AI Denoising Significantly Enhances Image Quality and Diagnostic Confidence in Interventional Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
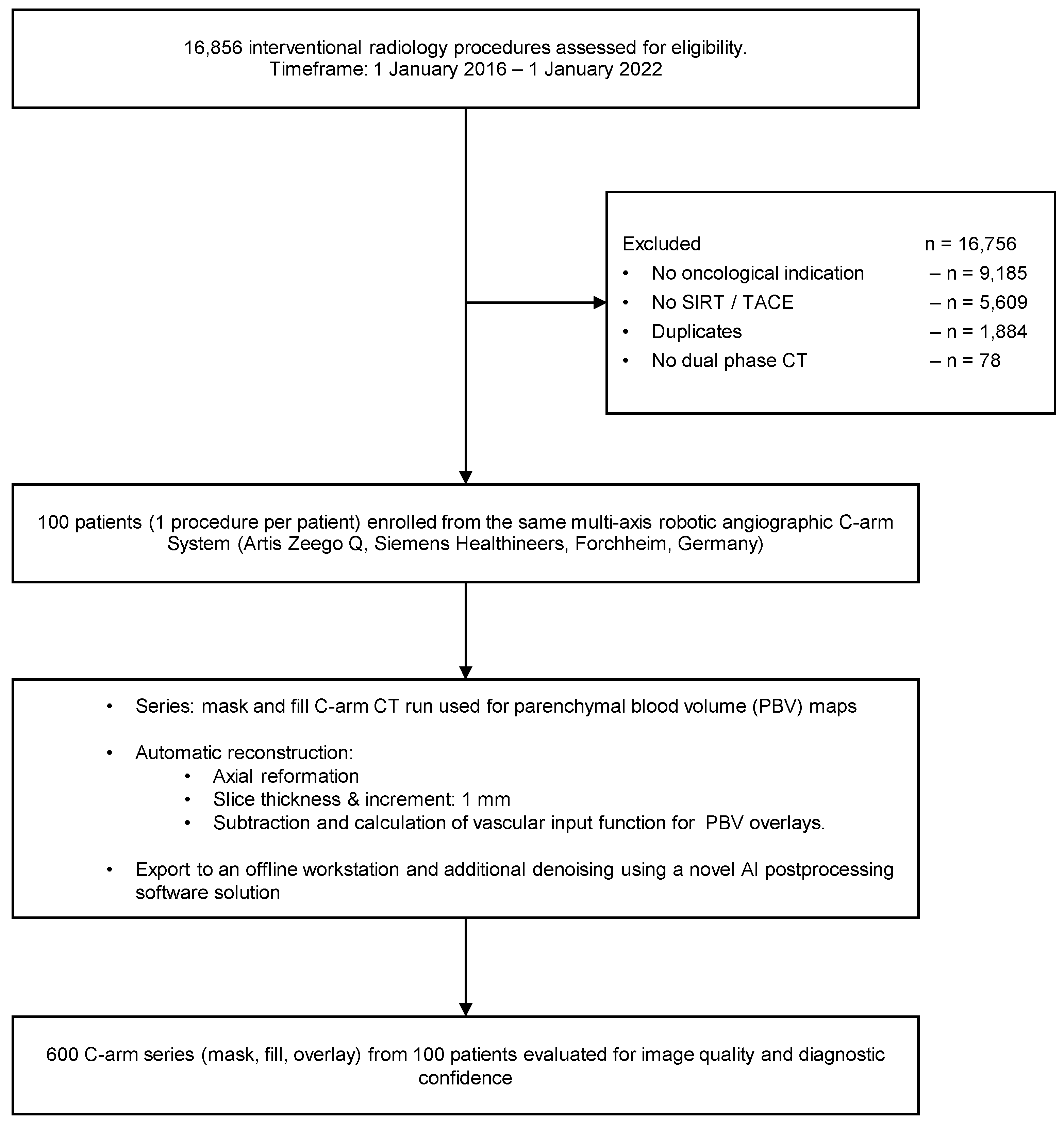
2.1. Study Population and Radiation Dose
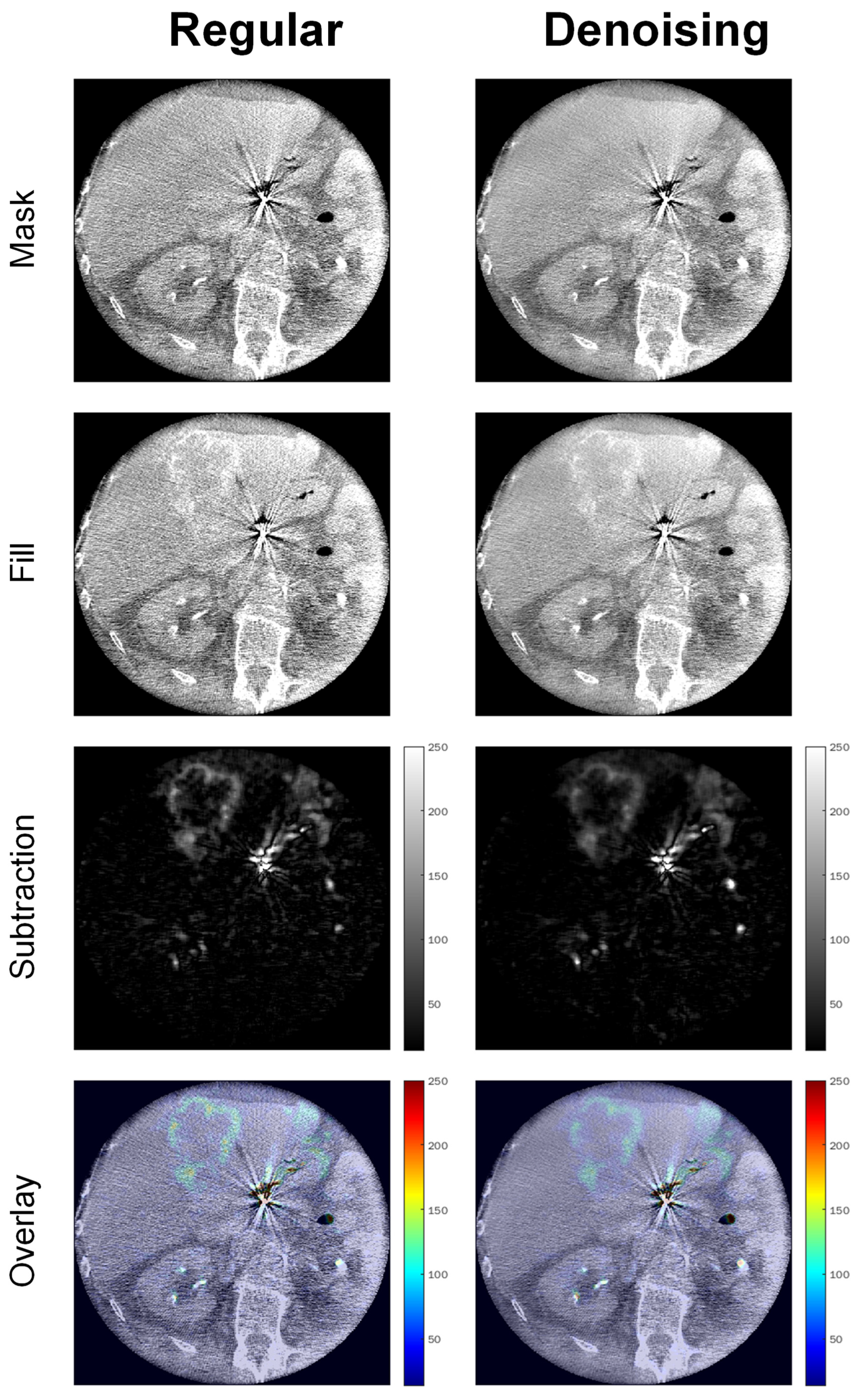
2.2. Image Acquisition, Reconstruction, and Postprocessing
2.3. Objective Image Quality
2.4. Diagnostic Confidence
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Radiation Dose
