Systematic Evaluation of Imaging Features of Early Bladder Cancer Using Computed Tomography Performed before Pathologic Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobruch, J.; Daneshmand, S.; Fisch, M.; Lotan, Y.; Noon, A.P.; Resnick, M.J.; Shariat, S.F.; Zlotta, A.R.; Boorjian, S.A. Gender and Bladder Cancer: A Collaborative Review of Etiology, Biology, and Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, J.J.; Boormans, J.L.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Seiler, R.; Boorjian, S.A.; Konety, B.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Wheeler, T.; Svatek, R.S.; Porten, S.P.; et al. Distribution of Molecular Subtypes in Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Is Driven by Sex-specific Differences. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palou, J.; Sylvester, R.J.; Faba, O.R.; Parada, R.; Peña, J.A.; Algaba, F.; Villavicencio, H. Female gender and carcinoma in situ in the prostatic urethra are prognostic factors for recurrence, progression, and disease-specific mortality in T1G3 bladder cancer patients treated with bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Stief, C.; Brookman-May, S.; Otto, W.; Gilfrich, C.; Roigas, J.; Zacharias, M.; Wieland, W.F.; Fritsche, H.-M.; Hofstädter, F.; et al. Gender-dependent cancer-specific survival following radical cystectomy. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, E.M. Financial Toxicity of Having Bladder Cancer. Bladder Cancer 2018, 4, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, N.D.; Silverman, D.T.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Abnet, C.C. Association between smoking and risk of bladder cancer among men and women. JAMA 2011, 306, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, O.; Dobruch, J.; Knowles, M.A.; Burger, M.; Alemozaffar, M.; Nielsen, M.E.; Lotan, Y. Bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.; Catto, J.W.; Dalbagni, G.; Grossman, H.B.; Herr, H.; Karakiewicz, P.; Kassouf, W.; Kiemeney, L.A.; La Vecchia, C.; Shariat, S. Bladder Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.I.; López, J.F.; Vivaldi, B.; Coz, F. Long-term impact of arsenic in drinking water on bladder cancer health care and mortality rates 20 years after end of exposure. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanic, C.M.; Kogevinas, M.; Silverman, D.T.; Tardon, A.; Serra, C.; Malats, N.; Real, F.X.; Carrato, A.; Garcia-Closas, R.; Sala, M.; et al. Occupation and bladder cancer in a hospital-based case-control study in Spain. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008, 65, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenis, A.T.; Lec, P.M.; Chamie, K. Bladder cancer a review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 324, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumberbatch, M.G.; Rota, M.; Catto, J.W.; La Vecchia, C. The Role of Tobacco Smoke in Bladder and Kidney Carcinogenesis: A Comparison of Exposures and Meta-analysis of Incidence and Mortality Risks. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Dominguez, M.; Castelao, J.E.; Yuan, J.-M.; Yu, M.C.; Ross, R.K. Use of permanent hair dyes and bladder-cancer risk. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.D.; Koutros, S.; Colt, J.S.; Kogevinas, M.; Garcia-Closas, M.; Real, F.X.; Friesen, M.C.; Baris, D.; Stewart, P.; Schwenn, M.; et al. Modification of Occupational Exposures on Bladder Cancer Risk by Common Genetic Polymorphisms. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, H.; He, S.-H.; Leng, X.-Y.; Xu, X.-F.; Huang, Q.; Weng, H.; Zhu, C.; Li, L.-Y.; Gu, J.-M.; Li, X.-H.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of kidney, bladder, and prostate cancers and their attributable risk factors, 1990–2019. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassell, A.; Yunusa, B.; Jalloh, M.; Mbodji, M.M.; Diallo, A.; Ndoye, M.; Diallo, Y.; Labou, I.; Niang, L.; Gueye, S.M. Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Review of the Current Trend in Africa. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Bochner, B.H.; Chou, R.; Dreicer, R.; Kamat, A.M.; Lerner, S.P.; Lotan, Y.; Meeks, J.J.; Michalski, J.M.; Morgan, T.M.; et al. Treatment of Non-Metastatic Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO Guideline. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, R.J.; van der Meijden, A.P.; Oosterlinck, W.; Witjes, J.A.; Bouffioux, C.; Denis, L.; Newling, D.W.; Kurth, K. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.C.; Chang, S.S.; Dalbagni, G.; Pruthi, R.S.; Seigne, J.D.; Skinner, E.C.; Wolf, J.S.; Schellhammer, P.F. Guideline for the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (stages Ta, T1, and Tis): 2007 Update. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 2314–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettler, F.A.; Bhargavan, M.; Faulkner, K.; Gilley, D.B.; Gray, J.E.; Ibbott, G.S.; Lipoti, J.A.; Mahesh, M.; McCrohan, J.L.; Stabin, M.G.; et al. Radiologic and Nuclear Medicine Studies in the United States and Worldwide: Frequency, Radiation Dose, and Comparison with Other Radiation Sources—1950–2007. Radiology 2009, 253, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Nettleton, J.; Hotston, M.; Bradley, A.; Maskell, G. Incidental urological findings in patients undergoing computed tomography colonography for investigation of suspected colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Urol. 2019, 12, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgrano, M.; Mucelli, F.P.; Spadacci, A.; Pizzolato, R.; Zappetti, R.; Cova, M. Prevalence of extravascular collateral findings during 64-slice CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and lower limbs. Radiol. Medica 2010, 115, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, J.; Gough, S.; Ahmed, H.; Gabara, L.; Rawlins, J.; Calver, A.; Shah, B.N.; Rakhit, D.; Shambrook, J.; Harden, S.; et al. Frequency and impact of incidental findings on computed tomography during work-up for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Single centre experience and review of the literature. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, M.