Prediction of Ablation Volume in Percutaneous Lung Microwave Ablation: A Single Centre Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
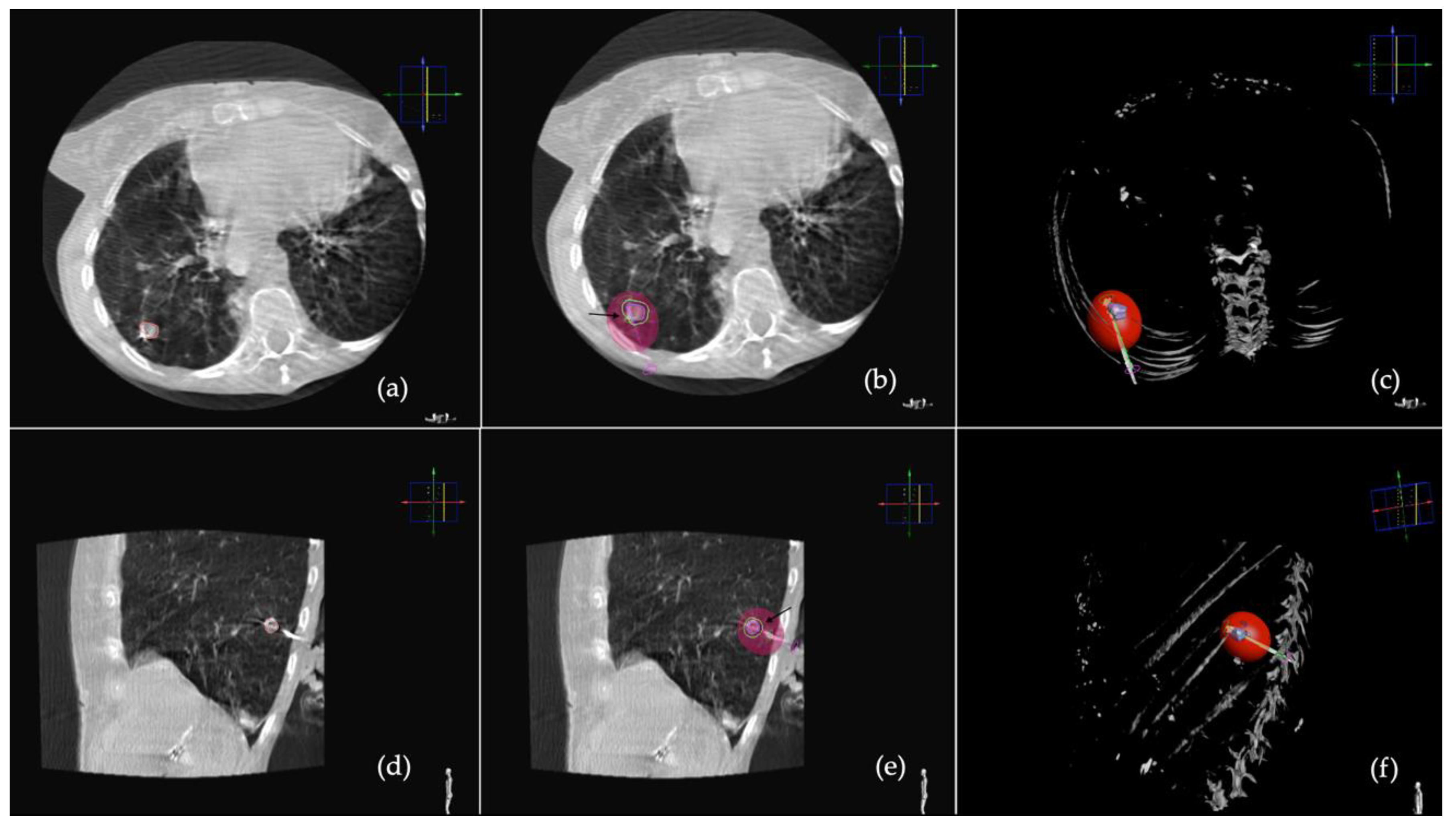
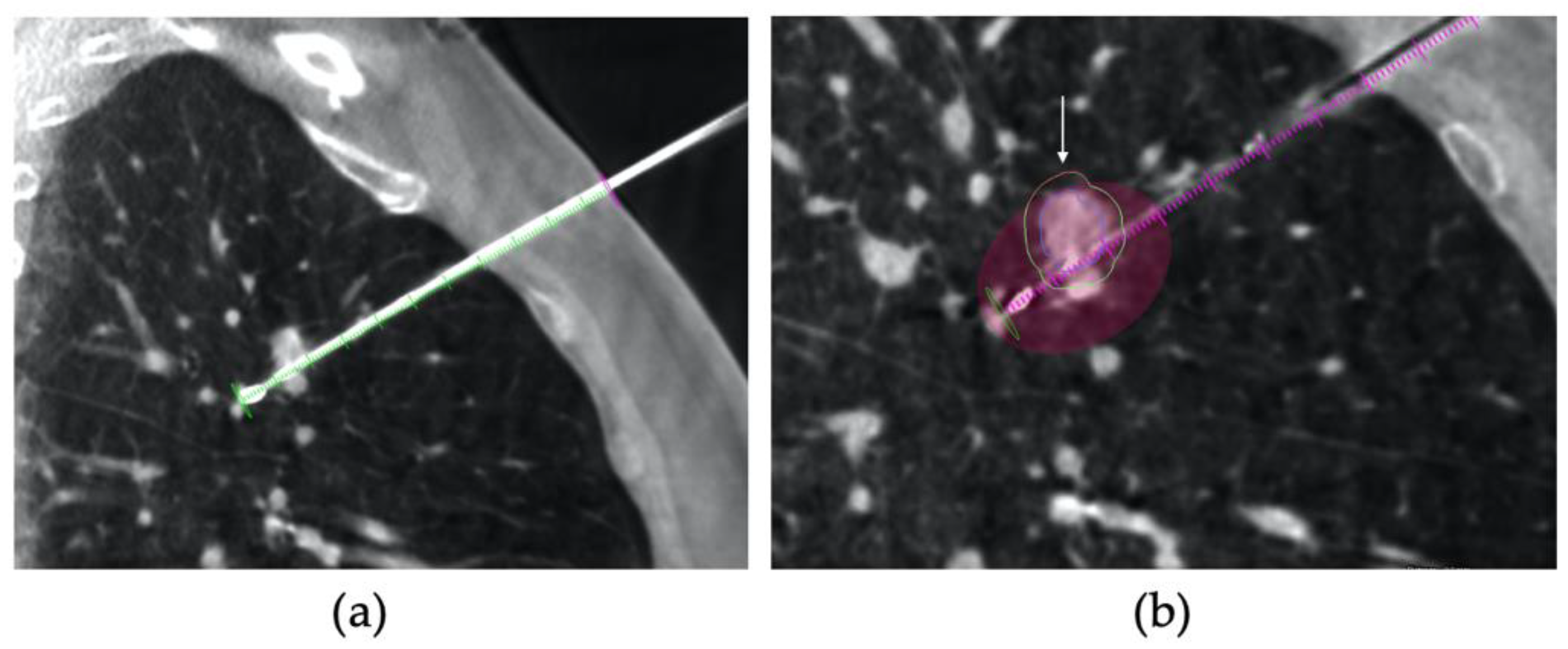
2.2. Procedure
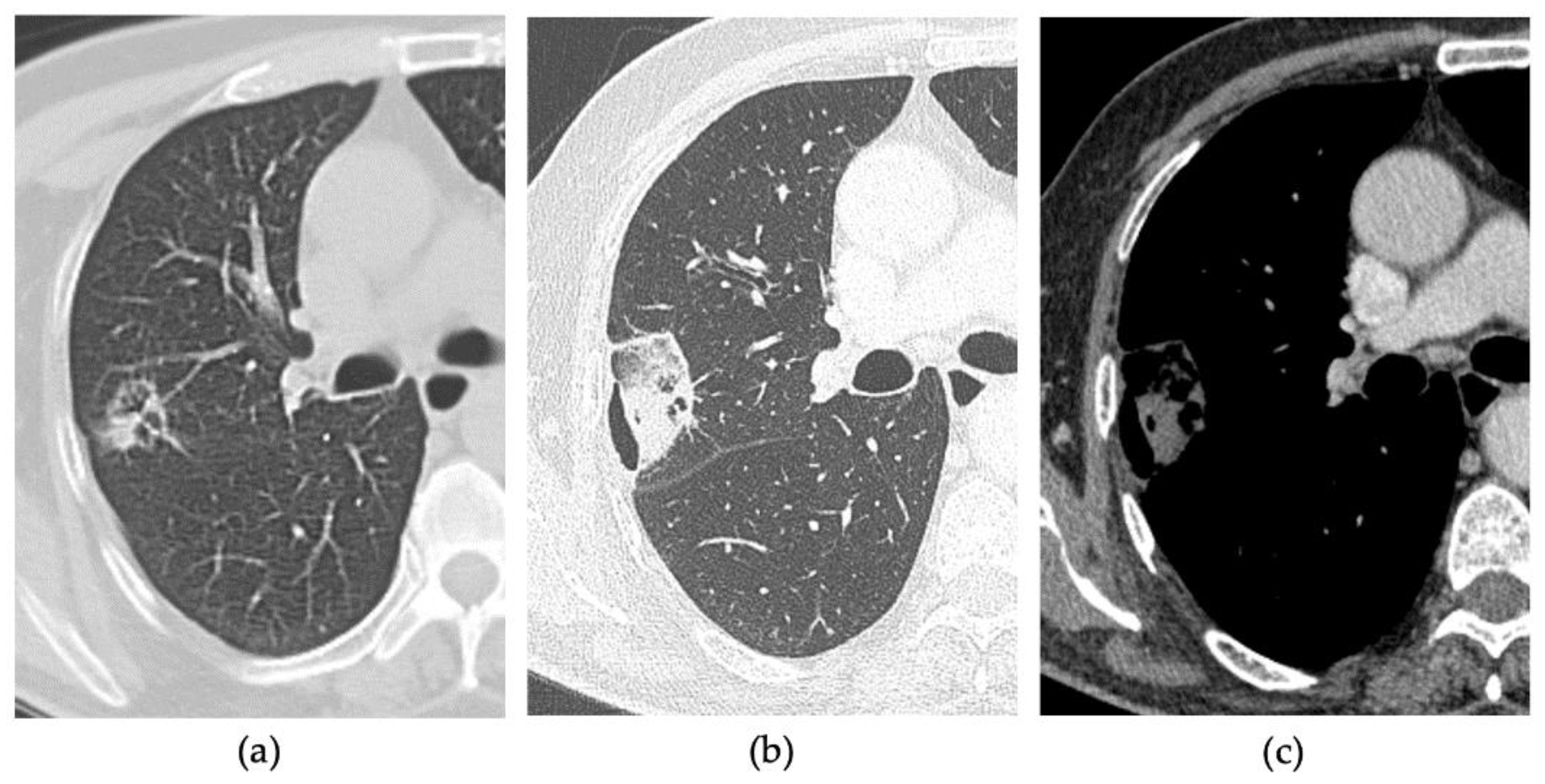
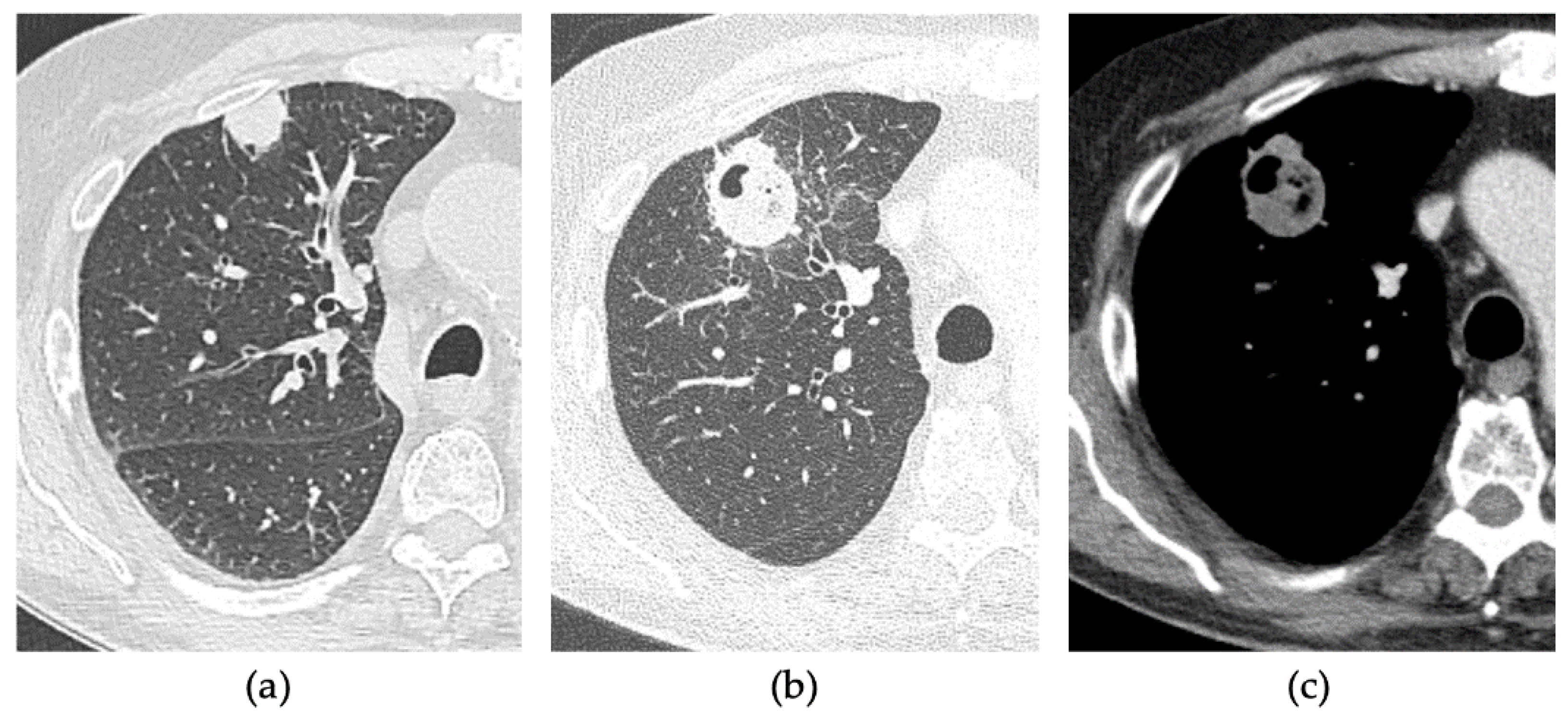
2.3. CT Follow-Up
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Data and Tumour Characteristics
3.1.1. Group 1
3.1.2. Group 2
3.2. Overall Local Tumour Control and Procedural Data
3.2.1. Group 1
3.2.2. Group 2
3.3. Early Complications
3.3.1. Group 1
3.3.2. Group 2
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: Sources, Methods and Major Patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, H.; Lynch, T.; Beck, M. Surgical Treatment of Lung Cancer. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 31, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Okumura, T.; Ohde, Y.; Nakagawa, K. Surgical Treatment for Metastatic Malignancies. Pulmonary Metastasis: Indications and Outcomes. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 10, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piltz, S.; Meimarakis, G.; Wichmann, M.W.; Hatz, R.; Schildberg, F.W.; Fuerst, H. Long-Term Results after Pulmonary Resection of Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastases. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 73, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannschmidt, J.; Dienemann, H.; Hoffmann, H. Surgical Resection of Pulmonary Metastases From Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review of Published Series. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 84, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ager, B.J.; Wells, S.M.; Gruhl, J.D.; Stoddard, G.J.; Tao, R.; Kokeny, K.E.; Hitchcock, Y.J. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy versus Percutaneous Local Tumor Ablation for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 138, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuy, D.E. Image-Guided Thermal Ablation of Lung Malignancies. Radiology 2011, 260, 633–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.R.; Han, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Min, K.H.; Lee, M.H.; Chung, C.R.; Kim, M.H.; Jin, G.Y.; Lee, Y.C. Comparison between Surgery and Radiofrequency Ablation for Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, F.J.; Grand, D.J.; Machan, J.T.; DiPetrillo, T.A.; Mayo-Smith, W.W.; Dupuy, D.E. Microwave Ablation of Lung Malignancies: Effectiveness, CT Findings, and Safety in 50 Patients. Radiology 2008, 247, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.; Nour-Eldin, N.-E.; Albrecht, M.; Kaltenbach, B.; Hohenforst-Schmidt, W.; Lin, H.; Panahi, B.; Eichler, K.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Roman, A. Thermal Ablation of Lung Tumors: Focus on Microwave Ablation. Fortschr. Röntgenstr. 2017, 189, 828–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, Y.; Singh, S.; Bandula, S.; Illing, R. Percutaneous High-Energy Microwave Ablation for the Treatment of Pulmonary Tumors: A Retrospective Single-Center Experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchi, M.; Belfiore, M.P.; Floridi, C.; Serra, N.; Belfiore, G.; Carmignani, L.; Grasso, R.F.; Mazza, E.; Pusceddu, C.; Brunese, L.; et al. Radiofrequency versus Microwave Ablation for Treatment of the Lung Tumours: LUMIRA (Lung Microwave Radiofrequency) Randomized Trial. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aufranc, V.; Farouil, G.; Abdel-Rehim, M.; Smadja, P.; Tardieu, M.; Aptel, S.; Guibal, A. Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Primary and Secondary Lung Tumors: Comparison between Microwave and Radiofrequency Ablation. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.P.; Barry, C.; Schöder, H.; Camacho, J.C.