Evaluation of a Deep Learning Reconstruction for High-Quality T2-Weighted Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MRI Protocols
2.2. Deep Learning Reconstruction
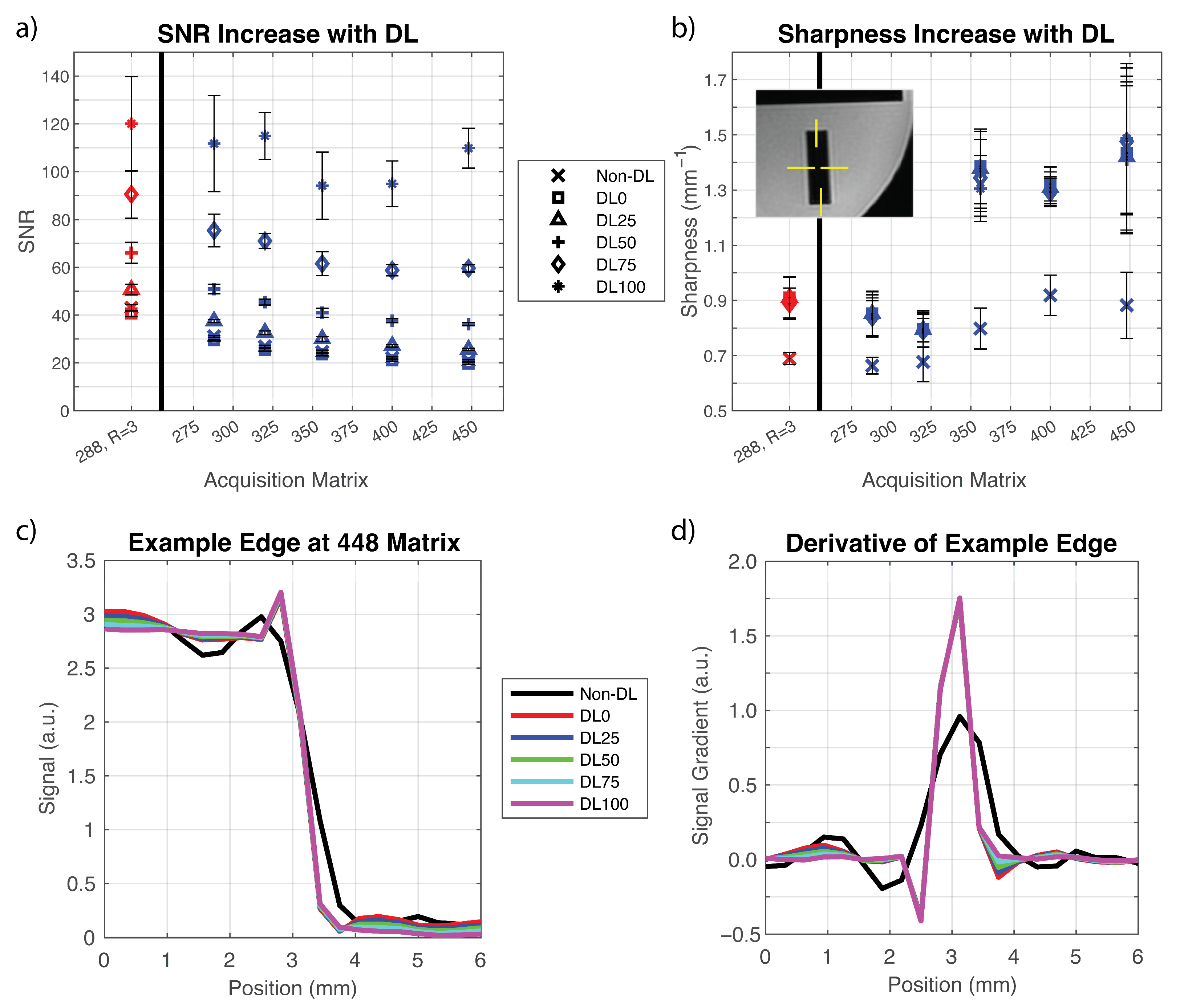
2.3. Technical Analysis in Phantoms
2.4. Retrospecive SOC Imaging
2.4.1. Quantitative Assessment
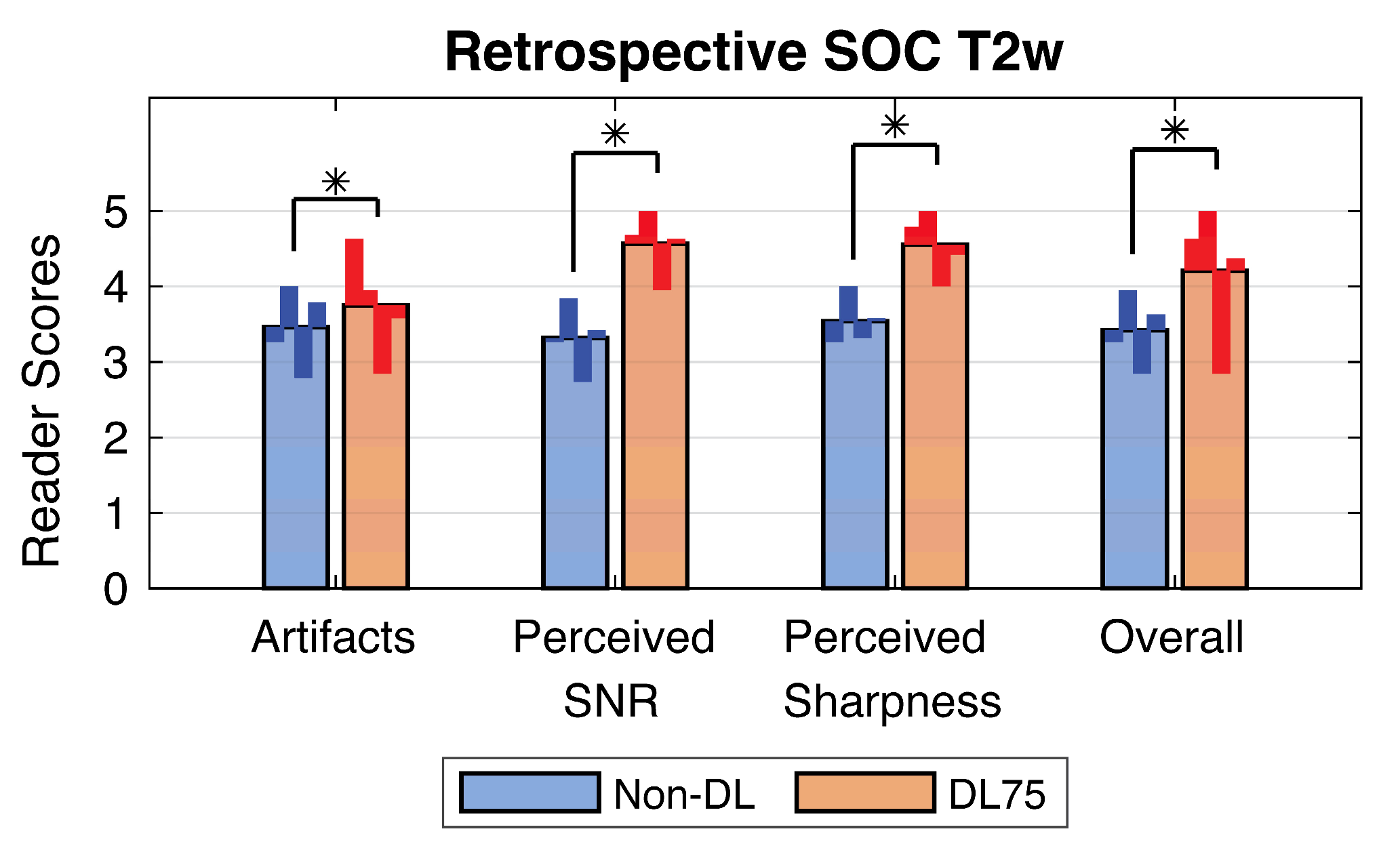
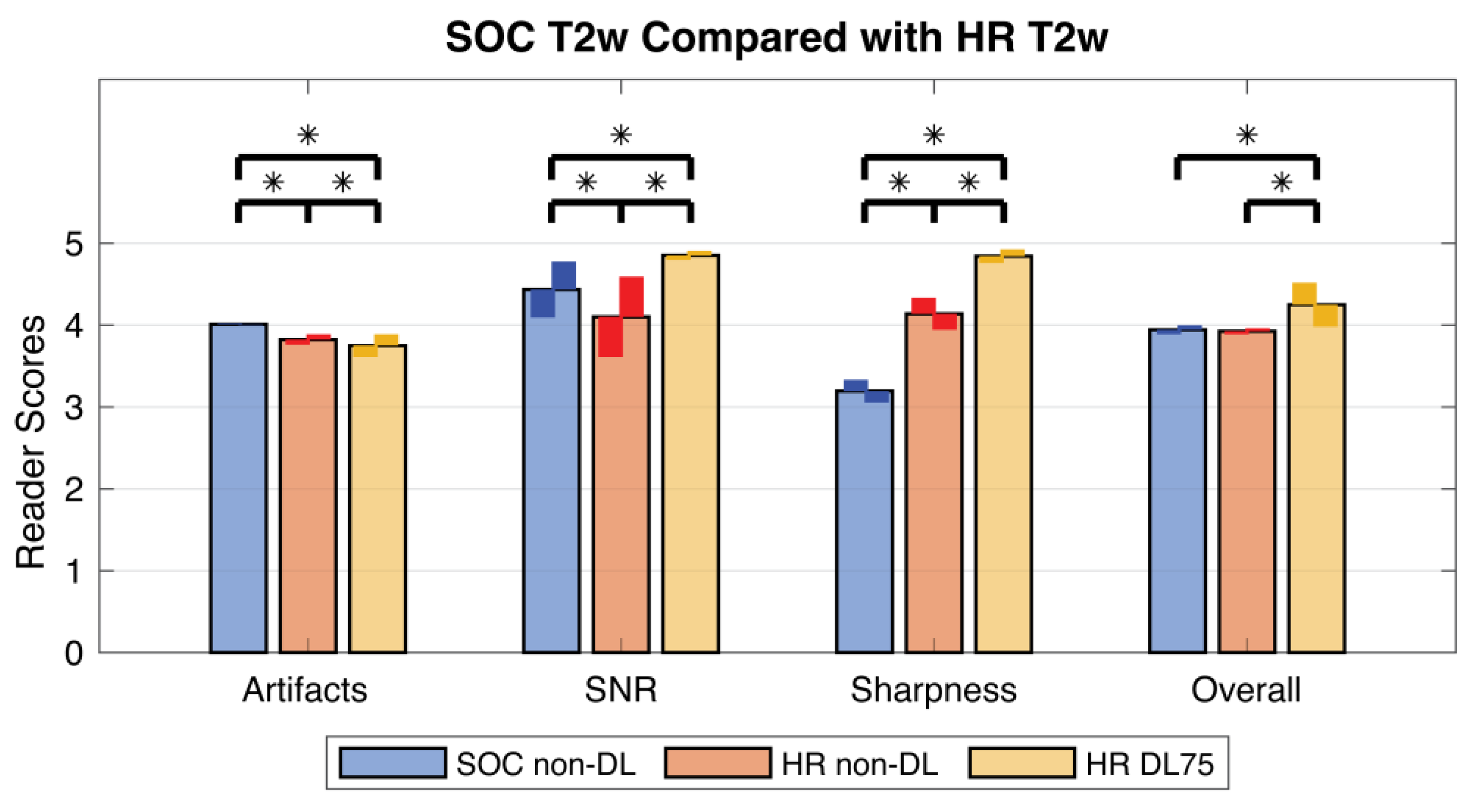
2.4.2. Qualitative Assessment
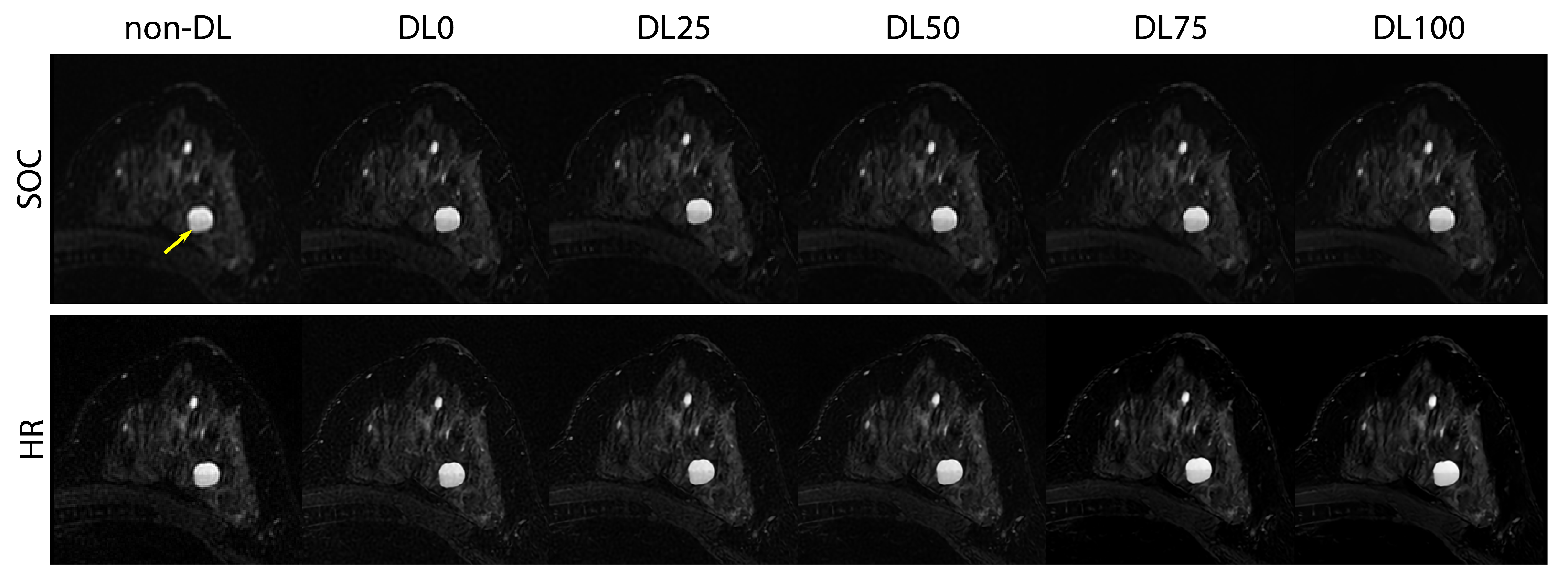
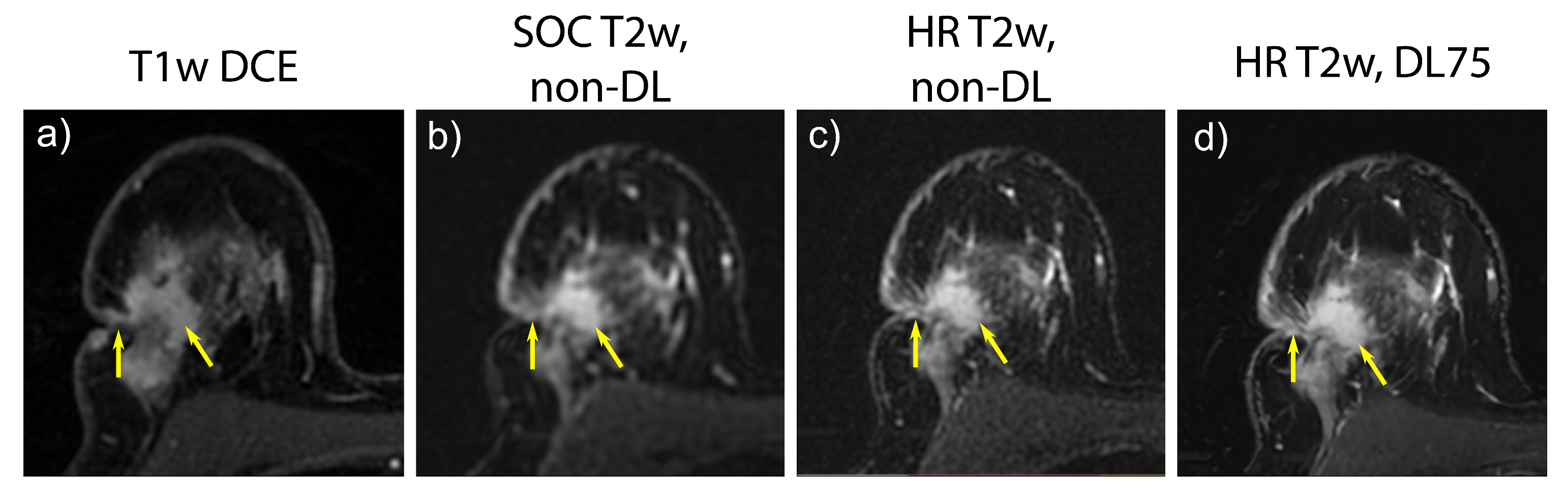
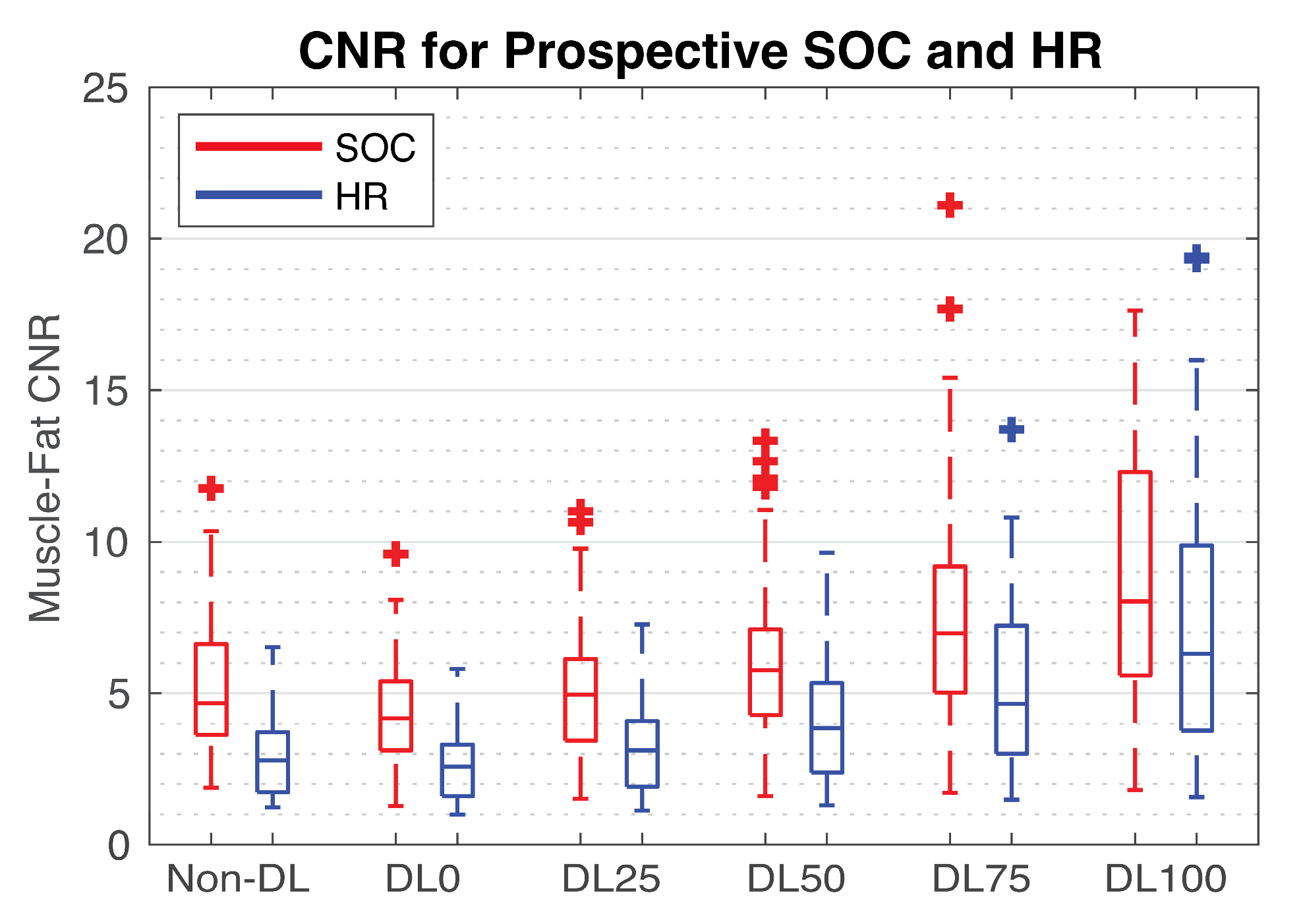
2.5. Prospective SOC and HR Imaging
3. Results
3.1. Phantom Experiments
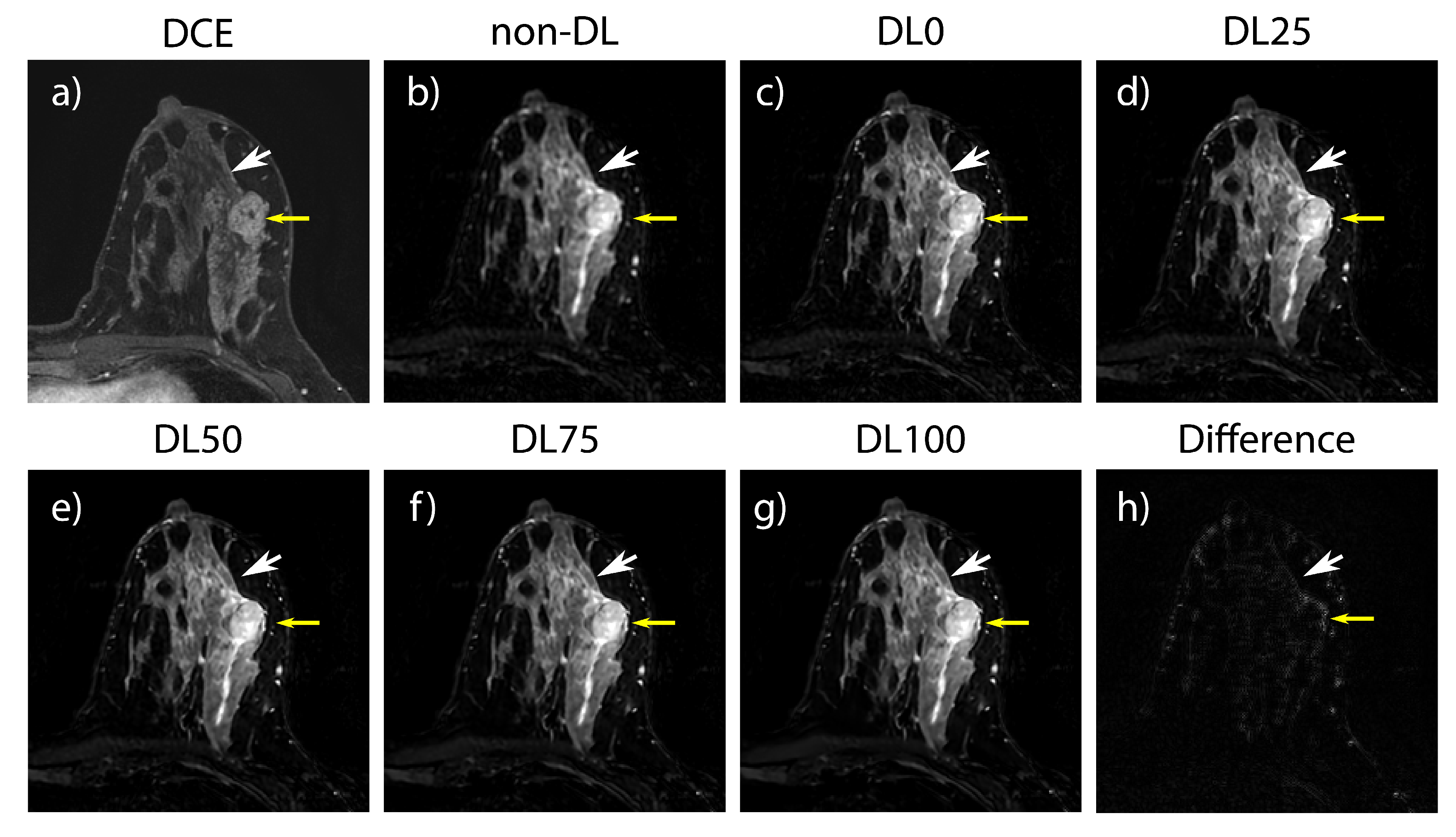
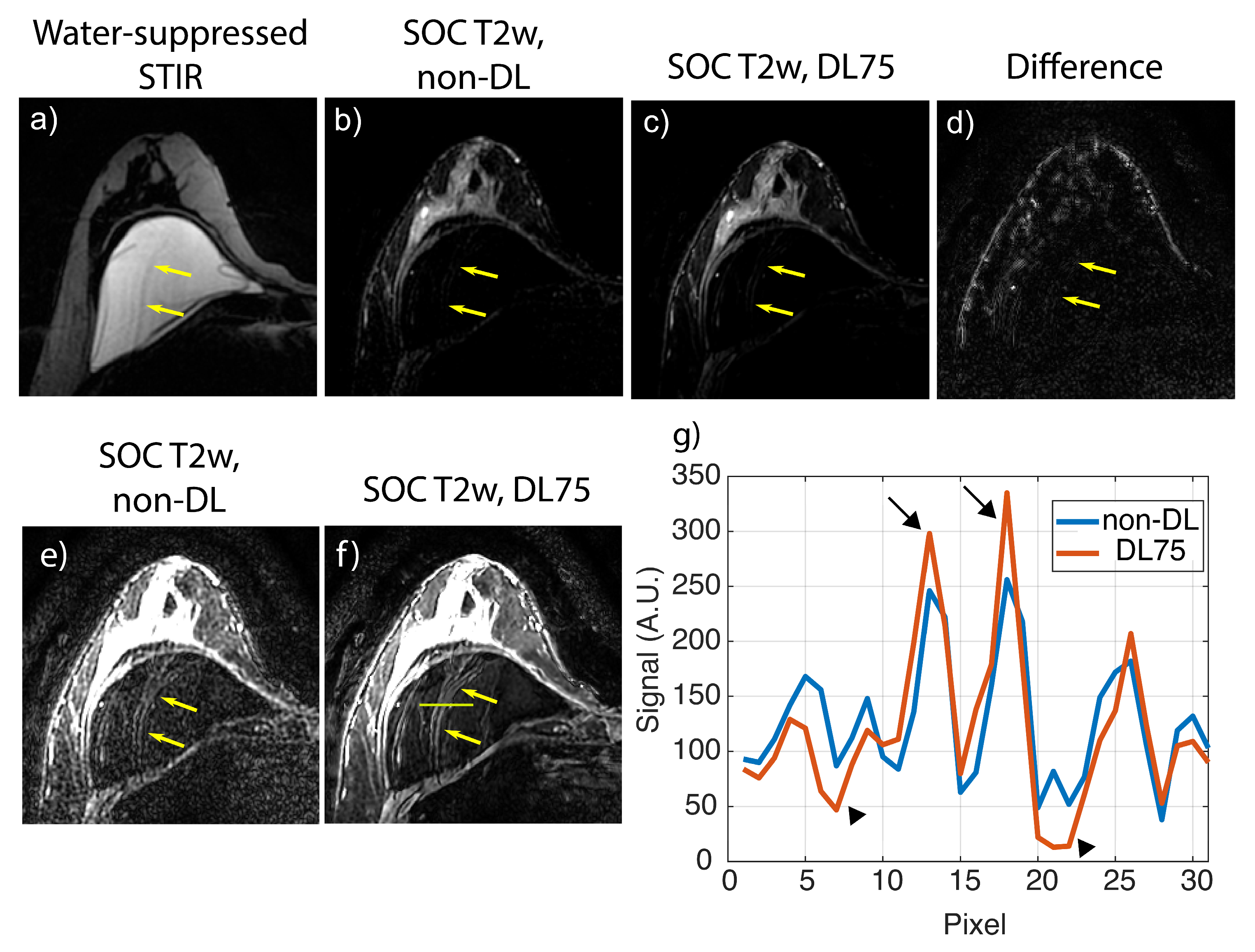
3.2. Retrospective SOC Imaging
3.3. Prospective SOC and HR Imaging
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2021; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, R.M.; Kuhl, C.K.; Kinkel, K.; Boetes, C. Breast MRI: Guidelines from the European Society of Breast Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardanelli, F.; Boetes, C.; Borisch, B.; Decker, T.; Federico, M.; Gilbert, F.J.; Helbich, T.; Heywang-Köbrunner, S.H.; Kaiser, W.A.; Kerin, M.J.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: Recommendations from the EUSOMA working group. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1296–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Radiology. Practice Parameter for the Performance of Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CE-MRI) of the Breast. 