Collagen-Based Biomaterials with Possible Therapeutic Effects
Abstract
:Introduction
- The epidermolytic form (cleavage of keratinocytes with autosomal dominant, recessive or x-linked transmission);
- The dermolytic (or dystrophic) form cleavage in superficial dermal papillae and autosomal dominant or recessive transmission;
- The mixed form (Kindler syndrome).
- Autosomal dominant, recessive or x-linked intra- epithelial forms with loci in regions 8q24, 12q13, 17q12- q21, Xq 27-3qter;
- Junctional forms show autosomal recessive mutations in the region 1q31, 1q32, 1q25-q31, 10q24-3, 17q11-qter, 18q 11.2;
- The dermolytic forms are due to dominant or recessive mutations of the α1 polypeptide gene VII (COL7A) that determine collagen synthesis and are located in the region 3p 21.3. There are “de novo” mutations due to genes of unknown location.
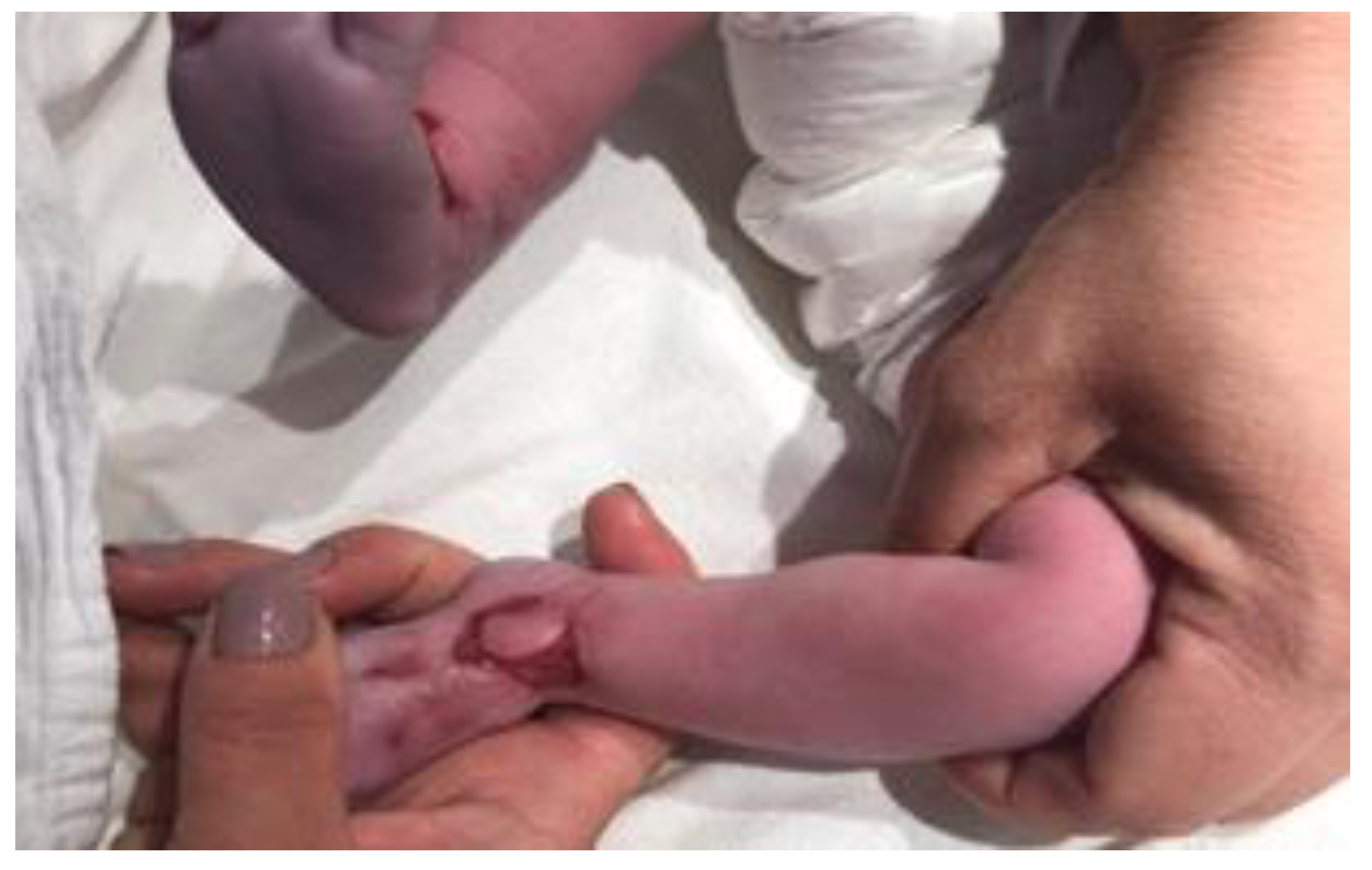
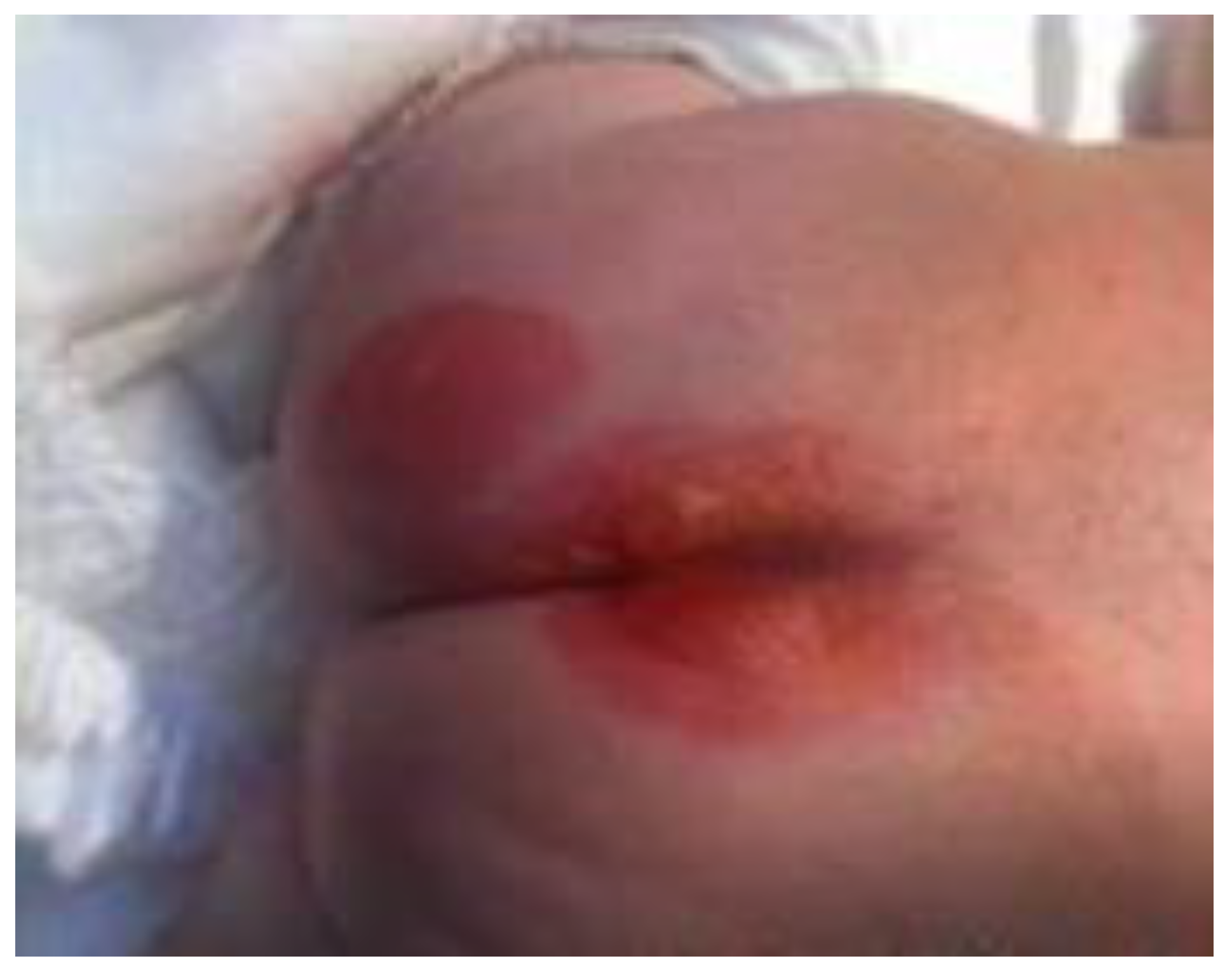
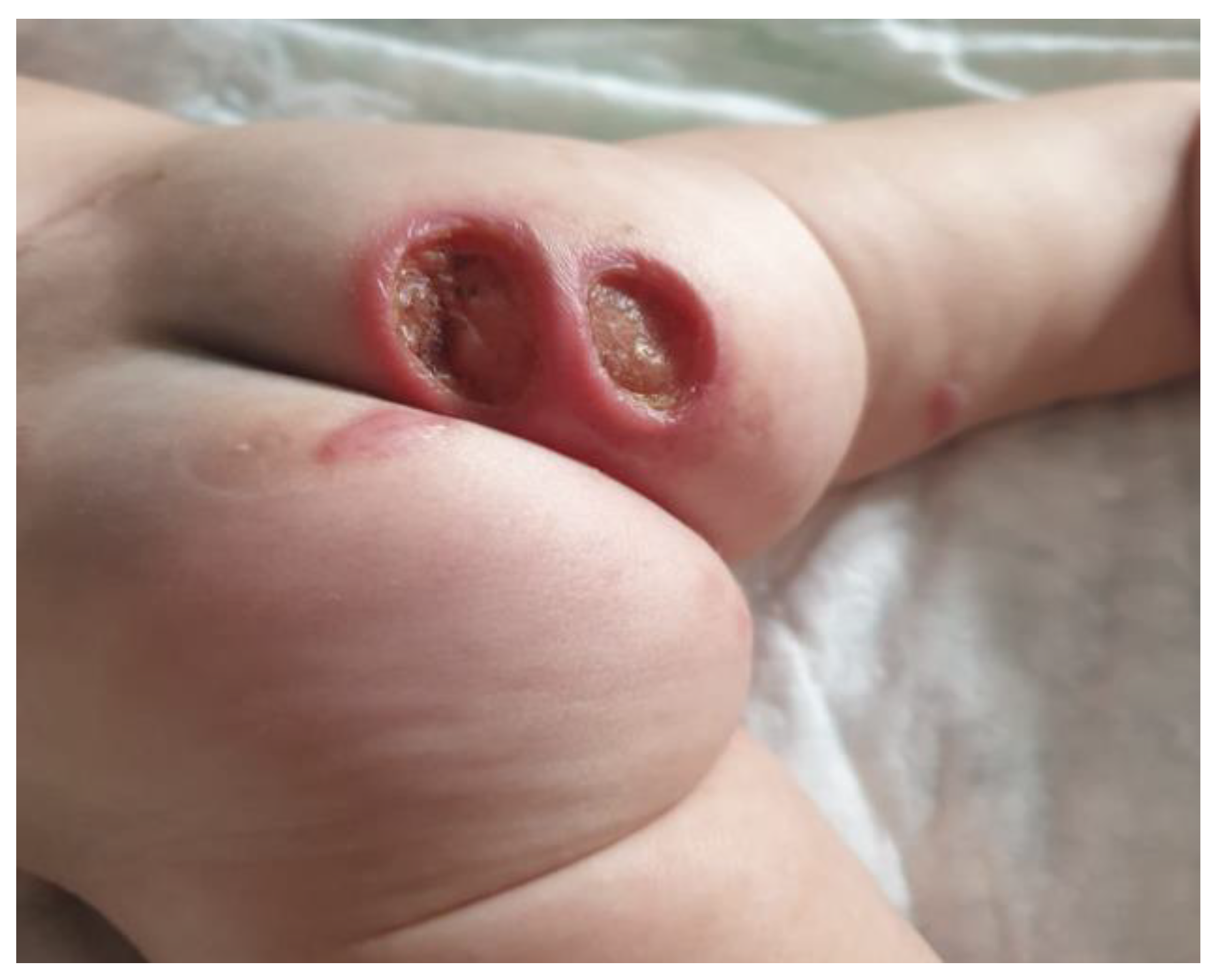
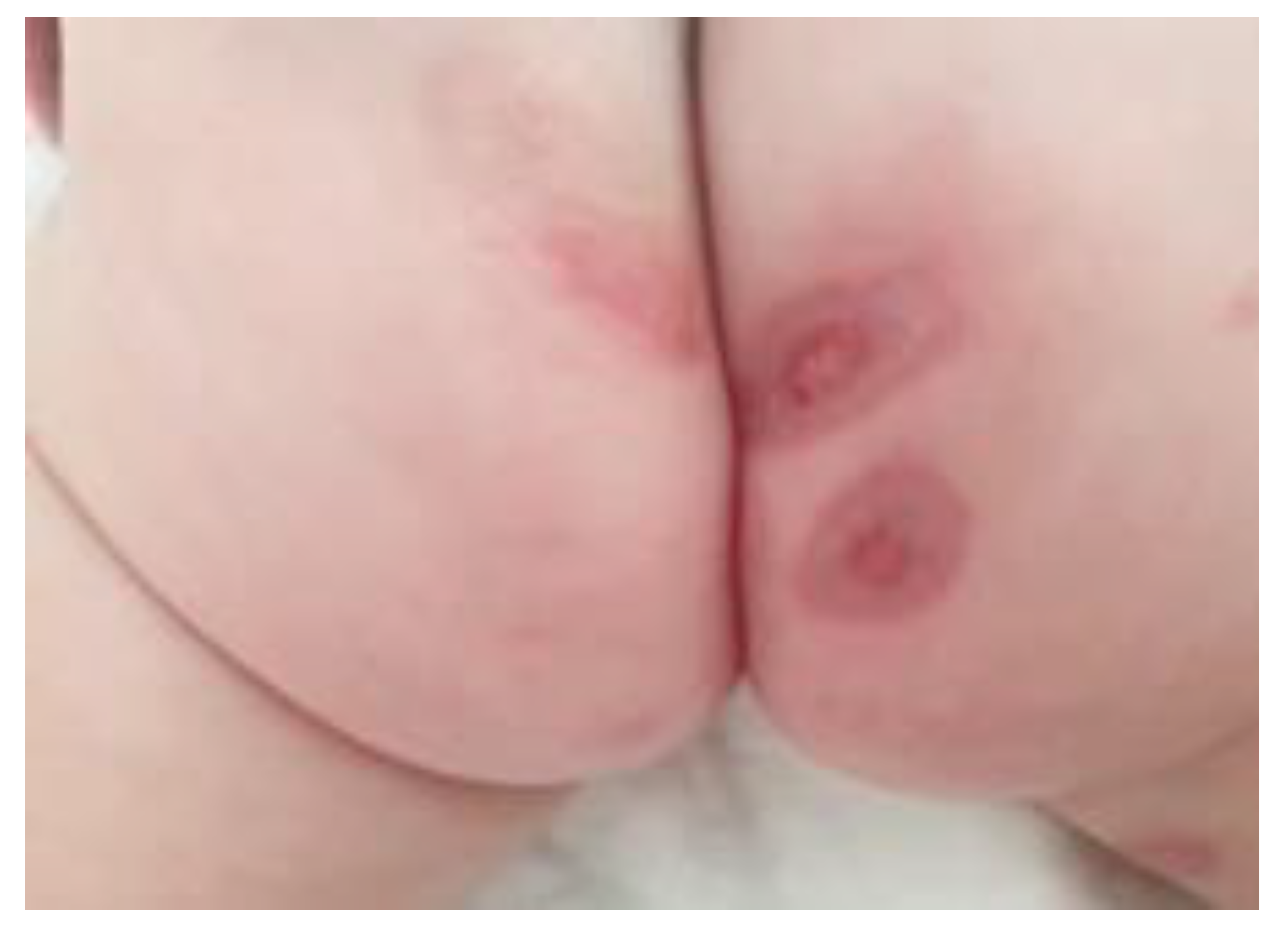
Case presentation
Therapeutic options and decisions in our case
Discussions
