Automated Placement of Scan and Pre-Scan Volumes for Breast MRI Using a Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
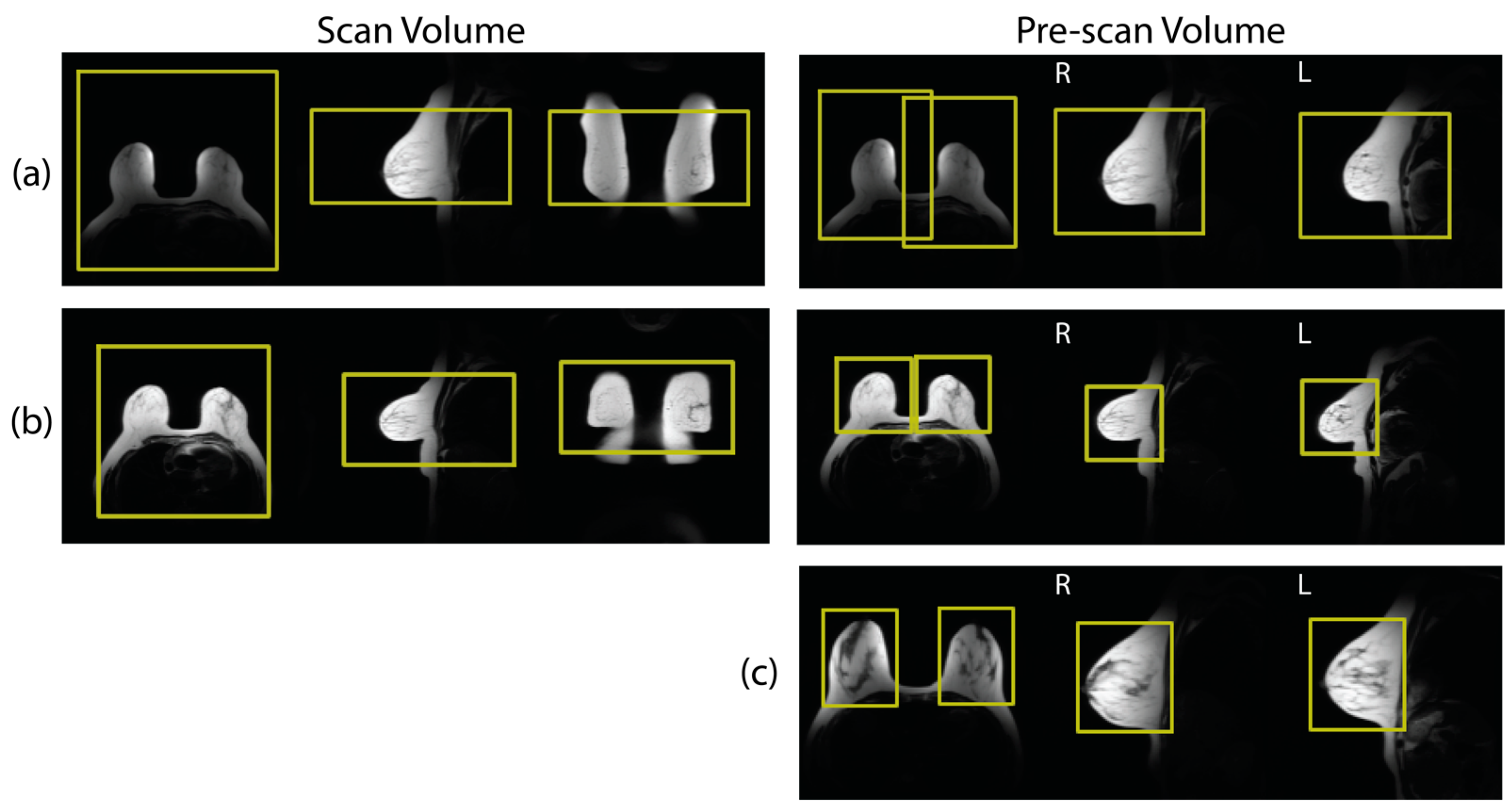
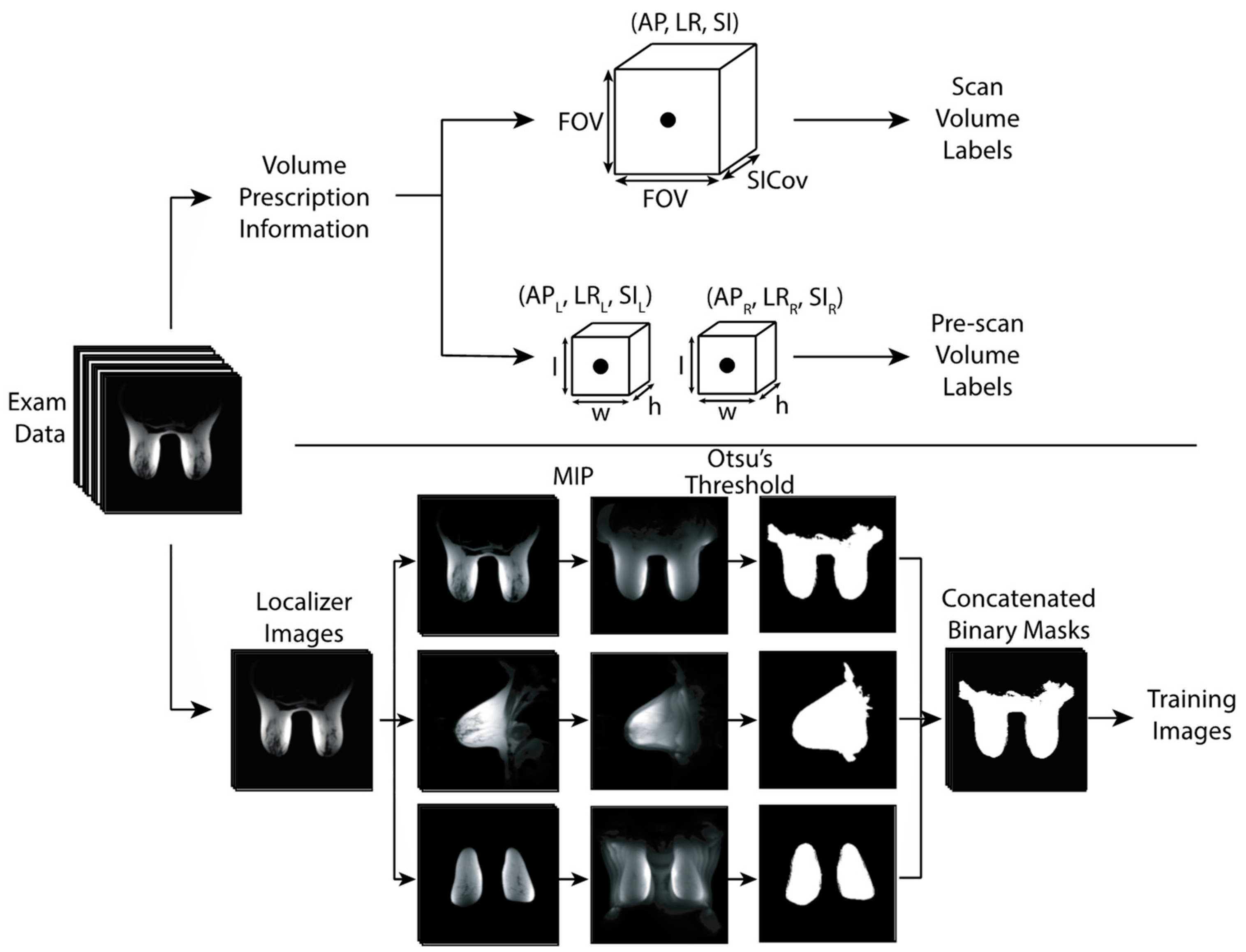
2.1. Data Collection and Curation
2.2. Network Training
2.3. Model Performance
3. Results
3.1. Data Collection
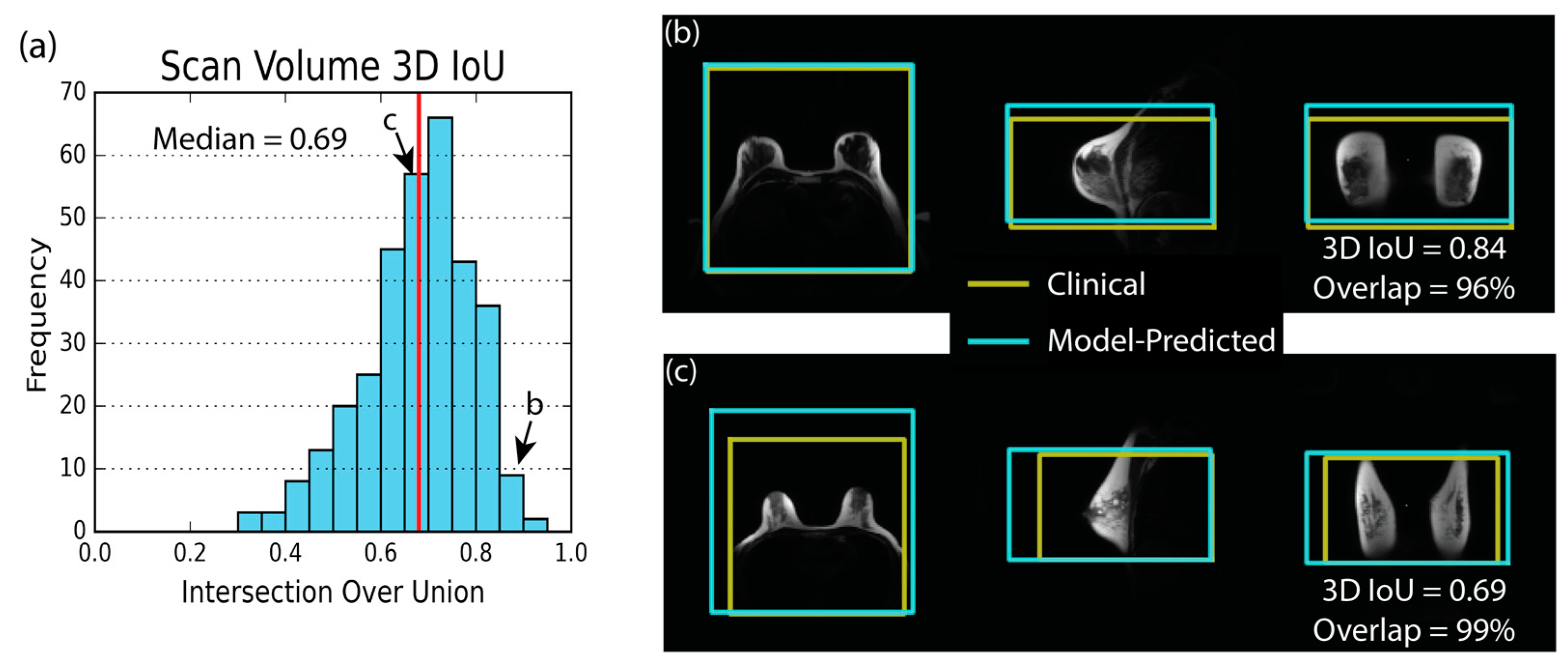
3.2. Model Performance—Scan Volume
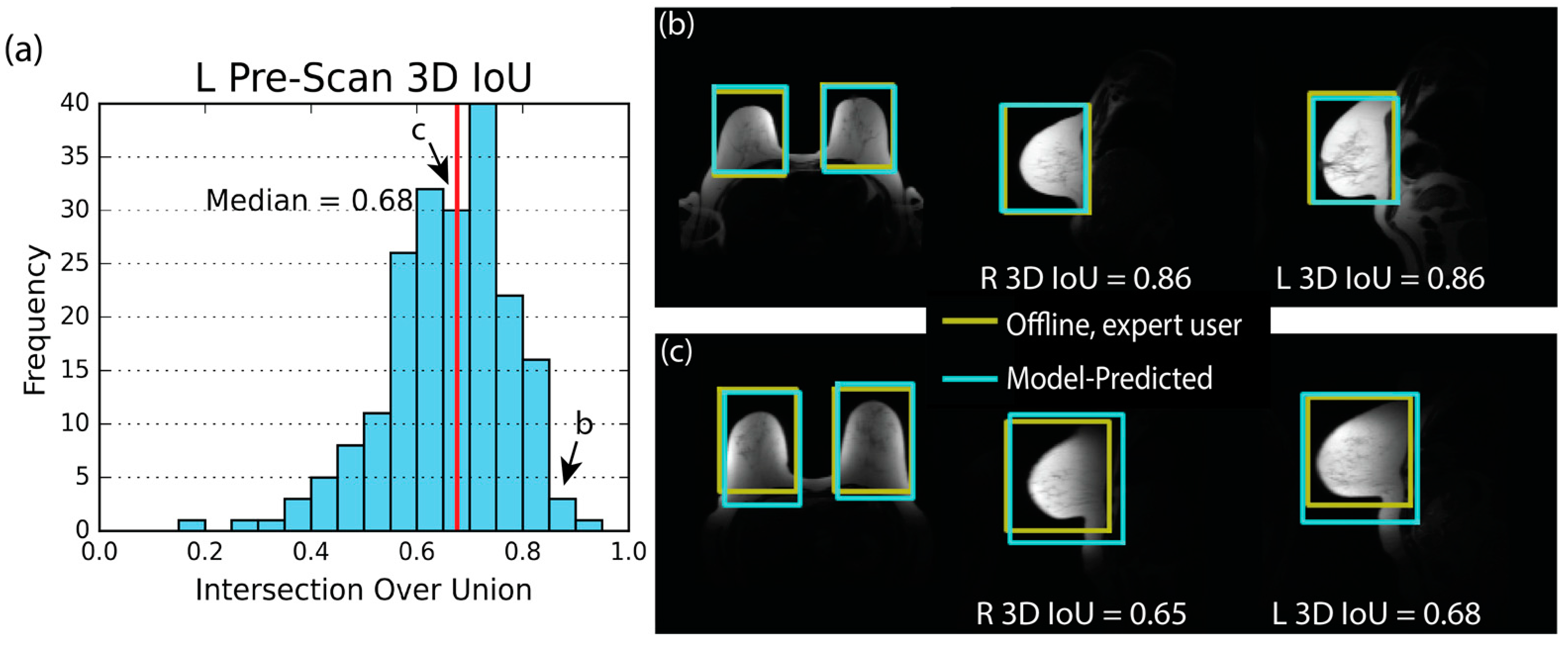
3.3. Model Performance—Pre-Scan
3.4. Uncertainty Estimate
3.5. Overall Model Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, R.M.; Cho, N.; Moy, L. Breast MRI: State of the Art. Radiology 2019, 292, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, C.K. Abbreviated Breast MRI for Screening Women with Dense Breast: The EA1141 Trial. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Schrading, S.; Strobel, K.; Schild, H.H.; Hilgers, R.D.; Bieling, H.B. Abbreviated Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): First Postcontrast Subtracted Images and Maximum-Intensity Projection—A Novel Approach to Breast Cancer Screening with MRI. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Favazza, C.P.; Axmacher, J.A.; Trzasko, J.D.; Geske, J.R.; Lee, C.U. Evaluation of Shimming Techniques on MRI Breast Image Quality at 1.5T. J. Breast Imaging 2019, 1, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Hancu, I. Patient-to-Patient Variation of Susceptibility-Induced B0 Field in Bilateral Breast MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maril, N.; Collins, C.M.; Greenman, R.L.; Lenkinski, R.E. Strategies for Shimming the Breast. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancu, I.; Govenkar, A.; Lenkinski, R.; Lee, S.