The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease; A Narrative Review
Abstract
Introduction
Discussions
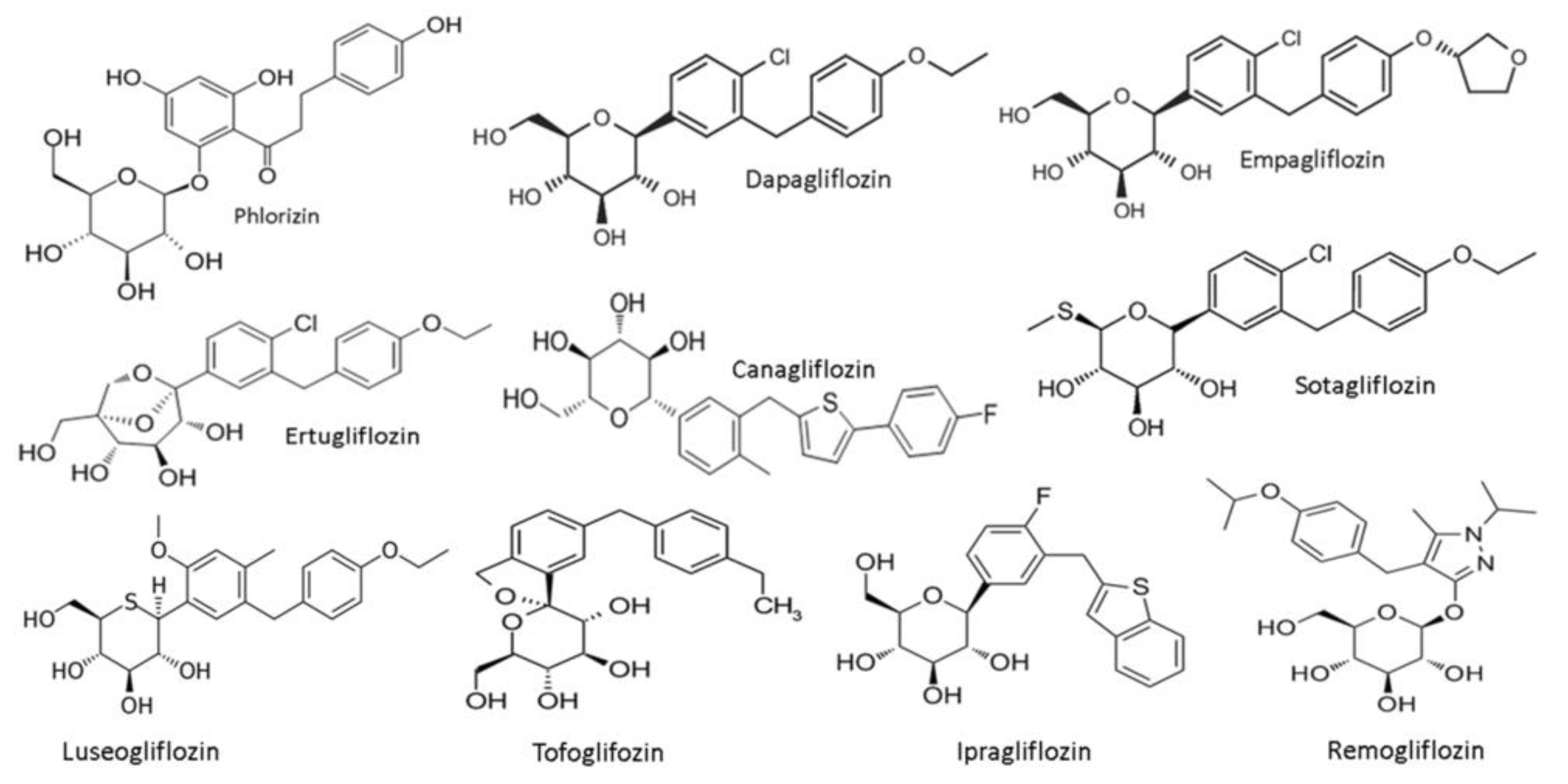
SGLT2 inhibitors-general features
The role of SGLT-2 inhibitors in the current treatment of type 2 diabetes
Current recommendations for the use of SGLT 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes therapy
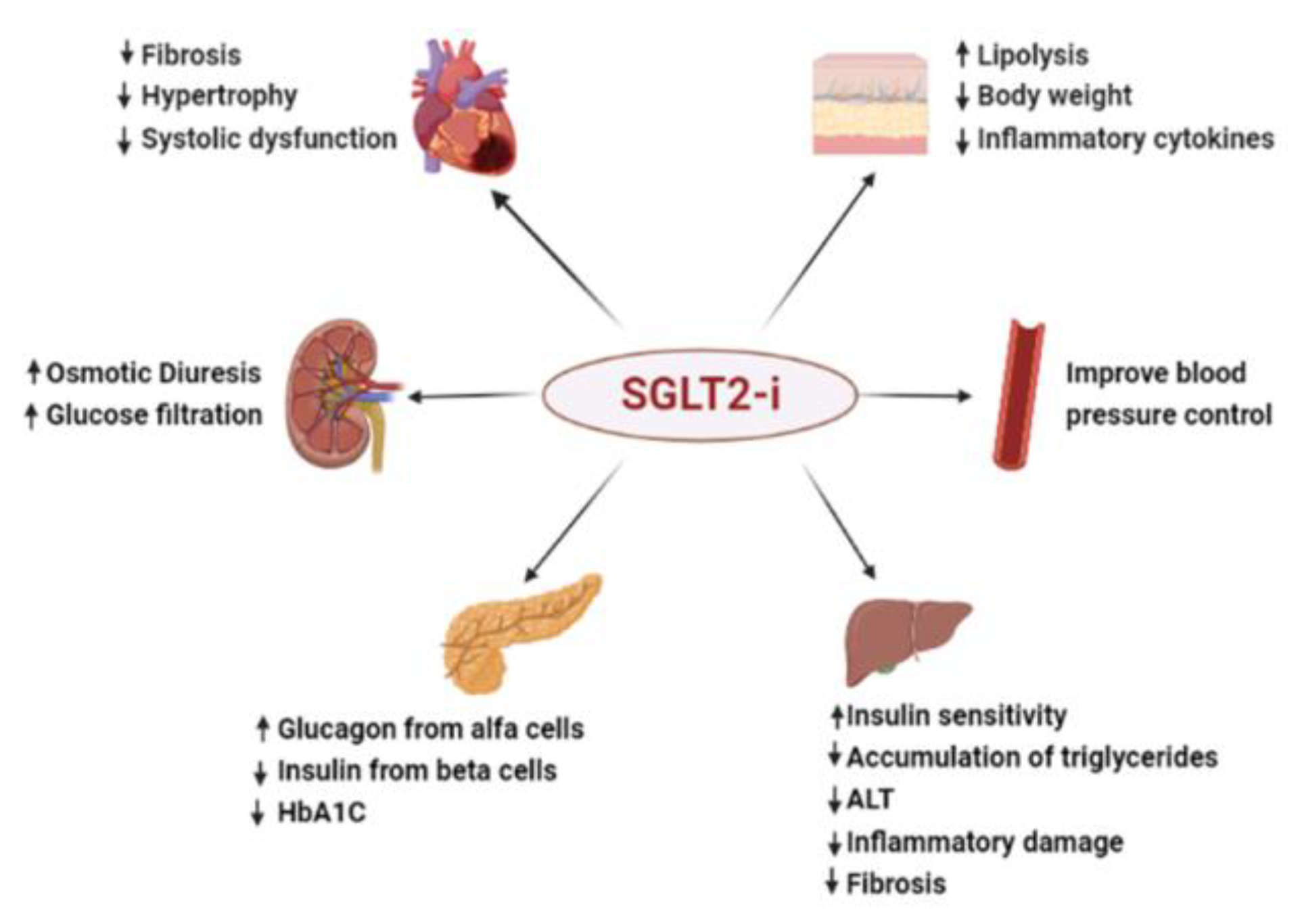
Effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on insulin resistance
Glycemic lowering effect
Reduction of the daily dose of insulin
- ○
- Insulin resistance and inflammation are reduced by SGLT2 inhibitors through polarizing M2 macrophages. Obesity, insulin resistance, and T2DM are all linked to chronic inflammation [52,53]. In addition to increasing immune cell recruitment and innate immune responses, obesity and heterotopic fat deposition also alter the phenotype of macrophages and enhance the infiltration of proinflammatory immune cells into metabolic organs, which leads to the development of insulin resistance [54,55]. Macrophage recruitment and polarization in particular, are key to obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Inhibition of M1 macrophage polarization and activation of the alternative M2 macrophage could prevent worsening of inflammation and insulin resistance [53,55,56]. Empagliflozin has been shown to decrease macrophage accumulation and promote the M2-dominant phenotypic differentiation of liver and white adipose tissue macrophages, hence reducing inflammation caused by obesity [57]. Empagliflozin may also attenuate inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity by decreasing M1 macrophage and T-cell accumulation and increasing the number of M2 macrophages [58].
