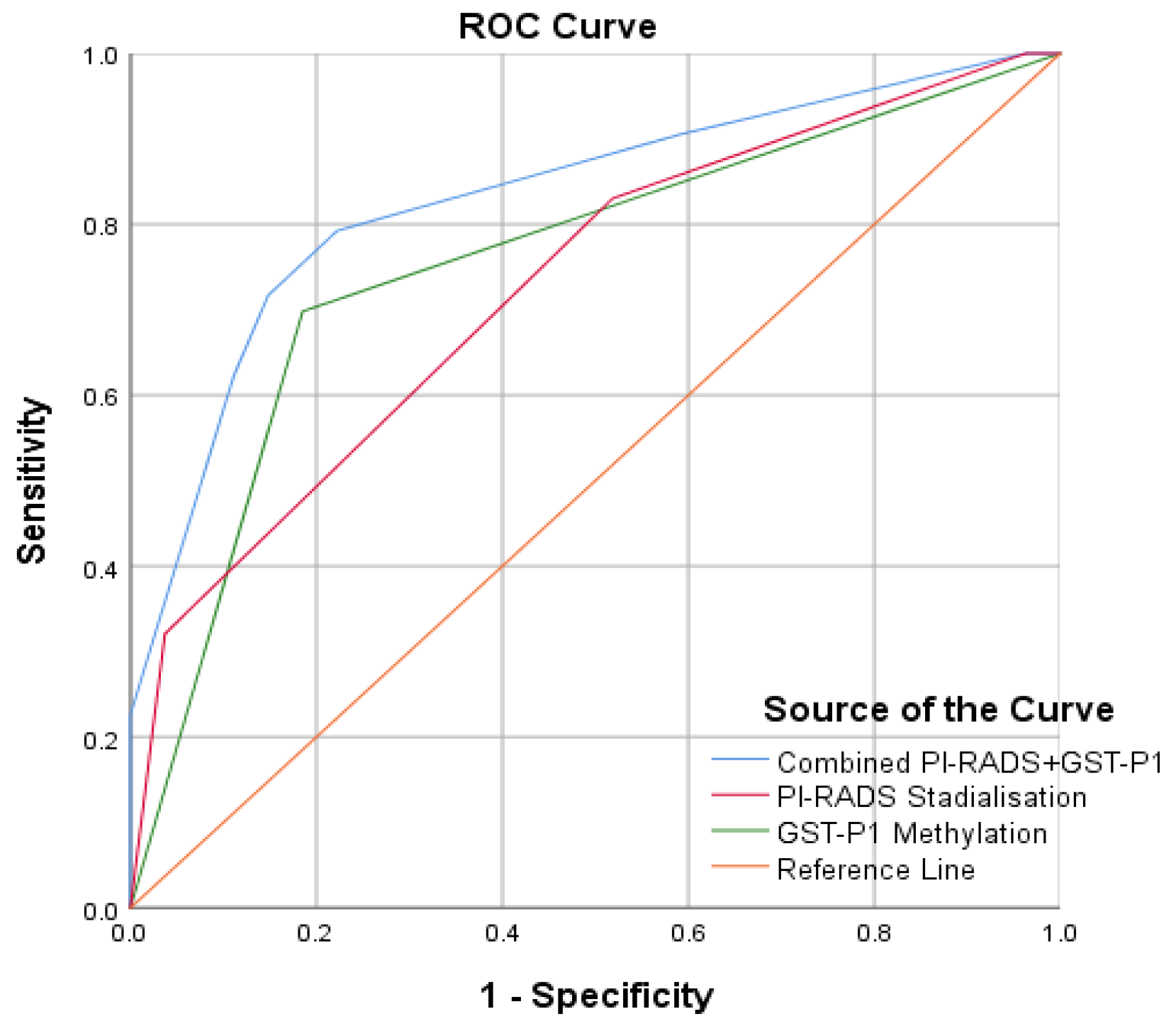
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
Highlights
- ✓
- Early diagnosis in prostate cancer is extremely important for achieving a high 5 years survival rate.
