What Findings on Chest CTs Can Delay Diagnosis of Pleuropulmonary Paragonimiasis?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
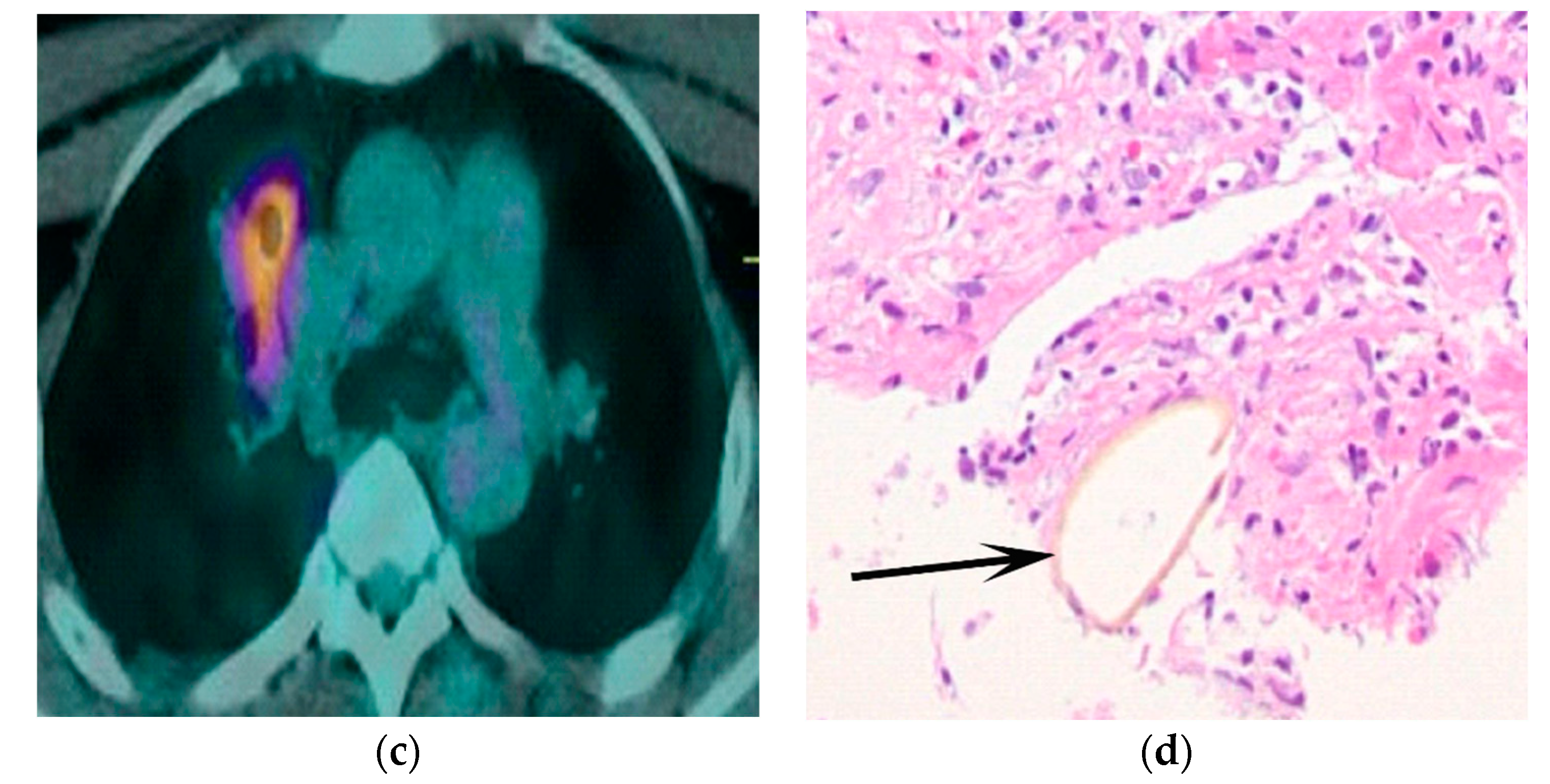
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doanh, P.N.; Dung, D.T.; Thach, D.T.C.; Horii, Y.; Shinohara, A.; Nawa, Y. Human paragonimiasis in Viet Nam: Epidemiological survey and identification of the responsible species by DNA sequencing of eggs in patients’ sputum. Parasitol. Int. 2011, 60, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, D.; Xu, Z.B.; Agatsuma, T. Paragonimiasis and the genus Paragonimus. Adv. Parasitol. 1999, 42, 113–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kong, Y.; Kang, S.Y. Epidemiology of paragonimiasis in Korea. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1997, 28 (Suppl. 1), 32–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Kong, Y.; Yang, H.J. Metacercarial infections of Paragonimus westermani in freshwater crabs sold in markets in Seoul. Kisaengch’unghak Chapchi. Korean J. Parasitol. 1991, 29, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.-H.; Dai, F.; Bai, X.; Kim, T.-I.; Yang, H.-J.; Kim, T.-S.; Cho, S.-H.; Hong, S.-J. Recent Incidence of Metacercariae in Freshwater Crayfish,, from Two Enzootic Sites in Jeollanam-do, Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2017, 55, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.C.; Chang, J.H.; Kang, S.R.; Yang, H.J.; Sung, S.H. Paragonimus westermani found in the tip of a little finger. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, S.Y.; Cho, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.-W.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, J.-I.; Sung, Y.M.; Lee, S.P. A paragonimiasis patient with allergic reaction to praziquantel and resistance to triclabendazole: Successful treatment after desensitization to praziquantel. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Han, J.; Shim, S.S.; Jeon, K.; Koh, W.