- ○
- SGLT2 inhibitors impact the hormones produced by adipocytes. Serum leptin levels in T2DM patients [59] and FGF-21 [60] is increased while the level of serum adiponectin is decreased [61]; these alterations are thought to be closely connected to the start and progression of insulin resistance [62,63]. According to Tahara et al., mice and people with T2D have different levels of these adipocyte-derived hormones, but these alterations can be undone if the diabetic condition is stabilized. These results suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors decrease insulin resistance in T2DM [64]. The Matsuda-DeFronzo index and mood index, which are recognized markers of insulin secretion and insulin resistance, respectively, improved after administration of long-acting SGLT2 inhibitors, demonstrating that SGLT2 inhibitors reduce insulin resistance and secretion to insulin [65]. Long-acting SGLT2 inhibitors may lower daily blood glucose excursion, safeguard pancreatic function, and enhance glucose tolerance and insulin resistance as compared to intermediate-acting SGLT2 inhibitors [65].
- ○
- The development of numerous β-cell-related factors is encouraged by SGLT2 inhibitors. A larger mass of pancreatic beta cells was seen in mice receiving luseogliflozin treatment because of increased cell proliferation and decreased apoptosis. The levels of β-cell-related elements, including as insulin, MafA, PDX1, the GLP-1 receptor, and the glucose transporter Glut2, were elevated in mice receiving empagliflozin treatment. After empagliflozin treatment for one week, β-cell growth was encouraged and its protective effects against pancreatic β-cells were noticed [66].
