Stereotactic Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Impact of Tumor Size and Minimal Ablative Margin on Therapeutic Success
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
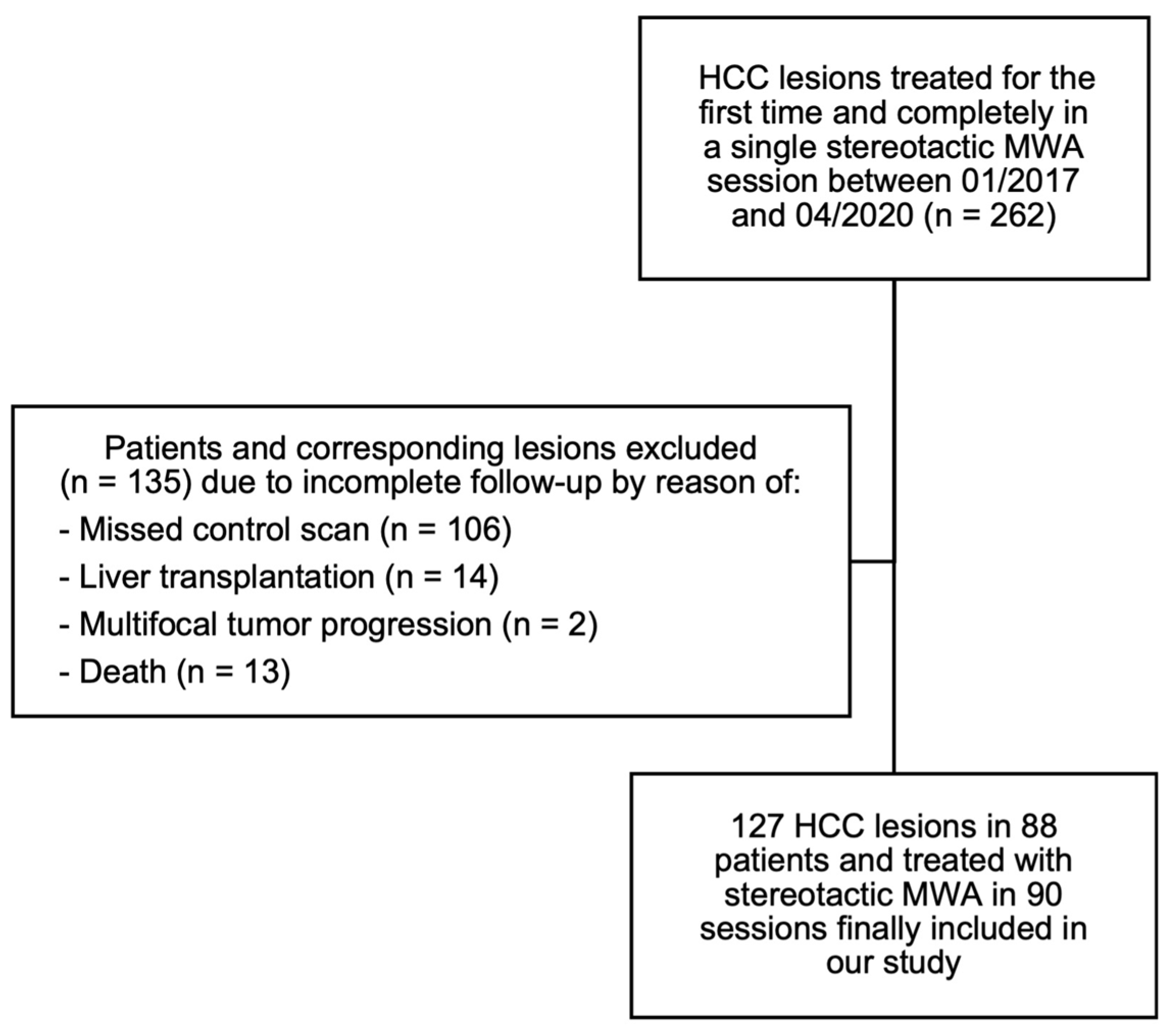
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Stereotactic Microwave Ablation Procedure and Imaging
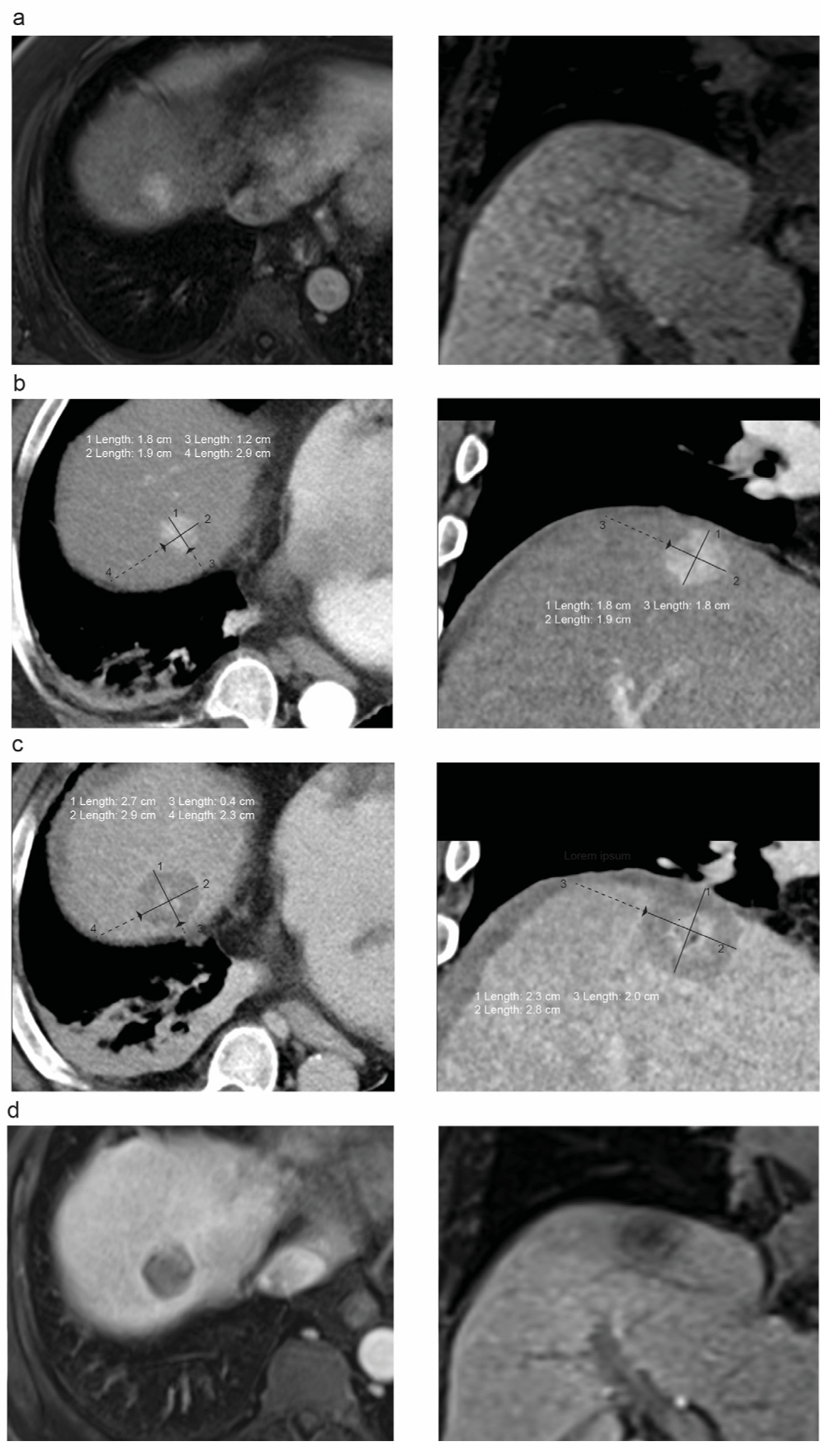
2.3. Evaluation of the Ablation Margin
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voesch, S.; Bitzer, M.; Blödt, S.; Follmann, M.; Freudenberger, P.; Langer, T.; Lorenz, P.; Jansen, P.L.; Steubesand, N.; Galle, P.; et al. S3-Leitlinie: Diagnostik und Therapie des hepatozellulären Karzinoms: Langversion 2.0–Juni 2021, AWMF-Registernummer: 032–053OL. Z. Für Gastroenterol. 2022, 60, e56–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, L.; Luerken, L. Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. In Liver Diseases; Radu-Ionita, F., Pyrsopoulos, N.T., Jinga, M., Tintoiu, I.C., Sun, Z., Bontas, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Bale, R.; Widmann, G.; Schullian, P.; Haidu, M.; Pall, G.; Klaus, A.; Weiss, H.; Biebl, M.; Margreiter, R. Percutaneous stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, B.J.J.; Yeong, C.H.; Goh, K.L.; Yoong, B.K.; Ho, G.F.; Yim, C.C.W.; Kulkarni, A. Robotic-assisted thermal ablation of liver tumours. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbalisike, E.C.; Vogl, T.J.; Zangos, S.; Eichler, K.; Balakrishnan, P.; Paul, J. Image-guided microwave thermoablation of hepatic tumours using novel robotic guidance: An early experience. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, L.P.; Pregler, B.; Niessen, C.; Dollinger, M.; Graf, B.M.; Müller, M.; Schlitt, H.J.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Robot-assisted microwave thermoablation of liver tumors: A single-center experience. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2016, 11, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari, C.M.; Magagna, M.; Bedoya, M.; Lee, F.T.; Lubner, M.G.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Ziemlewicz, T.; Brace, C.L. Microwave Ablation: Comparison of Simultaneous and Sequential Activation of Multiple Antennas in Liver Model Systems. Radiology 2016, 278, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, P.; Moreau-Gaudry, A.; Silvent, A.