-D.; Peitzman, A.B.; Hostler, D.P.; Wolfson, A.B. Frequency and Follow-up of Incidental Findings on Trauma Computed Tomography Scans: Experience at a Level One Trauma Center. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 38, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayn, K.N.; Hale, G.R.; Bloom, J.B.; Gold, S.A.; Carvalho, F.L.; Mehralivand, S.; Czarniecki, M.; Wood, B.J.; Merino, M.J.; Choyke, P.; et al. Incidental bladder cancers found on multiparametric MRI of the prostate gland: A single center experience. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 24, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouriet, F.; Tissot-Dupont, H.; Casalta, J.-P.; Hubert, S.; Cammilleri, S.; Riberi, A.; Lepidi, H.; Habib, G.; Raoult, D. FDG-PET/CT Incidental Detection of Cancer in Patients Investigated for Infective Endocarditis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.M.; Rubin, G.; McPhail, S.; Lyratzopoulos, G. Incidentally diagnosed cancer and commonly preceding clinical scenarios: A cross-sectional descriptive analysis of English audit data. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönhofen, J.; Mohan, V.; Schumacher, M.C.; Bechir, M.; Keo, H.H.; Schönhofen, H.; Joder, T.; Diehm, C.; Kalka, C.; Diehm, N. Incidental findings during computed tomographic angiography diagnostic work-up in patients with arteriogenic erectile dysfunction. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2019, 149, w20154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, P.S.; Butt, M.W.; Pollock, G.; Kirk, J.; Bungay, P.; De Nunzio, M.; Thurley, P. Incidental extravascular findings in CT angiograms in patients post endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: Clinical relevance and frequency. CVIR Endovasc. 2018, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Mahendran, K.; Collins, M.; Abdelaziz, M.; Khogali, S.; Luckraz, H. Incidental abnormal CT scan findings during transcatheter aortic valve implantation assessment: Incidence and implications. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong-You-Cheong, J.J.; Woodward, P.J.; Manning, M.A.; Sesterhenn, I.A. From the Archives of the AFIP: Neoplasms of the urinary bladder: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2006, 26, 553–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helenius, M.; Dahlman, P.; Lonnemark, M.; Brekkan, E.; Wernroth, L.; Magnusson, A. Comparison of post contrast CT urography phases in bladder cancer detection. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvarness, H.; Skjoldbye, B.; Jakobsen, H. Urinary bladder volume measurements: Comparison of three ultrasound calculation methods. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2002, 36, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skipper, P.L.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Ross, R.K.; Yu, M.C. Nonsmoking-related arylamine exposure and bladder cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2003, 12, 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Shinagare, A.B.; Sadow, C.A.; Sahni, V.A.; Silverman, S.G. Urinary bladder: Normal appearance and mimics of malignancy at CT urography. Cancer Imaging 2011, 11, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, L.P.; Fishman, E.K. Bladder imaging using multidetector row computed tomography, volume rendering, and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2003, 27, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a significant risk factor for bladder cancer in diabetic patients: A population-based cohort study using the National Health Insurance in Taiwan. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Chokkalingam, A.P.; Gridley, G.; Nyren, O.; Johansson, J.E.; Adami, H.O.; Silverman, D.; Hsing, A.W. Benign prostatic hyperplasia and subsequent risk of bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.-W.; Liao, C.-H.; Wu, S.-C.; Muo, C.-H. Association of benign prostatic hyperplasia and subsequent risk of bladder cancer: An Asian population cohort study. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, K.H.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.