- Hallopeau-Siemens autosomal recessive EB - the most severe form, with congenital blisters on a large percentage of the body surface and sometimes with portions absent from the integument (caused by traumas during birth). The blisters also affect the mucous membranes, subsequently causing integumentary scarring in the digestive tract (esophagus, buccal cavity) as well, thus leading to significant complications: post-keloid scar contraction, fusion of fingers, nail disappearance, eye inflammation, chronic malnutrition. On the long term, there is an increased risk of squamous, lethal carcinoma.
- Autosomal recessive non-Hallopeau-Siemens EB - the blisters are usually more limited on the hands and feet (elbows, knees), post-bulging scars occur, not very mutilating, as well as nail malformative changes.
- Autosomal dominant EB is the mildest form of EB, the blisters are usually confined to the hands, feet, knees elbows.
Highlights
- ✓
- Epidermolysis bullosa is a rare condition with genetic determinism, with a significant polymorphism of the clinical forms.
- ✓
- The follow-up should carefully monitor the cutaneous mucosal relapses, the growth and development of the child and the possible sequelae.
- ✓
- Shortening the healing time with collagen membranes will reduce the risk of further septic complications, dehydration and hydro-electrolytic imbalance.
Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest disclosure
Compliance with ethical standards
References
- Commission on the European Communities. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions on Rare Diseases - Europe's challenges {SEC(2008)2713} {SEC(2008)2712}. 2008. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/c8a042d8-ffb9-4b01-9c91- c1497a2b3fd7/language-en (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Oliveira, Z.N.; Périgo, A.M.; Fukumori, L.M.; Aoki, V. Immunological mapping in hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. An Bras Dermatol. 2010, 85, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, Y.M.; Falabella, A.F.; Schachner, L.A. Management of epidermolysis bullosa in infants and children. Clin Dermatol. 2003, 21, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dascalu, A.M.; Tudosie, M.S.; Smarandache, G.C.; Serban, D. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic upon ophthalmological clinical practice. Rom J Leg Med. 2020, 28, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeraraghavan, V.; Srinivasan, K. Work