-S.; Frandon, J.; Chipon, E.; Medici, M.; Bricault, I. Computer assisted electromagnetic navigation improves accuracy in computed tomography guided interventions: A Prospect. randomized clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrand, J.; Toporek, G.; Harbut, P.; Jonas, E.; Nilsson, H.; Freedman, J. Stereotactic CT-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of Liver Tumors With the Use of High-Frequency Jet Ventilation: An Accuracy Procedural Safety Study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, L.P.; Lürken, L.; Verloh, N.; Haimerl, M.; Michalik, K.; Schaible, J.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Stereotactically navigated percutaneous microwave ablation (MWA) compared to conventional MWA: A matched pair analysis. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Percutaneous microwave ablation of larger hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Cheng, Y.T.; Lin, S.M. The effectiveness of multiple electrode radiofrequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with lesions more than 3 cm in size and barcelona clinic liver cancer stage A to B2. Liver Cancer 2016, 5, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, N.; Liu, P.; Wu, P.; Peng, Z.; Qian, G. Percutaneous microwave ablation of 5–6 cm unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Local efficacy and long-term outcomes. Int. J. Hyperth. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Hyperthermic Oncol. N. Am. Hyperth. Group 2017, 33, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouda, D.; Barrau, V.; Raynaud, L.; Dioguardi Burgio, M.; Paulatto, L.; Roche, V.; Sibert, A.; Moussa, N.; Vilgrain, V.; Ronot, M. Factors Associated with Tumor Progression After Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Comparison Between Monopolar Radiofrequency and Microwaves. Results of a Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.-H.; Choi, B.I.; De Baère, T.; Dodd, G.D., III; et al. Image-guided Tumor Ablation: Standardization of Terminology and Reporting Criteria—A 10-Year Update. Radiology 2014, 273, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, W.J.; Rhim, H.; Lim, H.K.; Choi, D.; Lee, J.Y. The Minimal Ablative Margin of Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (>2 and <5 cm) Needed to Prevent Local Tumor Progression: 3D Quantitative Assessment Using, C.T. Image Fusion. