Current Concepts on Drug Abuse and Dependence
Abstract
:Introduction
Discussion
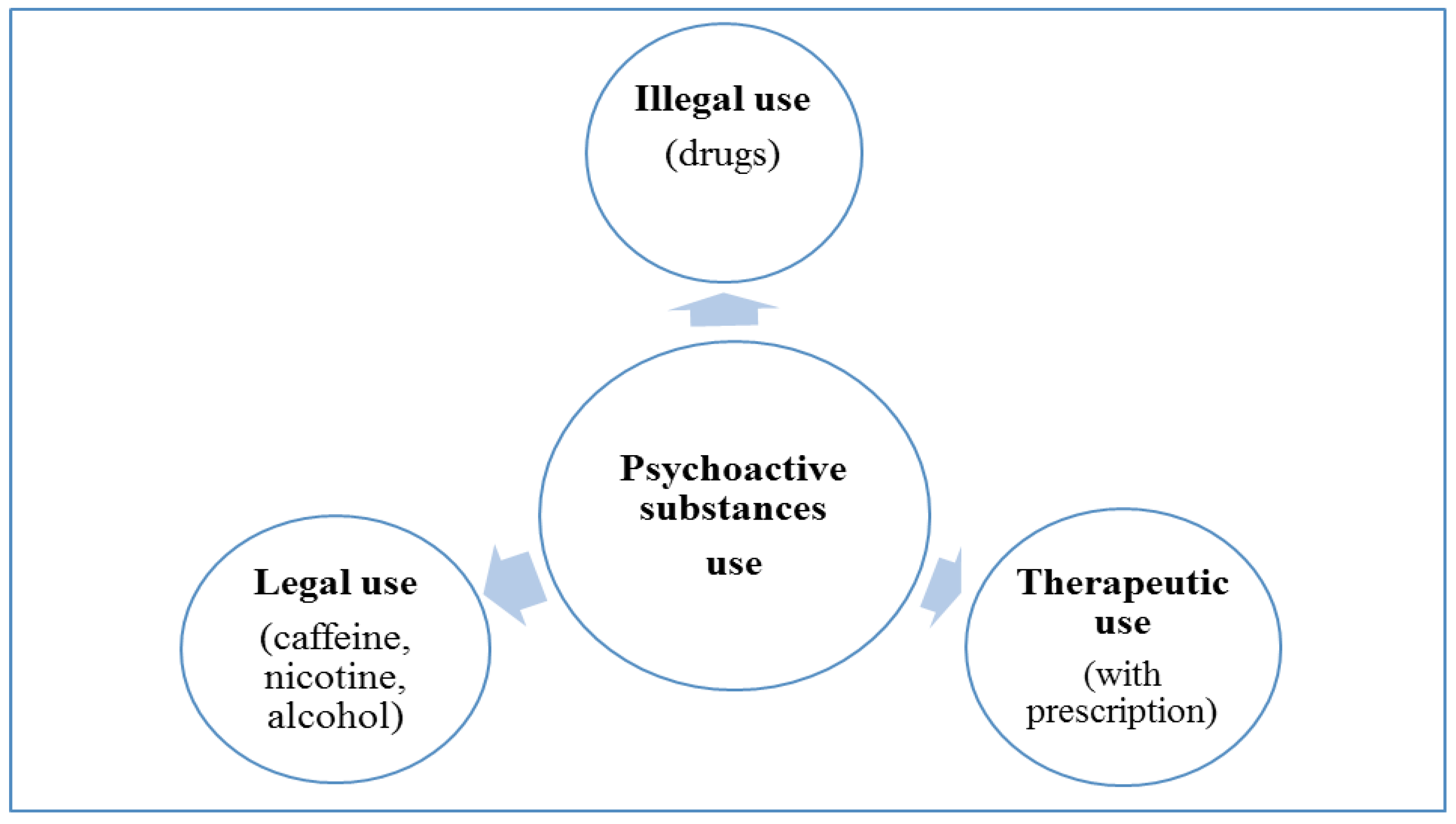
Classification of the psychoactive substances.
