AI Denoising Improves Image Quality and Radiological Workflows in Pediatric Ultra-Low-Dose Thorax Computed Tomography Scans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
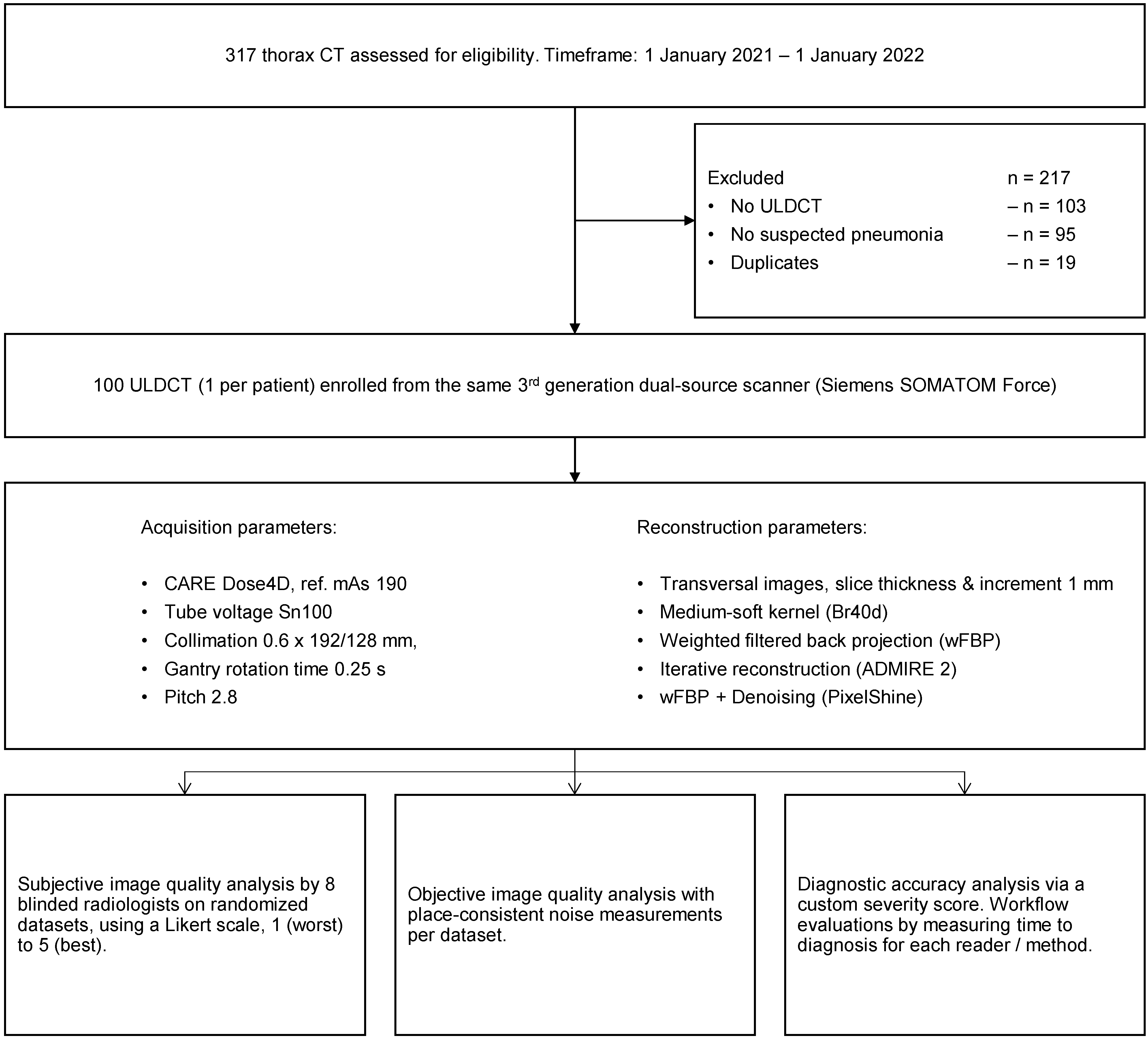
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Population, and Radiation Dose
2.2. Image Acquisition and Reconstruction Parameters
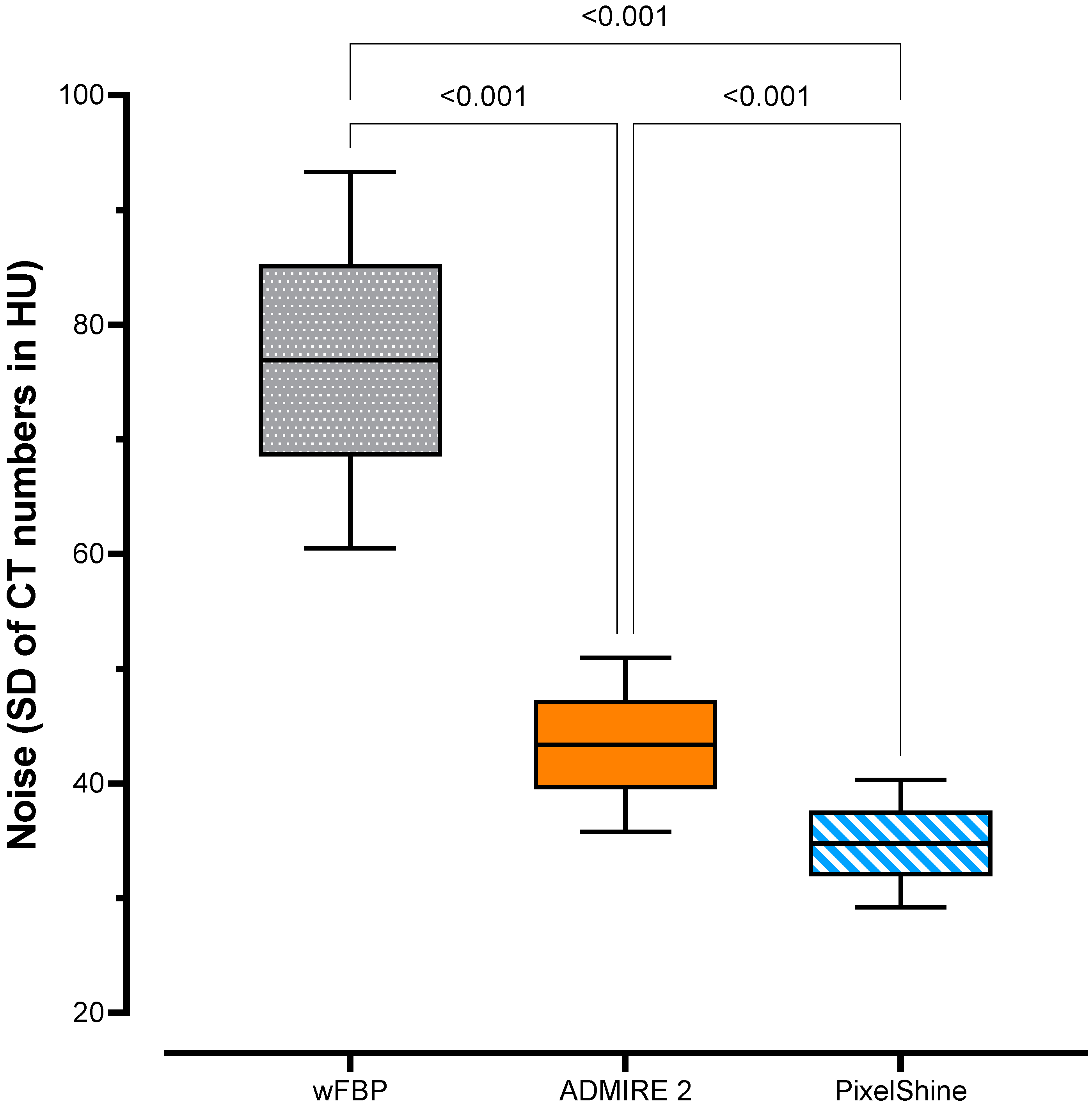
2.3. Objective Image Quality
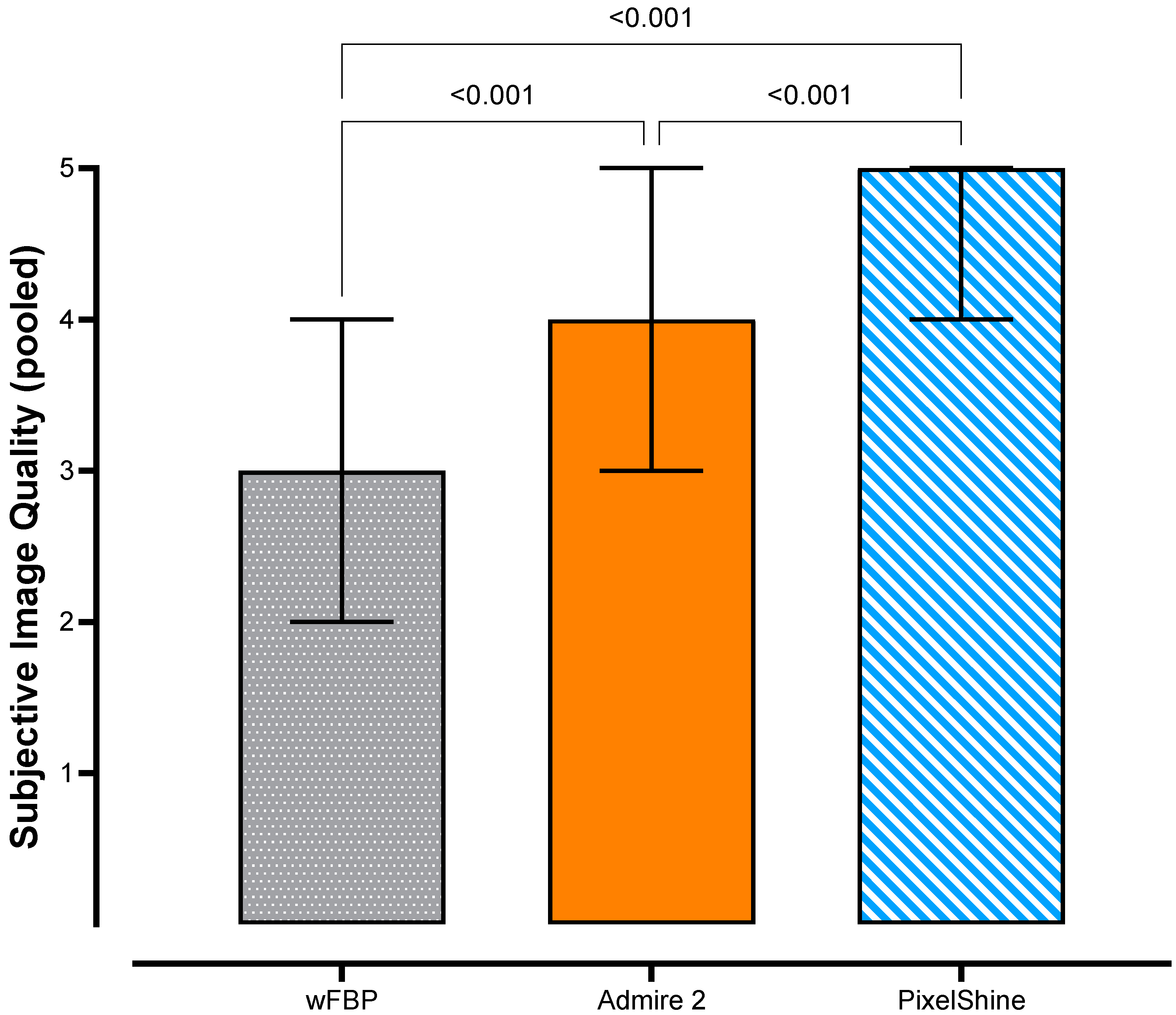
2.4. Subjective Image Quality
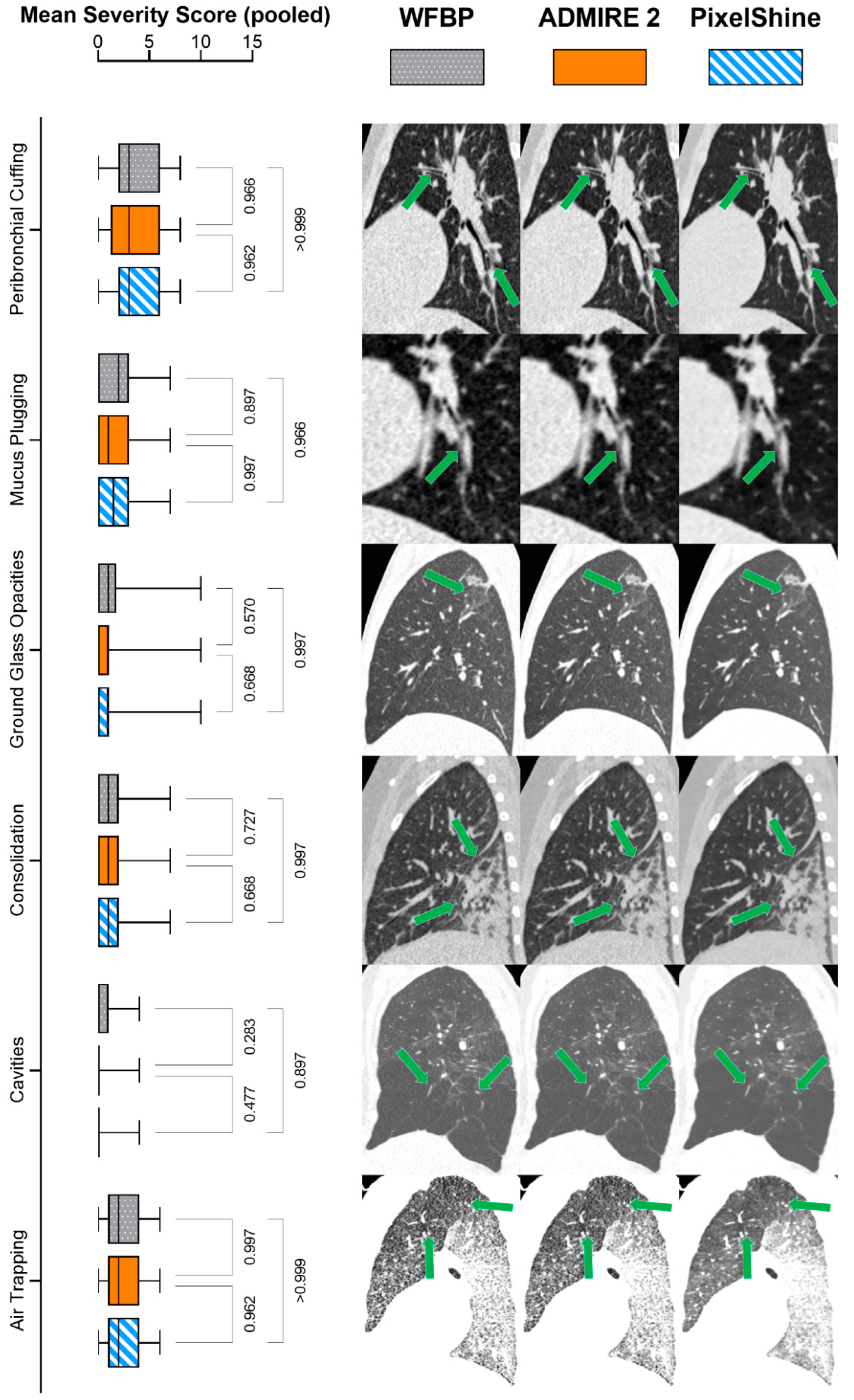
2.5. Diagnostic Accuracy
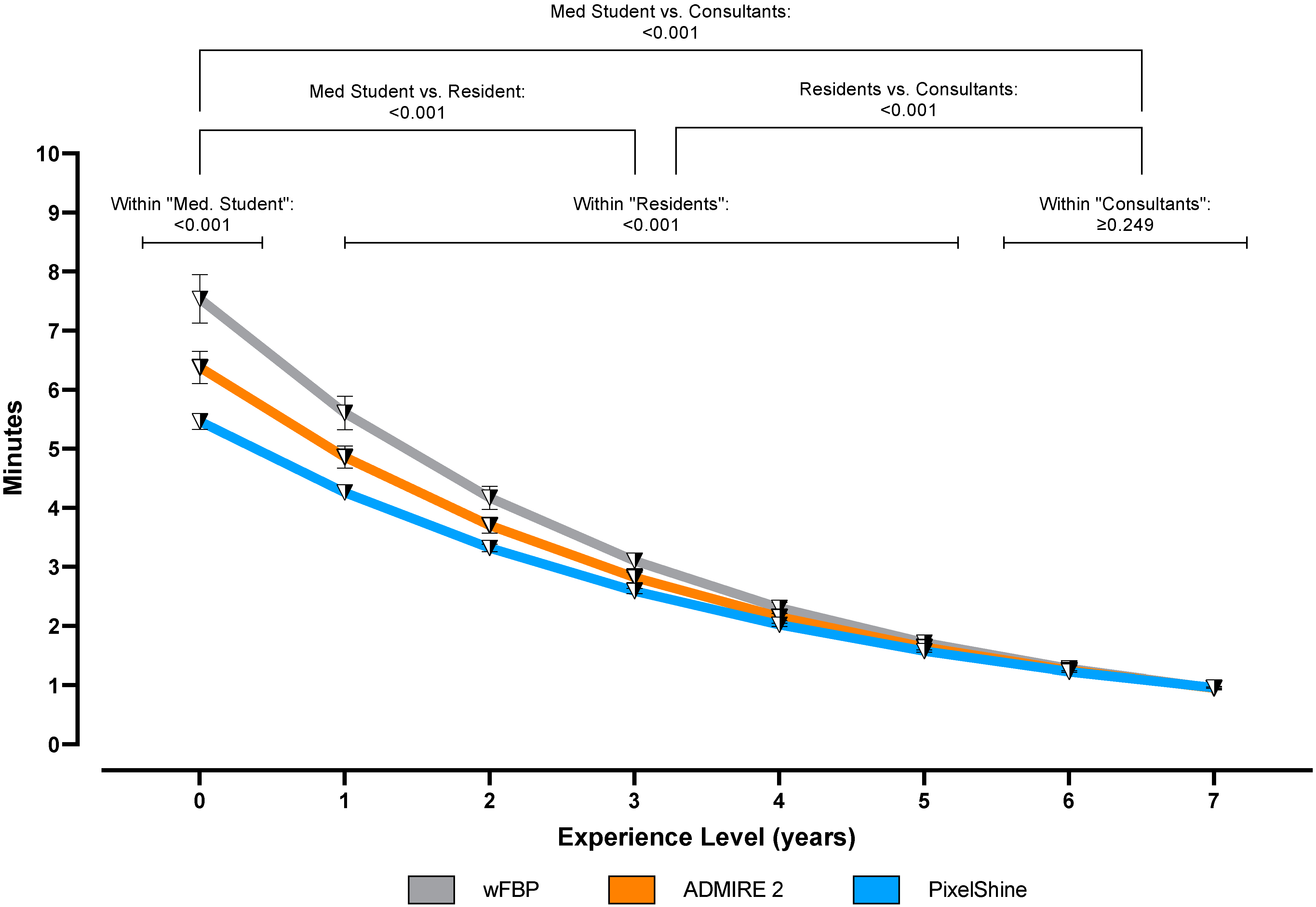
2.6. Time to Diagnosis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. Objective Image Quality
3.3. Subjective Image Quality
3.4. Diagnostic Accuracy
3.5. Time to Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, W.; Li, J.; Zou, N.; Guan, W.; Pan, J.; Xu, W. Clinical features of pediatric patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, A.; Nozaki, T.; Makidono, A.; Okabe, T.; Morita, Y.; Fujita, K.; Matsusako, M.; Kono, T.; Kurihara, Y.; Hasegawa, D.; et al. Pediatric oncologic emergencies: Clinical and imaging review for pediatricians. Pediatrics Int. 2019, 61, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goralski, J.L.; Stewart, N.J.; Woods, J.C. Novel imaging techniques for cystic fibrosis lung disease. Pediatric Pulmonol. 2021, 56, S40–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.; Carroll, W.D.; Cunningham, P.; Ho, S.-A.; Jones, M.; Lenney, W.; Thompson, D.; Gilchrist, F.J. Radiation dose from common radiological investigations and cumulative exposure in children with cystic fibrosis: An observational study from a single UK centre. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zondervan, R.L.; Hahn, P.F.; Sadow, C.A.; Liu, B.; Lee, S.I. Frequent body CT scanning of young adults: Indications, outcomes, and risk for radiation-induced cancer. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2011, 8, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.S.; Salotti, J.A.; Little, M.P.; McHugh, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.P.; Howe, N.L.; Ronckers, C.M.; Rajaraman, P.; Craft, A.W. Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordic, S.; Morsbach, F.; Schmidt, B.; Allmendinger, T.; Flohr, T.; Husarik, D.; Baumueller, S.; Raupach, R.; Stolzmann, P.; Leschka, S.; et al. Ultralow-Dose Chest Computed Tomography for Pulmonary Nodule Detection: First Performance Evaluation of Single Energy Scanning With Spectral Shaping. Investig. Radiol. 2014, 49, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haubenreisser, H.; Meyer, M.; Sudarski, S.; Allmendinger, T.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Henzler, T. Unenhanced third-generation dual-source chest CT using a tin filter for spectral shaping at 100 kVp. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelle, B.; Fischbach, C.; Booz, C.; Yel, I.; Frellesen, C.; Kaup, M.; Beeres, M.; Vogl, T.J.; Scholtz, J.-E. Single-energy pediatric chest computed tomography with spectral filtration at 100 kVp: Effects on radiation parameters and image quality. Pediatric Radiol. 2017, 47, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, F.M.; Johnson, T.R.C.; Sommer, W.H.; Thierfelder, K.M.; Meinel, F.G. Chest CT using spectral filtration: Radiation dose, image quality, and spectrum of clinical utility. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendlin, A.S.; Plajer, D.; Chaika, M.; Wrazidlo, R.; Estler, A.; Tsiflikas, I.; Artzner, C.P.; Afat, S.; Bongers, M.N. AI Denoising Significantly Improves Image Quality in Whole-Body Low-Dose Computed Tomography Staging. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwakar, M.; Kumar, M. A review on CT image noise and its denoising. Biomed. Signal Processing Control 2018, 42, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, P.; Mileto, A.; Yu, L.; Leng, S.; Guimaraes, L.S.; Missert, A.D.; Jensen, C.T.; Gong, H.; McCollough, C.H.; Fletcher, J.G. CT Noise-Reduction Methods for Lower-Dose Scanning: Strengths and Weaknesses of Iterative Reconstruction Algorithms and New Techniques. RadioGraphics 2021, 41, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G* Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boone, J.; Strauss, K.; Cody, D.; McCollough, C.; McNitt-Gray, M.; Toth, T.; Goske, M.; Frush, D. AAPM Report n. 204: Size-Specific Dose Estimates (SSDE) in Pediatric and Adult Body CT Examinations; The Report of AAPM Task Group: College Park, MD, USA, 2011; Volume 204. [Google Scholar]
- McCollough, C.; Bakalyar, D.M.; Bostani, M.; Brady, S.; Boedeker, K.; Boone, J.M.; Chen-Mayer, H.H.; Christianson, O.I.; Leng, S.; Li, B. Use of water equivalent diameter for calculating patient size and size-specific dose estimates (SSDE) in CT: The report of AAPM task group 220. AAPM Rep. 2014, 2014, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bongartz, G.; Golding, S.J.; Jurik, A.G.; Leonardi, M.; van Meerten, E.v.P.; Geleijns, J.; Jessen, K.A.; Panzer, W.; Shrimpton, P.C.; Tosi, G.; et al. European Guidelines on Quality Criteria for Computed Tomography; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Suntharalingam, S.; Mikat, C.; Wetter, A.; Guberina, N.; Salem, A.; Heil, P.; Forsting, M.; Nassenstein, K. Whole-body ultra-low dose CT using spectral shaping for detection of osteolytic lesion in multiple myeloma. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2273–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzl, M.; May, M.S.; Weinmann, D.; Hammon, M.; Treutlein, C.; Zeilinger, M.; Kiefer, A.; Trollmann, R.; Woelfle, J.; Uder, M.; et al. Dual-source computed tomography of the lung with spectral shaping and advanced iterative reconstruction: Potential for maximum radiation dose reduction. Pediatric Radiol. 2020, 50, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Storz, C.; Kim, J.H.; Weiss, J.; Afat, S.; Nikolaou, K.; Bamberg, F.; Othman, A.E. Effect of a novel denoising technique on image quality and diagnostic accuracy in low-dose CT in patients with suspected appendicitis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Leng, S. Use of artificial intelligence in computed tomography dose optimisation. Ann. ICRP 2020, 49, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yan, P.; Kalra, M.K.; Wang, G. CT image denoising with perceptive deep neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.07019. [Google Scholar]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Lacson, R.; Khorasani, R. Workflow Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Radiology and an Overview of Available Tools. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 17, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikici, E.; Bigelow, M.; Prevedello, L.; White, R.; Erdal, B. Integrating AI into radiology workflow: Levels of research, production, and feedback maturity. J. Med. Imaging 2020, 7, 016502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Rating | Spearman Correlation Coefficient | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | ||||||||||
| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Reader 3 | Reader 4 | Reader 5 | Reader 6 | Reader 7 | Reader 8 | |||
| wFBP | Reader 1 | 3 (2–3) | 1.000 | 0.843 | 0.975 | 0.834 | 0.962 | 0.823 | 0.953 | 0.813 |
| Reader 2 | 3 (2–4) | 0.843 | 1.000 | 0.814 | 0.991 | 0.803 | 0.980 | 0.794 | 0.970 | |
| Reader 3 | 3 (2–4) | 0.975 | 0.814 | 1.000 | 0.805 | 0.988 | 0.794 | 0.979 | 0.784 | |
| Reader 4 | 3 (2–4) | 0.834 | 0.991 | 0.805 | 1.000 | 0.793 | 0.989 | 0.785 | 0.979 | |
| Reader 5 | 3 (2–4) | 0.962 | 0.803 | 0.988 | 0.793 | 1.000 | 0.782 | 0.991 | 0.772 | |
| Reader 6 | 3 (2–4) | 0.823 | 0.980 | 0.794 | 0.989 | 0.782 | 1.000 | 0.774 | 0.990 | |
| Reader 7 | 3 (2–4) | 0.953 | 0.794 | 0.979 | 0.785 | 0.991 | 0.774 | 1.000 | 0.764 | |
| Reader 8 | 3 (2–4) | 0.813 | 0.970 | 0.784 | 0.979 | 0.772 | 0.990 | 0.764 | 1.000 | |
| ADMIRE 2 | Reader 1 | 4 (3–5) | 1.000 | 0.970 | 0.944 | 0.933 | 0.922 | 0.917 | 0.912 | 0.908 |
| Reader 2 | 4 (3–5) | 0.970 | 1.000 | 0.971 | 0.957 | 0.945 | 0.939 | 0.933 | 0.928 | |
| Reader 3 | 4 (3–5) | 0.944 | 0.971 | 1.000 | 0.985 | 0.971 | 0.964 | 0.957 | 0.951 | |
| Reader 4 | 4 (3–5) | 0.933 | 0.957 | 0.985 | 1.000 | 0.985 | 0.978 | 0.971 | 0.964 | |
| Reader 5 | 4 (3–5) | 0.922 | 0.945 | 0.971 | 0.985 | 1.000 | 0.992 | 0.985 | 0.978 | |
| Reader 6 | 4 (3–5) | 0.917 | 0.939 | 0.964 | 0.978 | 0.992 | 1.000 | 0.992 | 0.985 | |
| Reader 7 | 4 (3–5) | 0.912 | 0.933 | 0.957 | 0.971 | 0.985 | 0.992 | 1.000 | 0.992 | |
| Reader 8 | 4 (3–5) | 0.908 | 0.928 | 0.951 | 0.964 | 0.978 | 0.985 | 0.992 | 1.000 | |
| PixelShine | Reader 1 | 5 (4–5) | 1.000 | 0.921 | 0.882 | 0.845 | 0.826 | 0.808 | 0.808 | 0.790 |
