CT Scan-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology for Lung Cancer Diagnosis through the COVID-19 Pandemic: What We Have Learned
Abstract
1. Introduction
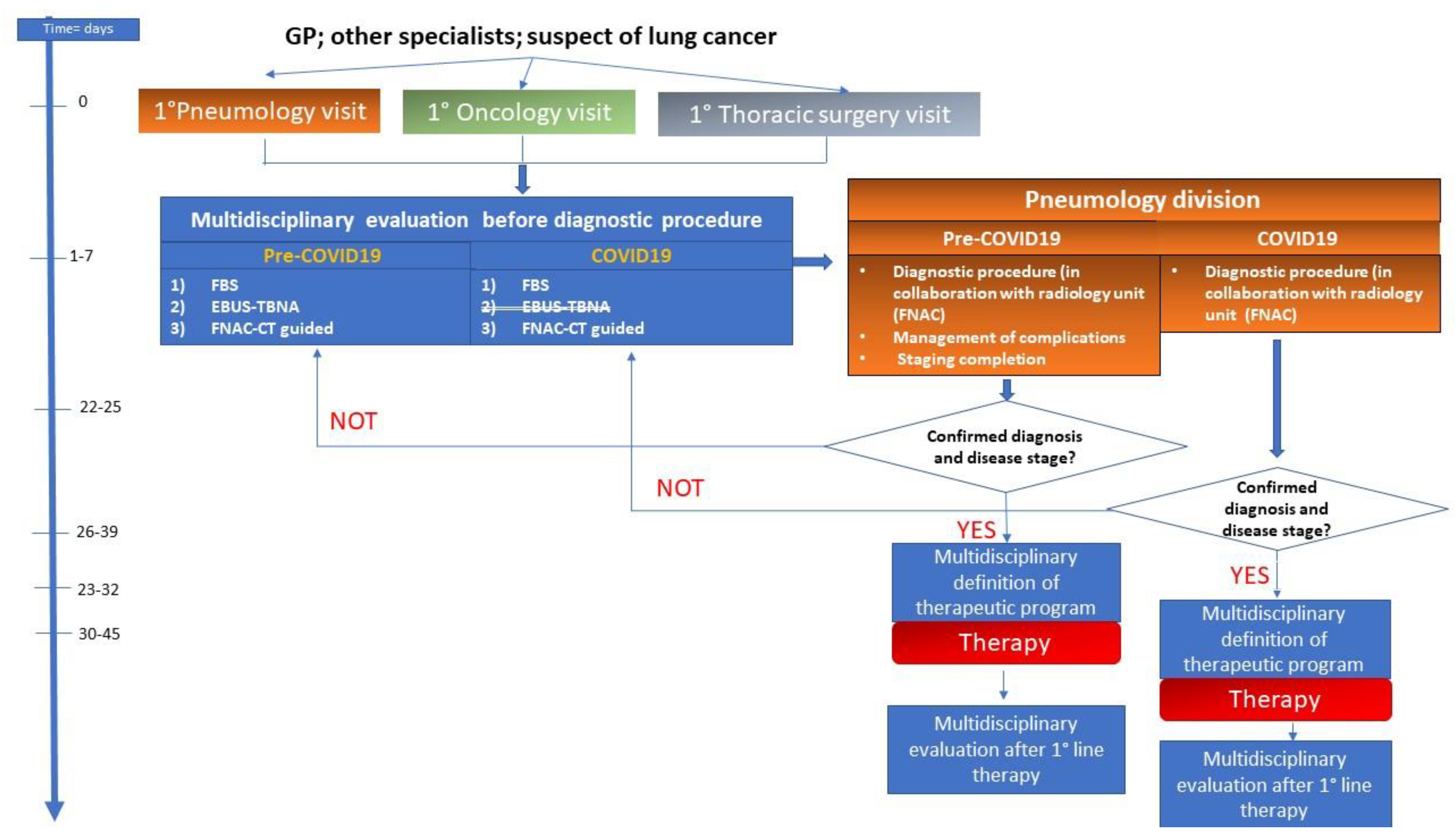
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garassino, M.C.; Whisenant, J.G.; Huang, L.C.; Trama, A.; Torri, V.; Agustoni, F.; Baena, J.; Banna, G.; Berardi, R.; Bettini, A.C.; et al. COVID-19 in patients with thoracic malignancies (TERAVOLT): First results of an international, registry-based, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haren, M.R.; Delman, A.M.; Turner, K.M.; Waits, B. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Lung Cancer Screening Program and Subsequent Lung Cancer. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2021, 232, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasymjanova, G.; Anwar, A.; Cohen, V.; Sultanem, K.; Pepe, C.; Sakr, L.; Friedmann, J.; Agulnik, J.S. The Impact of COVID-19 on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer at a Canadian Academic Center: A Retrospective Chart Review. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4247–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, H.W.; Chen, Z.; Niles, J.; Fesko, Y. Changes in the Number of US Patients with Newly Identified Cancer Before and During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2017267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovlund, C.W.; Friis, S.; Dehlendorff, C.; Nilbert, M.C.; Mørch, L.S. Hidden morbidities: Drop in cancer diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic in Denmark. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, T.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, H.I.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.; Hwang, Y.I.; Jung, K.S.; Jang, S.H. Collateral effects of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on lung cancer diagnosis in Korea. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maringe, C.; Spicer, J.; Morris, M.; Purushotham, A.; Nolte, E.; Sullivan, R.; Rachet, B.; Aggarwal, A. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: A national, population-based, modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z.K.; Yang, X.; Bai, J.; Liu, L.; Dai, T.; Feng, G.; Li, Q.; Du, X. Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 on Clinical Characteristics in Patients with Lung Cancer: A Large Single-Centre Retrospective Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 693002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, S.; Kaidar-Person, O.; Lawrence, Y.R.; Ben-Ayun, M.; Katzman, T.; Bar, J.; Mansano, A.; Symon, Z. The Coronavirus Pandemic in Israel: Implications for Radiation Oncology Departments. IMAJ 2020, 22, 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotto, C.; Maglia, C.; Ciuffreda, A.; Coretti, M.; Catania, R.; Antonacci, F.; Carnevale, S.; Sarotto, I.; Dore, R.; Filippi, A.R.; et al. The growth of non-solid neoplastic lung nodules is associated with low PDL1 expression, irrespective of sampling technique. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, G.M.; Bortolotto, C.; Filippi, A.R. Intrathoracic core needle biopsy and repeat biopsy for PD-L1 evaluation in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10 (Suppl. 33), S4031–S4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBardino, D.M.; Yarmus, L.B.; Semaan, R.W. Transthoracic needle biopsy of the lung. J. Thor. Dis. 2015, 7 (Suppl. 4), S304–S311. [Google Scholar]