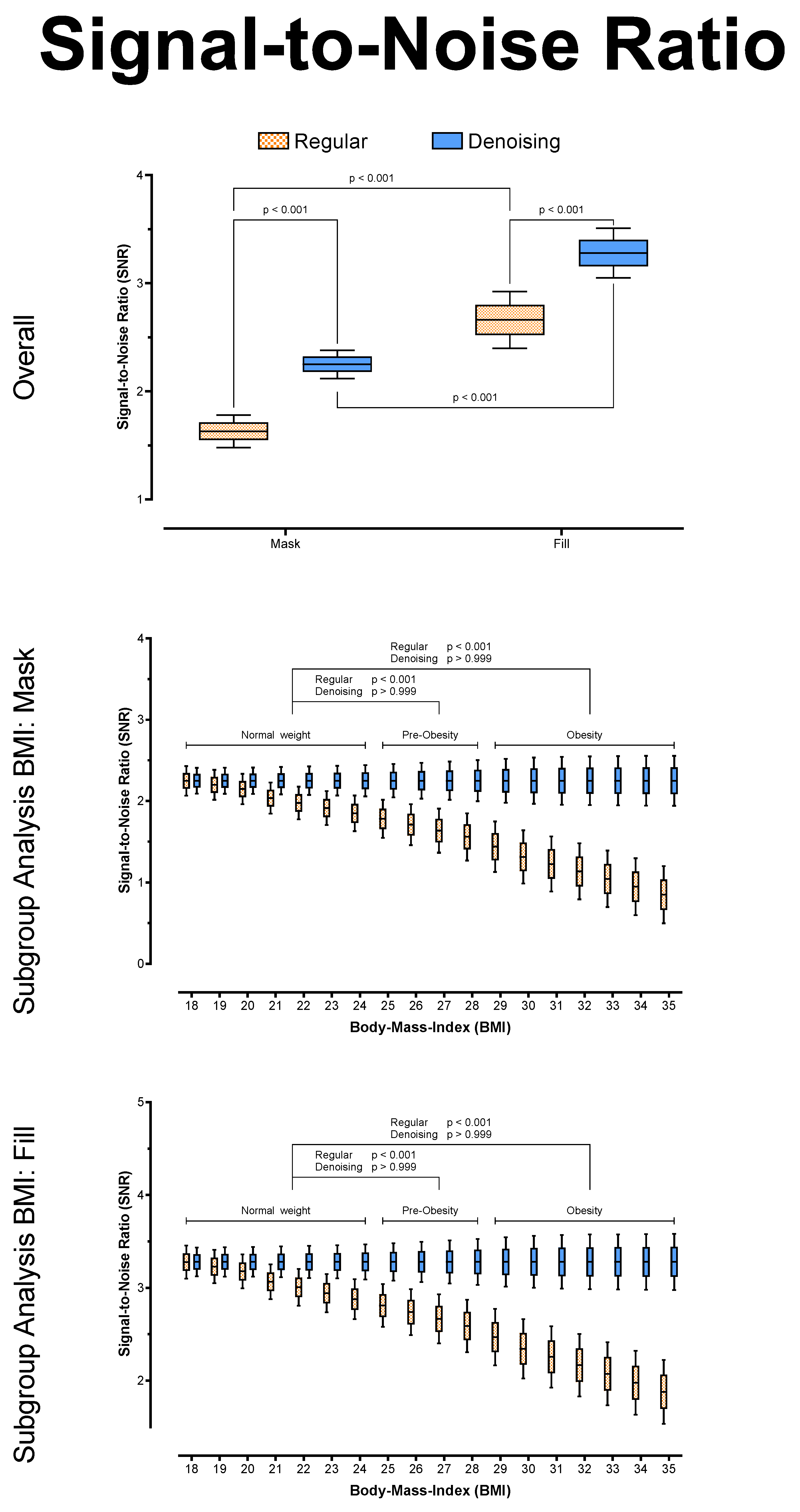
3.2. Objective Image Quality Analysis
3.3. Diagnostic Confidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bester, L.; Meteling, B.; Pocock, N.; Pavlakis, N.; Chua, T.C.; Saxena, A.; Morris, D.L. Radioembolization versus Standard Care of Hepatic Metastases: Comparative Retrospective Cohort Study of Survival Outcomes and Adverse Events in Salvage Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German Guideline Program in Oncology (German Cancer Society, G.C.A., AWMF). S3-Guideline Colorectal Cancer, Long Version 2.1, 2019, AWMF Registrationnumber: 021-007OL. Available online: https://www.leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Leitlinien/Kolorektales_Karzinom/Version_2/LL_KRK_Langversion_2.1.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2022).