-J.; Lee, I.; Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.J. Pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis: CT findings in 31 patients. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.; Koh, W.-J.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.J.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, K.S.; Han, J. Clinical features of recently diagnosed pulmonary paragonimiasis in Korea. Chest 2005, 128, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.S.; Lane, M.A.; Weil, G.J.; Bailey, T.C.; Bhalla, S. Chest CT features of North American paragonimiasis. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.N.; Kananbala, S.; Devi, K.S. Pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis mimicking pulmonary tuberculosis-A report of three cases. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 23, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, J.U.; Um, S.W.; Koh, W.J.; Suh, G.Y.; Chung, M.P.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.J.; Jeon, K. Pulmonary paragonimiasis mimicking lung cancer in a tertiary referral centre in Korea. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. Off. J. Int. Union Against Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2011, 15, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Choi, C.M.; Kwon, H.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, S.Y.; Hwang, H.S. A Case of Pulmonary Paragonimiasis Mimicking Lung Cancer Diagnosed by EBUS-TBNA. Korean J. Med. 2013, 84, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.-E.; Song, H.-Y.; Jung, J.-W.; Oh, S.-J.; Yoon, K.-H.; Park, D.-S.; Jeong, E.-T.; Kim, H.-R. Pleural fluid characteristics of pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis masquerading as pleural tuberculosis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2015, 30, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.-H.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.-D.; Zhao, J.-S.; Li, S.-H.; Wang, M.-M.; Wang, W.-Q.; Tian, M.; He, S.-M.-Q.; Ma, Z.