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Osaki, Y.; Iguchi, E.; Takeda, H.; Matsuda, F.; Nakajima, J.; Sakamoto, A.; Hatamaru, K.; Saito, S.; Nasu, A.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: The relationship between a new grading system for the ablative margin and clinical outcomes. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Petre, E.N.; Gonen, M.; Do, K.G.; Brown, K.T.; Covey, A.M.; Brody, L.A.; Alago, W.; et al. Margin size is an independent predictor of local tumor progression after ablation of colon cancer liver metastases. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Tang, Y.; Hong, J.; Chen, T.; Mai, C.; Jiang, P. A measure to assess the ablative margin using 3D-CT image fusion after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB Off. J. Int. Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc. 2015, 17, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Liu, K.-W.; Lin, C.-C.; Jeng, W.-J.; Chen, W.-T.; Sheen, I.-S.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-M. Insufficient ablative margin determined by early computed tomography may predict the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocquelet, A.; Trillaud, H.; Frulio, N.; Papadopoulos, P.; Balageas, P.; Salut, C.; Meyer, M.; Blanc, J.-F.; Montaudon, M.; de Senneville, B.D. Three-Dimensional Measurement of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Ablation Zones and Margins for Predicting Local Tumor Progression. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1038–1045.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Makino, Y.; Imai, Y.; Igura, T.; Kogita, S.; Sawai, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Okabe, J.; Takamura, M.; Fujita, N.; et al. Feasibility of Extracted-Overlay Fusion Imaging for Intraoperative Treatment Evaluation of Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2016, 5, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, Y.; Minami, T.; Chishina, H.; Kono, M.; Arizumi, T.; Takita, M.; Yada, N.; Hagiwara, S.; Ida, H.; Ueshima, K.; et al. US-US Fusion Imaging in Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Metastases. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Shin, S.S.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, J.W.; Heo, S.H.; Lim, H.S.; Jeong, Y.Y. Imaging evaluation of ablative margin and index tumor immediately after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison between multidetector-row CT and MR imaging. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 2527–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-Y.; Li, J.-G.; Wu, S.-S.; Ye, H.-L.; He, X.-Q.; Zeng, Q.-J.; Zheng, R.-Q.; An, C.; Li, K. An Optimal Ablative Margin of Small Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Image-Guided Percutaneous Thermal Ablation and Local Recurrence Prediction Base on the Ablative Margin: A Multicenter Study. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Kontchou, G.; Mahamoudi, A.; Aout, M.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Grando, V.; Coderc, E.; Vicaut, E.; Trinchet, J.C.; Sellier, N.; Beaugrand, M.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, S.; Tateishi, R.; Arano, T.; Uchino, K.; Enooku, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Asaoka, Y.; Sato, T.; Masuzaki, R.; Kondo, Y.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 569–577; quiz 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as first-line treatment: Long-term results and prognostic factors in 162 patients with cirrhosis. Radiology 2014, 270, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardini, A.C.; Marisi, G.; Canale, M.; Foschi, F.G.; Donati, G.; Ercolani, G.; Valgiusti, M.; Passardi, A.; Frassineti, G.L.; Scarpi, E. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis of overall survival and recurrence-free survival. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 6555–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, M.; Cassinotto, C.; Piron, L.; Aho-Glélé, S.; Guillot, C.; Schembri, V.; Allimant, C.; Jaber, S.; Pageaux, G.-P.; Assenat, E.; et al. Multimodal Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Predictive Factors of Recurrence and Survival in Western Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Di Maso, M.; Muscatiello, N. Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Hyperth. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Hyperthermic Oncol. N. Am. Hyperth. Group 2016, 32, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Maralakunte, M.; Kumar, M.P.; Chandel, K.; Chaluvashetty, S.B.; Bhujade, H.; Kalra, N.; Sandhu, M.S. Overall survival and local recurrence following RFA, MWA, and cryoablation of very early and early HCC: A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5400–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laimer, G.; Schullian, P.; Jaschke, N.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Alzaga, A.; Odisio, B.; Bale, R. Minimal ablative margin (MAM) assessment with image fusion: An independent predictor for local tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2463–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinguely, P.; Paolucci, I.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; Weber, S.; de Jong, K.P.; Candinas, D.; Freedman, J.; Engstrand, J. Stereotactic and Robotic Minimally Invasive Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 713685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laimer, G.; Schullian, P.; Scharll, Y.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Oberhuber, G.; Bale, R. Stereotactic radiofrequency ablation as a valid first-line treatment option for hepatocellular adenomas. Int. J. Hyperth. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Hyperthermic Oncol. N. Am. Hyperth. Group 2022, 39, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, J.; Pregler, B.; Bäumler, W.; Einspieler, I.; Jung, E.-M.; Stroszczynski, C.; Beyer, L.P. Safety margin assessment after microwave ablation of liver tumors: Inter- and intrareader variability. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbiati, M.; Muglia, R.; Goldberg, S.N.; Ierace, T.; Rotilio, A.; Passera, K.M.; Marre, I.; Solbiati, L. A novel software platform for volumetric assessment of ablation completeness. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Patients (n in total) | 88 |
| Female, n (%) | 6 (6.7) |
| Male, n (%) | 84 (93.3) |
| Age in years (range) | 65 (9.3 (43–95) |
| Child-Pugh score, n (%) | |
| Child A | 67 (76.1) |
| Child B | 21 (23.9) |
| BCLC-Classification, n (%) | |
| BCLC 0 and A | 55 (62.5) |
| BCLC B | 29 (33.0) |
| BCLC C | 4 (4.5) |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| HCC lesions ablated per patient, n (%) | |