Body weight reduction
Effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on plasma lipid values
Lipid biogenesis
Cholesterol homeostasis
Absorption/Transport of lipids
The effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on inflammation
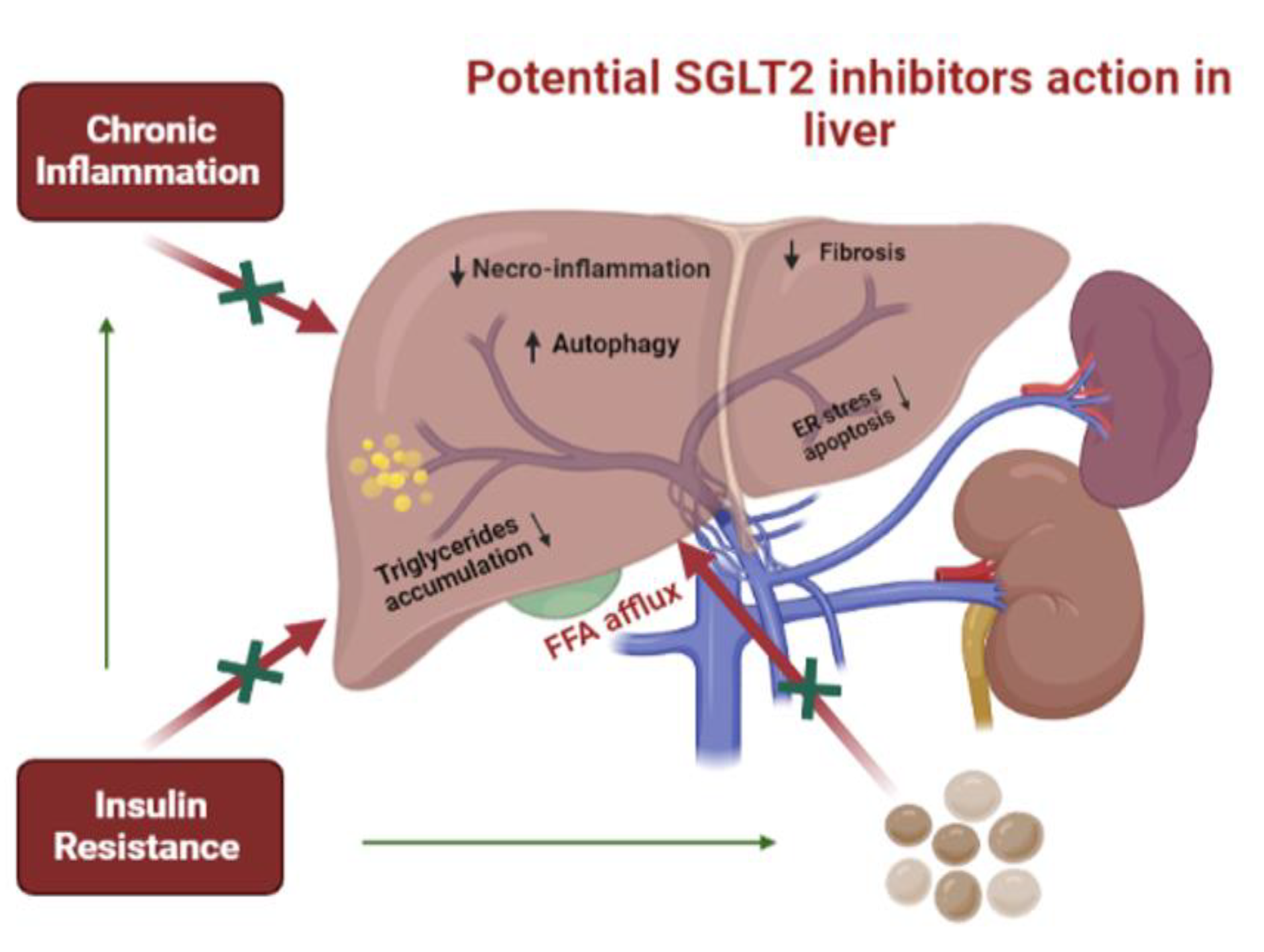
Effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with MAFLD (NAFLD or NASH)
Conclusions
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francque, S.M.; Marchesini, G.; Kautz, A.; Walmsley, M.; Dorner, R.; Lazarus, J.V.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Hallsworth, K.; Busetto, L.; Frühbeck, G.; et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A patient guideline. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Associazione Italiana per lo Studio del Fegato (AISF); Società Italiana di Diabetologia (SID); Società Italiana dell’Obesità (SIO). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults 2021: A clinical practice guideline of the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF), the Italian Society of Diabetology (SID) and the Italian Society of Obesity (SIO). Eat. Weight. Disord. -Stud. Anorexia, Bulim. Obes. 2022, 27, 1603–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, T.G.; Rinella, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease 2020: The State of the Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1851–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, C.; Sandu, C.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Sarbu, E.; Stoica, R.A.; Gherghiceanu, F.; Bohiltea, R.E.; Stefan, S.D.; Stoian, A.P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A major challenge in type 2 diabetes mellitus (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2387–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotti, A.; Caletti, M.T.; Sasdelli, A.S.; Brodosi, L.; Marchesini, G. Pathophysiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Lifestyle-Gut-Gene Interaction. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34 (Suppl 3), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Maurantonio, M.; Marrazzo, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Adinolfi, L.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Evolving paradigms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6571–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlehurst, J.M.; Woods, C.; Marjot, T.; Cobbold, J.F.; Tomlinson, J.W. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo-Sanchez, P.; Bril, F.; Maximos, M.; Lomonaco, R.; Biernacki, D.; Orsak, B.; Subbarayan, S.; Webb, A.; Hecht, J.; Cusi, K. High Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Plasma Aminotransferase Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Wong, R.; Fraysse, J.; Shreay, S.; Li, S.; Harrison, S.; Gordon, S.C. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression rates to cirrhosis and progression of cirrhosis to decompensation and mortality: a real world analysis of Medicare data. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, T.V.; Succurro, E.; Sciacqua, A.; Andreozzi, F.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with cardiovascular disease in subjects with different glucose tolerance. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Ben, Q.; Qiu, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, L. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 130, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbas, O.; Erdogan, M.A.; Khalilnezhad, A.; Gürkan, F.T.; Yiğittürk, G.; Meral, A.; Taskiran, D. Neurobehavioral effects of long-term maternal fructose intake in rat offspring. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 69, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.K.C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Animal models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: current perspectives and recent advances. J. Pathol. 2016, 241, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmison, J.; McCullough, A.J. Pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Human Data. Clin. Liver Dis. 2007, 11, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitturi, S.; Farrell, G.C. Etiopathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2001, 21, 027–042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62 (Suppl. 1), S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Day, C.P. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Class effect for SGLT-2 inhibitors: a tale of 9 drugs. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffo, S.; Taddei, T. SGLT2 inhibitors and cirrhosis: A unique perspective on the comanagement of diabetes mellitus and ascites. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 11, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.I.; Yazdi, Z.S.; Beitelshees, A.L. Pharmacological treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, Y.-H.; Ko, S.-H.; Zimmet, P.; Son, H.-Y. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006, 368, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, N.; Davies, M.J.; Grant, P.J.; Mathieu, C.; Petrie, J.R.; Cosentino, F.; Buse, J.B. Guideline recommendations and the positioning of newer drugs in type 2 diabetes care. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, C.; Kerr-Conte, J.; Gmyr, V.; Queniat, G.; Moerman, E.; Thévenet, J.; Beaucamps, C.; Delalleau, N.; Popescu, I.; Malaisse, W.J.; et al. Inhibition of the glucose transporter SGLT2 with dapagliflozin in pancreatic alpha cells triggers glucagon secretion. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, R.G.; Colagiuri, S.; Pollock, C. SGLT2 inhibitors: New medicines for addressing unmet therapeutic needs in type 2 diabetes. Australas. Med J. 2014, 7, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, Y. SGLT2 Inhibitors: The Star in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes? Diseases 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Leung, P.S. Inhibition of the sodium glucose co-transporter-2: its beneficial action and potential combination therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Muscelli, E.; Frascerra, S.; Baldi, S.; Mari, A.; Heise, T.; Broedl, U.C.; Woerle, H.-J. Metabolic response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Krishan, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Farooqui, K.J.; Singh, M.K.; Wasir, J.S.; Bansal, B.; Kaur, P.; Jevalikar, G.; Gill, H.K.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Liver Fat in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial (E-LIFT Trial). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Fitchett, D.; Hantel, S.; George, J.T.; Zinman, B. Empagliflozin is associated with improvements in liver enzymes potentially consistent with reductions in liver fat: results from randomised trials including the EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, J.W.; Lundkvist, P.; Jansson, P.-A.; Johansson, L.; Kvarnström, M.; Moris, L.; Miliotis, T.; Forsberg, G.-B.; Risérus, U.; Lind, L.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin and n-3 carboxylic acids on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in people with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2021, 45 (Suppl. 1), S144–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, D.K.; Shih, W.J.; Cosentino, F.; Charbonnel, B.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Pratley, R.; Greenberg, M.; Wang, S.; Huyck, S.; et al. Association of SGLT2 Inhibitors With Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2461–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Wexler, D.J.; Tsapas, A.; Rossing, P.; Mingrone, G.; Mathieu, C.; D’alessio, D.A.; Davies, M.J. 2019 update to: Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2019, 63, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Nolan, C.J. Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, F.; Arora, P.S.; Dyck, P.J.; Bekris, L.; Lernmark, A.; Achenbach, S.J.; Oberg, A.L.; Rizza, R.A. Effects of Duration of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Insulin Secretion. Endocr. Pr. 2006, 12, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M. Update on developments with SGLT2 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 1335–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Griffen, S.C.; Boulton, D.W.; Leil, T.A. Use of systems pharmacology modeling to elucidate the operating characteristics of SGLT1 and SGLT2 in renal glucose reabsorption in humans. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 274–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. (.; Lee, T.; DeFronzo, R.A. Why Do SGLT2 Inhibitors Inhibit Only 30–50% of Renal Glucose Reabsorption in Humans? Diabetes 2012, 61, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Pan, H.; Zou, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Zhu, H. Safety and efficiency of SGLT2 inhibitor combining with insulin in subjects with diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2017, 96, e6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; de Zeeuw, D.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Fulcher, G.; Ways, K.; Desai, M.; Shaw, W.; Capuano, G.; Alba, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Canagliflozin, an Inhibitor of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2, When Used in Conjunction With Insulin Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Jelaska, A.; Zeller, C.; Kim, G.; Broedl, U.C.; Woerle, H.J.; on behalf of the EMPA-REG BASAL trial investigators. Impact of empagliflozin added on to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin: a 78-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Jelaska, A.; Frappin, G.; Salsali, A.; Kim, G.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Improved Glucose Control With Weight Loss, Lower Insulin Doses, and No Increased Hypoglycemia With Empagliflozin Added to Titrated Multiple Daily Injections of Insulin in Obese Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Woo, V.; Rohwedder, K.; Sugg, J.; Parikh, S.; Dapagliflozin 006 Study Group. Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin: efficacy and safety over 2 years. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2013, 16, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.; Woo, V.; Soler, N.G.; Pahor, A.; Sugg, J.; Rohwedder, K.; Parikh, S. Long-Term Efficacy of Dapagliflozin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Receiving High Doses of Insulin: a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 156, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.; Norwood, P.; T’Joen, C.; Bastien, A.; List, J.F.; Fiedorek, F.T. A Study of Dapagliflozin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Receiving High Doses of Insulin Plus Insulin Sensitizers: applicability of a novel insulin-independent treatment. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merovci, A.; Solis-Herrera, C.; Daniele, G.; Eldor, R.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Tripathy, D.; Xiong, J.; Perez, Z.; Norton, L.; Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin improves muscle insulin sensitivity but enhances endogenous glucose production. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, H.; Habich, C.; Eckel, J. Adaptive immunity in obesity and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accu-mulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Benkdane, M.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Bonnafous, S.; Louvet, A.; Lafdil, F.; Pecker, F.; Tran, A.; Gual, P.; Mallat, A.; et al. M2 Kupffer cells promote M1 Kupffer cell apoptosis: A protective mechanism against alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 59, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsouris, D.; Li, P.-P.; Thapar, D.; Chapman, J.; Olefsky, J.M.; Neels, J.G. Ablation of CD11c-Positive Cells Normalizes Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Insulin Resistant Animals. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Nagata, N.; Nagashimada, M.; Zhuge, F.; Ni, Y.; Chen, G.; Mayoux, E.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. SGLT2 Inhibition by Empagliflozin Promotes Fat Utilization and Browning and Attenuates Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Polarizing M2 Macrophages in Diet-induced Obese Mice. EBioMedicine 2017, 20, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Shi, Z.; Yuan, B.; Dai, Y.; Wu, G.; Hussain, A. Association between Serum Leptin Concentrations and Insulin Resistance: A Population-Based Study from China. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e54615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, A.O.; Molina-Carrion, M.; Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Folli, F.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Tripathy, D. Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Is Elevated in Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Type 2 Diabetes and Correlates With Muscle and Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Funahashi, T.; Arita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Matsuda, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Iwahashi, H.; Kuriyama, H.; Ouchi, N.; Maeda, K.; et al. Plasma Concentrations of a Novel, Adipose-Specific Protein, Adiponectin, in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporez, J.P.G.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Petersen, M.C.; Pesta, D.; Guigni, B.A.; Serr, J.