Deep Learning Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Using MRI and Other Clinical Data: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
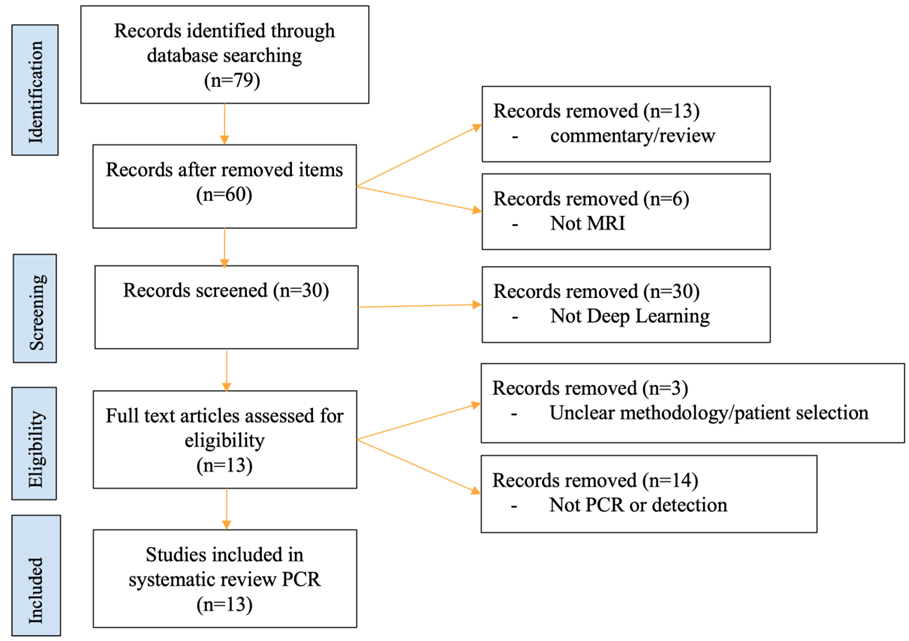
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CNN Prediction of pCR
3.2. Single Post-Contrast vs. DCE Dynamic Data
3.3. Multiparametric MRI Data
3.4. Data with Multiple Treatment Time Points
3.5. Axillary Lymph Nodes
3.6. Current Challenges to Routine Clinical Applications
3.7. How Could DL Be Employed in Practice?
3.8. Limitations
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spring, L.M.; Fell, G.; Arfe, A.; Sharma, C.; Greenup, R.; Reynolds, K.L.; Smith, B.L.; Alexander, B.; Moy, B.; Isakoff, S.J.; et al. Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Survival: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, J.P.M.; Gasior, S.A.; Davey, M.G.; O’Malley, E.; Lowery, A.J.; McGarry, J.; O’Connell, A.M.; Kerin, M.J.; McCarthy, P. The accuracy of breast MRI radiomic methodologies in predicting pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 157, 110561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, B.J. Pretreatment prediction of pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: Perfusion metrics of dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Los Santos, J.F.; Cantor, A.; Amos, K.D.; Forero, A.; Golshan, M.; Horton, J.K.; Hudis, C.A.; Hylton, N.M.; McGuire, K.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of pathologic response in patients treated with neoadjuvant systemic treatment for operable breast cancer. Translational Breast Cancer Research Consortium trial 017. Cancer 2013, 119, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, R.C. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.K.; Ferreira Junior, J.R.; Wada, D.T.; Tenorio, A.P.M.; Barbosa, M.H.N.; Marques, P.M.A. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, computer-aided diagnosis, and radiomics: Advances in imaging towards to precision medicine. Radiol. Bras. 2019, 52, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschandl, P.; Codella, N.; Akay, B.N.; Argenziano, G.; Braun, R.P.; Cabo, H.; Gutman, D.; Halpern, A.; Helba, B.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; et al. Comparison of the accuracy of human readers versus machine-learning algorithms for pigmented skin lesion classification: An open, web-based, international, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killock, D. AI outperforms radiologists in mammographic screening. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, C.; Ahn, J.H.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, H.H.; Shin, H.J.; Ahn, S.H.; Son, B.H.; Gong, G. Impact of immunohistochemistry-based molecular subtype on chemosensitivity and survival in patients with breast cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Breast Cancer 2012, 15, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Gullo, R.; Eskreis-Winkler, S.; Morris, E.A.; Pinker, K. Machine learning with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of the breast for early prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast 2020, 49, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debelee, T.G.; Schwenker, F.; Ibenthal, A.; Yohannes, D. Survey of deep learning in breast cancer image analysis. Evol. Syst. 2020, 11, 143–163. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Yu, X.; Gao, T. Machine learning with magnetic resonance imaging for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 150, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braman, N.; El Adoui, M.; Vulchi, M.; Turk, P.; Etesami, M.; Fu, P.; Bera, K.; Drisis, S.; Varadan, V.; Plecha, D.; et al. Deep learning-based prediction of response to HER2-targeted neoadjuvant chemotherapy from pre-treatment dynamic breast MRI: A multi-institutional validation study. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.08570. [Google Scholar]