| 1 | 61 (67.8) |
| 2 | 21 (23.3) |
| 3 | 8 (8.9) |
| Mean maximum tumor diameter in mm (range) | 19.9 ± 10.3 (6–53) |
| Complications | |
| Minor (Grade 1 and 2) | 11 (12.2) |
| Major (Grade 3 to 6) | 1 (1.1) |
| Tumor size subdivisions, n (%) | |
| <30 mm | 104 (81.9) |
| 30–50 mm | 22 (17.3) |
| >50 mm | 1 (0.8) |
| Mean MAM in mm (range) | 4.2 ± 4.2 (0–24) |
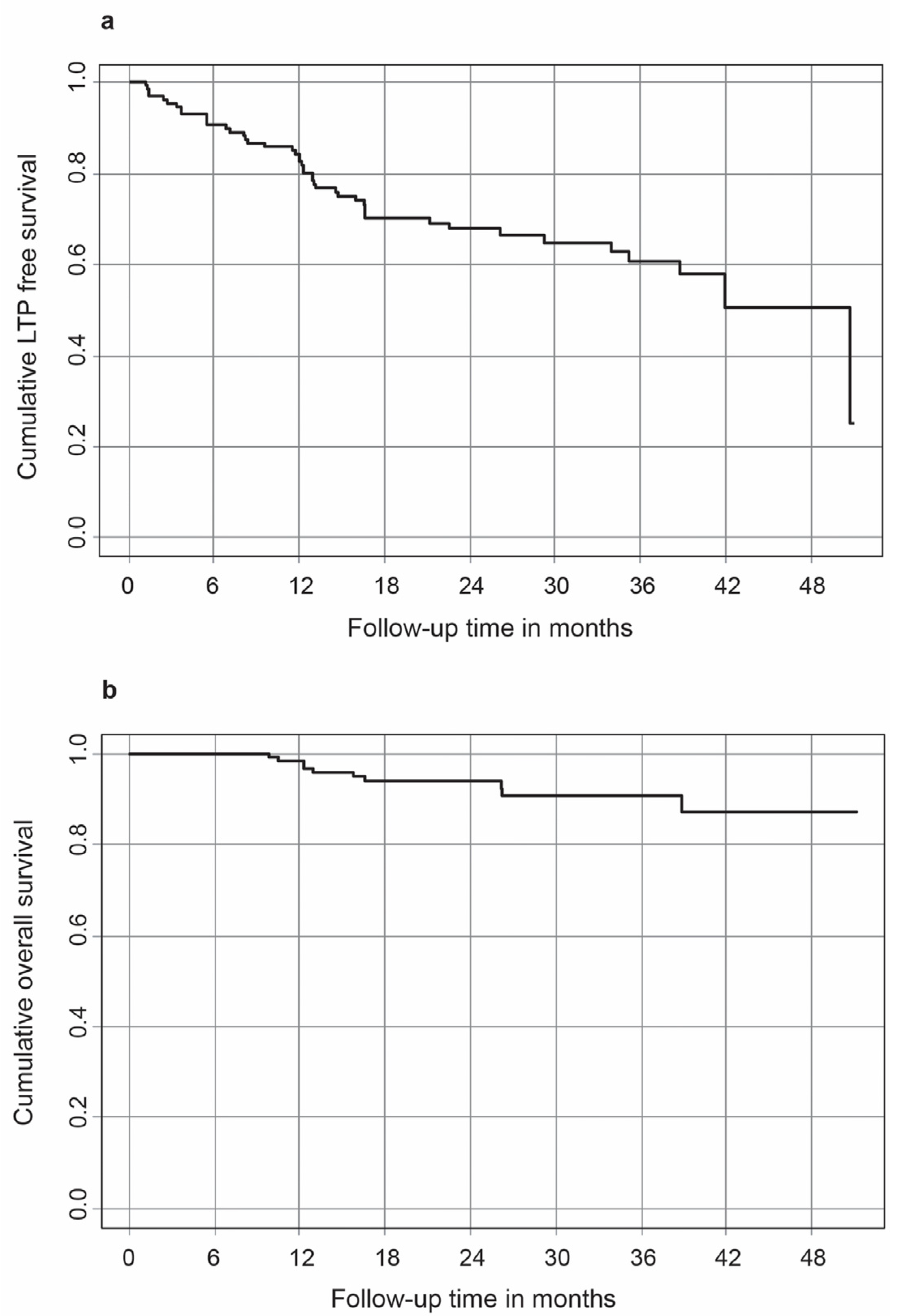
| Mean follow-up period in months | 25.8 ± 11.6 |
| Mean time to LTP in months | 12.6 ± 11.4 |
| Mean LTP rate (%) | |
| Per session | 41.1 |
| Per ablated HCC | 31.0 |
| OS rates (%) | |
| 1 st year | 98.4 |
| 2 nd year | 94 |
| 3 rd year | 90.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pausch, A.-M.; Ghali, T.; Wertheimer, T.; Zeman, F.; Mueller, K.; Doppler, M.C.; Einspieler, I.; Beyer, L.P.; Schleder, S.; Stroszczynski, C.; et al. Stereotactic Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Impact of Tumor Size and Minimal Ablative Margin on Therapeutic Success. Tomography 2023, 9, 50-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010005
Pausch A-M, Ghali T, Wertheimer T, Zeman F, Mueller K, Doppler MC, Einspieler I, Beyer LP, Schleder S, Stroszczynski C, et al. Stereotactic Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Impact of Tumor Size and Minimal Ablative Margin on Therapeutic Success. Tomography. 2023; 9(1):50-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010005
Chicago/Turabian StylePausch, Antonia-Maria, Tamam Ghali, Tobias Wertheimer, Florian Zeman, Karolina Mueller, Michael Christian Doppler, Ingo Einspieler, Lukas Philipp Beyer, Stephan Schleder, Christian Stroszczynski, and et al. 2023. "Stereotactic Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Impact of Tumor Size and Minimal Ablative Margin on Therapeutic Success" Tomography 9, no. 1: 50-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010005
APA StylePausch, A.-M., Ghali, T., Wertheimer, T., Zeman, F., Mueller, K., Doppler, M. C., Einspieler, I., Beyer, L. P., Schleder, S., Stroszczynski, C., & Luerken, L. (2023). Stereotactic Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Impact of Tumor Size and Minimal Ablative Margin on Therapeutic Success. Tomography, 9(1), 50-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010005