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Cellular Mechanisms by Which FGF21 Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Kataria, M.A.; Saini, V.; Yadav, A. Role of leptin and adiponectin in insulin resistance. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 417, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, A.; Takasu, T.; Yokono, M.; Imamura, M.; Kurosaki, E. Characterization and comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Part 2. Antidiabetic effects in type 2 diabetic mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 131, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimo, N.; Matsuoka, T.-A.; Miyatsuka, T.; Takebe, S.; Tochino, Y.; Takahara, M.; Kaneto, H.; Shimomura, I. Short-term selective alleviation of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity ameliorates the suppressed expression of key β-cell factors under diabetic conditions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.B.; Mequanint, S.; Miller, K.; Reichert, S.M.; Spaic, T. When Insulin Therapy Fails: The Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, e141–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suceveanu, A.I.; Stoian, A.P.; Parepa, I.; Voinea, C.; Hainarosie, R.; Manuc, D.; Nitipir, C.; Mazilu, L.; Suceveanu, A.P. Gut Microbiota Patterns in Obese and Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) Patients from Romanian Black Sea Coast Region. Revista. de Chimie (Rev Chim) 2018, 69, 2260–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, A.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Sato, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Takamoto, I.; Katsuyama, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukazawa, M.; et al. Tofogliflozin Improves Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle and Accelerates Lipolysis in Adipose Tissue in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2015, 157, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ota, T. Emerging roles of SGLT2 inhibitors in obesity and insulin resistance: Focus on fat browning and macrophage polarization. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Manabe, I.; Nagasaki, M.; Eto, K.; Yamashita, H.; Ohsugi, M.; Otsu, M.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Sugiura, S.; et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkau, B.; Home, P.D.; Vincent, M.; Marre, M.; Freemantle, N. Factors Associated With Weight Gain in People With Type 2 Diabetes Starting on Insulin. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2108–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiroli, A.E.; Miele, L.; Morabito, A. Increase of body weight during the first year of intensive insulin treatment in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, H.; Jansen, M.; Koerts, J.; Verschoor, L. Prevention of weight gain in type 2 diabetes requiring insulin treatment. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2004, 6, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Combined Thiazolidinedione-Insulin Therapy: should we be concerned about safety? Drug Saf. 2004, 27, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.; Burden, A.F.; Paisey, R.B.; Cull, C.A.; Holman, R.R.; U. K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group Sulfonylurea Inadequacy: efficacy of addition of insulin over 6 years in patients with type 2 diabetes in the U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 57). Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.H.; Yoon, J.; Hahn, S.; Cho, Y.M. Comparison between SGLT2 inhibitors and DPP4 inhibitors added to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review with indirect comparison meta-analysis. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2016, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Kang, Y.M.; Lee, S.E.; Park, J.; Lee, W.J.; Jung, C.H. Comparison between sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and pioglitazone as additions to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review with an indirect comparison meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, R. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors or sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as an add-on to insulin therapy: A comparative review. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devenny, J.J.; Godonis, H.E.; Harvey, S.J.; Rooney, S.; Cullen, M.J.; Pelleymounter, M.A. Weight Loss Induced by Chronic Dapagliflozin Treatment Is Attenuated by Compensatory Hyperphagia in Diet-Induced Obese (DIO) Rats. Obesity 2012, 20, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.M.; A Rizvi, A.; Giglio, R.V.; Stoian, A.P.; Ligi, D.; Mannello, F. Impact of Glucose-Lowering Medications on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Risk in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.M.; Carruba, G.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Banach, M.; Nikolic, D.; Giglio, R.V.; Terranova, A.; Soresi, M.; Giannitrapani, L.; Montalto, G.; et al. Daily Use of Extra Virgin Olive Oil with High Oleocanthal Concentration Reduced Body Weight, Waist Circumference, Alanine Transaminase, Inflammatory Cytokines and Hepatic Steatosis in Subjects with the Metabolic Syndrome: A 2-Month Intervention Study. Metabolites 2020, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghe, G.; Stoian, A.P.; Gaman, M.-A.; Socea, B.; Neagu, T.P.; Stanescu, A.M.A.; Bratu, O.G.; Mischianu, D.L.D.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Diaconu, C.C. The Benefits and Risks of Antioxidant Treatment in Liver Diseases. Revista. de Chimie. (Rev. Chim.) 2019, 70, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, D.; Wang, Q.; Abdulla, A.; Xie, X.-J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Yang, E.S.; Liu, L.-P.; Vaitheesvaran, B.; et al. Regulation of lipogenesis by cyclin-dependent kinase 8–mediated control of SREBP-1. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2417–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducheix, S.; Lobaccaro, J.; Martin, P.; Guillou, H. Liver X Receptor: an oxysterol sensor and a major player in the control of lipogenesis. Chem Phys Lipids. 