- German Guideline Program in Oncology (German Cancer Society, G.C.A., AWMF). S3-Guideline Hepatocellular and Hepatobiliary Carcinoma, Long Version 2.0, 2021, AWMF Registrationnumber: 032/053OL. Available online: https://www.leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Leitlinien/HCC/Version_2/LL_HCC_bili%C3%A4re_Karzinome_Langversion_2.0.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2022).
- German Guideline Program in Oncology (German Cancer Society, G.C.A., AWMF). S3-Guideline Melanoma, Long Version 3.3, 2020, AWMF Registrationnumber: 032/024OL. Available online: https://www.leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Leitlinien/Melanom/Melanom_Version_3/LL_Melanom_Langversion_3.3.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2022).
- Pawlik, T.M.; Izzo, F.; Cohen, D.S.; Morris, J.S.; Curley, S.A. Combined Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation for Advanced Hepatic Malignancies: Results in 172 Patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 10, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, V.P.; Chee, K.G.; Petrelli, N.J. Modern multimodality approach to hepatic colorectal metastases: Solutions and controversies. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 16, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peisen, F.; Maurer, M.; Grosse, U.; Nikolaou, K.; Syha, R.; Artzner, C.; Bitzer, M.; Horger, M.; Grözinger, G. Intraprocedural cone-beam CT with parenchymal blood volume assessment for transarterial chemoembolization guidance: Impact on the effectiveness of the individual TACE sessions compared to DSA guidance alone. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 140, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissinger, M.; Vogel, J.; Kupferschläger, J.; Dittmann, H.; Castaneda Vega, S.G.; Grosse, U.; Artzner, C.; Nikolaou, K.; La Fougere, C.; Grözinger, G. Correlation of C-arm CT acquired parenchymal blood volume (PBV) with 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin (MAA) SPECT/CT for radioembolization work-up. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floridi, C.; Radaelli, A.; Abi-Jaoudeh, N.; Grass, M.; De Lin, M.; Chiaradia, M.; Geschwind, J.-F.; Kobeiter, H.; Squillaci, E.; Maleux, G.; et al. C-arm cone-beam computed tomography in interventional oncology: Technical aspects and clinical applications. La Radiol. Med. 2014, 119, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syha, R.; Grözinger, G.; Grosse, U.; Maurer, M.; Zender, L.; Horger, M.; Nikolaou, K.; Ketelsen, D. C-arm computed tomography parenchymal blood volume measurement in evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma before transarterial chemoembolization with drug eluting beads. Cancer Imaging 2015, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tacher, V.; Radaelli, A.; Lin, M.; Geschwind, J.-F. How I Do It: Cone-Beam CT during Transarterial Chemoembolization for Liver Cancer. Radiology 2015, 274, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppot, R.N. Technical challenges of imaging & image-guided interventions in obese patients. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, R.M.; Harder, D.; Amsler, F.; Voigt, J.; Fieselmann, A.; Falkowski, A.L.; Stieltjes, B.; Hirschmann, A. Initial Assessment of a Prototype 3D Cone-Beam Computed Tomography System for Imaging of the Lumbar Spine, Evaluating Human Cadaveric Specimens in the Upright Position. Investig. Radiol. 