Petrotympanic Fissure Architecture and Malleus Location in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
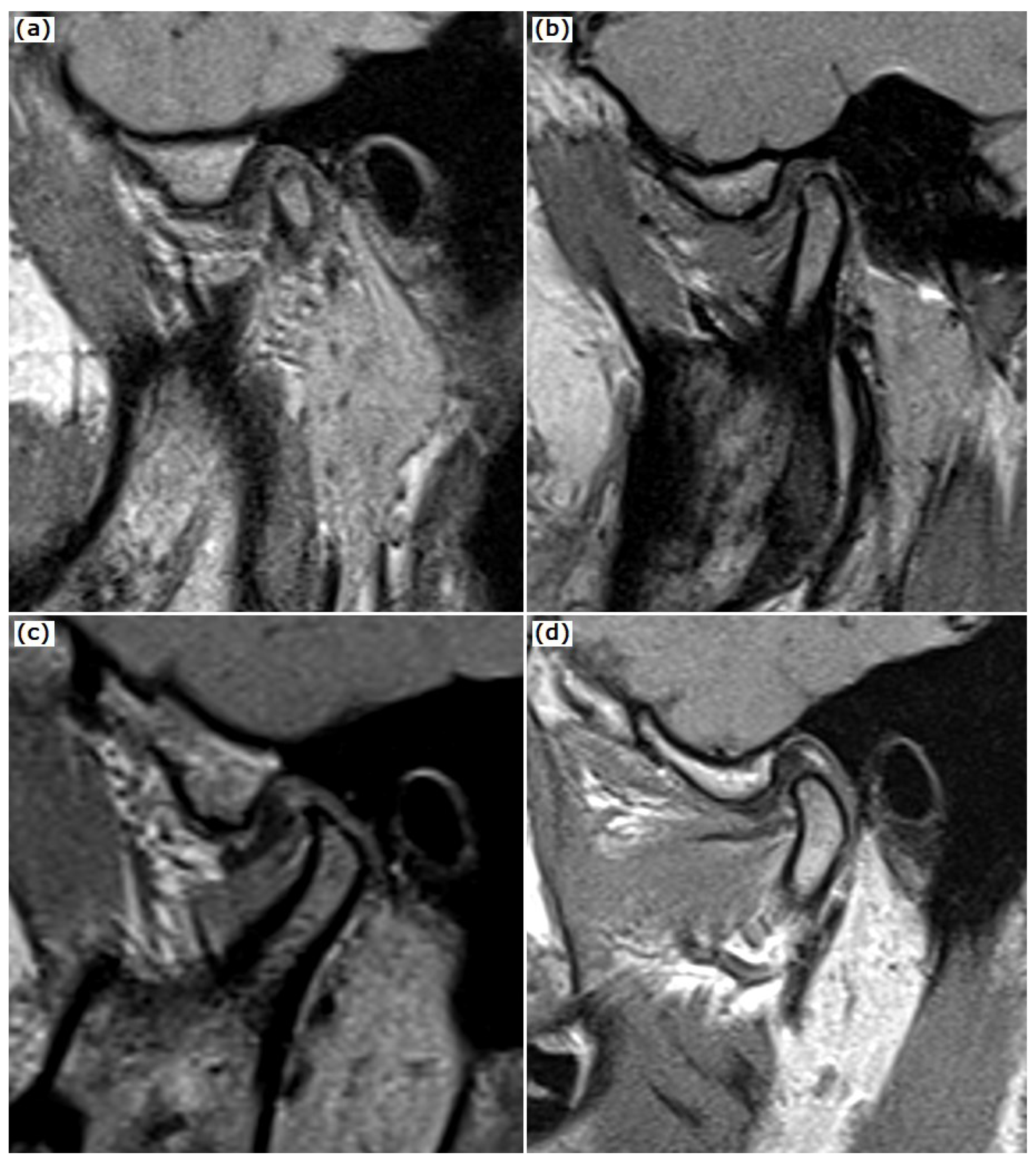
2.1. MRI Examination
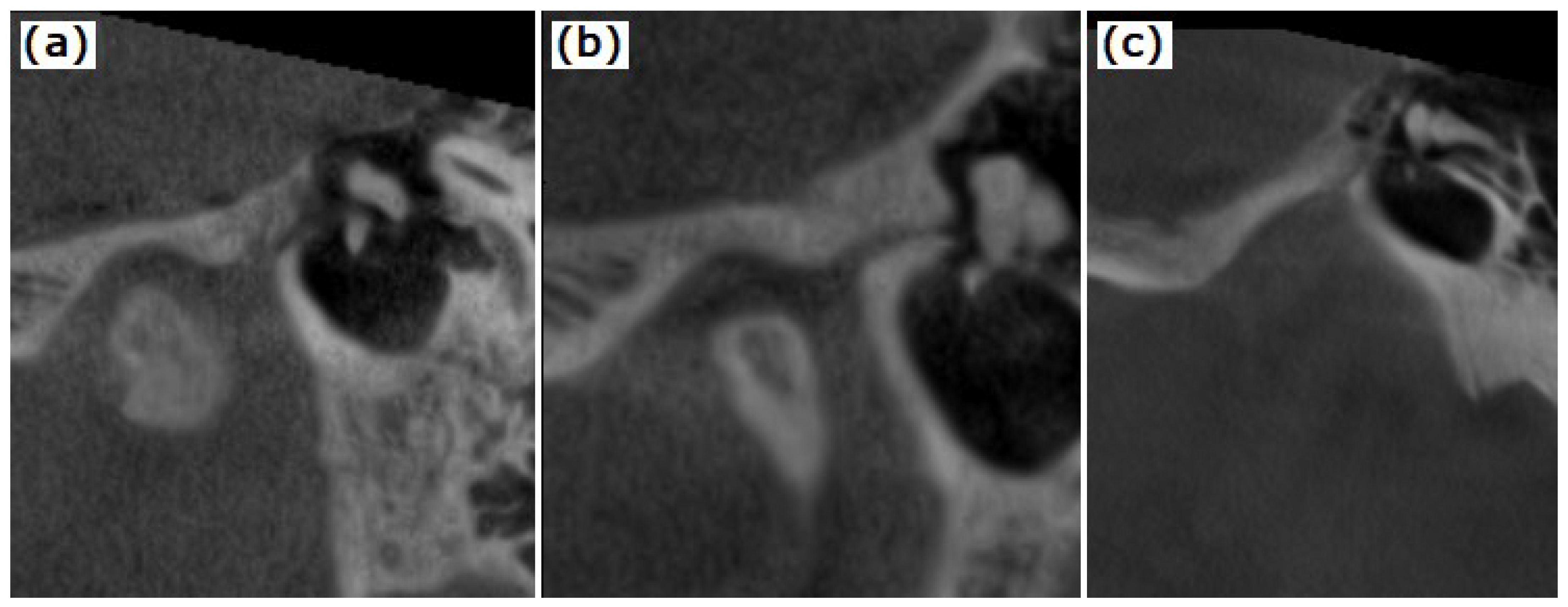
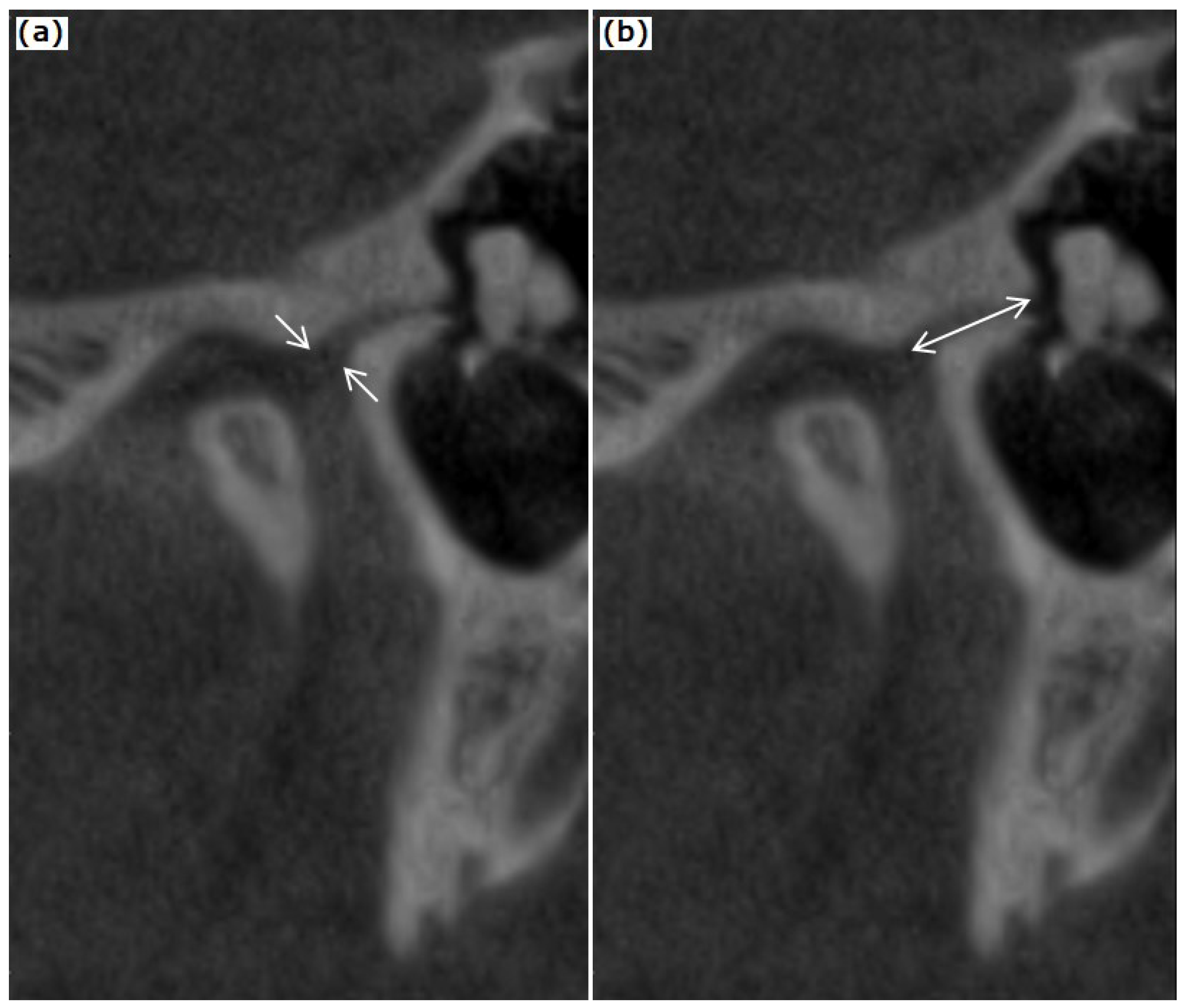
2.2. CBCT Examination of the TMJ and the Temporal Bone
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinto, O.F. A New Structure Related to the Temporomandibular Joint and Middle Ear. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1962, 12, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Sato, I. Anatomical Study of the Human Discomallear Ligament Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging and Morphological Observations. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 2011, 88, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ioannides, C.A.; Hoogland, G.A. The Disco-Malleolar Ligament: A Possible Cause of Subjective Hearing Loss in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 1983, 11, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakur, B.; Yaşa, Y. Correlation between Tinnitus and Petrotympanic Fissure Status Among Patients With Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakur, B.; Sümbüllü, M.A.; Durna, D.; Akgül, H.M. Prevalence of the Types of the Petrotympanic Fissure in the Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction. Acta Radiol. 2011, 52, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, H.S.; Kwak, H.H.; Shim, K.S.; Hu, K.S.; Park, H.D.; Park, H.W.; Chung, I.H. The Discomallear Ligament and the Anterior Ligament of Malleus: An Anatomic Study in Human Adults and Fetuses. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2004, 26, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughner, B.A.; Larkin, L.H.; Mahan, P.E. Discomalleolar and Anterior Malleolar Ligaments: Possible Causes of Middle Ear Damage during Temporomandibular Joint Surgery. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1989, 68, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowicki, T.; Zakrzewska, J. A Study of the Discomalleolar Ligament in the Adult Human. Folia Morphol. 