2011, 164, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.G.; Doumas, M.; Imprialos, K.P.; Stavropoulos, K.; Georgianou, E.; Katsimardou, A.; Karagiannis, A. Diabetes and lipid metabolism. Hormones 2018, 17, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojima, T.; Tomotsune, T.; Iijima, T.; Akimoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Aso, Y. Empagliflozin (an SGLT2 inhibitor), alone or in combination with linagliptin (a DPP-4 inhibitor), prevents steatohepatitis in a novel mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2016, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritsen, K.M.; Voigt, J.H.; Pedersen, S.B.; Hansen, T.K.; Møller, N.; Jessen, N.; Gormsen, L.C.; Søndergaard, E. Effects of SGLT2 inhibition on lipid transport in adipose tissue in type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e210558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osataphan, S.; Macchi, C.; Singhal, G.; Chimene-Weiss, J.; Sales, V.; Kozuka, C.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Pan, H.; Tangcharoenpaisan, Y.; Morningstar, J.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition reprograms systemic metabolism via FGF21-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 4, e123130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.A.; Ford, R.J.; Lu, J.H.; Lu, R.; Lundenberg, L.; Desjardins, E.M.; Green, A.E.; Lally, J.S.; Schertzer, J.D.; Steinberg, G.R. The SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin suppresses lipid synthesis and interleukin-1 beta in ApoE deficient mice. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 2347–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, S.A.; Ford, R.J.; Smith, B.K.; Gowans, G.J.; Mancini, S.J.; Pitt, R.D.; Day, E.A.; Salt, I.P.; Steinberg, G.R.; Hardie, D.G. The Na+/Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitor Canagliflozin Activates AMPK by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Function and Increasing Cellular AMP Levels. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2784–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. Cholesterol metabolism and homeostasis in the brain. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenen, A.G.; Halmos, B.; Tall, A.R.; Westerterp, M. Cholesterol efflux pathways, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 56, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Ballester, M.; Herrero-Cervera, A.; Vinué, Á.; Martínez-Hervás, S.; González-Navarro, H. Impact of Cholesterol Metabolism in Immune Cell Function and Atherosclerosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Huggins, L.-A.; Scerbo, D.; Obunike, J.; Mullick, A.E.; Rothenberg, P.L.; Di Prospero, N.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Goldberg, I.J. Mechanism of Increased LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) and Decreased Triglycerides With SGLT2 (Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2) Inhibition. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadini, G.P.; Bonora, B.M.; Zatti, G.; Vitturi, N.; Iori, E.; Marescotti, M.C.; Albiero, M.; Avogaro, A. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on HDL cholesterol, particle size, and cholesterol efflux capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkan, E. Effects of dapagliflozin on serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Eur. J. Ther. 2020, 26, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, A.; Simental-Mendía, M.; Millán-Alanís, J.M.; Simental-Mendía, L.E. Effect of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 48 randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, Y.; Ishii, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Asano, H.; Miake, S.; Kanda, E.; Urata, H.; Yoshida, M. Potential Impact on Lipoprotein Subfractions in Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Med. Insights: Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 12, 1179551419866811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Li, H.; Shen, L.; Fu, J.; Ma, J.; Gu, Z.; Lin, H. High-dose sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors are superior in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.-A.; Park, Y.-M.; Yun, J.-S.; Lim, T.-S.; Song, K.-H.; Yoo, K.-D.; Ahn, Y.-B.; Ko, S.-H. A comparison of effects of DPP-4 inhibitor and SGLT2 inhibitor on lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2017, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.; Ott, C.; Jung, S.; Striepe, K.; Karg, M.V.; Kannenkeril, D.; Dienemann, T.; Schmieder, R.E. How does empagliflozin improve arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? Sub analysis of a clinical trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejiri, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Kihara, H.; Hata, Y.; Nagano, T.; Takaishi, A.; Toda, H.; Namba, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Akagi, S.; et al. Effects of luseogliflozin and voglibose on high-risk lipid profiles and inflammatory markers in diabetes patients with heart failure. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, C.J.; Myles, L.A.M.; Merlo, E.M. Eating Disorders in Men: A Comprehensive Summary. J. Mind Med Sci. 2022, 9, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socea, B.; Silaghi, A.; Rebegea, L.F.; Balan, D.G.; Balalau, C.; Tenea-Cojan, T.Ș.; Mihai, D.A.; Paunica, I. Diabetes mellitus: interdisciplinary medical, surgical and psychological therapeutic approach. J. Mind Med Sci. 2023, 10, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvind, A.; Osganian, S.A.; Cohen, D.E.; Corey, K.E. Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism in Liver Disease. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth (MA), 21 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wallenius, K.; Kroon, T.; Hagstedt, T.; Löfgren, L.; Sörhede-Winzell, M.; Boucher, J.; Lindén, D.; Oakes, N.D. The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin promotes systemic FFA mobilization, enhances hepatic β-oxidation, and induces ketosis. J. Lipid Res. 2022, 63, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.E.; Yahya, G.; Popoviciu, M.S.; Cavalu, S.; Abd-Eldayem, M.A.; Saber, S. Unlocking the Full Potential of SGLT2 Inhibitors: Expanding Applications beyond Glycemic Control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Correa, J.I.; Correa-Rotter, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Van Gaal, L.; Leiter, L.A.; Vijapurkar, U.; List, J.; Cuddihy, R.; Ren, J.; Davies, M.J. Effects of canagliflozin versus glimepiride on adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2018, 85, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R.; Boden, G.; Smith, S.; Chalamandaris, A.-G.; Duchesne, D.; Iqbal, N.; List, J. Changes in Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion with the Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2014, 16, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Kang, B.; Zhou, J. The current role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus management. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; et al. An Overview of the Cardiorenal Protective Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.