Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Imaging Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Relationships of CTDIvol with Body Size Indices
3.2. Relationships of DLP with Body Size Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pearce, M.S.; Salotti, J.A.; Little, M.P.; McHugh, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.P.; Howe, N.L.; Ronckers, C.M.; Rajaraman, P.; Craft, A.W.; et al. Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, J.D.; Forsythe, A.V.; Brady, Z.; Butler, M.W.; Goergen, S.K.; Byrnes, G.B.; Giles, G.G.; Wallace, A.B.; Anderson, P.R.; Guiver, T.A.; et al. Cancer risk in 680,000 people exposed to computed tomography scans in childhood or adolescence: Data linkage study of 11 million Australians. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2013, 346, f2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulepas, J.M.; Ronckers, C.M.; Smets, A.M.J.B.; Nievelstein, R.A.J.; Gradowska, P.; Lee, C.; Jahnen, A.; van Straten, M.; de Wit, M.Y.; Zonnenberg, B.; et al. Radiation exposure from pediatric CT scans and subsequent cancer risk in The Netherlands. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Managing patient dose in multi-detector computed tomography(MDCT). ICRP Publication 102. Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM). The Measurement, Reporting, and Management of Radiation Dose in CT (Task Group 23); American Association of Physicists in Medicine: College Park, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM). Size-Specific Dose Estimates (SSDE) in Pediatric and Adult Body CT Examinations (Task Group 204); American Association of Physicists in Medicine: College Park, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Diagnostic reference levels in medical imaging. ICRP Publication 135. Ann. ICRP 2017, 46, 1–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, M.K.; Maher, M.M.; Toth, T.L.; Schmidt, B.; Westerman, B.L.; Morgan, H.T.; Saini, S. Techniques and applications of automatic tube current modulation for CT. Radiology 2004, 233, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Goo, J.M.; Ye, H.J.; Ye, S.J.; Park, C.M.; Chun, E.J.; Im, J.G. Radiation dose modulation techniques in the multidetector CT era: From basics to practice. Radiographics 2008, 28, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y. Radiation dose modulation of computed tomography component in positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y. Radiation dose management in computed tomography: Introduction to the practice at a single