| Reader 2 | 5 (4–5) | 0.921 | 1.000 | 0.958 | 0.918 | 0.898 | 0.878 | 0.878 | 0.858 | |
| Reader 3 | 5 (4–5) | 0.882 | 0.958 | 1.000 | 0.958 | 0.937 | 0.916 | 0.916 | 0.895 | |
| Reader 4 | 5 (4–5) | 0.845 | 0.918 | 0.958 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.956 | 0.956 | 0.935 | |
| Reader 5 | 5 (4–5) | 0.826 | 0.898 | 0.937 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.978 | 0.956 | |
| Reader 6 | 5 (4–5) | 0.808 | 0.878 | 0.916 | 0.956 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.977 | |
| Reader 7 | 5 (4–5) | 0.808 | 0.878 | 0.916 | 0.956 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.977 | |
| Reader 8 | 5 (4–5) | 0.790 | 0.858 | 0.895 | 0.935 | 0.956 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 1.000 | |
| Severity Score | Spearman Correlation Coefficient | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mean ± SD) | ||||||||||
| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Reader 3 | Reader 4 | Reader 5 | Reader 6 | Reader 7 | Reader 8 | |||
| wFBP | Reader 1 | 11.90 ± 6.72 | 1.000 | 0.990 | 0.979 | 0.970 | 0.764 | 0.772 | 0.813 | 0.784 |
| Reader 2 | 11.70 ± 6.72 | 0.990 | 1.000 | 0.989 | 0.980 | 0.774 | 0.782 | 0.823 | 0.794 | |
| Reader 3 | 11.60 ± 6.83 | 0.979 | 0.989 | 1.000 | 0.991 | 0.785 | 0.793 | 0.834 | 0.805 | |
| Reader 4 | 11.50 ± 6.86 | 0.970 | 0.980 | 0.991 | 1.000 | 0.794 | 0.803 | 0.843 | 0.814 | |
| Reader 5 | 9.35 ± 5.92 | 0.764 | 0.774 | 0.785 | 0.794 | 1.000 | 0.991 | 0.953 | 0.979 | |
| Reader 6 | 9.15 ± 5.84 | 0.772 | 0.782 | 0.793 | 0.803 | 0.991 | 1.000 | 0.962 | 0.988 | |
| Reader 7 | 9.03 ± 5.88 | 0.813 | 0.823 | 0.834 | 0.843 | 0.953 | 0.962 | 1.000 | 0.975 | |