-F.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chiou, T.T.-Y.; Chu, T.-H.; Li, L.-C.; Ng, H.-Y.; Lee, W.-C.; Lee, C.-T. Emergence of SGLT2 Inhibitors as Powerful Antioxidants in Human Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntibeju, O.O. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation: examining the links. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 11, 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Theofilis, P.; Sagris, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Siasos, G.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in rodents. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, J.; Vlacho, B.; Ortega, E.; Vallés, J.A.; Mata-Cases, M.; Castelblanco, E.; Wittbrodt, E.T.; Fenici, P.; Kosiborod, M.; Mauricio, D.; et al. Cardiovascular and mortality benefits of sodium–glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: CVD-Real Catalonia. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoviciu, M.-S.; Păduraru, L.; Yahya, G.; Metwally, K.; Cavalu, S. Emerging Role of GLP-1 Agonists in Obesity: A Comprehensive Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshnbari, A.; Idris, I. Can sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor reduce the risk of adverse complications due to COVID-19? – Targeting hyperinflammation. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2022, 38, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Yasells-Garcia, A.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Villa-Jimenez, O.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; et al. Development and validation of a noninvasive prediction model for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis resolution after lifestyle intervention. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1875–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, E.; Takamura, T.; Sakurai, M.; Mizukoshi, E.; Zen, Y.; Takeshita, Y.; Kurita, S.; Arai, K.; Yamashita, T.; Sasaki, M.; et al. Histological Course of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Japanese Patients: tight glycemic control, rather than weight reduction, ameliorates liver fibrosis. Diabetes Care 2009, 33, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabiku, K. Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients With Concurrent Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Review of the Evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 768850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, G.; Xiong, J.; Solis-Herrera, C.; Merovci, A.; Eldor, R.; Tripathy, D.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Norton, L.; Abdul-Ghani, M. Dapagliflozin Enhances Fat Oxidation and Ketone Production in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2036–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Orlicky, D.J.; Myakala, K.; Yang, P.; Levi, M. The Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Prevents Renal and Liver Disease in Western Diet Induced Obesity Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Baldi, S.; Frascerra, S.; Astiarraga, B.; Heise, T.; Bizzotto, R.; Mari, A.; Pieber, T.R.; Muscelli, E. Shift to Fatty Substrate Utilization in Response to Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Subjects Without Diabetes and Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokono, M.; Takasu, T.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Mitsuoka, K.; Kihara, R.; Muramatsu, Y.; Miyoshi, S.; Tahara, A.; Kurosaki, E.; Li, Q.; et al. SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin reduces body fat mass by increasing fatty acid oxidation in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 727, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, E.; Mehrpour, M.; Botti, J.; Dupont, N.; Hamaï, A.; Nascimbeni, A.C.; Codogno, P. Autophagy: A Druggable Process. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, S.; Oelze, M.; Hanf, A.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Kashani, F.; Roohani, S.; Welschof, P.; Kopp, M.; Gödtel-Armbrust, U.; Xia, N.; et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin improves the primary diabetic complications in ZDF rats. Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 370–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terami, N.; Ogawa, D.; Tachibana, H.; Hatanaka, T.; Wada, J.; Nakatsuka, A.; Eguchi, J.; Horiguchi, C.S.; Nishii, N.; Yamada, H.; et al. Long-Term Treatment with the Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, Dapagliflozin, Ameliorates Glucose Homeostasis and Diabetic Nephropathy in db/db Mice. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, A.; Kurosaki, E.; Yokono, M.; Yamajuku, D.; Kihara, R.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Takasu, T.; Imamura, M.; Li, Q.; Tomiyama, H.; et al. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin on hyperglycaemia, oxidative stress, inflammation and liver injury in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Sodium–glucose cotransporter inhibitors and oxidative stress: An update. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3231–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, H.; Miki, T.; Kuno, A.; Mizuno, M.; Sato, T.; Tanno, M.; Yano, T.; Nakata, K.; Kimura, Y.; Abe, K.; et al. Empagliflozin, an SGLT2 Inhibitor, Reduced the Mortality Rate after Acute Myocardial Infarction with Modification of Cardiac Metabolomes and Antioxidants in Diabetic Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 368, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, H.; Coronel, I.; Arellano, A.; Pacheco, U.; Bautista, R.; Franco, M.; Escalante, B. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Inhibition Prevents Oxidative Stress in the Kidney of Diabetic Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 542042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, J.A.; Guirguis, E.; Thornby, K.-A. A Systematic Review of Newer Antidiabetic Agents in the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Nelliyanil, M.; Mendagudli, R.; Rajeshwari, S.; Kona, C.; Kundapur, R.; Sathyanath, S.; Kulkarni, V.; Aggarwal, S. Evaluation of risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in India: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Educ. Heal. Promot. 2023, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaağaç, Y. Sarcopenic obesity, pathogenesis, and treatment with a focus on exercise and protein intake. J. Mind Med Sci. 2023, 10, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Qu, T.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Rao, C. Therapeutic outcome of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Afr. Health Sci. 2023, 23, 416–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M.; Herman, R.; Janež, A.; Al Mahmeed, W.