2023. Available online: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Practice-Parameters/MR-Contrast-Breast.pdf?la=en (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Kuhl, C. The Current Status of Breast MR Imaging Part I. Choice of Technique, Image Interpretation, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Transfer to Clinical Practice. Radiology 2007, 244, 356–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMartini, W.; Lehman, C. A Review of Current Evidence-Based Clinical Applications for Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 19, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, C.D.; Isaacs, C.; Schnall, M.D.; Pisano, E.D.; Ascher, S.M.; Weatherall, P.T.; Bluemke, D.A.; Bowen, D.J.; Marcom, P.K.; Armstrong, D.K.; et al. Cancer Yield of Mammography, MR, and US in High-Risk Women: Prospective Multi-Institution Breast Cancer Screening Study. Radiology 2007, 244, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, L.; Biswas, M.; Kuppili, V.; Godia, E.C.; Suri, H.S.; Edla, D.R.; Omerzu, T.; Laird, J.R.; Khanna, N.N.; Mavrogeni, S.; et al. The present and future of deep learning in radiology. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 114, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.J.; Johnson, P.M.; Knoll, F.; Lui, Y.W. Artificial Intelligence for MR Image Reconstruction: An Overview for Clinicians. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 53, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, H.K.; Mani, M.P.; Jacob, M. MoDL: Model Based Deep Learning Architecture for Inverse Problems. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 38, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.; Koerzdoerfer, G.; Nickel, D.; Mostapha, M.; Nadar, M.; Gassenmaier, S.; Kuestner, T.; Othman, A.E. Feasibility and Implementation of a Deep Learning MR Reconstruction for TSE Sequences in Musculoskeletal Imaging. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Taviani, V.; Malkiel, I.; Cheng, J.Y.; Tamir, J.I.; Shaikh, J.; Chang, S.T.; Hardy, C.J.; Pauly, J.M.; Shreyas, S. Vasanawala Variable-density single-shot fast spin-echo MRI with deep learning reconstruction by using variational networks. Radiology 2018, 289, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuin, N.; Bustin, A.; Küstner, T.; Oksuz, I.; Clough, J.; King, A.P.; Schnabel, J.A.; Botnar, R.M.; Prieto, C. A multi-scale variational neural network for accelerating motion-compensated whole-heart 3D coronary MR angiography. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2020, 70, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, B.; Heacock, L.; Geras, K.J.; Moy, L. Machine learning in breast MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 998–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkenende, L.; Teuwen, J.; Mann, R.M. Application of Deep Learning in Breast Cancer Imaging. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Chang, Y.W.; Sung, J.K.; Thomas, B. Feasibility of deep learning k-space-to-image reconstruction for diffusion weighted imaging in patients with breast cancers: Focus on image quality and reduced scan time. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 157, 110608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessling, D.; Gassenmaier, S.; Olthof, S.C.; Benkert, T.; Weiland, E.; Afat, S.; Preibsch, H. Novel deep-learning-based diffusion weighted imaging sequence in 1.5 T breast MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 166, 110948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pan, X.; Zhu, K.; Xiao, Y.; Yue, X.; Peng, P.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Accelerated 3D high-resolution T2-weighted breast MRI with deep learning constrained compressed sensing, comparison with conventional T2-weighted sequence on 3.0 T. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 156, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, R.M. Performance characterization of a novel deep learning-based MR image reconstruction pipeline. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.06559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.E.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Lebel, M.R. Thin-slice pituitary mri with deep learning–based reconstruction: Diagnostic performance in a postoperative setting. Radiology 2021, 298, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velde, N.; Hassing, H.C.; Bakker, B.J.; Wielopolski, P.A.; Lebel, R.M.; Janich, M.A.; Kardys, I.; Budde, R.P.J.; Hirsch, A. Improvement of late gadolinium enhancement image quality using a deep learning–based reconstruction algorithm and its influence on myocardial scar quantification. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3846–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Bhosale, P.; Rovira, J.J.I.; Qayyum, A.; Sun, J.; Bayram, E.; Szklaruk, J. Novel deep learning-based noise reduction technique for prostate magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 3378–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, K.M.; Sherafati, M.; Arpinar, V.E.; Bhave, S.; Ausman, R.; Nencka, A.S.; Lebel, R.M.; McKinnon, G.; Kaushik, S.S.; Vierck, D.; et al. Analysis and evaluation of a deep learning reconstruction approach with denoising for orthopedic MRI. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e200278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEMA MS 1-2008; Determination of Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) in Diagnostic Magnetic Resonance Imaging. NEMA Standards Publication: Arlington, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 1–19. Available online: http://www.nema.org/standards/pages/determination-of-signal-to-noise-ratio-in-diagnostic-magnetic-resonance-imaging.aspx?