| Reader 8 | 9.03 ± 5.81 | 0.784 | 0.794 | 0.805 | 0.814 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.975 | 1.000 | |
| ADMIRE 2 | Reader 1 | 11.60 ± 6.72 | 1.000 | 0.996 | 0.993 | 0.989 | 0.782 | 0.778 | 0.783 | 0.777 |
| Reader 2 | 11.50 ± 6.76 | 0.996 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.994 | 0.784 | 0.779 | 0.785 | 0.780 | |
| Reader 3 | 11.40 ± 6.76 | 0.993 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.790 | 0.787 | 0.794 | 0.786 | |
| Reader 4 | 11.30 ± 6.71 | 0.989 | 0.994 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 0.797 | 0.795 | 0.802 | 0.794 | |
| Reader 5 | 9.17 ± 5.7 | 0.782 | 0.784 | 0.790 | 0.797 | 1.000 | 0.996 | 0.985 | 0.989 | |
| Reader 6 | 9.12 ± 5.78 | 0.778 | 0.779 | 0.787 | 0.795 | 0.996 | 1.000 | 0.986 | 0.991 | |
| Reader 7 | 9.00 ± 5.85 | 0.783 | 0.785 | 0.794 | 0.802 | 0.985 | 0.986 | 1.000 | 0.990 | |
| Reader 8 | 9.02 ± 5.81 | 0.777 | 0.780 | 0.786 | 0.794 | 0.989 | 0.991 | 0.990 | 1.000 | |
| PixelShine | Reader 1 | 11.20 ± 6.45 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.996 | 0.996 | 0.830 | 0.831 | 0.861 | 0.826 |
| Reader 2 | 11.10 ± 6.49 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.831 | 0.832 | 0.864 | 0.827 | |
| Reader 3 | 11.00 ± 6.43 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.845 | 0.845 | 0.878 | 0.840 | |
| Reader 4 | 11.00 ± 6.45 | 0.996 | 0.996 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.846 | 0.846 | 0.879 | 0.841 | |
| Reader 5 | 9.26 ± 5.93 | 0.830 | 0.831 | 0.845 | 0.846 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 0.989 | 0.998 | |
| Reader 6 | 9.23 ± 5.92 | 0.831 | 0.832 | 0.845 | 0.846 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.990 | 0.999 | |