2018, 53, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, A.; Ishihara, T.; Thomas, M.A.; Pan, T. Noise reduction profile: A new method for evaluation of noise reduction techniques in CT. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwakar, M.; Kumar, M. A review on CT image noise and its denoising. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 42, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, P.; Mileto, A.; Yu, L.; Leng, S.; Guimaraes, L.S.; Missert, A.D.; Jensen, C.T.; Gong, H.; McCollough, C.H.; Fletcher, J.G. CT Noise-Reduction Methods for Lower-Dose Scanning: Strengths and Weaknesses of Iterative Reconstruction Algorithms and New Techniques. RadioGraphics 2021, 41, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yousefi, H.; Mirian, N.; De Lin, M.; Menard, D.; Gregory, M.; Aboian, M.; Boustani, A.; Chen, M.-K.; Saperstein, L.; et al. PET Image Denoising using a Deep-Learning Method for Extremely Obese Patients. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, K.; Boomen, M.v.d.; Eder, R.; Michelhaugh, S.A.; Spahillari, A.; Kim, J.; Parajuli, S.; Reese, T.G.; Mekkaoui, C.; Das, S.; et al. Accelerated in Vivo Cardiac Diffusion-Tensor MRI Using Residual Deep Learning–based Denoising in Participants with Obesity. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2021, 3, e200580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendlin, A.S.; Plajer, D.; Chaika, M.; Wrazidlo, R.; Estler, A.; Tsiflikas, I.; Artzner, C.P.; Afat, S.; Bongers, M.N. AI Denoising Significantly Improves Image Quality in Whole-Body Low-Dose Computed Tomography Staging. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G* Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fryar, C.D.; Gu, Q.; Ogden, C.L.; Flegal, K.M. Anthropometric Reference Data for Children and Adults: United States, 2011–2014; Vital Health Stat 3; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2016; Volume 39, pp. 1–46. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/40572 (accessed on 19 February 2022).
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, O.; Ward, E.; Ryan, A.; Colin, W.; Snow, A.; Torreggiani, W.C. European obesity and the radiology department. What can we do to help? Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fursevich, D.M.; LiMarzi, G.M.; O’Dell, M.C.; Hernandez, M.A.; Sensakovic, W.F. Bariatric CT Imaging: Challenges and Solutions. RadioGraphics 2016, 36, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, A.; Nakayama, M.; Ota, Y.; Kamata, M.; Hirota, Y.; Sone, M.; Hamano, M.; Tanaka, R.; Yoshioka, K. Feasibility of thin-slice abdominal CT in overweight patients using a vendor neutral image-based denoising algorithm: Assessment of image noise, contrast, and quality. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Ning, R.; Conover, D. Image denoising based on multiscale singularity detection for cone beam CT breast imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Kwan, A.L.C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Packard, N.J.; Boone, J.M. Noise power properties of a cone-beam CT system for breast cancer detection. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 5317–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, M.; Storz, C.; Kim, J.H.; Weiss, J.; Afat, S.; Nikolaou, K.; Bamberg, F.; Othman, A.E. Effect of a novel denoising technique on image quality and diagnostic accuracy in low-dose CT in patients with suspected appendicitis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.J.; Chang, W.; Ye, J.C.; Kang, E.; Oh, D.