%5Cnpapers2://publication/uuid/CDE4FB6F-AC32-4A9E-B2F8-C0ADB3715C24 (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Knoll, F.; Murrell, T.; Sriram, A.; Yakubova, N.; Zbontar, J.; Rabbat, M.; Defazio, A.; Muckley, M.J.; Sodickson, D.K.; Zitnick, C.L.; et al. Advancing machine learning for MR image reconstruction with an open competition: Overview of the 2019 fastMRI challenge. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 3054–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muckley, M.J.; Riemenschneider, B.; Radmanesh, A.; Kim, S.; Jeong, G.; Ko, J.; Jun, Y.; Shin, H.; Hwang, D.; Mostapha, M.; et al. Results of the 2020 fastMRI Challenge for Machine Learning MR Image Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 2306–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zochowski, K.C.; Tan, E.T.; Argentieri, E.C.; Lin, B.; Burge, A.J.; Queler, S.C.; Lebel, R.M.; Sneag, D.B. Improvement of peripheral nerve visualization using a deep learning-based MR reconstruction algorithm. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2022, 85, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodine, C.F.; Kundel, H.L. Using eye movements to study visual search and to improve tumor detection. RadioGraphics 1987, 7, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Scanner 1 | Scanner 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2w Acquisition | SOC | HR | SOC | HR |