facility. Tomography 2023, 9, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commision. European Guidelines on Diagnostic Reference Levels for Paediatric Imaging; Radiation Protection Volume 185; European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Söderberg, M.; Gunnarsson, M. Automatic exposure control in computed tomography—An evaluation of systems from different manufacturers. Acta. Radiol. 2010, 51, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyssels, E.; Bohy, P.; Cornil, A.; van Muylem, A.; Howarth, N.; Gevenois, P.A.; Tack, D. Chest computed tomography radiation dose optimization: Comparison of automatic exposure control strength curves. J. Thorac. Imaging 2016, 31, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Nagahara, K.; Kudo, H.; Itoh, H. CT dose modulation using automatic exposure control in whole-body PET/CT: Effects of scout imaging direction and arm positioning. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2018, 8, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Sookpeng, S.; Martin, C.J.; Gentle, D.J.; Lopez-Gonzalez, M.R. Relationships between patient size, dose and image noise under automatic tube current modulation systems. J. Radiol. Prot. 2014, 34, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iball, G.R.; Tout, D. Computed tomography automatic exposure control techniques in 18F-FDG oncology PET-CT scanning. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2014, 35, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Nagahara, K.; Hayakawa, N.; Hanawa, H.; Hata, H. Monitoring dose-length product in computed tomography of the chest considering sex and body weight. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2016, 171, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanal, K.M.; Butler, P.F.; Sengupta, D.; Bhargavan-Chatfield, M.; Coombs, L.P.; Morin, R.L. U.S. diagnostic reference levels and achievable doses fo 10 adult CT examinations. Radiology 2017, 284, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, N.; Lecomte, R.; Mercure, S.; Rehani, M.M.; Nassiri, M.A. Simplified size adjusted dose reference levels for adult CT examinations: A regional study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 142, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulkens, T.H.; Bellinck, P.; Baeyaert, M.; Ghysen, D.; Van Dijck, X.; Mussen, E.; Venstermans, C.; Termote, J.L. Use of an automatic exposure control mechanism for dose optimization in multi-detector row CT examinations: Clinical evaluation. Radiology 2005, 237, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, G.M.; Cicchiello, L.; Brink, J.; Huda, W. Patient size and radiation exposure in thoracic, pelvic, and abdominal CT examinations performed with automatic exposure control. