Thirty Years of the DICOM Standard
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To state that, in medicine, the standardization of image format and image-related information, as well as their communication over a network, is essential.
- To remark that, for medical images, metadata is as important as pixel data.
- To be general enough to cover almost every medical imaging modality and flexible enough to follow their evolution over time.
2. Not Only Pixels: The Power of Metadata in Medical Images
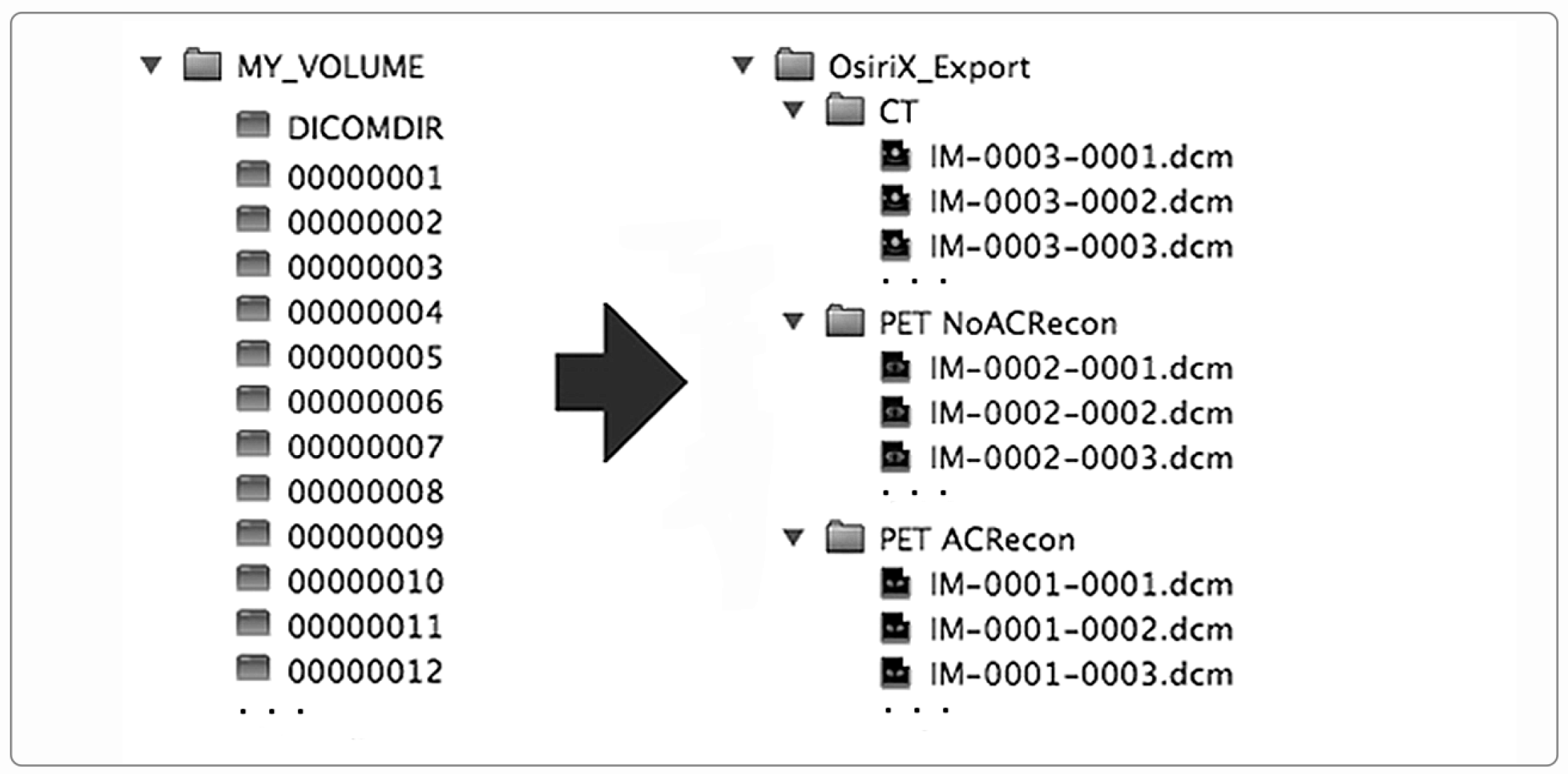
3. Rules and Tools for the Exchange of Medical Images and Related Information
4. DICOM’s Strengths and Weakness
4.1. Conformance (the DICOM Philosophy)
4.2. Private Tags
4.3. Data Protection (Privacy)
4.4. Quantitative Image Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACR | American College of Radiology |
| NEMA | National Electrical Manufacturers Association |
| OME | Open Microscopy Environment |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| TIFF | Tagged Image File Format |
| JPEG | Joint Photographic Experts Group |
| ICS | Image Cytometry Standard |
| BIDs | Brain Imaging Data Structure |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication Systems |
| HIS | Hospital Information Systems |
| RIS | Radiology Information Systems |
| TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol |
| HTTP | HyperText Transfer Protocol |
| IOD | Information Object Definition |
| IE | Information Entity |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| SUV | Standardized Uptake Ratio |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| XML | eXtensible Markup Language. |
References
- DICOM Standard Documentation. Available online: http://www.dicomstandard.org/ (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Bidgood, W.D., Jr.; Horii, S.C. Introduction to the ACR-NEMA DICOM standard. Radiographics 1992, 12, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, S.C. RSNA 1997, Primer on computers and information technology. Part four: A nontechnical introduction to DICOM. Radiographics 1997, 17, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidgood, W.D., Jr.; Horii, S.C.; Prior, F.W.; Van Syckle, D.E. Understanding and using DICOM, the data interchange standard for biomedical imaging. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 1997, 4, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clunie, D.A.; Carrino, J.A. DICOM. In PACS: A Guide to the Digital Revolution; Dreyer, K.J., Mehta, A., Thrall, J.H., Eds.; Springer Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenberger, P.; Eichelberg, M.; Martin, E. Introduction to the DICOM standard. Eur. Radiol. 2002, 12, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.N.J.; Perriss, R.W.; Scarsbrook, A.F. DICOM demystified: A review of digital file formats and their use in radiological practice. Clin. Radiol. 2005, 60, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medical Image Format FAQ. Available online: https://www.dclunie.com/medical-image-faq/html/toc.html (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Clunie, D.A. DICOM Format and Protocol Standardization—A Core Requirement for Digital Pathology Success. Toxicol. Pathol. 2021, 49, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DICOM Standard Committee, Working Group 26 (Pathology). Supplement 222: Microscopy Bulk Simple Annotations Storage SOP Class. Available online: https://www.dicomstandard.org/News-dir/ftsup/docs/sups/sup222.