| Plane | Axial | Axial | Axial | Axial |
| Type | 2D FSE | 2D FSE | 2D FSE | 2D FSE |
| TR/TE (ms) | 3500/85 | 3500/85 | 4000/85 | 4000/85 |
| Acquisition Matrix | 288 × 288 | 448 × 448 | 228 × 228 | 448 × 448 |
| FOV (cm) | 32–36 | 32–36 | 32–36 | 32–36 |
| Slice Thickness (mm) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| PI Factor | 3/SENSE | 3/SENSE | 3/GRAPPA | 3/GRAPPA |
| ETL | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Acquisition Time (s) | 247 | 308 | 237 | 284 |
| Score | Overall Image Quality |
|---|---|
| 5 | Excellent: no artifacts and anatomical detail well visualized |
| 4 | Good: minor artifacts, some blurriness, no impact on diagnostic capability |
| 3 | Fair: major or multiple minor artifacts, blurriness, no impact on diagnostic capability |
| 2 | Poor: multiple major or minor artifacts, loss of detail, impact on diagnostic capability |
| 1 | Non-diagnostic: severe artifacts, and complete loss of anatomical detail |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allen, T.J.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Unal, O.; Estkowski, L.D.; Cashen, T.A.; Korosec, F.; Strigel, R.M.; Kelcz, F.; Fowler, A.M.; Gegios, A.; et al. Evaluation of a Deep Learning Reconstruction for High-Quality T2-Weighted Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Tomography 2023, 9, 1949-1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050152
Allen TJ, Henze Bancroft LC, Unal O, Estkowski LD, Cashen TA, Korosec F, Strigel RM, Kelcz F, Fowler AM, Gegios A, et al. Evaluation of a Deep Learning Reconstruction for High-Quality T2-Weighted Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Tomography. 2023; 9(5):1949-1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050152
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllen, Timothy J., Leah C. Henze Bancroft, Orhan Unal, Lloyd D. Estkowski, Ty A. Cashen, Frank Korosec, Roberta M. Strigel, Frederick Kelcz, Amy M. Fowler, Alison Gegios, and et al. 2023. "Evaluation of a Deep Learning Reconstruction for High-Quality T2-Weighted Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Tomography 9, no. 5: 1949-1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050152
APA StyleAllen, T. J., Henze Bancroft, L. C., Unal, O., Estkowski, L. D., Cashen, T. A., Korosec, F., Strigel, R. M., Kelcz, F., Fowler, A. M., Gegios, A., Thai, J., Lebel, R. M., & Holmes, J. H. (2023). Evaluation of a Deep Learning Reconstruction for High-Quality T2-Weighted Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Tomography, 9(5), 1949-1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050152