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Al-Alawi, K.; Banach, M.; Banerjee, Y.; Ceriello, A.; Cesur, M.; et al. The Relationship between COVID-19 and Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis: A Large Spectrum from Glucocorticoid Insufficiency to Excess—The CAPISCO International Expert Panel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Hayashi, A.; Taguchi, T.; Arai, R.; Sasaki, S.; Takano, K.; Inoue, Y.; Shichiri, M. Effects of canagliflozin on body composition and hepatic fat content in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, A.N.; Kutz, A.; Christ, E.R.; Heim, M.H.; Ebrahimi, F. Canagliflozin and Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: New Insights From CANVAS. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Agrawal, P.K.; Doneria, J.; Nigam, A. Effects of Canagliflozin on Abnormal Liver Function Tests in Patients of Type 2 Diabetes with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Assoc Physicians India 2018, 66, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sumida, Y.; Murotani, K.; Saito, M.; Tamasawa, A.; Osonoi, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Osonoi, T. Effect of luseogliflozin on hepatic fat content in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective, single-arm trial (LEAD trial). Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, T.; Yoshida, O.; Matsuura, B.; Furukawa, S.; Hirooka, M.; Abe, M.; Tokumoto, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Takeshita, E.; et al. Additional Effect of Luseogliflozin on Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Complicated by Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Open-Label, Randomized, Parallel-Group Study. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Csermely, A.; Beatrice, G.; Targher, G. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metabolites 2020, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.-U.; Cusi, K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, N.; Perakakis, N.; Mantzoros, C. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Ex quo et quo vadimus? Metabolism 2019, 98, III. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Shimizu, S.; Inoue, K.; Saito, D.; Yanagisawa, M.; Inukai, K.; Akiyama, Y.; Morimoto, Y.; Noda, M.; Shimada, A. Comparison of Ipragliflozin and Pioglitazone Effects on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, 24-Week, Open-Label, Active-Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, T.; Isogawa, A.; Toda, N.; Tagawa, K. Effectiveness of Ipragliflozin, a Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitor, as a Second-line Treatment for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Who Do Not Respond to Incretin-Based Therapies Including Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analogs and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors. Clin. Drug Investig. 2016, 36, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seko, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Mori, K.; Taketani, H.; Ishiba, H.; Hara, T.; Okajima, A.; Umemura, A.; Nishikawa, T.; et al. Effect of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor on liver function tests in Japanese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, K.; Jojima, T.; Iijima, T.; Murohisa, T.; Iijima, M.; Takekawa, H.; Usui, I.; Hiraishi, H.; et al. Evaluation of the effects of dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, on hepatic steatosis and fibrosis using transient elastography in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, T.; Fushimi, N.; Kawai, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Hachiya, H.; Ito, S.; Kawai, H.; Ohashi, N.; Mori, A. Luseogliflozin improves liver fat deposition compared to metformin in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective randomized controlled pilot study. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuta, N.; Kawamura, Y.; Watanabe, C.; Nishimura, A.; Okubo, M.; Mori, Y.; Fujiyama, S.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Impact of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor on histological features and glucose metabolism of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease complicated by diabetes mellitus. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, S.; Gancheva, S.; Straßburger, K.; Herder, C.; Machann, J.; Katsuyama, H.; Kabisch, S.; Henkel, E.; Kopf, S.; Lagerpusch, M.; et al. Empagliflozin Effectively Lowers Liver Fat Content in Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 4, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2019, 43, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimiya, N.; Tajima, K.; Imajo, K.; Kameda, A.; Yoshida, E.; Togashi, Y.; Aoki, K.; Inoue, T.; Nakajima, A.; Utsunomiya, D.; et al. Effects of Canagliflozin on Hepatic Steatosis, Visceral Fat and Skeletal Muscle among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 3391–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


 |
 |
© 2024 by the authors. 2024 Mihaela Simona Popoviciu, Lorena Păduraru, Md Mominur Rahman, Fatema Akter Supti, Roxana Adriana Stoica, Delia Reurean-Pintilei, Cristina Ioana Bica, Simona Cavalu
Share and Cite
Popoviciu, M.S.; Paduraru, L.; Rahman, M.M.; Supti, F.A.; Stoica, R.A.; Reurean-Pintilei, D.; Bica, C.I.; Cavalu, S. The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease; A Narrative Review. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2024, 11, 62-77. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1439
Popoviciu MS, Paduraru L, Rahman MM, Supti FA, Stoica RA, Reurean-Pintilei D, Bica CI, Cavalu S. The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease; A Narrative Review. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2024; 11(1):62-77. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1439
Chicago/Turabian StylePopoviciu, Mihaela Simona, Lorena Paduraru, Md Mominur Rahman, Fatema Akter Supti, Roxana Adriana Stoica, Delia Reurean-Pintilei, Cristina Ioana Bica, and Simona Cavalu. 2024. "The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease; A Narrative Review" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 11, no. 1: 62-77. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1439
APA StylePopoviciu, M. S., Paduraru, L., Rahman, M. M., Supti, F. A., Stoica, R. A., Reurean-Pintilei, D., Bica, C. I., & Cavalu, S. (2024). The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease; A Narrative Review. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 11(1), 62-77. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1439