-K. On Shimming Approaches in 3T Breast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Radiology. MRI Exam-Specific Parameters: Breast. Revised: 24 February 2023. Available online: https://accreditationsupport.acr.org/support/solutions/articles/11000114407-mri-exam-specific-parameters-breast-revised-2-24-2023-#:~:text=MRI%20Exam-Specific%20Parameters%3A%20Breast%20%28Revised%202-24-2023%29%201%20Do,for%20the%20pre-contrast%20and%20the%20post-contrast%20sequences.%20 (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- American College of Radiology. Practice Parameter for the Performance of Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CE-MRI) of the Breast. Revised: 2018. Available online: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Practice-Parameters/MR-Contrast-Breast.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Itti, L.; Chang, L.; Ernst, T. Automatic Scan Prescription for Brain MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 45, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Deelchand, D.K.; Joers, J.M.; Hanna, B.; Berrington, A.; Gillen, J.S.; Kantarci, K.; Soher, B.J.; Barker, P.B.; Park, H.W.; et al. AutoVOI: Real-Time Automatic Prescription of Volume-of-Interest for Single Voxel Spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bystrov, D.; Pekar, V.; Young, S.; Dries, S.P.M.; Heese, H.S.; van Muiswinkel, A.M. Automated Planning of MRI Scans of Knee Joints. In Medical Imaging 2007: Visualization and Image-Guided Procedures; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 6509, p. 65092Z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Kabasawa, H. Automated Scan Prescription for MR Imaging of Deformed and Normal Livers. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2013, 12, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozhinsky, E.; Vigneron, D.B.; Chang, S.M.; Nelson, S.J. Automated Prescription of Oblique Brain 3D Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozhinsky, E.; Vigneron, D.B.; Nelson, S.J. Improved Spatial Coverage for Brain 3D PRESS MRSI by Automatic Placement of Outer-Volume Suppression Saturation Bands. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, R.; Sundaresan, M.; Starekova, J.; Buello, C.; Panagiotopoulos, N.; Ignaciuk, M.; Oechtering, T.H.; Reeder, S.B.; Hernando, D. Automated Image Prescription for Liver MRI Using Deep Learning. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med 2021, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, R.; Buelo, C.J.; Sundaresan, M.; Starekova, J.; Panagiotopoulos, N.; Oechtering, T.H.; Lawrence, E.M.; Ignaciuk, M.; Reeder, S.B.; Hernando, D. Automated MR Image Prescription of the Liver Using Deep Learning: Development, Evaluation, and Prospective Implementation. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S.; Hirata, M.; Shinohara, H.; Ueno, E. Reproducibility of Scan Prescription in Follow-up Brain MRI: Manual versus Automatic Determination. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2013, 6, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blansit, K.; Retson, T.; Masutani, E.; Bahrami, N.; Hsiao, A. Deep Learning–Based Prescription of Cardiac MRI Planes. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2019, 1, e180069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Syed, A.B.; Zhu, X.; Pauly, J.M.; Vasanawala, S.V. Automated MRI Field of View Prescription from Region of Interest Prediction by Intra-Stack Attention Neural Network. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompa, B.; Snoek, J.; Beam, A.L. Second Opinion Needed: Communicating Uncertainty in Medical Machine Learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combalia, M.; Vilaplana, V. Monte-Carlo Sampling Applied to Multiple Instance Learning for Histological Image Classification. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, A.; Hoebel, K.; Bridge, C.P.; Befano, B.; De Sanjosé, S.; Egemen, D.; Rodriguez, A.C.; Schiffman, M.; Campbell, J.P.