- ✓ Euphorica: euforic and narcotic substances that induce a state of physical and mental well: opium and opium compounds (morphin); cocaine)
- ✓ Phantastica: hallucinogenic substances of vegetable origin (mescal buttons, Cannabis)
- ✓ Inebriantia: substances that produce a first excitation followed by depression (alcohol, ether, chloroform)
- ✓ Hypnotica: sleep producing substances (chloral hydrate, barbiturates)
- ✓ Excitantia: substances that cause mental stimulation; substances from plants that produce general stimulation without impairment of consciousness (caffeine, tobacco, betel etc.)
- ✓ Psycholeptics (mental sedative): hypnotics (chloral hydrate, barbiturates); neuroleptics (phenothiazines, reserpine, butyrophenones); tranquilizers (meprobamate)
- ✓ Psychoanaleptic (mental stimulant): vigilance stimulants (amphetamines); mood stimulants (iproniazid, imipramine); other stimulants
- ✓ Psychedelics (producing mental deviation): hallucinogens, substances that produce depersonalization effects
- ✓ I - substances which activate the membrane receptors coupled to G-proteins (e.g. opiates, cannabinoids, LSD, mescaline etc.)
- ✓ II - substances which bind to the ionotropic receptors and ion channels (barbiturates, benzodiazepines, nicotine, phencyclidine etc.)
- ✓ III - substances which bind to the biogenic amine transporters (cocaine, amphetamine, Ecstasy)
The evolution of terminology
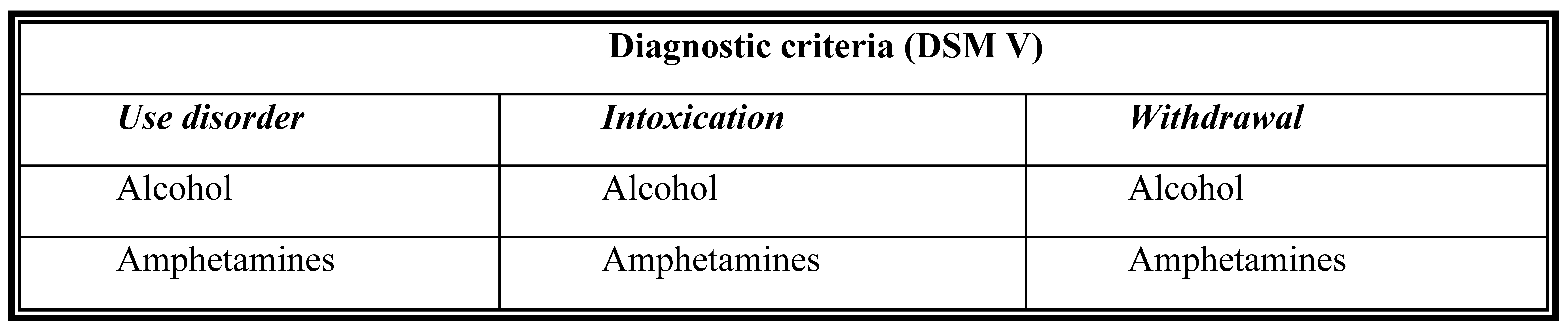
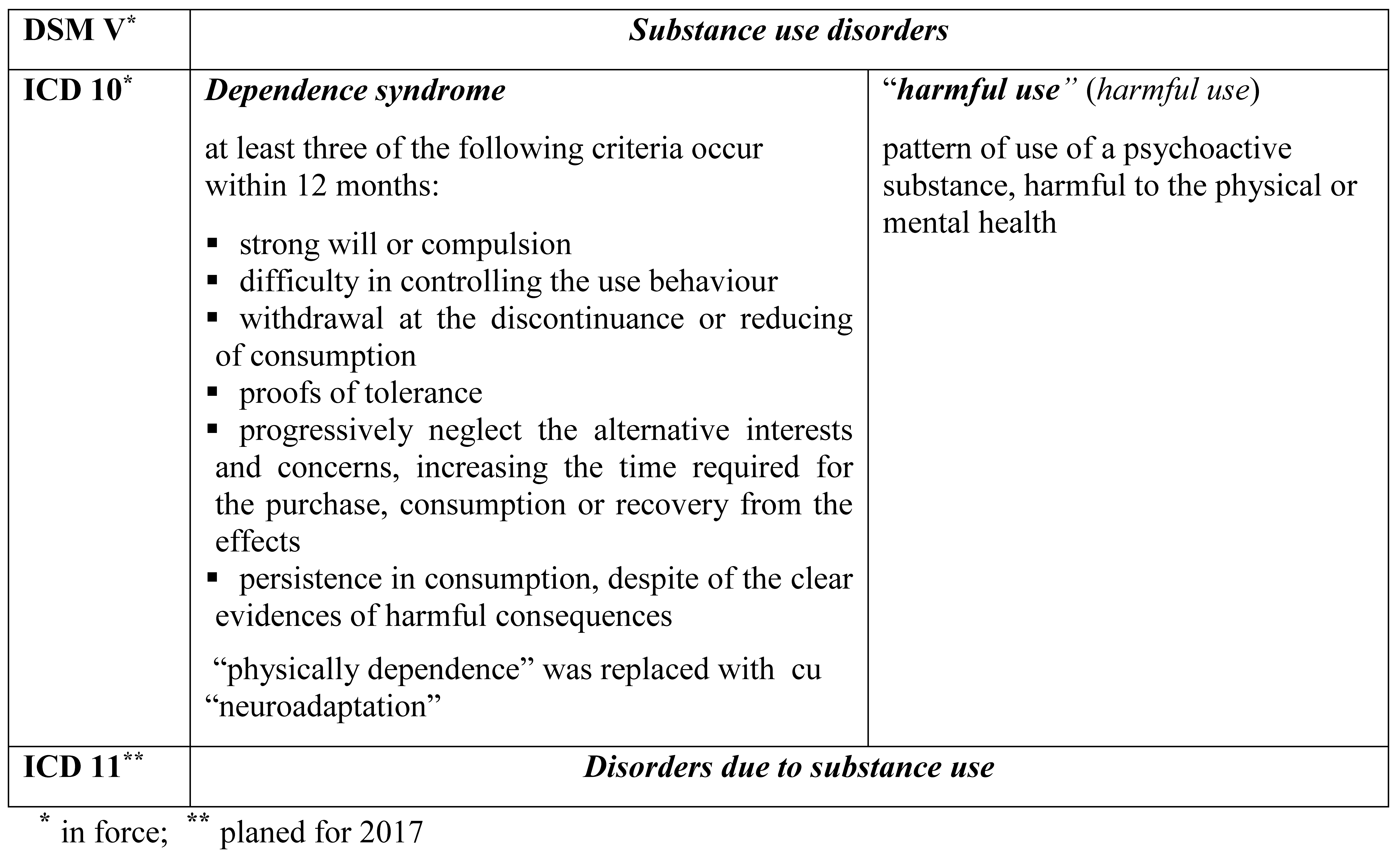
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) and International Classification (ICD)
- Recurrent substance use, resulting in failure to fulfil the major obligations at work, school or home
- The repeated use of the substance in situations of physical risk (driving a car, operating machinery)
- Keep consuming despite the persistence or recurrence of certain social or interpersonal problems caused or exacerbated by the effects of the substance
