Work Place Impact on Mental Wellbeing of Frontline Doctors
Abstract
:Introduction
COVID and healthcare workers
Materials and Methods
MEASURES
SCALES
- 1.
- Becks depression inventory
- 2.
- Becks anxiety inventory
SAMPLE SIZE CALCULATION
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Results
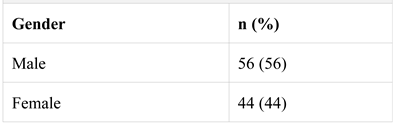
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY POPULATION
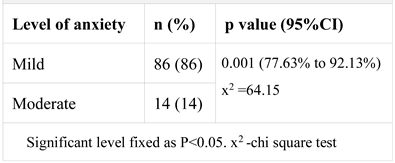
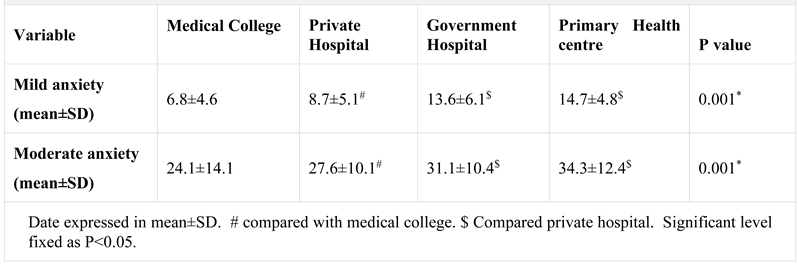
ANXIETY SCORES
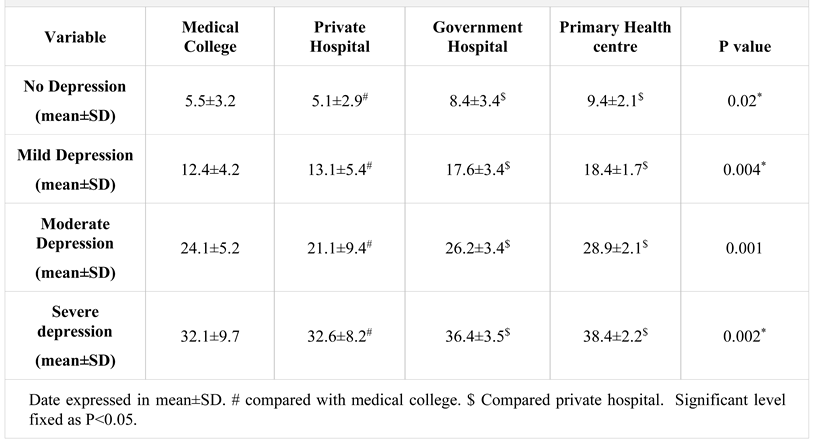
DEPRESSION SCORES
Discussions
MAIN FINDINGS
COMPARISON WITH PREVIOUS STUDIES
RELEVANCE IN HEALTH CARE POLICY
STRENGTH AND LIMITATIONS
Conclusions
Conflict of interest disclosure
Compliance with ethical standards
References
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, N. Generalized anxiety disorder, depressive symptoms and sleep quality during COVID-19 outbreak in China: a web-based cross-sectional survey. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 288, 112954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID 19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) (2020). Global research and innovation forum: towards a research roadmap. WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-public-health-emergency-of-international-concern-(pheic)-global-research-and-innovation-forum.
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galea, S.; Merchant, R.M.; Lurie, N. The Mental Health Consequences of COVID-19 and Physical Distancing: The Need for Prevention and Early Intervention. JAMA Intern Med. 2020, 180, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.; Wong, J.G.; McAlonan, G.M.; et al. Stress and psychological distress among SARS survivors 1 year after the outbreak. Can J Psychiatry. 2007, 52, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Shu, B.C.; Chang, Y.Y.; Lung, F.W. The mental health of hospital workers dealing with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Psychother Psychosom. 2006, 75, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlonan, G.M.; Lee, A.M.; Cheung, V.; et al. Immediate and sustained psychological impact of an emerging infectious disease outbreak on health care workers. Can J Psychiatry. 2007, 52, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, M.; Norris, F.H.; Galea, S. Differences in the determinants of posttraumatic stress disorder and depression after a mass traumatic event. Depress Anxiety. 2011, 28, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A. Doctors and healthcare workers at frontline of COVID 19 epidemic: Admiration, a pat on the back, and need for extreme caution. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020, 14, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, D.H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, S.H. Psychological effects on medical doctors from the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) outbreak: A comparison of whether they worked at the MERS occurred hospital or not, and whether they participated in MERS diagnosis and treatment. J Korean Neuropsychiat Assoc. 2017, 56, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- The State Council of China, 2020. A notification to set up nationwide psychological assistance hotlines against the 2019-nCoV outbreak. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2020-02/02/content_5473937.htm.
- Lai, J.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Factors Associated With Mental Health Outcomes Among Health Care Workers Exposed to Coronavirus Disease 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2020, 3, e203976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, M.L.R.; Almeida, H.G.; Esmeraldo, J.D.; et al. When health professionals look death in the eye: the mental health of professionals who deal daily with the 2019 coronavirus outbreak. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 288, 112972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Gupta, S.; Das, S.; Banerjee, B.B. Attitude, practice, behavior, and mental health impact of COVID-19 on doctors. Indian J Psychiatry. 2020, 62, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.H.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Epstein, N.; Brown, G.; Steer, R.A. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1988, 56, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, S. COVID-19 Affects Mental Health of Nurses, Frontline Workers More Than Others. HCP Live. 2020. Available online: https://www.hcplive.com/view/covid-19-affects-mental-health-nurses-frontline-more.
- Geoffroy, P.A.; Le Goanvic, V.; Sabbagh, O.; et al. Psychological Support System for Hospital Workers During the Covid-19 Outbreak: Rapid Design and Implementation of the Covid-Psy Hotline. Front Psychiatry. 2020, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
© 2020 by the author. 2020 Vishnupriya Veeraraghavan, Krishnan Srinivasan
Share and Cite
Veeraraghavan, V.; Srinivasan, K. Work Place Impact on Mental Wellbeing of Frontline Doctors. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2020, 7, 188-192. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.72.P188192
Veeraraghavan V, Srinivasan K. Work Place Impact on Mental Wellbeing of Frontline Doctors. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2020; 7(2):188-192. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.72.P188192
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeeraraghavan, Vishnupriya, and Krishnan Srinivasan. 2020. "Work Place Impact on Mental Wellbeing of Frontline Doctors" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 7, no. 2: 188-192. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.72.P188192
APA StyleVeeraraghavan, V., & Srinivasan, K. (2020). Work Place Impact on Mental Wellbeing of Frontline Doctors. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 7(2), 188-192. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.72.P188192