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J. Improving the Repeatability of Deep Learning Models with Monte Carlo Dropout. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a Bayesian Approximation: Representing Model Uncertainty in Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1050–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Leibig, C.; Allken, V.; Ayhan, M.S.; Berens, P.; Wahl, S. Leveraging Uncertainty Information from Deep Neural Networks for Disease Detection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Pereira, F., Burges, C.J., Bottou, L., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized Intersection over Union. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern REcognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geoggrey Hinton. Coursera Neural Networks for Machine Learning Lecture 6. Available online: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~tijmen/csc321/slides/lecture_slides_lec6.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Tong, C.; Yang, X.; Huang, Q.; Qian, F. NGIoU Loss: Generalized Intersection over Union Loss Based on a New Bounding Box Regression. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cases Collected | 413 |
| Exclusions | 80 |
| Implants | 42 |
| Surgical Changes * | 21 |
| Incomplete Data | 13 |
| Poor Scan Volume Placement | 4 |
| Inclusions | 333 |
| ID | Model | Field Strength (T) | Slice Quantity | FOV (cm) | ScanVolume | Pre-Scan Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SIGNA HDxt | 1.5 | 30–44 | 40 | 110 | 74 |
| 2 | SIGNA Artist | 1.5 | 45 | 38–46 | 21 | 7 |
| 3 | Optima MR450w | 1.5 | 35–60 | 40 | 22 | 22 |
| 4 | Optima MR450w | 1.5 | 45 | 38–44 | 24 | 12 |
| 5 | SIGNA HDxt | 1.5 | 45 | 40 | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | Discovery MR750 | 3 | 37 | 44–46 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | SIGNA Premier | 3 | 45 | 44 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | SIGNA Architect | 3 | 45 | 44 | 41 | 17 |