2006, 65, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Sencimen, M.; Yalçin, B.; Doğan, N.; Varol, A.; Okçu, K.M.; Ozan, H.; Aydintuğ, Y.S. Anatomical and Functional Aspects of Ligaments between the Malleus and the Temporomandibular Joint. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencimen, M.; Varol, A.; Baykal, B.; Altug, H.A.; Dogan, N.; Sahin, S.; Okcu, K.M.; Yalcin, B. Histological Characteristics of Ligaments between Middle Ear and Temporomandibular Joint. Eur. J. Dent. 2009, 3, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ogütcen-Toller, M.; Juniper, R.P. The Embryologic Development of the Human Lateral Pterygoid Muscle and Its Relationships with the Temporomandibular Joint Disc and Meckel’s Cartilage. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1993, 51, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulou, S.; Venieratos, D.; Antonopoulou, M. Temporomandibular Joint and Correlated Fissures: Anatomical and Clinical Consideration. CRANIO® 2008, 26, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, I.; Arai, H.; Asaumi, R.; Imura, K.; Kawai, T.; Yosue, T. Classifications of Tunnel-like Structure of Human Petrotympanic Fissure by Cone Beam CT. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2008, 30, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedesiu, M.; Marcu, M.; Salmon, B.; Pauwels, R.; Oenning, A.C.; Almasan, O.; Roman, R.; Baciut, M.; Jacobs, R. Irradiation Provided by Dental Radiological Procedures in a Pediatric Population. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 103, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, S.F.; LeResche, L. Research Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders: Review, Criteria, Examinations and Specifications, Critique. J. Craniomandib. Disord. 1992, 6, 301–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orhan, K.; Nishiyama, H.; Tadashi, S.; Murakami, S.; Furukawa, S. Comparison of Altered Signal Intensity, Position, and Morphology of the TMJ Disc in MR Images Corrected for Variations in Surface Coil Sensitivity. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2006, 101, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almăşan, O.C.; Hedeşiu, M.; Băciuţ, G.; Leucuţa, D.C.; Băciuţ, M. Disk and Joint Morphology Variations on Coronal and Sagittal MRI in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Matthias, G.; Jim, L.; Ian, S. Irr: Various Coefficients of Interrater Reliability and Agreement. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/irr/index.html (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- Gorurgoz, C.; Orhan, K.; Sinanoglu, E.A.; Avsever, I.H. Evaluation of Mallear Ligaments in Different Voxel Resolutions Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2019, 48, 20180125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emshoff, R.; Bertram, A.; Hupp, L.; Rudisch, A. A Logistic Analysis Prediction Model of TMJ Condylar Erosion in Patients with TMJ Arthralgia. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emshoff, R.; Bertram, A.; Hupp, L.; Rudisch, A. Condylar Erosion Is Predictive of Painful Closed Lock of the Temporomandibular Joint: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Head Face Med. 2021, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, M.R.; Rizzo, G.; Nicita, F.; Bramanti, A.; Milardi, D.; Macchi, V.; Brunetto, D.; Cascone, P.; Arco, A.; Nicita, A.; et al. Microscopic Reconstruction and Immunohistochemical Analysis of Discomalleolar Ligament. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvall, N.K.; Gunan, E.; Genitsaridi, E.; Lazar, A.; Mehraei, G.; Billing, M.; Tullberg, M.; Bulla, J.; Whitton, J.; Canlon, B.; et al. Impact of Temporomandibular Joint Complaints on Tinnitus-Related Distress. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algieri, G.M.A.; Leonardi, A.; Arangio, P.; Vellone, V.; Paolo, C.D.; Cascone, P. Tinnitus in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: Is It a Specific Somatosensory Tinnitus Subtype? Int. Tinnitus J. 2016, 20, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhy, O.A.; Koutb, A.R.; Abdel-Baki, F.A.; Ali, T.M.; El Raffa, I.Z.; Khater, A.H. Evaluation of Aural Manifestations in Temporo-Mandibular Joint Dysfunction. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2004, 29, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijak, E.; Szczepek, A.J.; Margielewicz, J. Association between Anatomical Features of Petrotympanic Fissure and Tinnitus in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Disorder Using CBCT Imaging: An Exploratory Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 1202751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, Ó.; Rojas, S.; Ortega, M.; Solano, A.; Rodríguez-Baeza, A. Evaluation of the Human Petrotympanic Fissure Using Anatomized Cadaveric Specimens and Multi-Detector CT Imaging. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2020, 42, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runci Anastasi, M.; Macchi, V.; Vellone, V.; Nastro Siniscalchi, E.; Anastasi, G.; Morra, A.; Porzionato, A.; De Caro, R.; De Ponte, F.S.; Cascone, P. The Discomallear Ligament: Anatomical, Microscopical, and Radiologic Analysis. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2020, 42, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Aristeguieta, L.M.; Ballesteros Acuña, L.E.; Sandoval Ortiz, G.P. A Direct Anatomical Study of the Morphology and Functionality of Disco-Malleolar and Anterior Malleolar Ligaments. Int. J. Morphol. 2009, 27, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disc Position | PTF Type 1 (n = 23) | PTF Type 2 (n = 14) | PTF Type 3 (n = 21) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDR, n (%) | 10 (43.48) | 7 (50) | 8 (38.1) | 0.56 |
| DDwR, n (%) | 7 (30.43) | 3 (21.43) | 3 (14.29) | |
| Normal, n (%) | 6 (26.09) | 4 (28.57) | 10 (47.62) |
| Characteristics | PTF Type 1 (n = 23) | PTF Type 2 (n = 14) | PTF Type 3 (n = 21) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTF characteristics | ||||
| PTF diameter (mm), median (IQR) | 1.5 (1.25–1.77) | 1.12 (0.86–2.09) | 1.4 (1.1–2.3) | 0.484 |
| PTF length (mm), median (IQR) | 3.90 (3.35–4.50) | 3.65 (3.35–4.21) | 4.35 (3.35–4.70) | 0.483 |
| Malleus position | ||||
| Malleus to tegmen tympani distance (mm), median (IQR) | 2.60 (1.73–3.12) | 2.35 (1.95–2.94) | 2.55 (2.05–3.25) | 0.708 |
| Malleus to PTF distance (mm), median (IQR) | 2.75 (2.22–3.45) | 2.65 (2.09–2.75) | 2.4 (2.05–2.9) | 0.249 |
| MRI Disc Position | DDR (n = 25) | DDwR (n = 13) | Normal (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTF characteristics | ||||
| PTF diameter (mm), median (IQR) | 3.94 (0.76) | 3.88 (0.91) | 3.94 (0.97) | 0.977 |