place impact on mental wellbeing of frontline doctors. J Mind Med Sci. 2020, 7, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, B.; Doinița, O.I.; Bălălău, C.; Scăunașu, R.; Manole, F.; Domuța, M.; Oancea, A.L. Fibroscopic examination on ENT patients in COVID-19 era. J Clin Invest Surg. 2020, 5, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șerban, D.; Brănescu, C.M.; Smarandache, G.C.; Tudor, C.; Tănăsescu, C.; Tudosie, M.S.; Stana, D.; Costea, D.O.; Dascălu, A.M.; Spătaru, R.I. Safe surgery in day care centers: focus on preventing medical legal issues. Rom J Leg Med. 2021, 29, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, D.; Smarandache, A.M.; Cristian, D.; Tudor, C.; Duta, L.; Dascalu, A.M. Medical errors and patient safety culture - shifting the healthcare paradigm in Romanian hospitals. Rom J Leg Med. 2020, 28, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, E.B.; Köglmeier, J.; Martinez, A.E.; Mellerio, J.E.; Haynes, L.; Sebire, N.J.; Lindley, K.J.; Shah, N. Gastrointestinal complications of epidermolysis bullosa in children. Br J Dermatol. 2008, 158, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruskay, D.M. Nutritional management in the child with epidermolysis bullosa. Arch Dermatol. 1988, 124, 760–761. [Google Scholar]