- ✓
- The use of GST-P1 and PI-RADS tests in patients with inconclusive PSA-levels, allows less over-diagnosing by non-invasive procedures, such as repeated biopsies.
Conflict of Interest disclosure
Compliance with ethical standards
References
- Lee, A.J.; Wnorowski, A.; Ye, N.; Xu, L.; Naslund, M.; Wood, B.J.; Merino, M.J.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.L.; Pinto, P.A.; Siddiqui, M.M. Validation of an MRI-based prostate cancer prebiopsy Gleason score predictive nomogram. Curr Urol. 2022, 16, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazilu, L.; Stanculeanu, D.L.; Gheorghe, A.D.; Voinea, F.; Suceveanu, A.P.; Pituru, S.; et al. Incidence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients in clinical practice. Farmacia. 2019, 67, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Zamora, E.; Mendoza-Cano, O.; Ríos-Silva, M.; Sánchez-Piña, R.A.; Higareda-Almaraz, M.A.; Higareda-Almaraz, E.; Lugo-Radillo, A. Disability-Adjusted Life Years for Cancer in 2010⁻2014: A Regional Approach in Mexico. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018, 15, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuhu, A.N.; Pantea-Stoian, A.M.; Nitipir, C.; et al. Assessment of cachexia in cancer patients with advanced disease. In Book Series, International Conference on Interdisciplinary Management of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications; 2017; pp. 139–139. [Google Scholar]
- Savlovschi, C.; Serban, D.; Andreescu, C.; Dascalu, A.; Pantu, H. Economic analysis of medical management applied for left colostomy. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013, 108, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nitipir, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Orlov, C.; Pantea-Stoian, A.; Hainarosie, R.; et al. The Necessity of Nutritional Intervention in the Oncological Patient. What is the Evidence? In Proceedings of the 35th Balkan Medical Week, Athens, Greece, 25–27 September 2018; pp. 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Netto, G.J.; Amin, M.B.; Compérat, E.M.; Gill, A.J.; Hartmann, A.; Moch, H.; Menon, S.; Raspollini, M.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Srigley, J.R.; Hoon Tan, P.; Tickoo, S.K.; Tsuzuki, T.; Turajlic, S.; Cree, I.; Berney, D.M. Prostate Adenocarcinoma Grade Group 1: Rationale for Retaining a Cancer Label in the 2022 World Health Organization Classification. Eur Urol 2022, S0302-2838(22)02644-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savlovschi, C.; Serban, D.; Trotea, T.; Borcan, R.; Dumitrescu, D. Post-surgery morbidity and mortality in colorectal cancer in elderly subjects. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013, 108, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Şavlovschi, C.; Comandaşu, M.; Şerban, D. Specifics of diagnosis and treatment in synchronous colorectal cancers (SCC). Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013, 108, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chirilă, S.; Rugină, S.; Broască, V. Neoplastic Diseases Incidence in Constanta County During 2007 – 2012. ARS Medica Tomitana. 2015, 20, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, P.; Maisonneuve, P.; Napalkov, P. Incidence of prostate cancer will double by the year 2030: the argument for. Eur Urol. 1996, 29, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, M.A.; Moradi, G.; Zareie, B.; Sofimajidpour, H.; Tozandehjani, S.; Zafari, H.; Gholami, F.; Shahsavari, S.; Hassani, P.; Mohammadian, M. Overall survival and prognostic factors prostate cancer in Kurdistan Province-Iran: a population-based study (2011-2018). BMC Cancer. 2021, 21, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenbach, L.F.; Deuker, M.; Collà-Ruvolo, C.; Nocera, L.; Tian, Z.; Maurer, T.; Tilki, D.; Briganti, A.; Saad, F.; Mirone, V.; Chun, F.K.H.; Graefen, M.; Karakiewicz, P.I. Differences between rural and urban prostate cancer patients. World J Urol. 2021, 39, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.W.; Park, J.; Yeob, K.E.; Yoon, S.J.; Jang, S.N.