- Comes, M.C.; Fanizzi, A.; Bove, S.; Didonna, V.; Diotaiuti, S.; La Forgia, D.; Latorre, A.; Martinelli, E.; Mencattini, A.; Nardone, A.; et al. Early prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy response by exploiting a transfer learning approach on breast DCE-MRIs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanmu, H.; Huang, P.B.; Brahmavar, S.; Lin, L.; Ren, T.; Kong, J.; Wang, F.; Duong, T.Q. Prediction of Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Deep Learning with Integrative Imaging, Molecular and Demographic Data. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 242–252. [Google Scholar]
- Duanmu, H.; Ren, T.; Duong, T.Q. Deep learning prediction of pathological complete response, residual cancer burden, and progression-free survival in breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- El Adoui, M.; Drisis, S.; Benjelloun, M. Multi-input deep learning architecture for predicting breast tumor response to chemotherapy using quantitative MR images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, R.; Chin, C.; Karcich, J.; Liu, M.Z.; Chang, P.; Mutasa, S.; Pascual Van Sant, E.; Wynn, R.T.; Connolly, E.; Jambawalikar, S. Prior to Initiation of Chemotherapy, Can We Predict Breast Tumor Response? Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks Approach Using a Breast MRI Tumor Dataset. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, B.Q.; Antropova, N.; Giger, M.L. Comparison of breast DCE-MRI contrast time points for predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy using deep convolutional neural network features with transfer learning. In Proceedings Volume 10134, Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; SPIE: Orlando, FL, USA, 2017; Volume 10134, p. 101340U. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, S.; Ko, E.S.; Kwon, S.; Jeon, E.; Jung, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Chung, M.J.; Im, Y.H. Multimodal deep learning models for the prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.Z.; Mutasa, S.; Chang, P.; Siddique, M.; Jambawalikar, S.; Ha, R. A novel CNN algorithm for pathological complete response prediction using an I-SPY TRIAL breast MRI database. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 73, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massafra, R.; Comes, M.C.; Bove, S.; Didonna, V.; Gatta, G.; Giotta, F.; Fanizzi, A.; La Forgia, D.; Latorre, A.; Pastena, M.I.; et al. Robustness Evaluation of a Deep Learning Model on Sagittal and Axial Breast DCE-MRIs to Predict Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Gong, C.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, J.; Shen, J. Pretreatment DCE-MRI-Based Deep Learning Outperforms Radiomics Analysis in Predicting Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 846775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.H.; Zhu, H.T.; Cao, K.; Li, X.T.; Ye, M.; Sun, Y.S. Prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer using a deep learning (DL) method. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, K.; Braman, N.; Janowczyk, A.; Madabhushi, A. A deep learning classifier for prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy from baseline breast DCE-MRI. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2018, 10575, 105750C-1. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, G.J.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Strigel, R.M.; Chitalia, R.D.; Kontos, D.; Moy, L.; Partridge, S.C.; Rahbar, H. Background parenchymal enhancement on breast MRI: A comprehensive review. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, R.; Chang, P.; Karcich, J.; Mutasa, S.; Van Sant, E.P.; Connolly, E.; Chin, C.; Taback, B.; Liu, M.Z.; Jambawalikar, S. Predicting Post Neoadjuvant Axillary Response Using a Novel Convolutional Neural Network Algorithm. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 3037–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Cattell, R.; Duanmu, H.; Huang, P.; Li, H.; Vanguri, R.; Liu, M.Z.; Jambawalikar, S.; Ha, R.; Wang, F.; et al. Convolutional Neural Network Detection of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis Using Standard Clinical Breast MRI. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, e301-e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattell, R.F.; Kang, J.J.; Ren, T.; Huang, P.B.; Muttreja, A.; Dacosta, S.; Li, H.; Baer, L.; Clouston, S.; Palermo, R.; et al. MRI Volume Changes of Axillary Lymph Nodes as Predictor of Pathologic Complete Responses to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, 68–79 e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Lin, S.; Huang, P.; Duong, T.Q. Convolutional Neural Network of Multiparametric MRI Accurately Detects Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients With Pre Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, R.; Chang, P.; Karcich, J.; Mutasa, S.; Fardanesh, R.; Wynn, R.T.; Liu, M.Z.; Jambawalikar, S. Axillary Lymph Node Evaluation Utilizing Convolutional Neural Networks Using MRI Dataset. J. Digit. Imaging 2018, 31, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, D.T.; Weisman, A.J.; Jeraj, R. Interpretation and visualization techniques for deep learning models in medical imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 04TR1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, L.; Huang, P.; Nguyen, T.; Lone, K.J.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.S.; Li, H.; Suh, D.Y.; Duong, T.Q. Machine learning classification of texture features of MRI breast tumor and peri-tumor of combined pre- and early treatment predicts pathologic complete response. Biomed. Eng. Online 2021, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Year | Image Type b | Pre-Trained or CNN Models | pCR/Non-pCR c | Molecular Subtypes | Multiple Time Points | Independ Validation d | Multisite | Transfer Learning | Data Augmentation | Heat Maps | AUC e | Accu f | Sens f | Spec f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Braman [16] a | 2020 | DCE | CNN | 76/81 | no | no | yes | yes | no | yes | no | 0.93 | 86.7% | 75% | 100% |
| Comes [17] | 2021 | CE, T2 | AlexNet | 37/78 | no | no | no | yes | yes | no | no | - | 92.3% | 85.7% | 94.7% |
| Duanmu [18] | 2020 | 3D-CE | VGG13 | 42/112 | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | yes | 0.80 | 83% | 68% | 88% |
| Duanmu [19] | 2022 | DCE, T2 | VGG13 | 42/110 | yes | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 81 ± 3% | 68 ± 8% | 86 ± 4% |
| El Adoui [20] | 2019 | CE | CNN | 14/28 | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no | 0.91 | 88% | 92.2% | 79.1% |
| Ha [21] | 2018 | CE | VGG16 | 46/95 | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no | 0.85 | 88 ± 0.6% | 95 ± 3% | 74 ± 5% |
| Huynh [22] | 2017 | DCE | VGGNet | 39/25 | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no | 0.85 ± 0.03 | - | - | - |
| Joo [23] | 2021 | DCE, T2 | ResNet-50 | 133/403 | yes | no | no | no | no | yes | no | 0.888 | - | 66.7% | 93.2% |
| Liu [24] | 2020 | DCE | VGG16 | 40/91 | no | no | no | yes | no | yes | no | 0.72 | 72.5% | 65.5% | 78.9% |
| Massafra [25] | 2022 | CE | AlexNet | 64/161 | no | no | yes | yes | yes | no | no | 0.78 | 77.3% | 71.4% | 80.0% |
| Peng [26] | 2022 | DCE | ResNeXt50 | 83/273 | yes | no | no | no | no | yes | yes | 0.83 | 77.2% | 78.1% | 7.69% |
| Qu [27] | 2020 | DCE | CNN | 132/170 | no | yes g | no | no | no | yes | no | 0.97 | - | 96% | 100% |
| Ravichandran [28] | 2018 | DCE | AlexNet | 49/117 | yes | no | no | yes | no | yes | yes | 0.85 | 85% | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, N.; Adam, R.; Huang, P.; Maldjian, T.; Duong, T.Q. Deep Learning Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Using MRI and Other Clinical Data: A Systematic Review. Tomography 2022, 8, 2784-2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8060232
Khan N, Adam R, Huang P, Maldjian T, Duong TQ. Deep Learning Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Using MRI and Other Clinical Data: A Systematic Review. Tomography. 2022; 8(6):2784-2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8060232
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Nabeeha, Richard Adam, Pauline Huang, Takouhie Maldjian, and Tim Q. Duong. 2022. "Deep Learning Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Using MRI and Other Clinical Data: A Systematic Review" Tomography 8, no. 6: 2784-2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8060232
APA StyleKhan, N., Adam, R., Huang, P., Maldjian, T., & Duong, T. Q. (2022). Deep Learning Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Using MRI and Other Clinical Data: A Systematic Review. Tomography, 8(6), 2784-2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8060232