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.H. Low-dose abdominal CT using a deep learning-based denoising algorithm: A comparison with CT reconstructed with filtered back projection or iterative reconstruction algorithm. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollough, C.H.; Leng, S. Use of artificial intelligence in computed tomography dose optimisation. Ann. ICRP 2020, 49, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.F.; Keat, N. Artifacts in CT: Recognition and Avoidance. RadioGraphics 2004, 24, 1679–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Female | Male | Overall | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIRT | TACE | Overall | SIRT | TACE | Overall | |||
| Number (n) | Overall | 13 | 12 | 25 | 37 | 38 | 75 | 100 |
| HCC | 4 | 9 | 13 | 12 | 35 | 47 | 60 | |
| mUM | 4 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 17 | ||
| CCC | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 8 | ||
| CRC | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 5 | ||
| NET | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 10 | |
| Age (y) | Overall | 61 ± 15 | 69 ± 9 | 65 ± 13 | 69 ± 12 | 69 ± 9 | 69 ± 11 | 68 ± 11 |
| HCC | 61 ± 17 | 70 ± 9 | 67 ± 12 | 70 ± 13 | 69 ± 9 | 69 ± 10 | 69 ± 11 | |
| mUM | 60 ± 9 | 73 | 62 ± 10 | 74 ± 10 | 74 ± 10 | 71 ± 11 | ||
| CCC | 40 | 40 | 67 ± 12 | 64 | 67 ± 11 | 63 ± 14 | ||
| CRC | 61 ± 30 | 62 | 61 ± 22 | 72 ± 8 | 72 ± 8 | 65 ± 17 | ||
| NET | 74 ± 3 | 61 | 70 ± 8 | 57 ± 12 | 69 ± 6 | 61 ± 11 | 63 ± 11 | |
| Heigth (cm) | Overall | 165 ± 6 | 161 ± 8 | 163 ± 7 | 173 ± 8 | 173 ± 8 | 173 ± 8 | 171 ± 9 |
| HCC | 168 ± 4 | 162 ± 9 | 164 ± 8 | 171 ± 6 | 173 ± 8 | 172 ± 7 | 171 ± 8 | |
| mUM | 164 ± 7 | 157 | 162 ± 6 | 173 ± 12 | 173 ± 12 | 170 ± 12 | ||
| CCC | 160 | 160 | 174 ± 6 | 172 | 174 ± 5 | 172 ± 7 | ||
| CRC | 172 ± 1 | 162 | 169 ± 6 | 177 ± 2 | 177 ± 2 | 172 ± 6 | ||
| NET | 159 ± 1 | 154 | 157 ± 3 | 176 ± 4 | 172 ± 11 | 175 ± 6 | 170 ± 10 | |
| Weight (kg) | Overall | 72 ± 9 | 70 ± 10 | 71 ± 9 | 80 ± 12 | 79 ± 14 | 79 ± 13 | 77 ± 12 |
| HCC | 71 ± 11 | 69 ± 11 | 70 ± 11 | 78 ± 9 | 79 ± 14 | 78 ± 13 | 77 ± 13 | |
| mUM | 73 ± 12 | 69 | 72 ± 10 | 81 ± 11 | 81 ± 11 | 79 ± 12 | ||
| CCC | 69 | 69 | 83 ± 14 | 86 | 84 ± 13 | 82 ± 13 | ||
| CRC | 79 ± 4 | 73 | 77 ± 4 | 98 ± 13 | 98 ± 13 | 85 ± 14 | ||
| NET | 70 ± 4 | 78 | 72 ± 6 | 70 ± 11 | 85 ± 9 | 74 ± 12 | 74 ± 10 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | Overall | 26 ± 3 | 27 ± 4 | 27 ± 3 | 27 ± 4 | 26 ± 4 | 27 ± 4 | 27 ± 4 |
| HCC | 25 ± 3 | 26 ± 4 | 26 ± 4 | 27 ± 3 | 26 ± 4 | 26 ± 4 | 26 ± 4 | |
| mUM | 27 ± 3 | 28 | 27 ± 3 | 27 ± 3 | 27 ± 3 | 27 ± 3 | ||
| CCC | 27 | 27 | 28 ± 4 | 29 | 28 ± 3 | 28 ± 3 | ||
| CRC | 27 ± 1 | 28 | 27 ± 1 | 32 ± 5 | 32 ± 5 | 29 ± 4 | ||
| NET | 28 ± 2 | 33 | 29 ± 4 | 22 ± 3 | 29 ± 1 | 24 ± 4 | 26 ± 4 | |
| Mask | Fill | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI-Group | Regular | Denoising | p (Two-Sided, Adjusted) | Regular | Denoising | p (Two-Sided, Adjusted) | |
| HU | Overall | 44.86 ± 5.79 | 44.77 ± 5.06 | >0.999 | 64.92 ± 7.5 | 64.79 ± 6.55 | >0.999 |
| Normal Weight | 44.29 ± 4.35 | 44.27 ± 3.80 | >0.999 | 64.1 ± 5.63 | 64.07 ± 4.92 | >0.999 | |
| Pre-Obesity | 44.83 ± 5.62 | 44.74 ± 4.92 | >0.999 | 64.87 ± 7.28 | 64.75 ± 6.36 | >0.999 | |
| Obesity | 45.39 ± 6.95 | 45.23 ± 6.08 | >0.999 | 65.69 ± 9.00 | 65.46 ± 7.86 | >0.999 | |
