Role of Intravascular Ultrasound in Pulmonary Embolism Patients Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
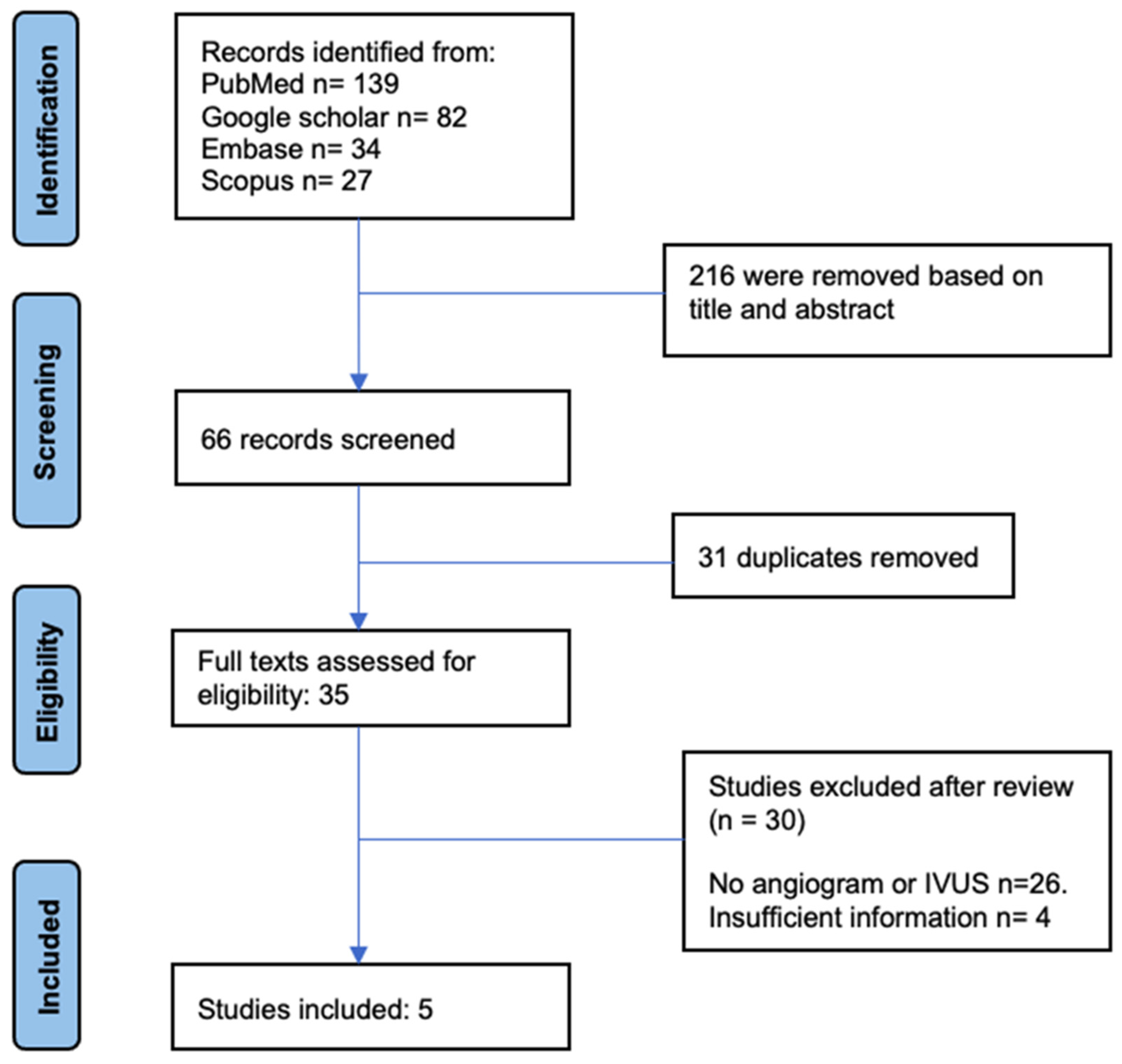
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Population Selection
2.3. Extraction of Data and Quality Evaluation
2.4. Synthesis and Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Epidemiology of Acute PE and Thrombectomy
4.2. Overall Impression of Its Efficacy and Impact on Outcomes
4.3. Cost-Effectiveness
4.4. Catheter-Based Mechanical Thrombectomy and Surgical Pulmonary Embolectomy
4.5. Strengths and Limitations of IVUS
4.6. Strengths and Limitations of This Review
4.7. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Venous thromboembolism in adult hospitalizations–United States, 2007–2009. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2012, 61, 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.-P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barco, S.; Mahmoudpour, S.H.; Planquette, B.; Sanchez, O.; Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G. Prognostic value of right ventricular dysfunction or elevated cardiac biomarkers in patients with low-risk pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Toma, C.; Tapson, V.F.; Adams, C.; Jaber, W.A.; Silver, M.; Khandhar, S.; Amin, R.; Weinberg, M.; Engelhardt, T.; et al. A Prospective, Single-Arm, Multicenter Trial of Catheter-Directed Mechanical Thrombectomy for Intermediate-Risk Acute Pulmonary Embolism. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucher, N.; Boekstegers, P.; Müller, O.J.; Kupatt, C.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Heitzer, T.; Tebbe, U.; Horstkotte, J.; Müller, R.; Blessing, E.; et al. Randomized, Controlled Trial of Ultrasound-Assisted Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis for Acute Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism. Circulation 2014, 129, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Weinberg, I.; Kadakia, M.B.; Wilensky, R.L.; Sardar, P.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Mukherjee, D.; Jaff, M.R.; Giri, J. Thrombolysis for Pulmonary Embolism and Risk of All-Cause Mortality, Major Bleeding, and Intracranial Hemorrhage: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2014, 311, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzinski, D.M.; Giri, J.; Rosenfield, K. Interventional Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 10, e004345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapson, V.F.; Sterling, K.; Jones, N.; Elder, M.; Tripathy, U.; Brower, J.; Maholic, R.L.; Ross, C.B.; Natarajan, K.; Fong, P.; et al. A Randomized Trial of the Optimum Duration of Acoustic Pulse Thrombolysis Procedure in Acute Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapson, V.F.; Davidson, C.J.; Gurbel, P.A.; Sheikh, K.H.; Kisslo, K.B.; Stadt, R.S. Rapid and Accurate Diagnosis of Pulmonary Emboli in a Canine Model Using Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging. Chest 1991, 100, 1410–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorge, G. Intravascular ultrasound in diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism. Lancet 1991, 337, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorge, G.; Schuster, S.; Ge, J.; Meyer, J.; Erbel, R. Intravascular ultrasound in patients with acute pulmonary embolism after treatment with intravenous urokinase and high dose heparin. Heart 1997, 77, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braaten, J.V.; Goss, R.A.; Francis, C.W. Ultrasound reversibly disaggregates fibrin fibers. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Brown, M.J.; Smith, E.; Benjamin, E.; McDaniel, M.; Sachdeva, R. Case series of patients with intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism in the setting of trauma undergoing mechanical thrombectomy. Cardiovasc. Revasculariz. Med. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanin, A.; Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, H.; Haidry, S.; Bali, A.; Goldberg, J.B. Simultaneous Real-Time Intravascular Ultrasound-Guided Transcatheter Pulmonary Embolectomy Improves Procedural Accuracy, Efficacy, and Safety. JACC Case Rep. 2022, 4, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Effoe, V.S.; Kumar, A.; Verma, I.; Sachdeva, R. Intravascular Ultrasound-Guided Catheter-Based Aspiration Thrombectomy in Patients with Acute Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Series. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2021, 36, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertot, J.H.; Marcusa, D.; Patel, P.; Gross, D.; Kirshenbaum, J.M.; Sabatine, M.S.; Kochar, A. Massive pulmonary embolism complicated by right heart failure managed with intravascular ultrasound-guided percutaneous thrombectomy and rvad. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Jaber, W.; Sachdeva, R. Intravascular Ultrasound Guidance in Percutaneous Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Single-Center Experience from the flash registry. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2023, 50, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effoe, V.S.; Kumar, G.; Sachdeva, R. Intravascular ultrasound-guided pulmonary artery embolectomy for saddle pulmonary embolism. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 97, E385–E389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Andersen, A.; Kabrhel, C.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E. Catheter-based therapies in acute pulmonary embolism. Eurointervention 2018, 13, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, J.; Sista, A.K.; Weinberg, I.; Kearon, C.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Desai, N.D.; Piazza, G.; Gladwin, M.T.; Chatterjee, S.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Interventional Therapies for Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Current Status and Principles for the Development of Novel Evidence: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e774–e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrasik, A.; Gąsecka, A.; Szarpak, Ł.; Pruc, M.; Kopiec, T.; Darocha, S.; Banaszkiewicz, M.; Niewada, M.; Grabowski, M.; Kurzyna, M. Catheter-Based Therapies Decrease Mortality in Patients with Intermediate and High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: Evidence from Meta-Analysis of 65,589 Patients. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 861307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnick, M.R.; Leonberg-Yoo, A.K.; Litt, H.I.; Cohen, R.M.; Hilton, S.; Reese, P.P. The Controversy of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy with Intravenous Contrast: What Is the Risk? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, M.S.; Khalatbari, S.; Dillman, J.R.; Cohan, R.H.; Caoili, E.M.; Ellis, J.H. Contrast Material–induced Nephrotoxicity and Intravenous Low-Osmolality Iodinated Contrast Material. Radiology 2013, 267, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.S.; Khalatbari, S.; Cohan, R.H.; Dillman, J.R.; Myles, J.D.; Ellis, J.H. Contrast Material—Induced Nephrotoxicity and Intravenous Low-Osmolality Iodinated Contrast Material: Risk Stratification by Using Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate. Radiology 2013, 268, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, C.; Jaber, W.A.; Weinberg, M.D.; Bunte, M.C.; Khandhar, S.; Stegman, B.; Gondi, S.; Chambers, J.; Amin, R.; Leung, D.A.; et al. Acute outcomes for the full US cohort of the FLASH mechanical thrombectomy registry in pulmonary embolism. Eurointervention 2022, 18, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaymaz, C.; Akbal, O.Y.; Hakgor, A.; Tokgoz, H.C.; Karagoz, A.; Tanboga, I.H.; Tanyeri, S.; Keskin, B.; Turkday, S.; Demir, D.; et al. A five-year, single-centre experience on ultrasound-assisted, catheter-directed thrombolysis in patients with pulmonary embolism at high risk and intermediate to high risk. Eurointervention 2018, 14, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.B.; Cohen, D.J. Why Is Intravascular Ultrasound Guidance Underutilized in Percutaneous Coronary Intervention? It Is Not “All About the Benjamins”. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2021, 14, e007844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, A.; Giudice, P.; Gelera, A.; Stefanini, L.; Priest, V.; Simmonds, M.; Lee, C.; Wasserman, M. Understanding the economic impact of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). Eur. J. Health Econ. 2015, 17, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- From, A.M.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Williams, A.W.; Cha, S.S.; McDonald, F.S. Mortality Associated with Nephropathy after Radiographic Contrast Exposure. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.M.; Kline, J.A.; Jones, A.E.; Tumlin, J.A. Major Adverse Events One Year After Acute Kidney Injury after Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2015, 66, 267–274.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liew, D.; Duffy, S.J.; Shaw, J.; Walton, A.; Chan, W.; Gerber, R.; Stub, D. Intravascular Ultrasound Versus Angiography-Guided Drug-Eluting Stent Implantation: A Health Economic Analysis. Circ.-Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2021, 14, e006789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hakim, R.; Park, J.K.; Bansal, A.; Genshaft, S.; Moriarty, J.M. Early Experience with AngioVac Aspiration in the Pulmonary Arteries. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, A.K.; Horowitz, J.M.; Tapson, V.F.; Rosenberg, M.; Elder, M.D.; Schiro, B.J.; Dohad, S.; Amoroso, N.E.; Dexter, D.J.; Loh, C.T.; et al. Indigo Aspiration System for Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Sista, A.K. Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis for Pulmonary Embolism: The State of Practice. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 21, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Patel, N.J.; Agnihotri, K.; Panaich, S.S.; Thakkar, B.; Patel, A.; Savani, C.; Patel, N.; Arora, S.; Deshmukh, A.; et al. Utilization of catheter-directed thrombolysis in pulmonary embolism and outcome difference between systemic thrombolysis and catheter-directed thrombolysis. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 86, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciampi-Dopazo, J.J.; Romeu-Prieto, J.M.; Sánchez-Casado, M.; Romerosa, B.; Canabal, A.; Rodríguez-Blanco, M.L.; Lanciego, C. Aspiration Thrombectomy for Treatment of Acute Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: Initial Single-Center Prospective Experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rosario, T.; Basta, M.; Agarwal, S. AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy Complicated by Thrombus Fragmentation and Distal Embolization Leading to Hemodynamic Collapse: A Case Report. A A Case Rep. 2017, 8, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, F.A.; Du, L.; Woods, M.; Jacobson, K. Percutaneous Vacuum-Assisted Thrombectomy Using AngioVac Aspiration System. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2020, 21, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, R.C.; Byrne, J.G.; Gosev, I.; Cohn, L.H.; Javed, Q.; Rawn, J.D.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Piazza, G.; Aranki, S.F.; Shekar, P.S.; et al. Surgical Embolectomy for Acute Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism in a Series of 115 Patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasrija, C.; Kronfli, A.; Rouse, M.; Raithel, M.; Bittle, G.J.; Pousatis, S.; Ghoreishi, M.; Gammie, J.S.; Griffith, B.P.; Sanchez, P.G.; et al. Outcomes after surgical pulmonary embolectomy for acute submassive and massive pulmonary embolism: A single-center experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 1095–1106.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | n (%) or Mean ± SD | N |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 55 ± 15 | 39 |
| Sex, Female | 21 (53.84%) | 39 |
| Presenting symptoms | ||
| Dyspnea + Chest pain | 31 (79.48%) | 39 |
| Syncope | 3 (7.92%) | 39 |
| Respiratory failure | 4 (10.25%) | 39 |
| Cardiac arrest/PEA | 1 (2.56%) | 39 |
| Type of PE | ||
| Saddle | 12 (30.77%) | 39 |
| Unilateral | 3 (7.69%) | 39 |
| Bilateral | 22 (56.41%) | 39 |
| Saddle + RPA + LPA | 28 (71.79%) | 39 |
| Elevated biomarkers | ||
| Trop, BNP | 35 (94.59%) | 37 |
| Reference (Author, Year, Country) | Age, Sex | Presenting Complaints | H/O Comorbities | RV/LV Ratio | Type of PE | PESI/SPESI Score | System Used for Thrombectomy | Mean PAP (in mmHg) (before ⇒ after) | Any Additional Intervention | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case reports | ||||||||||
| Bertot et al., 2023, USA [16] | 80, F | Syncope | Renal failure | >0.9 | Bilateral | - | Catheter thrombectomy using IVUS only | Right ventricular assistance device used | Resolution of shock and RHF | |
| Hassanin et al., 2022, USA [14] | 46, M | Dyspnea, chest pain, near syncope | Liver transplantation, Renal failure, Heart failure | 1.8 | RPA + LPA | sPESI = 1 | Catheter-directed embolectomy (FlowTriever, Inari Medical) with simultaneous IVUS guidance | 48 ⇒ 19 | Nil | Dyspnea resolved |
| Case series | ||||||||||
| Kumar et al., 2022, USA [15] | 30, F | Dyspnea, chest pain | Obesity, H/O Left pelvis and toe fractures | 1.33 | Saddle + RPA + LPA | PESI = 50 | Percutaneous pulmonary embolectomy using the INARI FlowTriever system | 34 ⇒ 25 | Nil | Significant improvement in dyspnea |
| Kumar et al., 2022, USA [15] | 53, M | Hypoxic respiratory failure | Obesity BMI 42, CAD, Multiple rib fractures × 2 days | 0.99 | Saddle + RPA + LPA | PESI = 83 | IVUS-guided only catheter-directed aspiration thrombectomy | 31 ⇒ 25 | Mechanical ventilation | Improvement in O2 sat |
| Kumar et al., 2022, USA [15] | 61, F | Exertional dyspnea | CKD, H/O PE, Obesity (BMI 47) | 2.05 | Saddle + RPA + LPA | PESI = 101 | Percutaneous pulmonary thrombo-embolectomy under IVUS guidance only | 53 ⇒ 49 | Nil | Dyspnea and oxygen saturation improved |
| Kumar et al., 2022, USA [15] | 67, F | Syncope | CKD, Colon CA | 1.86 | Saddle + RPA + LPA | PESI = 97 | IVUS-guided aspiration thrombectomy using the INARI FlowTriever system | 31 ⇒ 26 | Nil | |
| Kumar et al., 2022, USA [15] | 68, F | Dysnea, chest pain | CKD, CAD, DM, recent GI bleed, Obesity | 2.5 | Saddle + RPA + LPA | PESI = 88 | IVUS-guided aspiration thrombectomy using the INARI FlowTriever system | 24 ⇒ 18 | Nil | |