- Tolerance*, reflected in the need of a significantly higher dose in order to achieve the intoxication state or the desired effect or by substantially diminished effect on the continued use of the same amount
- Withdrawal*, manifested by the characteristic withdrawal syndrome or by taking the substance (or one related) to relieve or avoid withdrawal symptoms
- The substance is often taken in larger amounts or over longer periods than was intended
- Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to stop or control substance use
- Much of the time spent with activities for purchasing the substance, its use or for recovery from the effects produced
- Important social, professional or recreational activities are abandoned or reduced because of substance use
- The substance use is continued despite knowledge of some physical or mental problems, persistent or recurrent, caused or exacerbated by the substance used
- Craving, intense wish and or need for using a certain substance
- ✓ Substance intoxication
- ✓ Harmful use of substances
- ✓ Substance dependence
- ✓ Substance withdrawal
- ✓ Substance-induced mental disorders (specific types of mental or behavioural symptoms developing as a result of substance use).
Current concepts on drug dependence
- ✓ psychological dependence – impaired psychological control over drug use; it is the result of a interaction of a set of pharmacological (potential conditioning factors), psychological (primary conditioning factors) and social (group influences or the social acceptability of the drug) factors
- ✓ physical dependence - embodied in withdrawal syndrome at the interruption of the chronic consumption, on long periods or at reduction of the doses
- ✓ tolerance - reducing sensitivity to a substance after its repeated administration; is manifested by the need to increase the dose to achieve the same effect
- ✓ psychotoxicity - serious behavioural change, of psychotic grade, following prolonged use of high doses (obvious to alcohol, barbiturates, cocaine, LSD, amphetamines).