| Noise | Overall | 28.45 ± 6.45 | 19.84 ± 1.55 | <0.001 | 24.65 ± 3.35 | 19.70 ± 1.17 | <0.001 |
| Normal Weight | 22.48 ± 1.96 | 19.65 ± 1.17 | <0.001 | 21.34 ± 1.34 | 19.51 ± 0.88 | <0.001 | |
| Pre-Obesity | 26.9 ± 2.42 | 19.83 ± 1.50 | <0.001 | 24.03 ± 1.56 | 19.69 ± 1.13 | <0.001 | |
| Obesity | 35.74 ± 5.94 | 20.02 ± 1.85 | <0.001 | 28.38 ± 2.72 | 19.89 ± 1.39 | <0.001 | |
| SNR | Overall | 1.63 ± 0.30 | 2.25 ± 0.08 | <0.001 | 2.66 ± 0.33 | 3.28 ± 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Normal Weight | 1.97 ± 0.14 | 2.25 ± 0.06 | <0.001 | 3.00 ± 0.17 | 3.28 ± 0.10 | <0.001 | |
| Pre-Obesity | 1.66 ± 0.12 | 2.25 ± 0.08 | <0.001 | 2.69 ± 0.18 | 3.28 ± 0.14 | <0.001 | |
| Obesity | 1.29 ± 0.20 | 2.25 ± 0.10 | <0.001 | 2.32 ± 0.25 | 3.28 ± 0.17 | <0.001 | |
| Variable | B | SE | 95% CI (Asymptotic) | |t| | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 2.813 | 0.0152 | 2.783 to 2.843 | 185.60 | <0.001 |
| BMI | −0.0286 | 0.0068 | −0.0419 to −0.0153 | 4.21 | <0.001 |
| Radiation Exposure | −0.0053 | 0.0002 | −0.0058 to −0.0049 | 23.87 | <0.001 |
| Denoising | 0.6191 | 0.0048 | 0.6096 to 0.6286 | 127.90 | <0.001 |
| Pooled | Rater 1 | Rater 2 | r | p (Two-Sided, Adjusted) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regular | Overall | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 0.913 | <0.001 |
| Normal Weight | 5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 5 (3–5) | 0.951 | <0.001 | |
| Pre-Obesity | 4 (2–4) | 4 (3–4) | 4 (3–5) | 0.859 | <0.001 | |
| Obesity | 3 (1–3) | 3 (1–3) | 3 (1–3) | 0.926 | <0.001 | |
| Denoising | Overall | 5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 0.834 | <0.001 |
| Normal Weight | 5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 0.912 | <0.001 | |
| Pre-Obesity | 5 (3–5) | 5 (3–5) | 5 (3–5) | 0.925 | <0.001 | |
| Obesity | 4 (3–5) | 4 (4–5) | 4 (3–5) | 0.795 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brendlin, A.S.; Estler, A.; Plajer, D.; Lutz, A.; Grözinger, G.; Bongers, M.N.; Tsiflikas, I.; Afat, S.; Artzner, C.P. AI Denoising Significantly Enhances Image Quality and Diagnostic Confidence in Interventional Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Tomography 2022, 8, 933-947. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020075
Brendlin AS, Estler A, Plajer D, Lutz A, Grözinger G, Bongers MN, Tsiflikas I, Afat S, Artzner CP. AI Denoising Significantly Enhances Image Quality and Diagnostic Confidence in Interventional Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Tomography. 2022; 8(2):933-947. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020075
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrendlin, Andreas S., Arne Estler, David Plajer, Adrian Lutz, Gerd Grözinger, Malte N. Bongers, Ilias Tsiflikas, Saif Afat, and Christoph P. Artzner. 2022. "AI Denoising Significantly Enhances Image Quality and Diagnostic Confidence in Interventional Cone-Beam Computed Tomography" Tomography 8, no. 2: 933-947. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020075
APA StyleBrendlin, A. S., Estler, A., Plajer, D., Lutz, A., Grözinger, G., Bongers, M. N., Tsiflikas, I., Afat, S., & Artzner, C. P. (2022). AI Denoising Significantly Enhances Image Quality and Diagnostic Confidence in Interventional Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Tomography, 8(2), 933-947. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020075