| 9 | SIGNA PET/MR | 3 | 81 | 44 | 25 | 21 |
| 10 | Discovery MR750w | 3 | 40–44 | 40 | 72 | 42 |
| 11 | SIGNA Premier | 3 | 45 | 44 | 15 | 5 |
| Total | 333 | 202 |
| Metric | 5th % | Median | 95th % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D IoU | 0.46 | 0.69 | 0.85 |
| Axial IoU | 0.61 | 0.81 | 0.95 |
| Sagittal IoU | 0.53 | 0.73 | 0.89 |
| Coronal IoU | 0.6 | 0.78 | 0.92 |
| Distance (cm) | 0.9 | 2.7 | 6.6 |
| Volume Error (%) | −30 | 2 | 45 |
| Overlap (%) | 57 | 84 | 99 |
| RMSE (cm) | 0.9 | 1.9 | 3.6 |
| Parameter | Side | 5th % | Median | 95th % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D IoU | R | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.83 |
| L | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.83 | |
| Axial IoU | R | 0.52 | 0.75 | 0.90 |
| L | 0.60 | 0.78 | 0.90 | |
| Sagittal IoU | R | 0.51 | 0.73 | 0.87 |
| L | 0.53 | 0.73 | 0.87 | |
| Coronal IoU | R | 0.49 | 0.73 | 0.89 |
| L | 0.55 | 0.75 | 0.90 | |
| Distance (cm) | R | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.9 |
| L | 0.5 | 1.2 | 3.0 | |
| Volume Error (%) | N/A | −35 | −2 | 56 |
| RMSE (cm) | N/A | 0.6 | 1.2 | 2.2 |
| Scan Volume | Pre-Scan Volume | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | 5th % | Mean | 95th % | Parameter | 5th % | Mean | 95th % |
| AP Position | 1.3 | 2.2 | 3.4 | AP Position L | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| LR Position | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.3 | LR Position L | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 |
| SI Position | 0.9 | 1.4 | 2.2 | SI Position L | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| Axial Size (FOV) | 0.8 | 1.3 | 2.1 | AP Position R | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| SI Coverage | 1.0 | 1.7 | 2.6 | LR Position R | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 |