- Casale, S.; Bortolotto, C.; Stella, G.M.; Filippi, A.R.; Gitto, S.; Bottinelli, O.M.; Carnevale, S.; Morbini, P.; Preda, L. Recent advancement on PD-L1 expression quantification: The radiologist perspective on CT-guided FNAC. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 27, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veltri, A.; Bargellini, I.; Giorgi, L.; Almeida, P.A.M.S.; Akhan, O. CIRSE Guidelines on Percutaneous Needle Biopsy (PNB). Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanese, G.; Sabia, F.; Sestini, S.; Ledda, R.E.; Rolli, L.; Suatoni, P.; Sverzellati, N.; Sozzi, G.; Apolone, G.; Marchianò, A.V.; et al. Feasibility and Safety of Lung Cancer Screening and Prevention Program During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Chest 2021, 160, e5–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Nguyen, K.; Wiles, A.; Sayeed, S. Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Case Volumes: A Two-year Analysis of FNA biopsy Diagnostic Categories During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2021, 10, S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, R.; Migliatico, I.; Sgariglia, R.; Nacchio, M.; Iaccarino, A.; Malapelle, U.; Vigliar, E.; Salvatore, D.; Troncone, G.; Bellevicine, C. Thyroid fine-needle aspiration trends before, during, and after the lockdown: What we have learned so far from the COVID-19 pandemic. Endocrine 2021, 71, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czeisler, M.É.; Marynak, K.; Clarke, K.E.N.; Salah, Z.; Shakya, I.; Thierry, J.M.; Ali, N.; McMillan, H.; Wiley, J.F.; Weaver, M.D.; et al. Delay or Avoidance of Medical Care Because of COVID-19-Related Concerns—United States. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, A.; Pagliuca, F.; Zito Marino, F.; Montella, M.; Franco, R.; Cozzolino, I. Interventional cytopathology in the COVID-19 era. Cytopathology 2020, 31, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.; Bhatti, Y.; Buckley, J.; Sharma, D. Fast and frugal innovations in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellevicine, C.; Vigliar, E.; Troncone, G. Thyroid FNA in the time of coronavirus: The interventional cytopathologist point of view. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisapia, P.; Malapelle, U.; Salatiello, M.; Rosell, R.; Troncone, G. A narrative review of lung cancer cytology in the times of coronavirus: What physicians should know. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.; Schmitt, F. The role of breast fine needle aspiration during and post-COVID-19 pandemic: A fast and safe alternative to needle core biopsy. Cytopathology 2020, 31, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Hernández, N.J.; Caballero Silva, U.; Cabañero Sánchez, A.; Campo-Cañaveral de la Cruz, J.L.; Obeso Carillo, A.; Jarabo Sarceda, J.R.; Sevilla López, S.; Cilleruelo Ramos, Á.; Recuero Díaz, J.L.; Call, S.; et al. Effect of COVID-19 on Thoracic Oncology Surgery in Spain: A Spanish Thoracic Surgery Society (SECT) Survey. Cancers 2021, 13, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra Mitjà, P.; Àvila, M.; García-Olivé, I. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. Med. Clin. 2022, 158, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, T.; Tsutsumi, A.; Iwami, E.; Kuroda, A.; Nakajima, T.; Eguchi, K. Delayed visit and treatment of lung cancer during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Japan: A retrospective study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221097375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depypere, L.P.; Daddi, N.; Gooseman, M.R.; Batirel, H.F.; Brunelli, A. The impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on the practice of thoracic oncology surgery: A survey of members of the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons (ESTS). Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 58, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cosimo, S.; Susca, N.; Apolone, G.; Silvestris, N.; Racanelli, V. The worldwide impact of COVID-19 on cancer care: A meta-analysis of surveys published after the first wave of the pandemic. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 961380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, W. Challenges in Advanced Lung Cancer Diagnosis During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211050764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chang, S.H.; Kim, E.J.; Bessich, J.L.; Sabari, J.K.; Cooper, B.; Geraci, T.C.; Cerfolio, R.J. Dynamic Management of Lung Cancer Care During Surging COVID-19. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 663364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhribah, H.; Zeitouni, M.; Daghistani, R.A.; Almaghraby, H.Q.; Khankan, A.A.; Alkattan, K.M.; Alshehri, S.M.; Jazieh, A.R. Implications of COVID-19 pandemic on lung cancer management: A multidisciplinary perspective. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 156, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.; Thiboutot, J.; Yarmus, L.; Illei, P. The Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on FNA and Lung Cytology Utilization. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2021, 10, S66–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pre-COVID-19 Cohort | COVID-19 Cohort | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total scheduled procedures | 135 | 141 | |
| Procedures carried out | 109 (80.74%) | 120 (85.1%) | |
| Females | 42 (38.5%) | 41 (34.1%) | |
| Males | 67 (61.5%) | 79 (65) | |
| Smoking habit (current/past) | 101 (75.5%) | 107 (76%) | 0.001 |
| Average age (yrs) | 70.32 | 69.25 | |
| Procedures cancelled (% of scheduled) | 26 (19.26) | 21 (14.89) | 0.001 |
| Nodule resolution | 7 (26.92%) (2 GGO-5 solid) | 10 (47.6%) (3 GG0-7 solid) | 0.59 |
| Technical/Organization problems | 8 (30.76) | 6 (28.57) | |
| Health problems | 3 (11.53%) | 2 (9.5%) | |
| Poor patient cooperation | 6 (23.07%) | 1(4.7%) | |
| Sars-Cov2 infection | -- | 1 (4.7%) | |
| Not known | 2 (7.69%) | 1 (4.7%) | |
| Average nodule size (mm) | 30.219 | 32.3 | |
| Complications | 27 (24.77%) | 17 (14.1%) | 0.02 |
| Pneumothorax | 17 (62.29%) | 14 (82.35%) | 0.05 |
| Hemothorax/Hemoptoe | 10 (37.7) | 3 (17.64%) | 0.05 |
| Hospitalization | 13 (48%) | 0 | |
| Average days of resolution | 6.33 | 4.11 | |