Conclusions
Acknowledgment
References
- Gupta, S.; Kulhara, P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence: An overview and update. Indian J Psychiatry 2007, 49, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalivas, P.W. Neurocircuitry of addiction. In Neuropsychopharmacology: The Fifth Generation of Progress; Davis, K.L., Charney, D., Coyle, J.T., Nemeroff, C., Eds.; American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- ***Definition of Addiction. Available online: www.asam.org.
- ***Lexicon of alcohol and drug terms published by the World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/terminology/who_lexicon/en/.
- Baconi, D. Toxicomanii – note de curs; Editura Tehnoplast Company S.R.L.: Bucureşti, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Baconi, D.; Bălălău, C. Toxicologia substanțelor de abuz; Editura Universitară Carol Davila: București, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Crocq, M.A. Historical and cultural aspects of man's relationship with addictive drugs. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2007, 9, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, L. Phantastica: A Classic Survey on the Use and Abuse of Mind-Altering Plants; Inner Traditions/Bear & Co, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Delay, J. Psychopharmacology and psychiatry. Towards A Classification of Psychotropic Drugs. Available online: http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/bulletin/bulletin_1967-01-01_1_page002.html.
- Nahas, G. A pharmacological classification of drags of abuse. UNODC - Bulletin on Narcotics 1981, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher, C.; Ungless, M.A. The Mechanistic Classification of Addictive Drugs. PLoS Med 2006, 3, e437. [Google Scholar]
- Atreya, R.V.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Z. Exploring drug-target interaction networks of illicit drugs. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, S1. [Google Scholar]
- ***World Health Organization. Expert Committee on Drug Dependence; Technical Report Series No. 407; WHO: Geneva, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- ***American Psychiatric Association. In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; 2013.
- *** World Health Organization. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. [Google Scholar]
- ***American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, G. “The Evil Genius of the Habit”: DSM-5 Seen in Historical Context. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2012, 73, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hairston, T.; Laux, J. DSM V Heals All Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders. 2012. Available online: www.allohiocc.org.
- Kanehl, S. Overview of Substance Use Disorders, 2012. Available online: www.naswwv.org.
- O'Brien, C. Addiction and dependence in DSM-V. Addiction 2011, 106, 866–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Brien, C.P.; Volkow, N.; Li, T.K. What's in a word? Addiction versus dependence in DSM-V. Am J Psychiatr 2006, 163, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reed, G.M. Toward ICD-11: Improving the Clinical Utility of WHO’s International Classification of Mental Disorders. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice 2010, 41, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- ***World Health Organization. The International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision. Available online: http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/revision/en.
- Vetulani, J. Drug addiction. Part 1. Psychoactive substances in the past and presence. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wise, R.A.; Koob, G.F. The Development and Maintenance of Drug Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacolog, 2014, 39, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Volkow, N.D. The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. Am J Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


  |
 |
© 2015 by the author. 2015 Daniela Luiza Baconi, Anne-Marie Ciobanu, Ana Maria Vlăsceanu, Oana Denisa Cobani, Carolina Negrei, Cristian Bălălău
Share and Cite
Baconi, D.L.; Ciobanu, A.-M.; Vlăsceanu, A.M.; Cobani, O.D.; Negrei, C.; Bălălău, C. Current Concepts on Drug Abuse and Dependence. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2015, 2, 18-33. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1008
Baconi DL, Ciobanu A-M, Vlăsceanu AM, Cobani OD, Negrei C, Bălălău C. Current Concepts on Drug Abuse and Dependence. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2015; 2(1):18-33. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaconi, Daniela Luiza, Anne-Marie Ciobanu, Ana Maria Vlăsceanu, Oana Denisa Cobani, Carolina Negrei, and Cristian Bălălău. 2015. "Current Concepts on Drug Abuse and Dependence" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 2, no. 1: 18-33. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1008
APA StyleBaconi, D. L., Ciobanu, A.-M., Vlăsceanu, A. M., Cobani, O. D., Negrei, C., & Bălălău, C. (2015). Current Concepts on Drug Abuse and Dependence. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 2(1), 18-33. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1008