-P.; Cohan, R.H.; Caoili, E.M.; Paramagul, C.; Alva, A.; Weizer, A.Z. Bladder Cancer Segmentation in CT for Treatment Response Assessment: Application of Deep-Learning Convolution Neural Network—A Pilot Study. Tomography 2016, 2, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borhani, S.; Borhani, R.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A. Artificial intelligence: A promising frontier in bladder cancer diagnosis and outcome prediction. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2022, 171, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamecki, H.; Dębowska, M.; Nyk, Ł.; Przewor, A.; Demkow, T.; Sosnowski, R. The Clinical Features of Incidentally Diagnosed Urothelial Bladder Cancer: A Retrospective Data Analysis. Urol. Int. 2022, 106, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamecki, H.; Dębowska, M.; Poleszczuk, J.; Demkow, T.; Przewor, A.; Nyk, Ł.; Sosnowski, R. Incidental Diagnosis of Urothelial Bladder Cancer: Associations with Overall Survival. Cancers 2023, 15, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
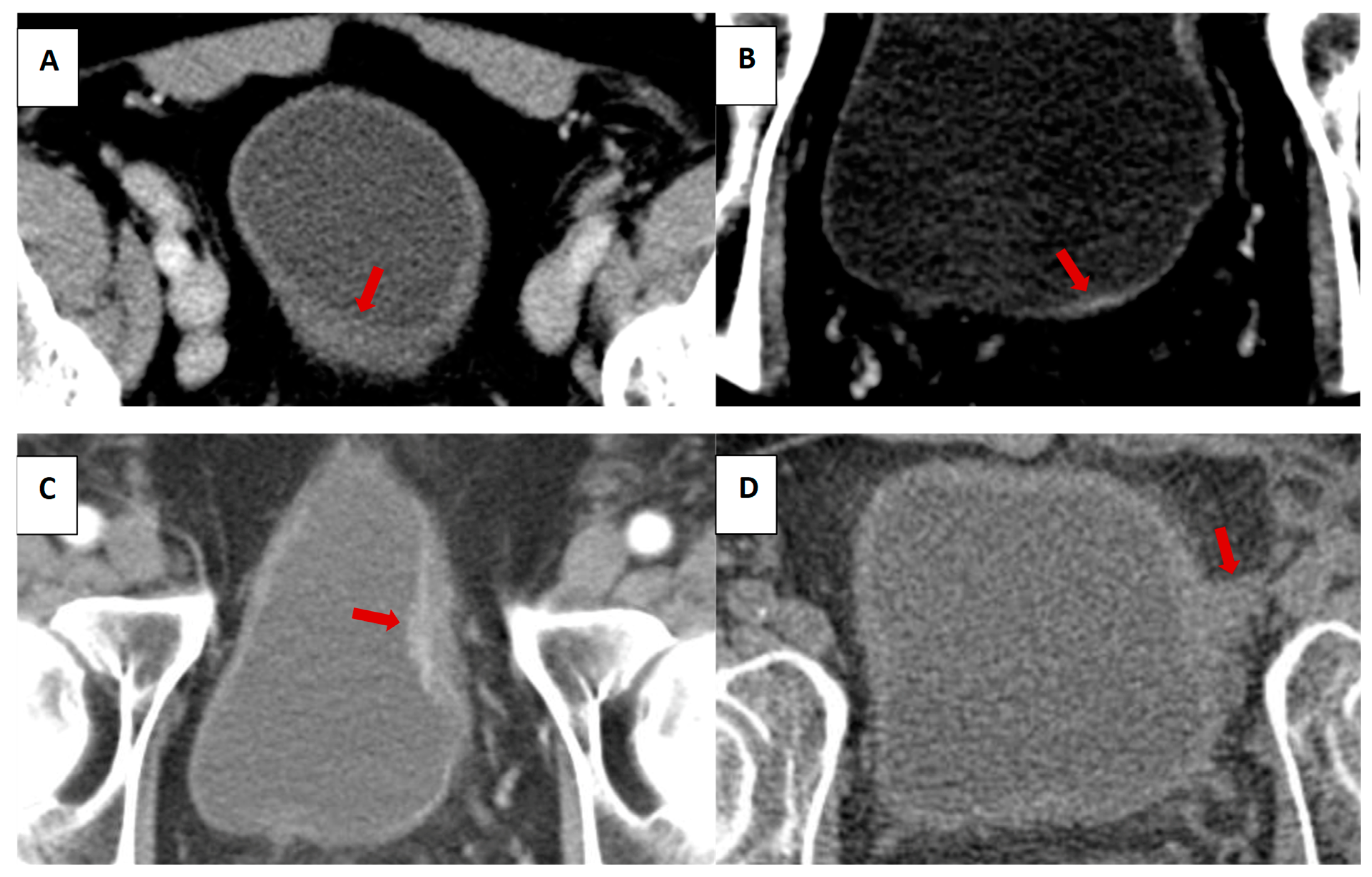

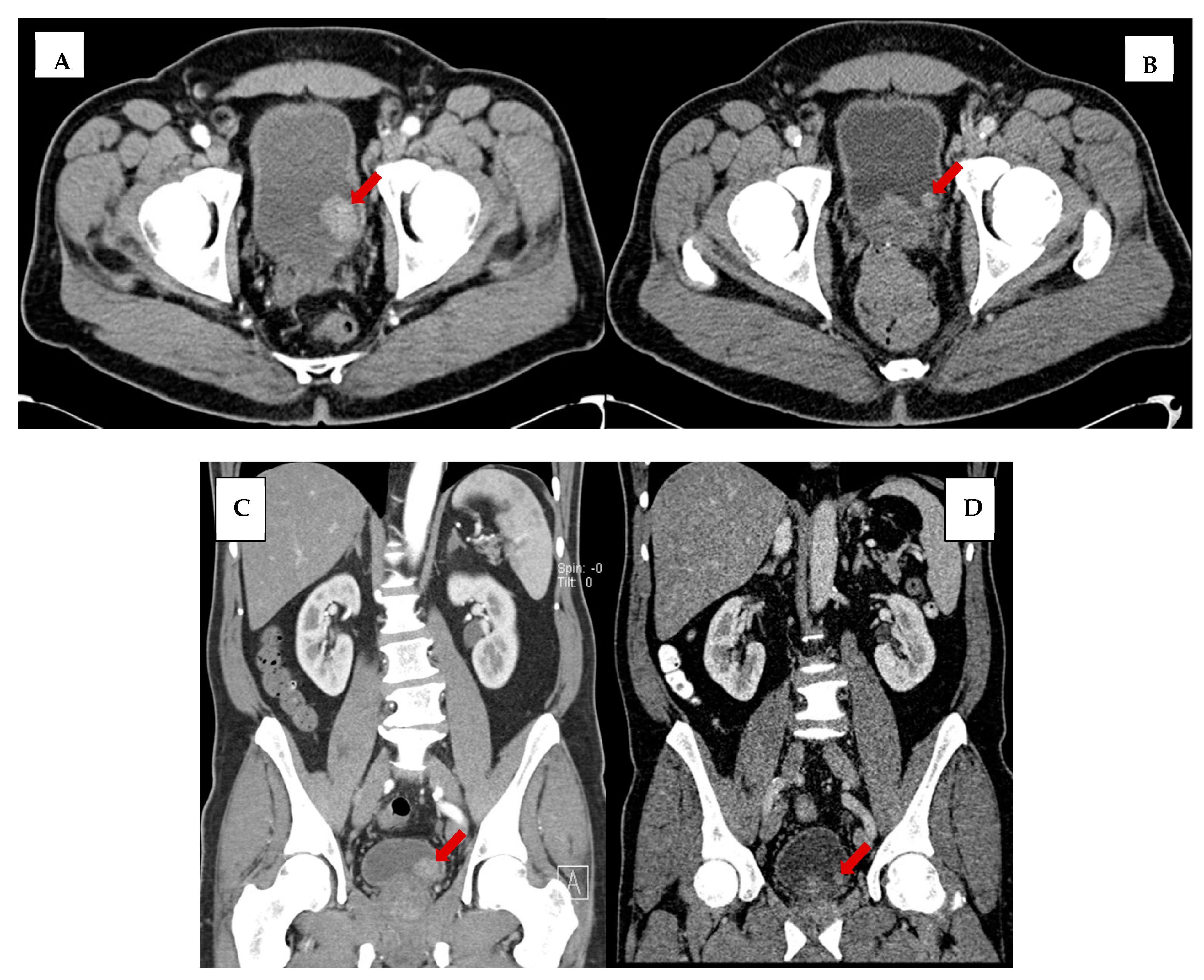
| Patient Cohort (n = 99) | |
|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 70 (51–88) |
| Male sex, no. (%) | 81 (82%) |
| History of gross hematuria, no. (%) | 78 (79%) |
| History of cigarette smoking, no. (%) | 65 (66%) |
| Imaging Studies (n = 226) | |
| No. of imaging studies reviewed per patient, median (range) | 1 (1–33) |
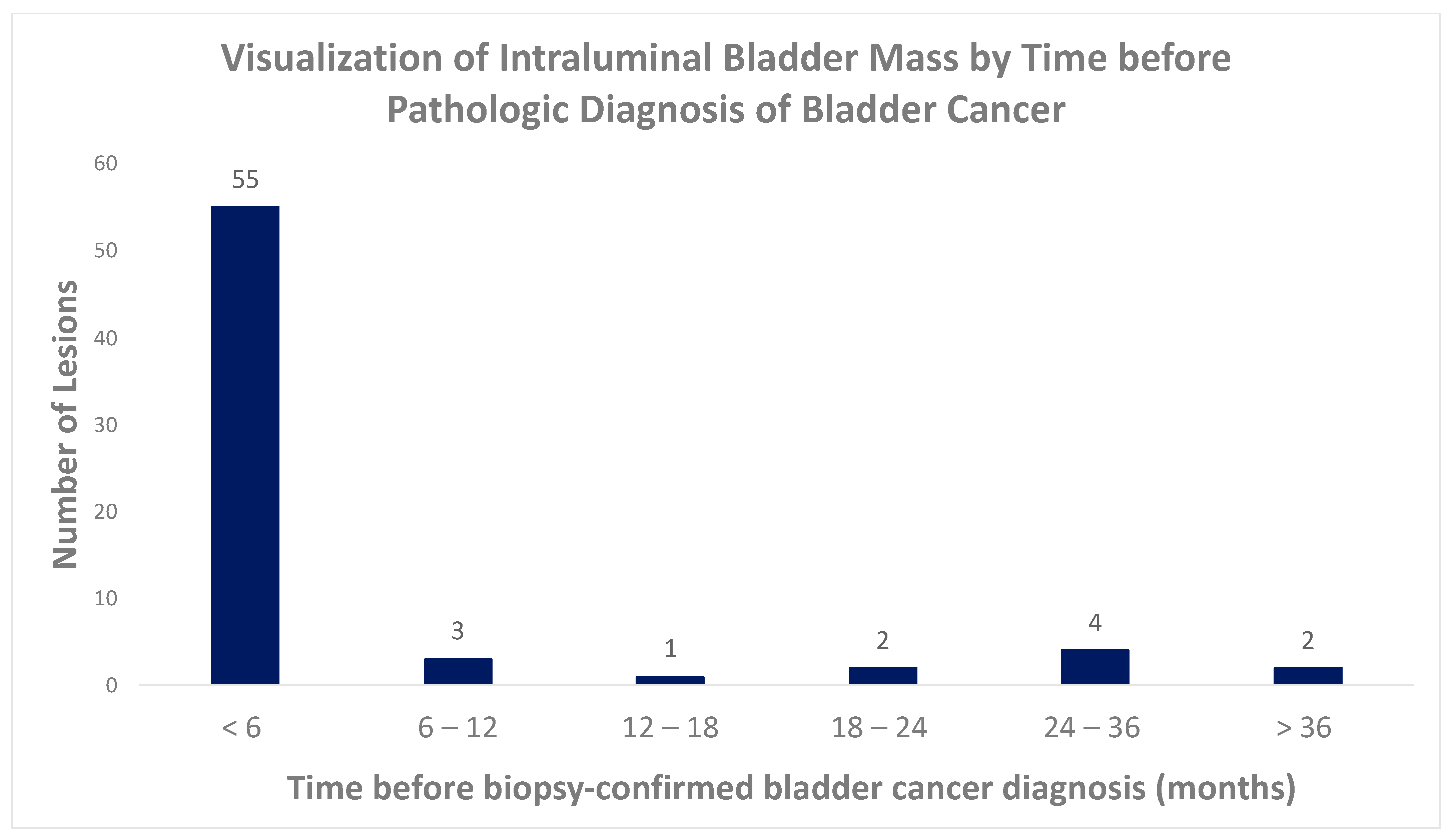
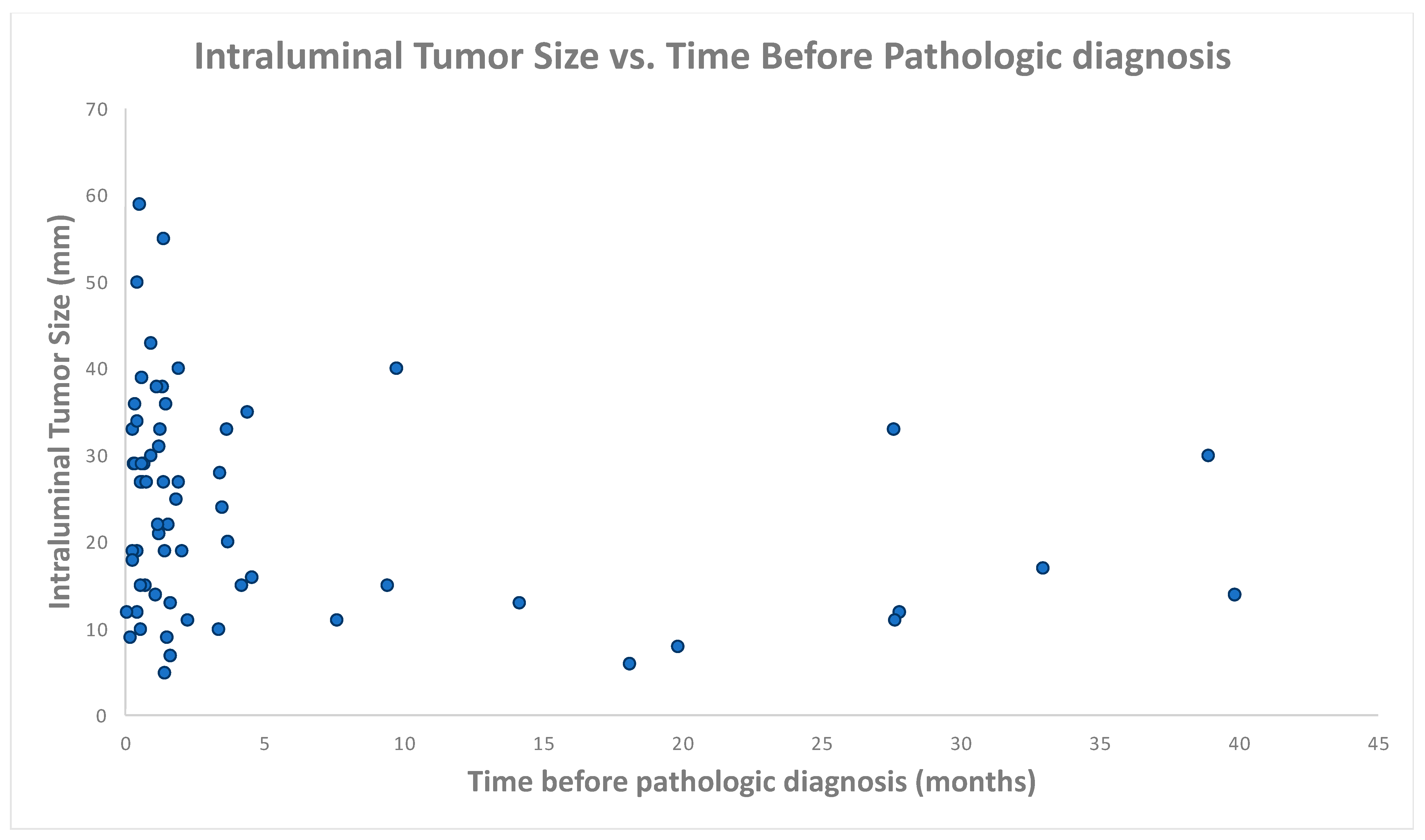
| Time interval between imaging and biopsy-confirmed bladder cancer diagnosis, median (range) | 14 months (1 day–58 months) |
| Time before Pathologic Diagnosis (Months) | No. of Imaging Studies | Wall Thickening | Wall Enhancement | Intraluminal Mass | Intramural Mass | Extramural Mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6 | 88 | 20% (18/88) | 14% (12/88) | 63% (55/88) | 6% (5/88) | 5% (4/88) |
| 6–12 | 14 | 29% (4/14) | 14% (2/14) | 21% (3/14) | 0% | 0% |
| 12–18 | 23 | 26% (6/23) | 17% (4/23) | 4% (1/23) | 4% (1/23) | 0% |