- Bohiltea, R.; Turcan, N.; Cavinder, C.M.; Ducu, I.; Paunica, I.; Andronache, L.F.; Cirstoiu, M.M. Risk factors, predictive markers and prevention strategies for intrauterine fetal death. An integrative review. J Mind Med Sci. 2020, 7, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, L.; Haynes, L.; Sklar, M.; Martinez, A.E.; Mellerio, J.E. The challenges of meeting nutritional requirements in children and adults with epidermolysis bullosa: proceedings of a multidisciplinary team study day. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011, 36, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birge, K. Nutrition management of patients with epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995, 95, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
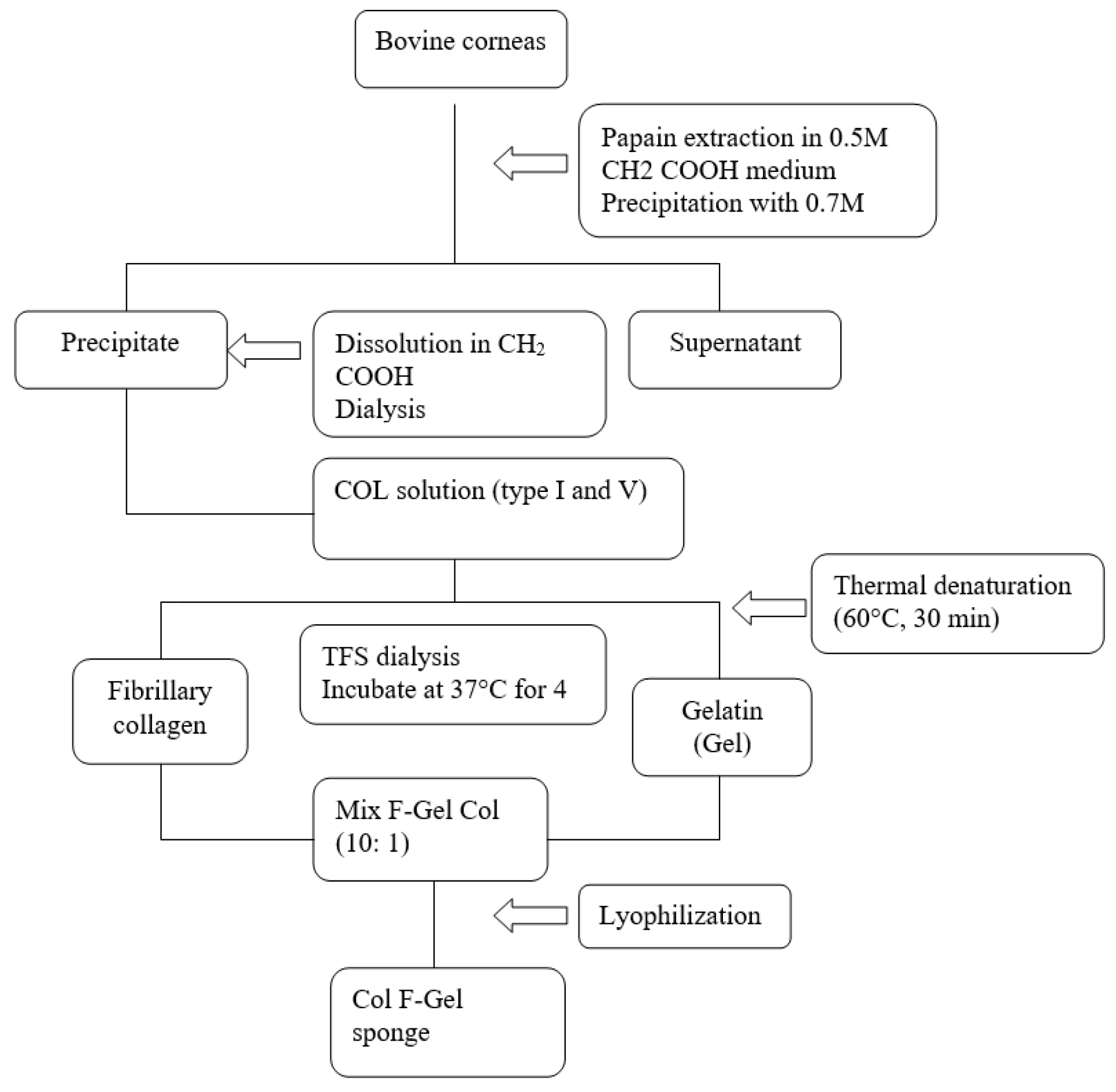
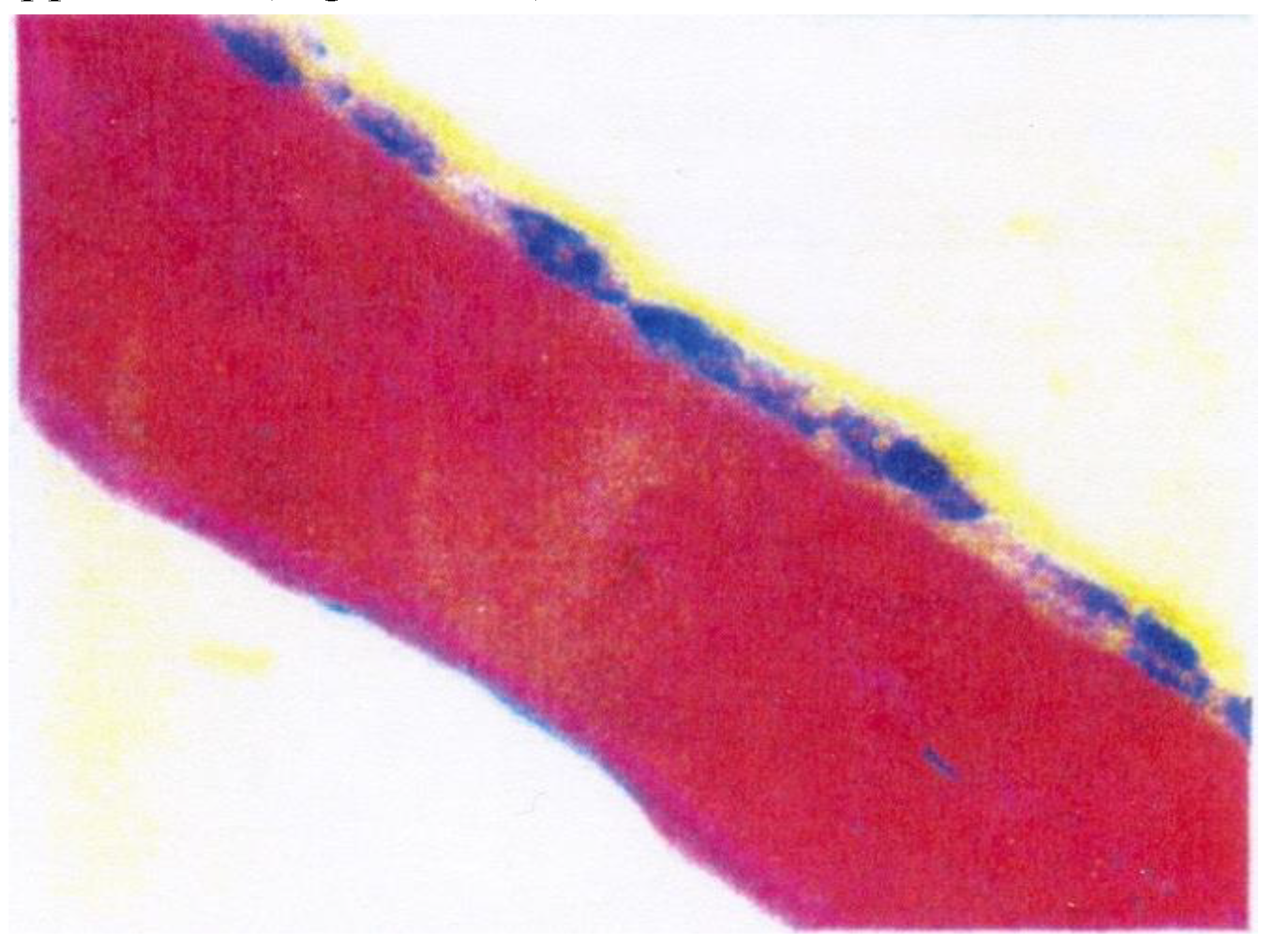
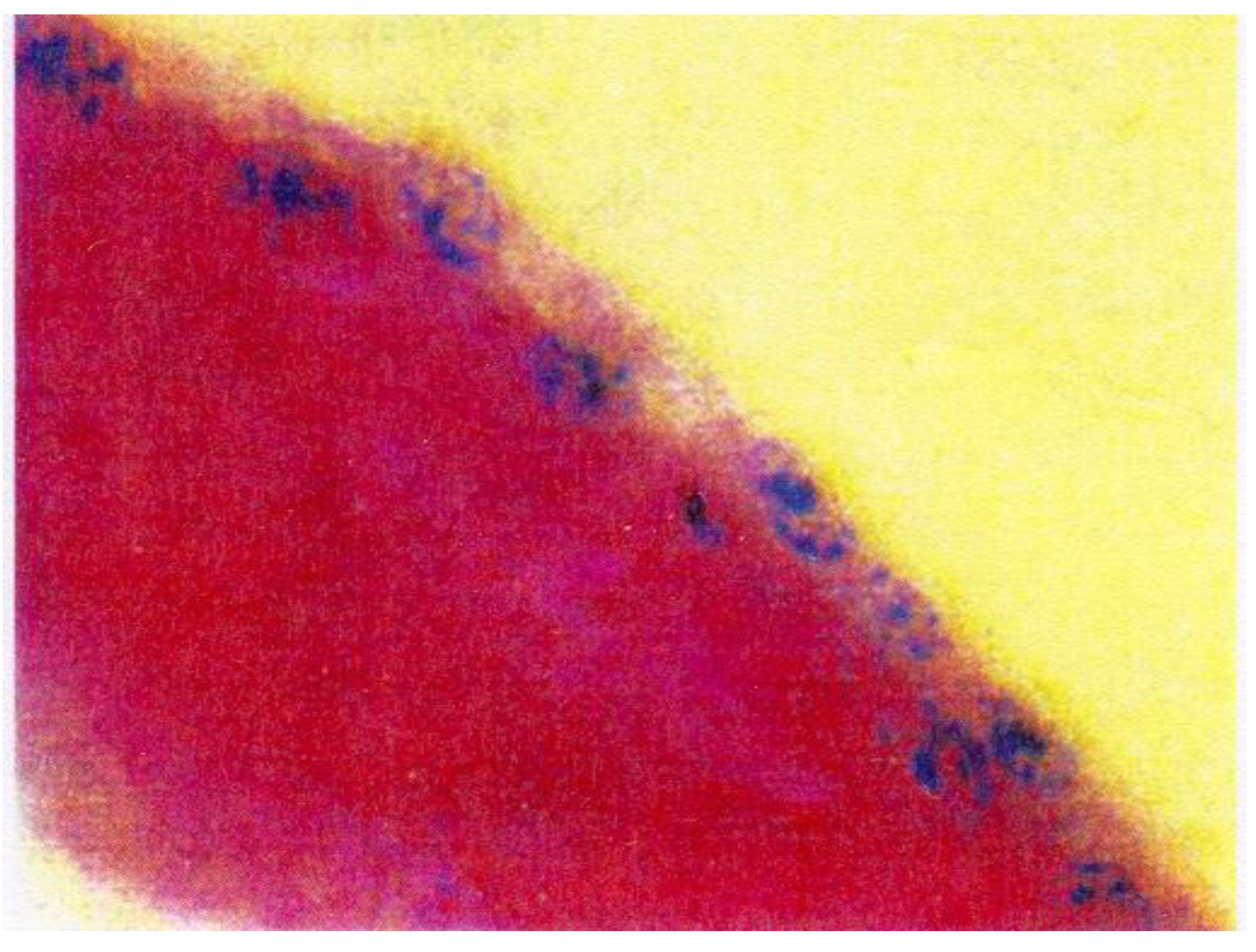
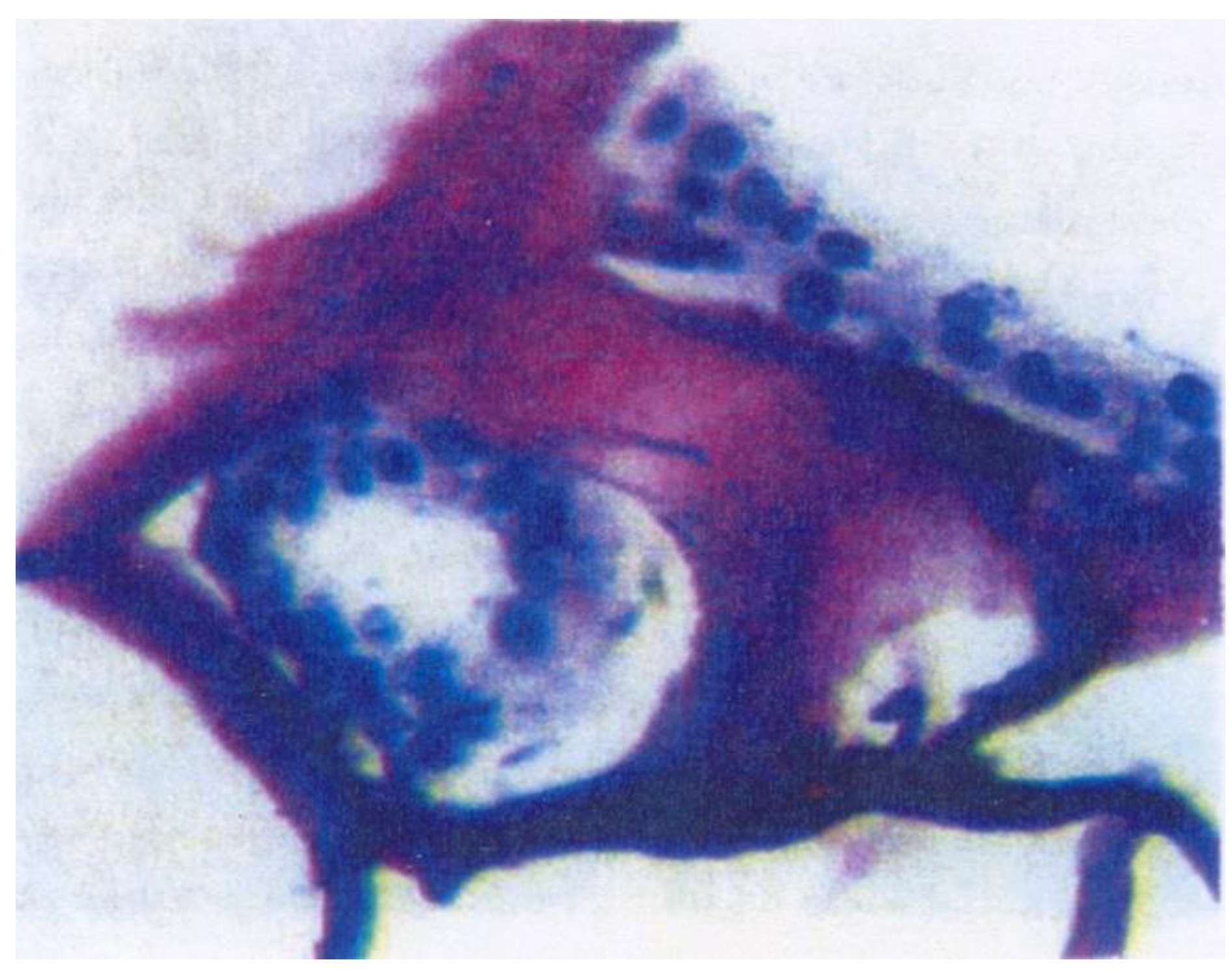