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kawachi, I. Disparities in prostate cancer diagnosis, treatment, and survival among men with disabilities: Retrospective cohort study in South Korea. Disabil Health J. 2021, 14, 101125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.L.; Qian, Y.; Min, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Urban-Rural Differences in Clinical Characteristics of Prostate Cancer at Initial Diagnosis: A Single-Center Observational Study in Anhui Province, China. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 704645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Landier, W.; Paskett, E.D.; Peters, K.B.; Merrill, J.K.; Phillips, J.; Osarogiagbon, R.U. Rural-Urban Disparities in Cancer Outcomes: Opportunities for Future Research. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanopol, I.A.; Baroiu, L.; Chirila, S.; Miulescu, M.; Anghel, L.; Nechita, L.; Dinu, C.A.; Stefanescu, V.; Bobeica, C.; Nechifor, A.; Tatu, A.L. The Influence of Living in Rural Areas on the Evolution and Management of Pediatric Ovarian Cystic Lesions: A Retrospective Study on a Cohort from South Eastern Romania. Int J Gen Med. 2022, 15, 5273–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, G.R.; Blizzard, C.L.; Stokes, B.; Skala, M.; Redwig, F.; Dickinson, J.L.; FitzGerald, L.M. Urban-rural prostate cancer disparities in a regional state of Australia. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, D.; Socea, B.; Badiu, C.D.; Tudor, C.; Balasescu, S.A.; Dumitrescu, D.; Trotea, A.M.; Spataru, R.I.; Vancea, G.; Dascalu, A.M.; Tanasescu, C. Acute surgical abdomen during the COVID-19 pandemic: Clinical and therapeutic challenges. Exp Ther Med. 2021, 21, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, A.; Torr, B.; Jones, M.E.; Broggio, J.; Scott, S.; Loveday, C.; Garrett, A.; Gronthoud, F.; Nicol, D.L.; Jhanji, S.; Boyce, S.A.; Williams, M.; Riboli, E.; Muller, D.C.; Kipps, E.; Larkin, J.; Navani, N.; Swanton, C.; Lyratzopoulos, G.; McFerran, E.; Lawler, M.; Houlston, R.; Turnbull, C. Effect of delays in the 2-week-wait cancer referral pathway during the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer survival in the UK: a modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwen, Z.R.; Mamawala, M.; Tosoian, J.J.; Druskin, S.C.; Ross, A.E.; Sokoll, L.J.; Epstein, J.I.; Carter, H.B.; Gorin, M.A.; Pavlovich, C.P. Prostate Health Index and multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging to predict prostate cancer grade reclassification in active surveillance. BJU Int. 2020, 126, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suceveanu, A.I.; Micu, I.S.; Baltatescu, G.I.; Petcu, L.C.; Dobrin, N.; Brinzan, C.; Nitipir, C.; Mazilu, L.; Botea, F.; Herlea, V.; Voinea, F.; Suceveanu, A.P. Overexpression of Survivin-1, TAG-72 and HERC5 in patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma in the Black Sea coast geographical area. Exp Ther Med. 2021, 21, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santric, V.; Djokic, M.; Suvakov, S.; Pljesa-Ercegovac, M.; Nikitovic, M.; Radic, T.; Acimovic, M.; Stankovic, V.; Bumbasirevic, U.; Milojevic, B.; Babic, U.; Dzamic, Z.; Simic, T.; Dragicevic, D.; Savic-Radojevic, A. GSTP1 rs1138272 Polymorphism Affects Prostate Cancer Risk. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020, 56, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cruz, E.; Otero, J.R.; Ineva, P.A.; Pérez, L.M.M.; Elías, L.P.; Asensio, A.A. Robot-assisted aquablation for resection of benign prostatic hyperplasia: A series of cases. J Clin Invest Surg. 2020, 5, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jiao, D.; Dou, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, X. Association of glutathione-S-transferase p1 gene promoter methylation and the incidence of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019, 145, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanec, S.H.; Bickel, H.; Wengert, G.J.; Arnoldner, M.; Clauser, P.; Susani, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Pinker, K.; Helbich, T.H.; Baltzer, P.A.T. Can the addition of clinical information improve the accuracy of PI-RADS version 2 for the diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer in positive MRI? Clin Radiol. 