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Miyatake, H.; Nagahara, K.; Iwasaki, R. Factors affecting dose-length product of computed tomography component in whole-body positron emission tomography/computed tomography. J. Radiol. Prot. 2022, 42, 021525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; McMillan, K.; Bostani, M.; Cagnon, C.; McNitt-Gray, M. Patient size-specific analysis of dose indexes from CT lung cancer screening. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, J.A.; Braun, N.N.; Jacobsen, M.C.; Carter, R.E.; Kofler, J.M.; McCollough, C.H. Size-specific dose estimates for adult patients at CT of the torso. Radiology 2012, 265, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boere, H.; Eijsvoogel, N.G.; Sailer, A.M.; Wildberger, J.E.; de Haan, M.W.; Das, M.; Jeukens, C.R.L.P.N. Implementation of size-dependent local diagnostic reference levels for CT angiography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, W226–W233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klosterkemper, Y.; Thomas, C.; Bethge, O.T.; Appel, E.; Aissa, J.; Boeven, J.; Antoch, G.; Boos, J. Implementation of institutional size-specific diagnostic reference levels for CT agiography. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Itoh, H.; Miyatake, H.; Hata, H.; Sasa, R.; Shiibashi, N.; Mitsui, K. Automatic exposure control attains radiation dose modulation matched with the head size in pediatric brain CT. Tomography 2022, 8, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM). Use of Water Equivalent Diameter for Calculating Patient Size and Size-Specific Dose Estimates (SSDE) in CT (Task Group 220); American Association of Physicists in Medicine: College Park, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- De Monte, F.; Sapignoli, S.; Laura Cortinovis, A.; Di Maggio, A.; Nardin, M.; Pizzirani, E.; Scagliori, E.; Volpe, A.; Paiusco, M.; Roggio, A. Effectiveness of body size stratification for patient exposure optimization in computed tomography. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 163, 110804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvinen, H.; Seuri, R.; Kortesniemi, M.; Lajunen, A.; Hallinen, E.; Savikurki-Heikkilä, P.; Laarne, P.; Perhomaa, M.; Tyrväinen, E. Indication-based national diagnostic reference levels for paediatric CT: A new approach with proposed values. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 165, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Itoh, H.; Waga, A.; Sasa, R.; Mitsui, K. Radiation dose management in pediatric brain CT according to age and weight as continuous variables. Tomography 2022, 82, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Bois, D.; Du Bois, E.F. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. 1916. Nutrition 1989, 5, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, D.; Crotty, D.J.; Stevens, G.M.; Schmidt, T.G. Technical Note: Phantom study to evaluate the dose and image quality effects of a computed tomography organ-based tube current modulation technique. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 6572–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.T.; Loader, R.J.; Stevens, G.C.; Rowles, N.P. An evaluation of organ dose modulation on a GE optima CT660-computed tomography scanner. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 17, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
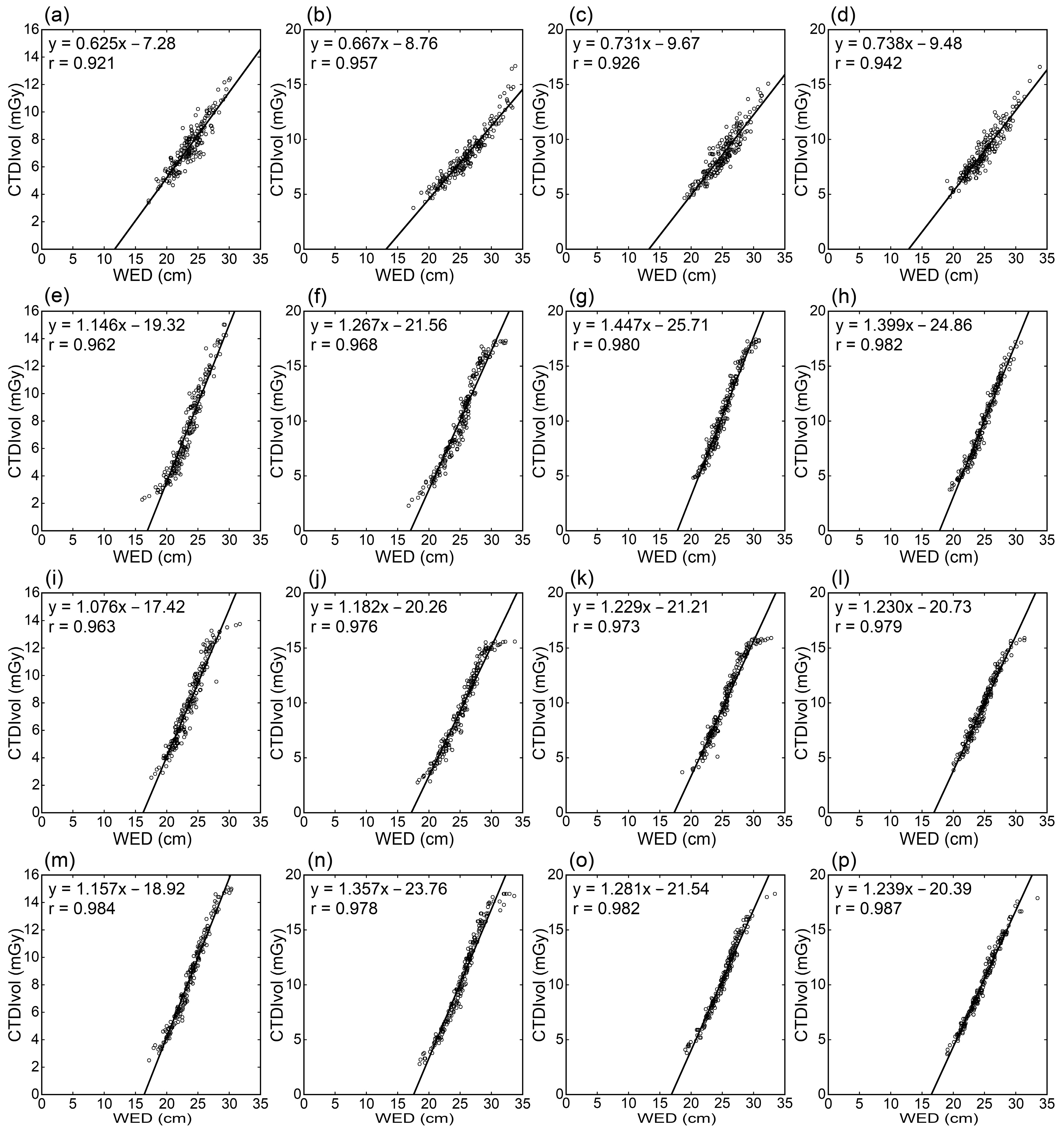

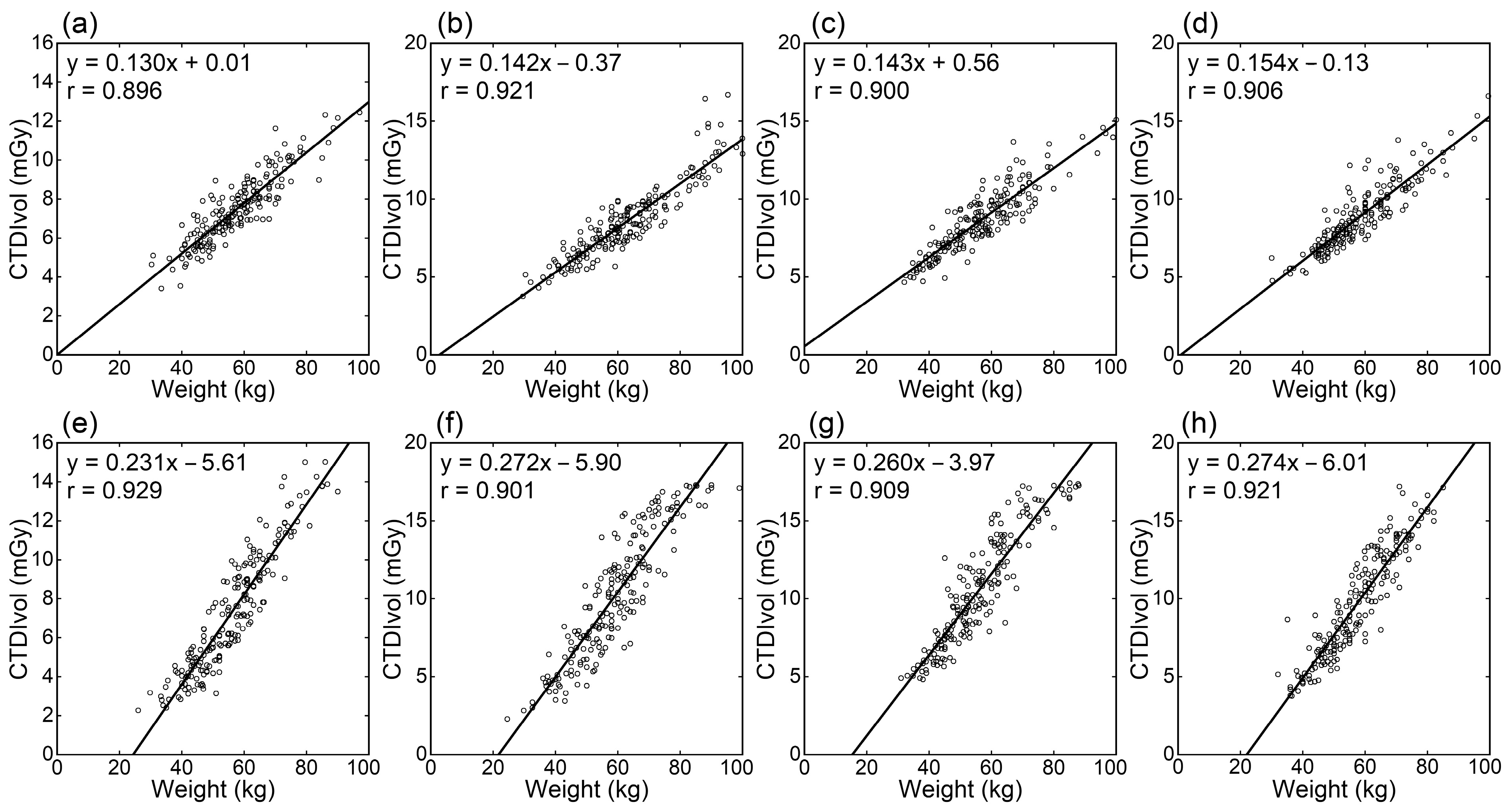
| Region | Scanner | Correlation Coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WED (cm) | ED (cm) | Weight (kg) | W/H (kg/m) | BMI (kg/m2) | BSA (m2) | ||
| T | Siemens | 0.921 | 0.913 | 0.896 | 0.888 | 0.799 | 0.873 |
| GEa | 0.962 | 0.952 | 0.929 | 0.926 | 0.846 | 0.901 | |
| GEb | 0.963 | 0.950 | 0.889 | 0.907 | 0.821 | 0.853 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.984 | 0.961 | 0.902 | 0.923 | 0.875 | 0.861 | |
| A | Siemens | 0.957 | 0.955 | 0.921 | 0.954 | 0.928 | 0.871 |
| GEa | 0.968 | 0.966 | 0.901 | 0.914 | 0.854 | 0.873 | |
| GEb | 0.976 | 0.971 | 0.908 | 0.918 | 0.865 | 0.885 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.978 | 0.967 | 0.889 | 0.898 | 0.842 | 0.864 | |
| AP | Siemens | 0.926 | 0.919 | 0.900 | 0.907 | 0.838 | 0.877 |
| GEa | 0.980 | 0.976 | 0.909 | 0.931 | 0.883 | 0.877 | |
| GEb | 0.973 | 0.966 | 0.909 | 0.927 | 0.881 | 0.883 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.982 | 0.976 | 0.922 | 0.953 | 0.914 | 0.881 | |
| TAP | Siemens | 0.942 | 0.940 | 0.906 | 0.935 | 0.895 | 0.859 |
| GEa | 0.982 | 0.975 | 0.921 | 0.949 | 0.883 | 0.871 | |
| GEb | 0.979 | 0.972 | 0.905 | 0.943 | 0.898 | 0.854 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.987 | 0.980 | 0.918 | 0.949 | 0.898 | 0.879 | |
| T | All | 0.957 | 0.944 | 0.904 | 0.911 | 0.836 | 0.872 |
| (0.026) | (0.021) | (0.017) | (0.018) | (0.033) | (0.021) | ||
| A | All | 0.970 | (0.965 | (0.905 | 0.921 | 0.872 | 0.873 |