| PTF length (mm), median (IQR) | 4.00 (3.35–4.50) | 4.10 (3.35–4.70) | 3.85 (3.34–4.50) | 0.993 |
| Malleus position | ||||
| Malleus to tegmen tympani distance (mm), median (IQR) | 2.40 (1.75–3.00) | 2.60 (1.90–2.95) | 2.42 (1.90–3.15) | 0.969 |
| Malleus to PTF distance (mm), median (IQR) | 2.75 (2.15–3.1) | 2.4 (2.1–3) | 2.52 (2.16–2.92) | 0.519 |
| Disc Shape | Folded (n = 6) | Lengthened (n = 16) | Thickened Posterior Band (n = 20) | Normal (n = 16) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTF diameter (mm), median (IQR) | 1.32 (1.14–1.48) | 1.25 (1.14–1.64) | 1.40 (0.90–1.92) | 1.68 (1.24–2.06) | 0.424 |
| PTF length (mm), median (IQR) | 3.60 (3.31–4.22) | 3.45 (3.00–4.50) | 4.15 (3.44–4.53) | 4.10 (3.50–4.74) | 0.487 |
| Malleus to tegmen tympani distance (mm), median (IQR) | 2.7 (1.95–3.19) | 2.67 (2.18–3.21) | 2.3 (1.86–2.95) | 2.3 (1.87–2.96) | 0.624 |
| Malleus to PTF distance (mm), median (IQR) | 2.85 (2.1–3.56) | 2.55 (2.11–3.29) | 2.65 (2.09–3.1) | 2.4 (2.19–2.75) | 0.891 |
| Condylar Changes | DDR (n = 25) | DDwR (n = 13) | Normal (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone cysts, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0.569 |
| Erosive changes, n (%) | 6 (24) | 8 (61.54) | 3 (15) | 0.012 |
| Condylar osteosclerosis, n (%) | 6 (24) | 5 (38.46) | 3 (15) | 0.33 |
| Condylar osteophytes, n (%) | 6 (24) | 9 (69.23) | 7 (35) | 0.023 |
| Condyle shape changes, n (%) | 9 (36) | 8 (61.54) | 10 (50) | 0.303 |
| Normal condyle, n (%) | 14 (56) | 3 (23.08) | 6 (30) | 0.08 |
| Characteristics | PTF Diameter (mm) | PTF Length (mm) | Malleus to Tegmen Tympani Distance (mm) | Malleus to PTF Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone cysts | ||||
| no (n = 57) | 1.40 (1.15–1.95) | 4.00 (3.35–4.50) | 2.50 (1.90–3.10) | 2.55 (2.15–3.10) |
| yes (n = 1) | 0.80 (0.80–0.80) | 1.80 (1.80–1.80) | 2.05 (2.05–2.05) | 1.50 (1.50–1.50) |
| p-value | 0.12 | 0.088 | 0.57 | 0.12 |
| Erosive changes | ||||
| no (n = 41) | 1.50 (1.20–1.95) | 3.95 (3.35–4.50) | 2.55 (1.90–3.25) | 2.75 (2.25–3.15) |
| yes (n = 17) | 1.25 (1.10–1.95) | 4.00 (3.00–4.70) | 2.50 (2.00–2.90) | 2.15 (1.85–2.75) |
| p-value | 0.338 | 0.584 | 0.351 | 0.029 |
| Condyle shape changes | ||||