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Halpenny, D.F. Imaging Following Thermal Ablation of Early Lung Cancers: Expected Post-Treatment Findings and Tumour Recurrence. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 864.e13–864.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.J.; Naguib, N.N.N.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Koitka, K.; Lehnert, T.; Nour-Eldin, N.-E.A. Microwave Ablation Therapy: Clinical Utility in Treatment of Pulmonary Metastases. Radiology 2011, 261, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ierardi, A.M.; Petrillo, M.; Xhepa, G.; Laganà, D.; Piacentino, F.; Floridi, C.; Duka, E.; Fugazzola, C.; Carrafiello, G. Cone Beam Computed Tomography Images Fusion in Predicting Lung Ablation Volumes: A Feasibility Study. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, M.; Cariati, M.; Marra, P.; Masala, S.; Pereira, P.L.; Carrafiello, G. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Thermal Ablation of Primary and Secondary Lung Tumours. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2020, 43, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespro, V.; Bonanno, M.C.; Andrisani, M.C.; Ierardi, A.M.; Phillips, A.; Tosi, D.; Mendogni, P.; Franzi, S.; Carrafiello, G. CT after Lung Microwave Ablation: Normal Findings and Evolution Patterns of Treated Lesions. Tomography 2022, 8, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardella, J.F.; Kundu, S.; Miller, D.L.; Millward, S.F.; Sacks, D. Society of Interventional Radiology Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, S189–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours: Revised RECIST Guideline (Version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.; McClenny, T.E.; Cardella, J.F.; Lewis, C.A. Society of Interventional Radiology Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, S199–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, G.R.; Pua, B.B. Ablation Planning Software for Optimizing Treatment: Challenges, Techniques, and Applications. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 22, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, L.P.; Wiggermann, P. Planning and Guidance: New Tools to Enhance the Human Skills in Interventional Oncology. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2017, 98, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebek, J.; Taeprasartsit, P.; Wibowo, H.; Beard, W.L.; Bortel, R.; Prakash, P. Microwave Ablation of Lung Tumors: A Probabilistic Approach for Simulation-based Treatment Planning. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 3991–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, P.; Berkhout, W.E.M.; Kaanen, C.I.; Sluijter, J.H.; Visser, I.J.; van den Dobbelsteen, J.J.; de Geus-Oei, L.F.; Webb, A.G.; Burgmans, M.C. Performance of the Emprint and Amica Microwave Ablation Systems in Ex Vivo Porcine Livers: Sphericity and Reproducibility Versus Size. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2021, 44, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, S.J.S.; Heerink, W.J.; de Jong, K.P. Liver Microwave Ablation: A Systematic Review of Various FDA-Approved Systems. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4026–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Basten, L.M.; Nour-Eldin, N.-E.A.; Kaltenbach, B.; Bodelle, B.; Wichmann, J.L.; Ackermann, H.; Naguib, N.N.N. Evaluation of Microwave Ablation of Liver Malignancy with Enabled Constant Spatial Energy Control to Achieve a Predictable Spherical Ablation Zone. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 34, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovac, F.; Cheng, P.; Campos-Nanez, E.; Kallakury, B.; Popa, T.; Wilson, E.; Abeledo, H.; Cleary, K. Radiofrequency Ablation of Lung Tumors in Swine Assisted by a Navigation Device with Preprocedural Volumetric Planning. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmon, S.H.; Sterner, R.M.; Eiken, P.W.; Vogl, T.J.; Pua, B.B.; Port, J.L.; Dupuy, D.E.; Callstrom, M.R. Technical and Safety Performance of CT-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation for Lung Tumors: An Ablate and Resect Study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 6827–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, E.K.; Borsic, A.; Patel, S.D. Validation of Software for Patient-Specific Real-Time Simulation of Hepatic Radiofrequency Ablation. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, E219–E227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisenauer, J.S.; Eiken, P.W.; Callstrom, M.R.; Johnson, G.B.; Pierson, K.; Lechtenberg, B.; Blackmon, S.H. A Prospective Trial of CT-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation for Lung Tumors. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Shapiro-Wilk | Group 1 | Group 2 | p-Value | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | - | 4/10 (40%) | 5/10 (50%) | 1 | Fisher |
| Female | - | 6/10 (60%) | 5/10 (50%) | |||
| Age | 0.29 | 67 ± 22 (median ± IQR; range: 57–87) | 71 ± 9.5 (median ± IQR; range: 57–80) | 0.739 | Mann-Whitney U test | |
| Tumour | primary | - | 4/10 (40%) | 5/10 (50%) | 1 | Fisher |
| metastasis | - | 6/10 (60%) | 5/10 (50%) | |||
| Maximal axial diameter | 0.012 | 12.7 ± 6.09 (mean ± SD; range: 5–22) | 15.1 ± 6.64 (mean ± SD; range: 5–22) | 0.411 | Student’ t-test | |
| DAP (mGy/cm2) | 0.279 | 63 ± 39.45 (mean ± SD; range: 9.68–107) | 29.85 ± 23.175 (mean ± SD; range: 13.1–63.1) | 0.0089 | Student’ t-test | |
| Procedure Time (minutes) | 0.01 | 33.5 ± 9.73 (mean ± SD; range: 15–50) | 34 ± 10.49 (mean ± SD; range: 15–50) | 0.913 | Student’ t-test | |