2020, 75, 157.e1–157.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafuri, A.; Iwata, A.; Shakir, A.; Iwata, T.; Gupta, C.; et al. Systematic Biopsy of the Prostate can Be Omitted in Men with PI-RADS™ 5 and Prostate Specific Antigen Density Greater than 15. J Urol. 2021, 206, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, Z.; Cowan, J.E.; Westphalen, A.C.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Chan, J.M.; Zhao, S.; Shinohara, K.; Carroll, P.R. Genomic Prostate Score, PI-RADS™ version 2 and Progression in Men with Prostate Cancer on Active Surveillance. J Urol. 2019, 201, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraphin, T.P.; Joko-Fru, W.Y.; Manraj, S.S.; Chokunonga, E.; Somdyala, N.I.M.; et al. Prostate cancer survival in sub-Saharan Africa by age, stage at diagnosis, and human development index: a population-based registry study. Cancer Causes Control. 2021, 32, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinea, F.; Mazilu, L.; Micu, I.S.; Suceveanu, A.P.; Iliescu, M.; Dumitru, A.; Constantin, V.D.; Paunica, I.; Suceveanu, A.I. Modern approaches for antiandrogen-resistant prostate cancer therapy. J Mind Med Sci. 2021, 8, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, S.; Christidis, D.; Perera, M.; Hong, S.K.; Manning, T.; Vela, I.; Lawrentschuk, N. Prostate cancer biomarkers: Are we hitting the mark? Prostate Int. 2016, 4, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hu, M.B.; Bai, P.D.; Zhu, W.H.; Liu, S.H.; Hou, J.Y.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Ding, Q.; Jiang, H.W. Proinflammatory cytokines in prostate cancer development and progression promoted by high-fat diet. Biomed Res Int. 2015, 2015, 249741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brănescu, C.; Serban, D.; Dascălu, A.M.; Oprescu, S.M.; Savlovschi, C. Interleukin 6 and lipopolysaccharide binding protein - markers of inflammation in acute appendicitis. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013, 108, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.C.; Hobisch, A.; Lin, D.L.; Culig, Z.; Keller, E.T. Interleukin-6 and prostate cancer progression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, D.; Papanas, N.; Dascalu, A.M.; Stana, D.; Nicolae, V.A.; Vancea, G.; Badiu, C.D.; Tanasescu, D.; Tudor, C.; Balasescu, S.A.; Pantea-Stoian, A. Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients With Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Systematic Review. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2021, 20, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, V.C.; Munteanu, R.A.; Gulei, D.; Schitcu, V.H.; Petrut, B.; Berindan Neagoe, I.; Achimas Cadariu, P.; Coman, I. PSA Based Biomarkers, Imagistic Techniques and Combined Tests for a Better Diagnostic of Localized Prostate Cancer. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Friend, C.; Dreher, A.; Allgar, V.; Macleod, U. The diagnostic test accuracy of rectal examination for prostate cancer diagnosis in symptomatic patients: a systematic review. BMC Fam Pract. 2018, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankerst, D.P.; Thompson, I.M. Sensitivity and specificity of prostate-specific antigen for prostate cancer detection with high rates of biopsy verification. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2006, 78, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, T.; Ahmed, K.; Raison, N.; Challacombe, B.; Dasgupta, P. Clarifying the PSA grey zone: The management of patients with a borderline PSA. Int J Clin Pract. 