| 18–24 | 13 | 46% (6/13) | 15% (2/13) | 15% (2/13) | 15% (2/13) | 0% |
| 24–36 | 31 | 26% (8/31) | 10% (3/31) | 13% (4/31) | 0% | 0% |
| >36 | 57 | 4% (2/57) | 0% | 4% (2/57) | 0% | 2% (1/57) |
| Total | 226 | 19% (44/226) | 10% (23/226) | 30% 67 (226) | 4% (8/226) | 2% (5/226) |
| Portal Venous Phase Exams (n = 90) | |
|---|---|
| Detection rate | 16% (14/90) |
| Mean tumor size | 21 mm |
| Mean bladder vol., exams w/detectable tumor | 211 mL |
| Mean bladder vol., exams w/o detectable tumor | 203 mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malik, R.F.; Berry, R.; Lau, B.D.; Busireddy, K.R.; Patel, P.; Patel, S.H.; Fishman, E.K.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Johnson, P.T.; Sedaghat, F. Systematic Evaluation of Imaging Features of Early Bladder Cancer Using Computed Tomography Performed before Pathologic Diagnosis. Tomography 2023, 9, 1734-1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050138
Malik RF, Berry R, Lau BD, Busireddy KR, Patel P, Patel SH, Fishman EK, Bivalacqua TJ, Johnson PT, Sedaghat F. Systematic Evaluation of Imaging Features of Early Bladder Cancer Using Computed Tomography Performed before Pathologic Diagnosis. Tomography. 2023; 9(5):1734-1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050138
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalik, Rubab F., Renu Berry, Brandyn D. Lau, Kiran R. Busireddy, Prasan Patel, Sunil H. Patel, Elliot K. Fishman, Trinity J. Bivalacqua, Pamela T. Johnson, and Farzad Sedaghat. 2023. "Systematic Evaluation of Imaging Features of Early Bladder Cancer Using Computed Tomography Performed before Pathologic Diagnosis" Tomography 9, no. 5: 1734-1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050138
APA StyleMalik, R. F., Berry, R., Lau, B. D., Busireddy, K. R., Patel, P., Patel, S. H., Fishman, E. K., Bivalacqua, T. J., Johnson, P. T., & Sedaghat, F. (2023). Systematic Evaluation of Imaging Features of Early Bladder Cancer Using Computed Tomography Performed before Pathologic Diagnosis. Tomography, 9(5), 1734-1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9050138