| no (n = 31) | 1.55 (1.15–2.05) | 3.95 (3.40–4.50) | 2.60 (1.90–3.25) | 2.75 (2.30–3.00) |
| yes (n = 27) | 1.35 (1.12–1.73) | 4.00 (3.17–4.65) | 2.30 (1.90–2.95) | 2.40 (1.92–3.12) |
| p-value | 0.31 | 0.749 | 0.382 | 0.221 |
| Condylar osteosclerosis | ||||
| no (n = 44) | 1.30 (1.05–1.91) | 3.83 (3.34–4.41) | 2.52 (1.90–3.25) | 2.60 (2.15–3.11) |
| yes (n = 14) | 1.68 (1.40–1.99) | 4.65 (3.51–4.91) | 2.40 (1.52–2.94) | 2.42 (2.10–2.94) |
| p-value | 0.113 | 0.055 | 0.331 | 0.501 |
| Condylar osteophytes | ||||
| no (n = 36) | 1.40 (0.90–1.83) | 3.67 (3.34–4.28) | 2.50 (1.87–3.35) | 2.75 (2.33–3.32) |
| yes (n = 22) | 1.55 (1.17–2.02) | 4.45 (3.50–4.77) | 2.50 (1.90–2.86) | 2.25 (1.91–2.75) |
| p-value | 0.208 | 0.039 | 0.199 | 0.015 |
| Nomal condyle | ||||
| no (n = 35) | 1.40 (1.15–1.95) | 4.05 (3.33–4.72) | 2.30 (1.90–2.92) | 2.50 (2.00–3.00) |
| yes (n = 23) | 1.40 (0.90–1.97) | 3.90 (3.42–4.30) | 2.90 (1.85–3.35) | 2.75 (2.30–3.20) |
| p-value | 0.644 | 0.622 | 0.184 | 0.169 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almășan, O.; Leucuța, D.-C.; Dinu, C.; Buduru, S.; Băciuț, M.; Hedeșiu, M. Petrotympanic Fissure Architecture and Malleus Location in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. Tomography 2022, 8, 2460-2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050204
Almășan O, Leucuța D-C, Dinu C, Buduru S, Băciuț M, Hedeșiu M. Petrotympanic Fissure Architecture and Malleus Location in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. Tomography. 2022; 8(5):2460-2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050204
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmășan, Oana, Daniel-Corneliu Leucuța, Cristian Dinu, Smaranda Buduru, Mihaela Băciuț, and Mihaela Hedeșiu. 2022. "Petrotympanic Fissure Architecture and Malleus Location in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders" Tomography 8, no. 5: 2460-2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050204
APA StyleAlmășan, O., Leucuța, D.-C., Dinu, C., Buduru, S., Băciuț, M., & Hedeșiu, M. (2022). Petrotympanic Fissure Architecture and Malleus Location in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. Tomography, 8(5), 2460-2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050204