| Reader 7 | 9.41 ± 5.93 | 0.861 | 0.864 | 0.878 | 0.879 | 0.989 | 0.990 | 1.000 | 0.988 | |
| Reader 8 | 9.18 ± 5.90 | 0.826 | 0.827 | 0.840 | 0.841 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.988 | 1.000 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brendlin, A.S.; Schmid, U.; Plajer, D.; Chaika, M.; Mader, M.; Wrazidlo, R.; Männlin, S.; Spogis, J.; Estler, A.; Esser, M.; et al. AI Denoising Improves Image Quality and Radiological Workflows in Pediatric Ultra-Low-Dose Thorax Computed Tomography Scans. Tomography 2022, 8, 1678-1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040140
Brendlin AS, Schmid U, Plajer D, Chaika M, Mader M, Wrazidlo R, Männlin S, Spogis J, Estler A, Esser M, et al. AI Denoising Improves Image Quality and Radiological Workflows in Pediatric Ultra-Low-Dose Thorax Computed Tomography Scans. Tomography. 2022; 8(4):1678-1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040140
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrendlin, Andreas S., Ulrich Schmid, David Plajer, Maryanna Chaika, Markus Mader, Robin Wrazidlo, Simon Männlin, Jakob Spogis, Arne Estler, Michael Esser, and et al. 2022. "AI Denoising Improves Image Quality and Radiological Workflows in Pediatric Ultra-Low-Dose Thorax Computed Tomography Scans" Tomography 8, no. 4: 1678-1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040140
APA StyleBrendlin, A. S., Schmid, U., Plajer, D., Chaika, M., Mader, M., Wrazidlo, R., Männlin, S., Spogis, J., Estler, A., Esser, M., Schäfer, J., Afat, S., & Tsiflikas, I. (2022). AI Denoising Improves Image Quality and Radiological Workflows in Pediatric Ultra-Low-Dose Thorax Computed Tomography Scans. Tomography, 8(4), 1678-1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040140