| SI Position R | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.0 | ||||
| AP Size | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | ||||
| LR Size | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | ||||
| SI Size | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.1 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allen, T.J.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Wang, K.; Wang, P.N.; Unal, O.; Estkowski, L.D.; Cashen, T.A.; Bayram, E.; Strigel, R.M.; Holmes, J.H. Automated Placement of Scan and Pre-Scan Volumes for Breast MRI Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Tomography 2023, 9, 967-980. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030079
Allen TJ, Henze Bancroft LC, Wang K, Wang PN, Unal O, Estkowski LD, Cashen TA, Bayram E, Strigel RM, Holmes JH. Automated Placement of Scan and Pre-Scan Volumes for Breast MRI Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Tomography. 2023; 9(3):967-980. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllen, Timothy J., Leah C. Henze Bancroft, Kang Wang, Ping Ni Wang, Orhan Unal, Lloyd D. Estkowski, Ty A. Cashen, Ersin Bayram, Roberta M. Strigel, and James H. Holmes. 2023. "Automated Placement of Scan and Pre-Scan Volumes for Breast MRI Using a Convolutional Neural Network" Tomography 9, no. 3: 967-980. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030079
APA StyleAllen, T. J., Henze Bancroft, L. C., Wang, K., Wang, P. N., Unal, O., Estkowski, L. D., Cashen, T. A., Bayram, E., Strigel, R. M., & Holmes, J. H. (2023). Automated Placement of Scan and Pre-Scan Volumes for Breast MRI Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Tomography, 9(3), 967-980. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030079