- Bobic, S.; Constantin, V.D.; Budu, V.A.; Socea, B.; Popescu, G.H.; Nica, E. Proactive therapeutical modulation of the postoperative intraperitoneal adhesions - the efficacy of the collagen-based biomaterials (simple and composite). Unified Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bobic, S.; Constantin, V.D.; Albu Kaya, M.; Marin, S; et al. Postoperative peritoneal adhesions prophylaxy using collagen-based biomaterials. ICAMS 2018 – 7th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems. 2018, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, V.D.; Carâp, A.; Bobic, S.; Budu, V; et al. Tissue engineering-collagen sponge dressing for chronic wounds. ICAMS 2018 – 7th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems. 2018, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socea, B.; Carâp, A.; Bratu, O.G.; Diaconu, C.C.; Dimitriu, M.; Socea, L.I.; Bobic, S.; Constantin, V.D. The role of the composite and biologic meshes in the trocar site hernia repair following laparoscopic surgery. Materiale Plastice. 2018, 55, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeles, F.; Murphy, M.; Rothe, M.J.; Grant-Kels, J.M. Nutrition and bullous skin diseases. Clin Dermatol. 2010, 28, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, E.; Lara-Corrales, I.; Mellerio, J.; Martinez, A.; Schultz, G.; Burrell, R.; Goodman, L.; Coutts, P.; Wagner, J.; Allen, U.; Sibbald, G. A consensus approach to wound care in epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012, 67, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fometescu, S.G.; Costache, M.; Coveney, A.; Oprescu, S.M.; Serban, D.; Savlovschi, C. Peritoneal fibrinolytic activity and adhesiogenesis. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013, 108, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, H.; Shah, R.; Sanghani, H.; Lakhani, N. Health related quality of life (HRQoL) and its associated surgical factors in diabetes foot ulcer patients. J Clin Invest Surg. 2020, 5, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiritsi, D.; Nyström, A. Recent advances in understanding and managing epidermolysis bullosa. F1000Res. 2018, 7, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Budhwar, J.; Maheshwary, A.; Bhatti, K.S. Blistering in a newborn: a rare case report. Int J Res Dermatol. 2020, 6, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Share and Cite