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Herrmann, M.D.; Clunie, D.A.; Fedorov, A.; Doyle, S.W.; Pieper, S.; Klepeis, V.; Le, L.P.; Mutter, G.L.; Milstone, D.S.; Schultz, T.J.; et al. Implementing the DICOM Standard for Digital Pathology. J. Pathol. Inform. 2018, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichelberg, M.; Riesmeier, J.; Wilkens, T.; Hewett, A.J.; Barth, A.; Jensch, P. Ten years of medical imaging standardization and prototypical implementation: The DICOM standard and the OFFIS DICOM toolkit (DCMTK). In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2004: PACS and Imaging Informatics, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–19 February 2004; Volume 5371, pp. 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- DCM4CHE. Available online: https://www.dcm4che.org/ (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- PyDICOM. Available online: https://pydicom.github.io/2017-pydicom-establishment (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- DICOM Standard—Working Groups & Minutes. Available online: https://www.dicomstandard.org/activity/wgs (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Berners-Lee, T. Weaving the Web: The Original Design and Ultimate Destiny of the World Wide Web by Its Inventor; HarperCollins Publishers: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Drnasin, I.; Grgić, M.; Gogić, G. JavaScript Access to DICOM Network and Objects in Web Browser. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genereaux, B.W.; Dennison, D.K.; Ho, K.; Horn, R.; Silver, E.L.; O’Donnell, K.; Kahn, C.E. DICOMweb: Background and Application of the Web Standard for Medical Imaging. J. Digit. Imaging 2018, 31, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, E.; Urban, T.; Brown, D.; Petts, J.; Pieper, S.D.; Lewis, R.; Hafey, C.; Harris, G.J. Open Health Imaging Foundation Viewer: An Extensible Open-Source Framework for Building Web-Based Imaging Applications to Support Cancer Research. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2020, 4, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, C.; Punzo, D.; Octaviano, I.; Pieper, S.; Longabaugh, W.J.R.; Clunie, D.A.; Kikinis, R.; Fedorov, A.Y.; Herrmann, M.D. Interoperable slide microscopy viewer and annotation tool for imaging data science and computational pathology. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clunie, D.A.; Dennison, D.K.; Cram, D.; Persons, K.R.; Bronkalla, M.D.; Primo, H.R. Technical Challenges of Enterprise Imaging: HIMSS-SIIM Collaborative White Paper. J. Digit. Imaging 2016, 29, 583–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.J.; Lannum, L.M.; Persons, K.R. A foundation for enterprise imaging: HIMSS-SIIM collaborative white paper. J. Digit. Imaging 2016, 29, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clunie, D.A.; Flanders, A.; Taylor, A.; Erickson, B.; Bialecki, B.; Brundage, D.; Gutman, D.; Prior, F.; Seibert, J.A.; Perry, J.; et al. Report of the Medical Image De-Identification (MIDI) Task Group--Best Practices and Recommendations. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10473. [Google Scholar]
- Neu, S.C.; Crawford, K.L.; Toga, A.W. Practical management of heterogeneous neuroimaging metadata by global neuroimaging data repositories. Front. Neuroinform. 2012, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Morgan, P.S.; Ashburner, J.; Smith, J.; Rorden, C. The first step for neuroimaging data analysis: DICOM to NIfTI conversion. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 264, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompan, I. Implementation of DICOM Parametric Maps for Perfusion MRI. In Proceedings of the MRI Together 2021–Session A1, Online Presentation, 13–17 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.B.; Sheen, H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kang, J.; Yoon, D.K.; Suh, T.S. Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) information conversion procedure for SUV calculation of PET scanners with different DICOM header information. Phys. Med. 2017, 44, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Freymann, J.B.; Kirby, J.S.; Perry, J.H.; Clunie, D.A.; Jaffe, C.C. Image data sharing for biomedical research—Meeting HIPAA requirements for de-identification. J. Digit. Imaging 2012, 25, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.M.; Maffitt, D.R.; Smith, K.E.; Kirby, J.S.; Clark, K.W.; Freymann, J.B. De-identification of Medical Images with Retention of Scientific Research Value. RadioGraphics 2015, 35, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larobina, M.; Murino, L. Medical Image File Formats. J. Digit. Imaging 2014, 27, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, A.; Clunie, D.; Ulrich, E.; Bauer, C.; Wahle, A.; Brown, B.; Beichel, R.R. DICOM for quantitative imaging biomarker development: A standards based approach to sharing clinical data and structured PET/CT analysis results in head and neck cancer research. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, C.P.; Gorman, C.; Pieper, S.; Doyle, S.W.; Lennerz, J.K.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Clunie, D.A.; Fedorov, A.Y.; Herrmann, M.D. Highdicom: A Python Library for Standardized Encoding of Image Annotations and Machine Learning Model Outputs in Pathology and Radiology. J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 1719–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larobina, M. The DICOM file format: Postprocessing features in MRI. Phys. Med. 2003, 19, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- Gorgolewski, K.J.; Auer, T.; Calhoun, V.D.; Craddock, R.C.; Das, S.; Duff, E.P.; Flandin, G.; Ghosh, S.S.; Glatard, T.; Halchenko, Y.O.; et al. The brain imaging data structure, a format for organizing and describing outputs of neuroimaging experiments. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.; Mascio, L.; Ow, D.; Sudar, D.; Mullikin, J. Proposed standard for image cytometry data files. Cytom. J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 1990, 11, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cradduck, T.D.; Bailey, D.L.; Hutton, B.F.; De Conninck, F.; Busemann-Sokole, E.; Bergmann, H.; Noelpp, U. A standard protocol for the exchange of nuclear medicine image files. Nucl. Med. Commun. 1989, 10, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, I.G.; Allan, C.; Burel, J.M.; Creager, D.; Falconi, A.; Hochheiser, H.; Johnston, J.; Mellen, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Swedlow, J.R. The Open Microscopy Environment (OME) Data Model and XML File: Open Tools for Informatics and Quantitative Analysis in Biological Imaging. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, R47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Basurto-Lozada, D.; Besson, S.; Bogovic, J.; Bragantini, J.; Brown, E.M.; Burel, J.M.; Casas Moreno, X.; de Medeiros, G.; Diel, E.E.; et al. OME-Zarr: A cloud-optimized bioimaging file format with international community support. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2023, 160, 223–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, A.; Longabaugh, W.J.R.; Pot, D.; Clunie, D.A.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Homeyer, A.; Lewis, R.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Bontempi, D.; et al. NCI Imaging Data Commons. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4188–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Henderson, R.; Mastronarde, D.; Ludtke, S.J.; Schoenmakers, R.H.; Short, J.; Marabini, R.; Dallakyan, S.; Agard, D.; Winn, M. MRC2014: Extensions to the MRC format header for electron cryo-microscopy and tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 192, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, T.; Hester, A.; Klinkert, I.; Both, J.-P.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Brunelle, A.; Laprévote, O.; Desbenoit, N.; Robbe, M.-F.; Stoeckli, M.; et al. imzML—A common data format for the flexible exchange and processing of mass spectrometry imaging data. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5106–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
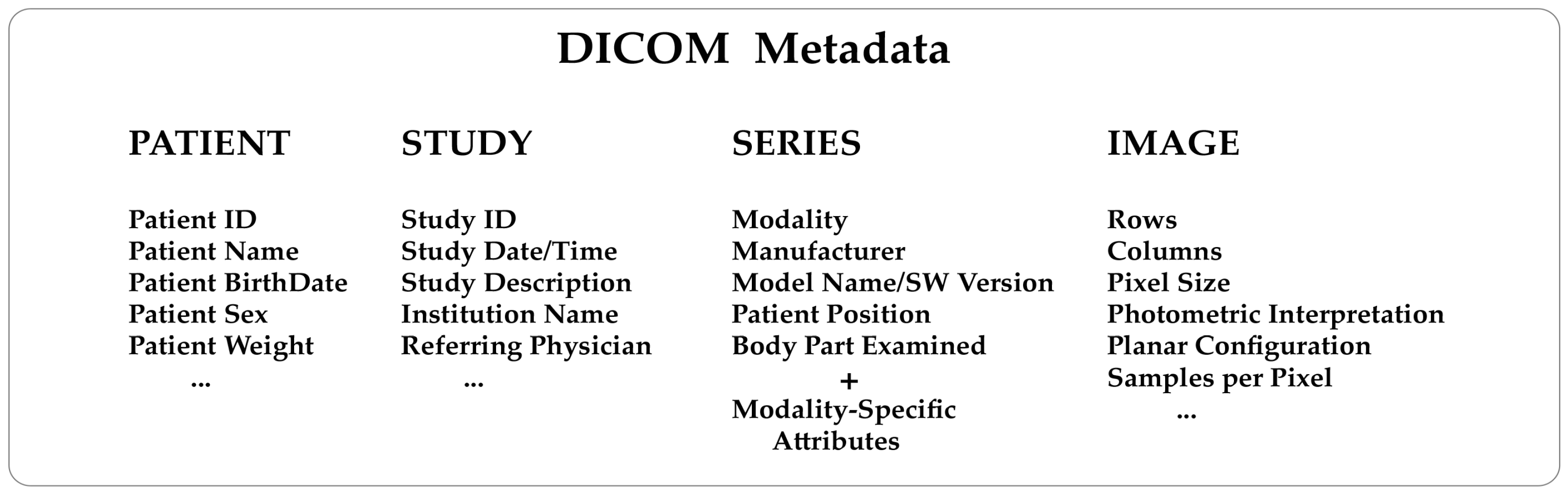
| C.7. Common Composite Image IOD Modules | C.8. Modality-Specific Modules |
|---|---|
| C.7.1. Common Patient IE Modules | C.8.1. Computed Radiography Modules |
| C.7.2. Common Study IE Modules | C.8.2. CT Modules |
| C.7.3. Common Series IE Modules | C.8.3. MR Modules |
| C.7.4. Common Frame of Reference IE Modules | C.8.4. Nuclear Medicine Modules |
| C.7.5. Common Equipment IE Modules | C.8.5. Ultrasound Modules |
| C.7.6. Common Image IE Modules | C.8.6. Secondary Capture Modules |
| C.7.7. (Retired) Patient Summary Module | C.8.7. X-ray Modules |
| C.7.8. (Retired) Study Content Module | C.8.8. Radiotherapy Modules |
| C.7.9. Palette Color Lookup Table Module | C.8.9. PET Modules |
| C.7.10. Common Acquisition IE Modules | … |
| C.7.11. Common Multi-Resolution Pyramid IE Modules | C.8.32. Parametric Map |
| C.8.33. Tractography Results Modules |
| Storage: it is the service required to archive images across a network. Typically, it is used by an acquisition modality to send images to a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) or a storage server. |
| Storage Commitment: it is an enhanced version of the Storage service with in addition a message sent by the storage provider to the user to confirm that “archiving was successful”, so that the user can safely delete the images locally. |
| Print: it is the service for printing images from an acquisition modality or a display station. |
| Query/Retrieve: it is the service enabling nodes on the DICOM network to query a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) or another storage unit in order to know the list of images available on it and then to retrieve them. |
| Modality worklist: it is the service able to manage the list of exams to be acquired for each patient. Each examination of the list is scheduled and its completion is made known to the system that updates the data. It is only possible in departments equipped with a computerized reservation/acceptance system (HIS/RIS) integrated into the DICOM network. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larobina, M. Thirty Years of the DICOM Standard. Tomography 2023, 9, 1829-1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050145
Larobina M. Thirty Years of the DICOM Standard. Tomography. 2023; 9(5):1829-1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050145
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarobina, Michele. 2023. "Thirty Years of the DICOM Standard" Tomography 9, no. 5: 1829-1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050145
APA StyleLarobina, M. (2023). Thirty Years of the DICOM Standard. Tomography, 9(5), 1829-1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050145