| Kumar et al., 2023, USA [15] | 30, F | SOB | H/O MVC × 12 days back, conservative management | 1.47 | Saddle | PESI = 110 | Mechanical thrombectomy using INARI FlowTriever system | 34 ⇒ 25 | Nil | Complete resolution of symptoms |
| Kumar et al., 2023, USA [15] | 68, M | PEA on POD-1 | H/O MVC–liver laceration, small bowel injury requiring exploratory laparotomy, small bowel resection, HTN, T2DM | 1.32 | Saddle | PESI = 188 | Mechanical thrombectomy using INARI FlowTriever system | 43 ⇒ 36 | Mechanical ventilation | Recovered |
| Kumar et al.,2023,USA [15] | 44, M | Hypoxemia on day 4 of hospitalization | Ground-level fall due to spinal canal stenosis | 1.9 | Bilateral | PESI = 124 | Mechanical thrombectomy using INARI FlowTriever system | 62 ⇒ 54 | Mechanical ventilation | Recovered, Expired after 5 months due to cardiac arrest caused by recent/remote PE |
| Kumar et al., 2023, USA [15] | 53, M | Acute hypoxic respiratory failure on POD-1 | MVC causing multiple rib fractures and flail chest requiring surgical intervention, HTN, HFrEF | 0.92 | Saddle | PESI = 113 | Mechanical thrombectomy using INARI FlowTriever system | 31 ⇒ 25 | Mechanical ventilation | Recovered |
| Kumar et al., 2023, USA [15] | 77, M | Syncope and fall | Ground-level fall c/b nasal bone fracture and soft tissue laceration of face, HTN, T2DM, H/O CVA | 1.43 | Saddle | PESI = 97 | Mechanical thrombectomy using INARI FlowTriever system | 36 ⇒ 23 | None | Recovered |
| Kumar et al., 2023, USA [15] | 51, F | Acute onset hypoxic respiratory failure on POD-3 | MVC c/b open tibial fracture requiring urgent surgery, HTN | 1.8 | Bilateral | PESI = 91 | Mechanical thrombectomy using INARI FlowTriever system | 36 ⇒ 26 | Three pressors | Expired on hospital day 16 due to worsening ARDS, septic shock c/b multi organ failure |
| Prospective | ||||||||||
| Kumar et al., 2023, USA (n = 26) [17] | Mean age 54.7 ± 13.5 Sex, F = (53.8%) | Dyspnea | Saddle = 8 (30.8%) Unilateral = 3 (11.5%) Bilateral = 15 (57.7%) | sPESI 1.9 ± 1.2 | IVUS-guided mechanical thrombectomy using INARI FlowTriever system | 34.8 ± 8.3 ⇒ 25.5 ± 7.3 | Nil | Improvement in dyspnea (nMRC score) Baseline = 2.6 ± 1.4 48 h = 0.9 ± 1.2 6 months = 0.5 ± 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Desai, R.; Raval, M.; Adompreh-Fia, K.S.; Nagarajan, J.S.; Ghadge, N.; Vyas, A.; Jain, A.; Paul, T.K.; Sachdeva, R.; Kumar, G. Role of Intravascular Ultrasound in Pulmonary Embolism Patients Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review. Tomography 2023, 9, 1393-1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040111
Desai R, Raval M, Adompreh-Fia KS, Nagarajan JS, Ghadge N, Vyas A, Jain A, Paul TK, Sachdeva R, Kumar G. Role of Intravascular Ultrasound in Pulmonary Embolism Patients Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review. Tomography. 2023; 9(4):1393-1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040111
Chicago/Turabian StyleDesai, Rupak, Maharshi Raval, Kokou Selom Adompreh-Fia, Jai Sivanandan Nagarajan, Nitin Ghadge, Ankit Vyas, Akhil Jain, Timir K. Paul, Rajesh Sachdeva, and Gautam Kumar. 2023. "Role of Intravascular Ultrasound in Pulmonary Embolism Patients Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review" Tomography 9, no. 4: 1393-1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040111
APA StyleDesai, R., Raval, M., Adompreh-Fia, K. S., Nagarajan, J. S., Ghadge, N., Vyas, A., Jain, A., Paul, T. K., Sachdeva, R., & Kumar, G. (2023). Role of Intravascular Ultrasound in Pulmonary Embolism Patients Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review. Tomography, 9(4), 1393-1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040111