| Fluoroscopy Time (seconds) | 0.001 | 83.9 ± 41.16 (mean ± SD; range: 61–186) | 135.8 ± 65.51 (mean ± SD; range: 62–284) | 0.048 | Student’ t-test | |
| Number of antenna repositioning | 0.145 | 2 ± 3 (median ± IQR; range: 0–4) | 1.5 ± 2 (median ± IQR; range: 0–5) | 0.481 | Mann-Whitney U test | |
| Residual disease after 1 month | - | 1/10 (10%) | 3/10 (30%) | 0.582 | Fisher | |
| Complications | - | 6/10 (60%) | 6/10 (60%) | 1 | Fisher | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ierardi, A.M.; Grillo, P.; Bonanno, M.C.; Coppola, A.; Vespro, V.; Andrisani, M.C.; Tosi, D.; Mendogni, P.; Franzi, S.; Venturini, M.; et al. Prediction of Ablation Volume in Percutaneous Lung Microwave Ablation: A Single Centre Retrospective Study. Tomography 2022, 8, 2475-2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050206
Ierardi AM, Grillo P, Bonanno MC, Coppola A, Vespro V, Andrisani MC, Tosi D, Mendogni P, Franzi S, Venturini M, et al. Prediction of Ablation Volume in Percutaneous Lung Microwave Ablation: A Single Centre Retrospective Study. Tomography. 2022; 8(5):2475-2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050206
Chicago/Turabian StyleIerardi, Anna Maria, Pasquale Grillo, Maria Chiara Bonanno, Andrea Coppola, Valentina Vespro, Maria Carmela Andrisani, Davide Tosi, Paolo Mendogni, Sara Franzi, Massimo Venturini, and et al. 2022. "Prediction of Ablation Volume in Percutaneous Lung Microwave Ablation: A Single Centre Retrospective Study" Tomography 8, no. 5: 2475-2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050206
APA StyleIerardi, A. M., Grillo, P., Bonanno, M. C., Coppola, A., Vespro, V., Andrisani, M. C., Tosi, D., Mendogni, P., Franzi, S., Venturini, M., & Carrafiello, G. (2022). Prediction of Ablation Volume in Percutaneous Lung Microwave Ablation: A Single Centre Retrospective Study. Tomography, 8(5), 2475-2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050206