| (0.009) | (0.007) | (0.013) | (0.023) | (0.038) | (0.009) | ||
| AP | All | 0.965 | 0.959 | (0.910 | 0.930 | 0.879 | 0.880 |
| (0.026 | (0.027 | (0.009 | (0.019 | (0.031 | (0.003 | ||
| TAP | All | 0.973 | 0.967 | 0.913 | 0.944 | 0.894 | 0.866 |
| (0.021) | (0.018) | (0.008) | (0.007) | (0.007) | (0.011) | ||
| All | Siemens | 0.937 | 0.932 | 0.906 | 0.921 | 0.865 | 0.870 |
| (0.016) | (0.019) | (0.011) | (0.029) | (0.058) | (0.008) | ||
| All | GEa | 0.973 | 0.967 | 0.915 | 0.930 | 0.867 | 0.880 |
| (0.010) | (0.011) | (0.012) | (0.014) | (0.019) | (0.014) | ||
| All | GEb | 0.972 | 0.965 | 0.903 | 0.924 | 0.866 | 0.869 |
| (0.007) | (0.010) | (0.009) | (0.015) | (0.033) | (0.018) | ||
| All | Fujifilm | 0.983 | 0.971 | 0.908 | 0.931 | 0.882 | 0.871 |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.015) | (0.026) | (0.031) | (0.010) | ||
| All | All | 0.966 | 0.959 | 0.908 | 0.926 | 0.870 | 0.873 |
| (0.020) | (0.020) | (0.012) | (0.020) | (0.035) | (0.013) | ||
| Region | Scanner | Correlation Coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WED (cm) | ED (cm) | Weight (kg) | W/H (kg/m) | BMI (kg/m2) | BSA (m2) | ||
| T | Siemens | 0.819 | 0.847 | 0.893 | 0.827 | 0.676 | 0.902 |
| GEa | 0.933 | 0.941 | 0.938 | 0.912 | 0.806 | 0.924 | |
| GEb | 0.914 | 0.938 | 0.923 | 0.896 | 0.757 | 0.910 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.959 | 0.954 | 0.912 | 0.902 | 0.819 | 0.890 | |
| A | Siemens | 0.945 | 0.933 | 0.919 | 0.938 | 0.897 | 0.876 |
| GEa | 0.950 | 0.944 | 0.896 | 0.906 | 0.842 | 0.866 | |
| GEb | 0.959 | 0.947 | 0.906 | 0.910 | 0.852 | 0.883 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.962 | 0.945 | 0.884 | 0.884 | 0.818 | 0.861 | |
| AP | Siemens | 0.922 | 0.913 | 0.922 | 0.911 | 0.819 | 0.904 |
| GEa | 0.969 | 0.961 | 0.919 | 0.926 | 0.860 | 0.892 | |
| GEb | 0.969 | 0.961 | 0.916 | 0.921 | 0.859 | 0.894 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.968 | 0.959 | 0.930 | 0.946 | 0.889 | 0.895 | |
| TAP | Siemens | 0.921 | 0.919 | 0.937 | 0.923 | 0.834 | 0.914 |
| GEa | 0.964 | 0.959 | 0.951 | 0.942 | 0.834 | 0.919 | |
| GEb | 0.965 | 0.961 | 0.939 | 0.943 | 0.858 | 0.906 | |
| Fujifilm | 0.975 | 0.969 | 0.951 | 0.944 | 0.846 | 0.930 | |
| T | All | 0.906 | 0.920 | 0.917 | 0.884 | 0.765 | 0.907 |
| (0.061) | (0.049) | (0.019) | (0.039) | (0.065) | (0.014) | ||
| A | All | 0.954 | 0.942 | 0.901 | 0.909 | 0.852 | 0.871 |
| (0.008) | (0.006) | (0.015) | (0.022) | (0.033) | (0.010) | ||
| AP | All | 0.957 | 0.948 | 0.922 | 0.926 | 0.857 | 0.896 |
| (0.023) | (0.024) | (0.006) | (0.015) | (0.029) | (0.005) | ||