Nedelcuţă, R.M.; Călin, G.; Nedelcuţă, M.C.; Baleanu, V.D.; Davitoiu, D.V.; Socea, B.; Stănoiu, B.-P. Collagen-Based Biomaterials with Possible Therapeutic Effects. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2021, 8, 324-329. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.82.P324329
Nedelcuţă RM, Călin G, Nedelcuţă MC, Baleanu VD, Davitoiu DV, Socea B, Stănoiu B-P. Collagen-Based Biomaterials with Possible Therapeutic Effects. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2021; 8(2):324-329. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.82.P324329
Chicago/Turabian StyleNedelcuţă, Ramona Mihaela, Gigi Călin, Mihai Cristian Nedelcuţă, Vlad Dumitru Baleanu, Dragos Virgil Davitoiu, Bogdan Socea, and Bogdan-Petre Stănoiu. 2021. "Collagen-Based Biomaterials with Possible Therapeutic Effects" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 8, no. 2: 324-329. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.82.P324329
APA StyleNedelcuţă, R. M., Călin, G., Nedelcuţă, M. C., Baleanu, V. D., Davitoiu, D. V., Socea, B., & Stănoiu, B.-P. (2021). Collagen-Based Biomaterials with Possible Therapeutic Effects. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 8(2), 324-329. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.82.P324329