| Hospitalized pts | 8.28 | 0 | |
| Non-diagnostic procedures (% of performed) | 10 (9.17) | 7 (5.8) | 0.59 |
| Repeated procedures | 5 (50%) | 0 | |
| Diagnostic confirmation on repeated procedures | 5 | 0 | |
| Days between the first visit and procedure | 23.25 | 19.95 | |
| Days between diagnosis and start of treatment | 32.75 | 39.47 | |
| Nodule pattern | |||
| GGO | |||
| Total number | 7 (4.58%) | 10 (8.33) | 0.59 |
| Spontaneous resolution | 2 (38.57%) | 3 (30%) | |
| Biopsies | 5 | 7 | |
| ADC | 4 (80%) | 6 (85%) | |
| Non-diagnostic | 1 (20%) | 1 (15%) | |
| MIXED | |||
| Total number | 3 (2.75%) | 2 (1.6%) | 0.47 |
| Spontaneous resolution | 0 | 0 | |
| Biopsies | 3 | 2 (1.6%) | |
| ADC | 2 | 2 (1.6%) | |
| Metastatic lesion | 1 (ovary) | 0 | |
| Non diagnostic | 1 | 0 | |
| SOLID | |||
| Total number | 101 | 114 | 0.56 |
| % planned procedures | 74.81 | 80.85 | |
| Biopsies | 97 (88.9%) | 111 (78.72) | |
| ADC | 37 (38.14%) | 53 (47.7%) | |
| EGFR activating mutations (% of ADCs) | 11.5 | 12.7 | |
| ALK rearrangement (% of ADCs) | 2 | 2 | |
| SCC | 13 (13.40%) | 17 (15.3%) | |
| NSCLC undiff. | 3 (3.09%) | 9 (8.1) | |
| PDL1 TPS 5–50% (% of all NSCLCs) | 32.5 | 35.6 | |
| Metastatic lesions | 8 (8.24%) | 3 (2.7%) | |
| SCLC | 3 (3.09%) | 2 (1.8%) | |
| Carcinoid | 2 (2.06%) | 2 (1.8%) | |
| Chondromas | 2 (2.06%) | 1 | |
| Mycobacteria | 2 (2.06%) | 0 | |
| Inflammation | 1 | 5 (0.5%) | |
| Fungal infection | 0 | 2 | |
| Sarcoidosis | 1 | 0 | |
| Hamartoma | 1 | 0 | |
| Abscess | 1 | 0 | |
| Myxoid chondroma | 1 | 0 | |
| Non diagnostic for cancer | 8 (8.24) | 9 (8.1%) | |
| Non diagnostic | 9 (9.27) | 7 (6.3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stella, G.M.; Chino, V.; Putignano, P.; Bertuccio, F.; Agustoni, F.; Saracino, L.; Tomaselli, S.; Saddi, J.; Piloni, D.; Bortolotto, C. CT Scan-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology for Lung Cancer Diagnosis through the COVID-19 Pandemic: What We Have Learned. Tomography 2023, 9, 759-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020061
Stella GM, Chino V, Putignano P, Bertuccio F, Agustoni F, Saracino L, Tomaselli S, Saddi J, Piloni D, Bortolotto C. CT Scan-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology for Lung Cancer Diagnosis through the COVID-19 Pandemic: What We Have Learned. Tomography. 2023; 9(2):759-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020061
Chicago/Turabian StyleStella, Giulia Maria, Vittorio Chino, Paola Putignano, Francesco Bertuccio, Francesco Agustoni, Laura Saracino, Stefano Tomaselli, Jessica Saddi, Davide Piloni, and Chandra Bortolotto. 2023. "CT Scan-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology for Lung Cancer Diagnosis through the COVID-19 Pandemic: What We Have Learned" Tomography 9, no. 2: 759-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020061
APA StyleStella, G. M., Chino, V., Putignano, P., Bertuccio, F., Agustoni, F., Saracino, L., Tomaselli, S., Saddi, J., Piloni, D., & Bortolotto, C. (2023). CT Scan-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology for Lung Cancer Diagnosis through the COVID-19 Pandemic: What We Have Learned. Tomography, 9(2), 759-767. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020061