| TAP | All | 0.956 | 0.952 | 0.945 | 0.938 | 0.843 | 0.917 |
| (0.024) | (0.022) | (0.007) | (0.010) | (0.012) | (0.010) | ||
| All | Siemens | 0.902 | 0.903 | 0.918 | 0.900 | 0.806 | 0.899 |
| (0.056) | (0.038) | (0.018) | (0.050) | (0.093) | (0.016) | ||
| All | GEa | 0.954 | 0.951 | 0.926 | 0.922 | 0.835 | 0.900 |
| (0.016) | (0.010) | (0.024) | (0.016) | (0.022) | (0.027) | ||
| All | GEb | 0.952 | 0.951 | 0.921 | 0.917 | 0.832 | 0.898 |
| (0.025) | (0.011) | (0.014) | (0.020) | (0.050) | (0.012) | ||
| All | Fujifilm | 0.966 | 0.957 | 0.919 | 0.919 | 0.843 | 0.894 |
| (0.007) | (0.010) | (0.028) | (0.031) | (0.033) | (0.028) | ||
| All | All | 0.943 | 0.941 | 0.921 | 0.914 | 0.829 | 0.898 |
| (0.038) | (0.029) | (0.020) | (0.030) | (0.052) | (0.020) | ||
| Scanner | CTDI at 60 kg (mGy) | DLP at 60 kg (mGy∙cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | A | AP | TAP | T | A | AP | TAP | |
| Siemens | 7.81 | 8.16 | 9.14 | 9.13 | 276.6 | 217.4 | 437.8 | 616.6 |
| GEa | 8.25 | 10.45 | 11.62 | 10.42 | 308.3 | 297.4 | 576.6 | 714.6 |
| GEb | 8.45 | 9.48 | 10.57 | 10.35 | 311.1 | 269.8 | 526.3 | 707.6 |
| Fujifilm | 9.03 | 10.32 | 11.46 | 10.79 | 331.2 | 294.7 | 571.7 | 747.2 |
| Scanner | Increase Ratio of CTDIvol | Increase Ratio of DLP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | A | AP | TAP | T | A | AP | TAP | |
| Siemens | 33.3 | 34.9 | 31.3 | 33.8 | 35.4 | 44.5 | 38.9 | 37.7 |
| GEa | 56.0 | 52.1 | 44.7 | 52.6 | 57.9 | 59.2 | 50.8 | 56.8 |
| GEb | 47.2 | 52.8 | 44.4 | 46.8 | 50.3 | 59.5 | 51.0 | 50.7 |
| Fujifilm | 51.1 | 55.6 | 44.5 | 44.4 | 51.9 | 63.4 | 50.7 | 48.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inoue, Y.; Itoh, H.; Nagahara, K.; Hata, H.; Mitsui, K. Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography. Tomography 2023, 9, 1381-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040110
Inoue Y, Itoh H, Nagahara K, Hata H, Mitsui K. Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography. Tomography. 2023; 9(4):1381-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040110
Chicago/Turabian StyleInoue, Yusuke, Hiroyasu Itoh, Kazunori Nagahara, Hirofumi Hata, and Kohei Mitsui. 2023. "Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography" Tomography 9, no. 4: 1381-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040110
APA StyleInoue, Y., Itoh, H., Nagahara, K., Hata, H., & Mitsui, K. (2023). Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography. Tomography, 9(4), 1381-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9040110