2016, 70, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceausu, Z.; Socea, B.; Dimitriu, M.C.T.; Predescu, D.; Constantin, V.D.; Bacalbaşa, N.; Cîrstoveanu, C.; Costache, M.; Ceausu, M. Dormant cardiac stem cells: A promising tool in cardiac regeneration. Exp Ther Med. 2020, 20, 3452–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, D.; Djulbegovic, M.; Jung, J.H.; Hwang, E.C.; Zhou, Q.; Cleves, A.; Agoritsas, T.; Dahm, P. Prostate cancer screening with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2018, 362, k3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, M.H.; et al. Performance of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1 for Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021, 54, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubihal, V.; Kundra, V.; Lanka, V.; Sharma, S.; Das, P.; Nayyar, R.; Das, C.J. Prospective evaluation of PI-RADS v2 and quantitative MRI for clinically significant prostate cancer detection in Indian men - East meets West. Arab J Urol. 2022, 20, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Values |
| Patients (n=80) | |
| Age (mean±sd, years) | 68.0±9.16 |
| PSA (mean±sd, ng/ml) | 7.1±1.82 |
| GST-P1 Methylation | |
| Negative (n, %) | 38 (47.5%) |
| Positive (n, %) | 42 (52.5%) |
| PI-RAIDS 2 | |
| 1 - Very Low (n, %) | 1 (1.3%) |
| 2 - Low (n, %) | 21 (26.3%) |
| 3 - Intermediate (n, %) | 40 (50%) |
| 4 - High (n, %) | 18 (22.5%) |
| 5 - Very High (n, %) | 0 (0%) |
| Prostate Cancer | |
| Positive (n, %) | 53 (66.3%) |
| Negative (n, %) | 27 (33.8%) |
| Criterion | Sensitivity | 95% CI | Specificity | 95% CI |
| ≥1 | 100.00 | 93.3 - 100.0 | 0.00 | 0.0 - 12.8 |
| >1 | 100.00 | 93.3 - 100.0 | 3.70 | 0.09 - 19.0 |
| >2 | 83.02 | 70.2 - 91.9 | 48.15 | 28.7 - 68.1 |
| >3 | 32.08 | 19.9 - 46.3 | 96.30 | 81.0 - 99.9 |
| >4 | 0.00 | 0.0 - 6.7 | 100.00 | 87.2 - 100.0 |
| B | S.E. | Wald | df | p | Odds Ratio | 95% C.I. for Odds Ratio | ||
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| GST-P1 Methylation (1) | 2.07 | .61 | 11.66 | 1 | .001 | 7.92 | 2.41 | 25.95 |
| PI-RADS Stabilization | 1.13 | .43 | 6.84 | 1 | .009 | 3.01 | 1.33 | 7.23 |
| Constant | -3.43 | 1.25 | 7.46 | 1 | .006 | .032 | ||
© 2022 by the author. 2022 Marius Stan, Vladimir Botnarciuc, Andra I. Suceveanu, Andreea C. Costea, Adrian P. Suceveanu, Laura Mazilu, Ciprian Iorga, Tony Hangan, Corneliu Tudor, Dragos Epistatu, Sergiu Chirila, Viorel Gherghina and Felix Voinea
Share and Cite
Stan, M.; Botnarciuc, V.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Costea, A.C.; Suceveanu, A.P.; Mazilu, L.; Iorga, C.; Hangan, T.; Tudor, C.; Epistatu, D.; et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Score (Pi-Rads) and Glutathione S-Transferase P1 Methylation Status (Gst-P1) in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Patients With Borderline PSA Values. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2022, 9, 304-309. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1354
Stan M, Botnarciuc V, Suceveanu AI, Costea AC, Suceveanu AP, Mazilu L, Iorga C, Hangan T, Tudor C, Epistatu D, et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Score (Pi-Rads) and Glutathione S-Transferase P1 Methylation Status (Gst-P1) in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Patients With Borderline PSA Values. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2022; 9(2):304-309. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1354
Chicago/Turabian StyleStan, Marius, Vladimir Botnarciuc, Andra I. Suceveanu, Andreea C. Costea, Adrian P. Suceveanu, Laura Mazilu, Ciprian Iorga, Tony Hangan, Corneliu Tudor, Dragos Epistatu, and et al. 2022. "Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Score (Pi-Rads) and Glutathione S-Transferase P1 Methylation Status (Gst-P1) in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Patients With Borderline PSA Values" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 9, no. 2: 304-309. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1354
APA StyleStan, M., Botnarciuc, V., Suceveanu, A. I., Costea, A. C., Suceveanu, A. P., Mazilu, L., Iorga, C., Hangan, T., Tudor, C., Epistatu, D., Chirila, S., Gherghina, V., & Voinea, F. (2022). Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Score (Pi-Rads) and Glutathione S-Transferase P1 Methylation Status (Gst-P1) in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Patients With Borderline PSA Values. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 9(2), 304-309. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1354