-Q.; et al. Analysis of the misdiagnosis of 8 adult cases of paragonimiasis with lung masses as the main manifestation in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, J.G.; Whang, H.Y.; Kim, W.S.; Han, M.C.; Shim, Y.S.; Cho, S.Y. Pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis: Radiologic findings in 71 patients. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 159, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Im, J.-G.; Goo, J.M.; Lee, H.J.; Hong, S.-T.; Shen, C.H.; Chung, D.H.; Son, K.R.; Chang, J.M.; Eo, H. Serial CT findings of Paragonimus infested dogs and the Micro-CT findings of the worm cysts. Korean J. Radiol. 2007, 8, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, J.; Choe, K.; Joo, S.; Kim, M. The role of contrast enhanced computed tomography in the diagnosis of low density pulmonary nodules. Yonsei Med. J. 1995, 36, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, O.; Tsubamoto, M.; Inoue, A.; Johkoh, T.; Tomiyama, N.; Hamada, S.; Mihara, N.; Sumikawa, H.; Natsag, J.; Nakamura, H. Pulmonary cavitary nodules on computed tomography: Differentiation of malignancy and benignancy. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2007, 31, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, K.S. Pulmonary tuberculosis: Up-to-date imaging and management. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrill, J.; Williams, C.J.; Bain, G.; Conder, G.; Hine, A.L.; Misra, R.R. Tuberculosis: A radiologic review. Radiogr. Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc. 2007, 27, 1255–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, K.; Matsunobe, S.; Tsuda, T.; Okuda, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Oyanagi, H.; Konishi, J. Intratumoral necrosis of lung carcinoma: A potential diagnostic pitfall in incremental dynamic computed tomography analysis of solitary pulmonary nodules? J. Thorac. Imaging 1997, 12, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.U.; Lee, K.; Park, H.-K.; Jeong, Y.J.; Yu, H.S.; Lee, M.K. A pulmonary paragonimiasis case mimicking metastatic pulmonary tumor. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vourtsi, A.; Gouliamos, A.; Moulopoulos, L.; Papacharalampous, X.; Chatjiioannou, A.; Kehagias, D.; Lamki, N. CT appearance of solitary and multiple cystic and cavitary lung lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Swensen, S.J. Cystic and cavitary lung diseases: Focal and diffuse. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.G.; Jung, E.J.; Lim, G.I.; Yang, S.B.; Im, H.H. A Case of Atypical Distribution of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Bedridden Patient with Quadriplegia. Tuberc Respir. Dis. 2010, 69, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hollings, N.; Shaw, P. Diagnostic imaging of lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 19, 722–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouroux, J.; Padovani, B.; Elkaïm, D.; Richelme, H. Should cavitated bronchopulmonary cancers be considered a separate entity? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1996, 61, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukae, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Iiboshi, H.; Ashitani, J.; Matsukura, S.; Nawa, Y. Clinicoradiologic features of pleuropulmonary Paragonimus westermani on Kyusyu Island, Japan. Chest 2001, 120, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, A.M.; Virk, A.; Swanson, K.; Poeschla, E.M. Severe pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis 8 years after emigration from a region of endemicity. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2002, 35, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokogawa, M. Paragonimus and paragonimiasis. Adv. Parasitol. 1969, 7, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoonuan, T.; Vanvanitchai, Y.; Dekumyoy, P.; Komalamisra, C.; Kojima, S.; Waikagul, J. Paragonimiasis prevalences in Saraburi Province, Thailand, measured 20 years apart. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
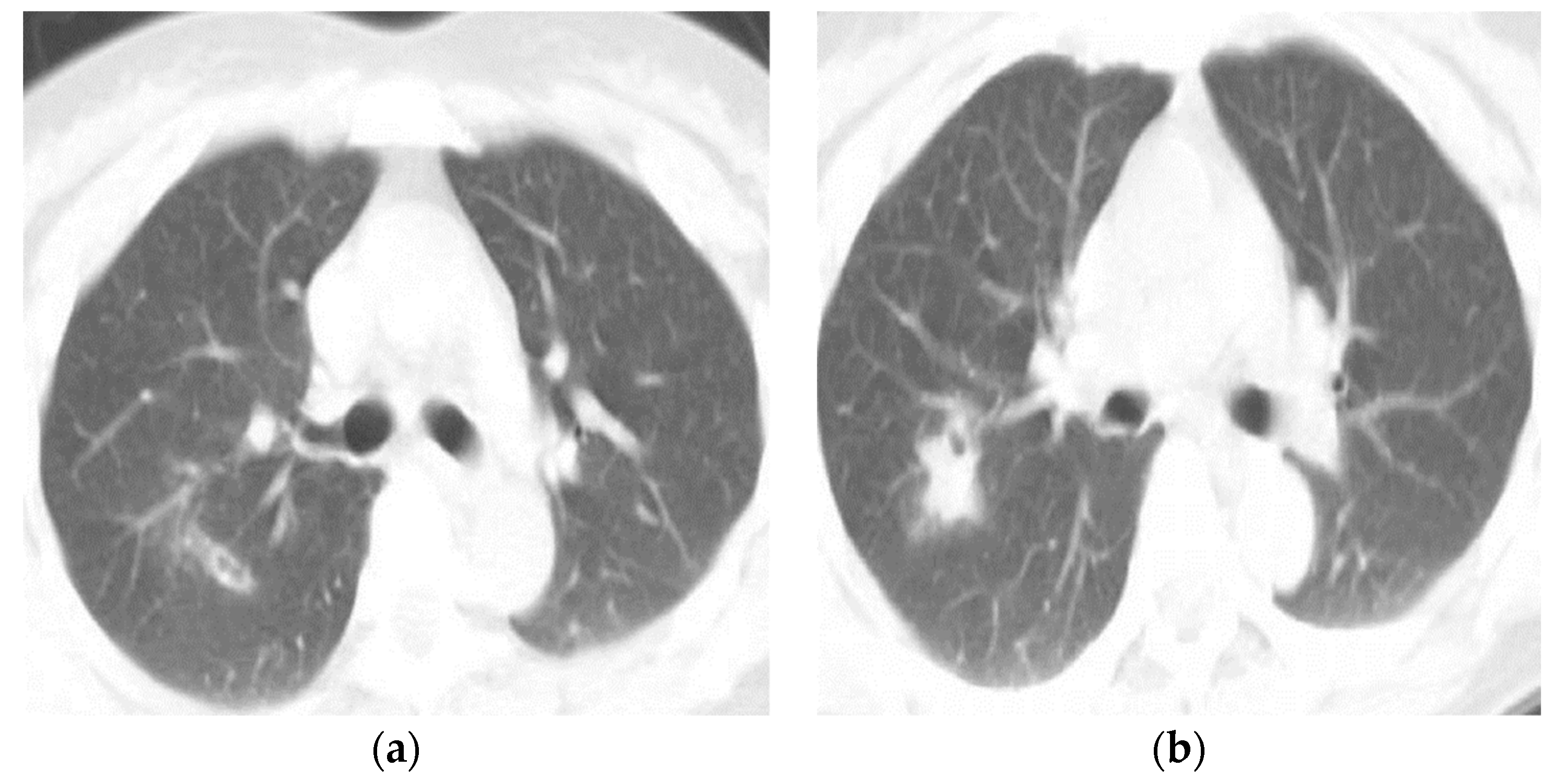
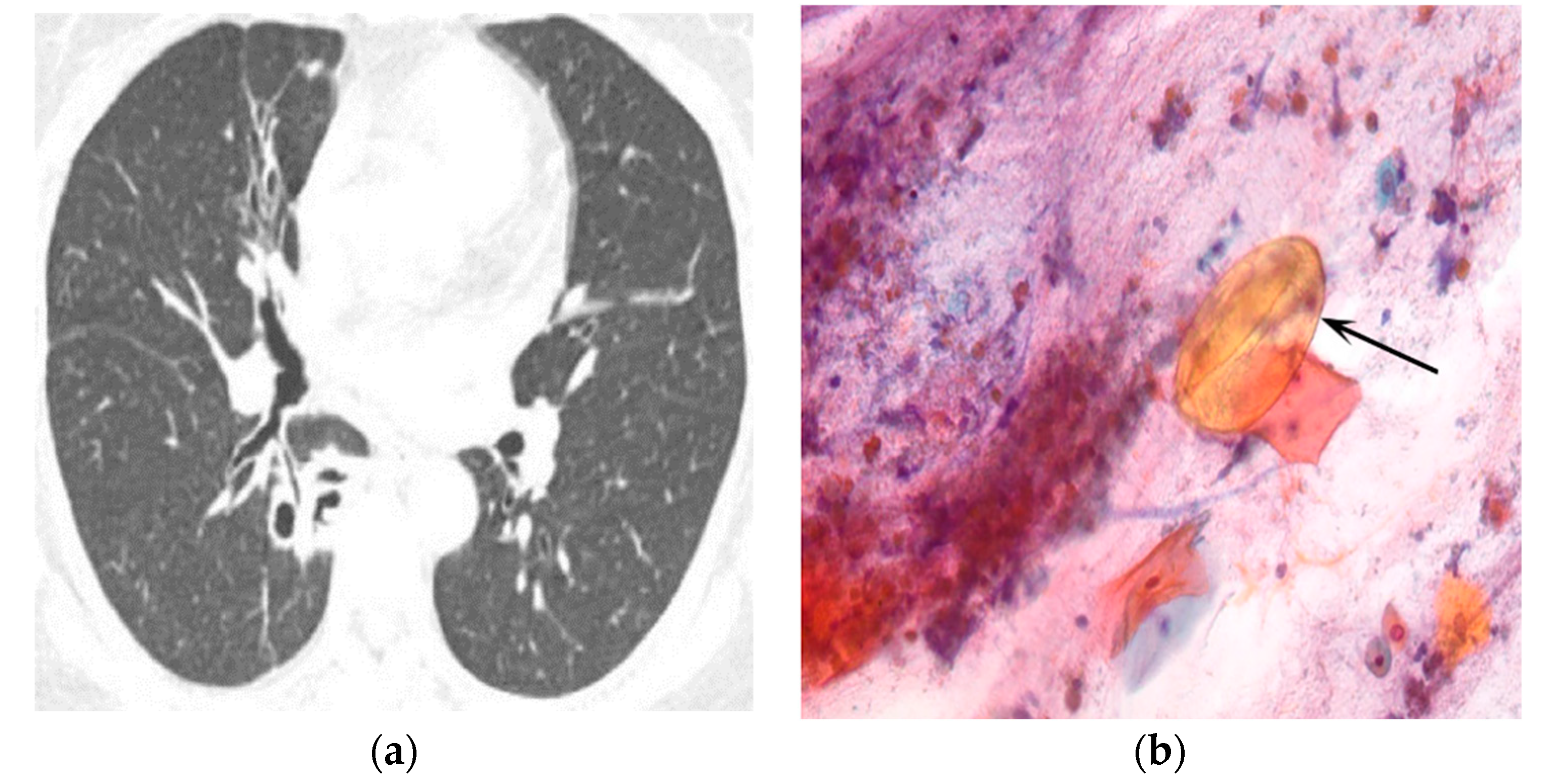
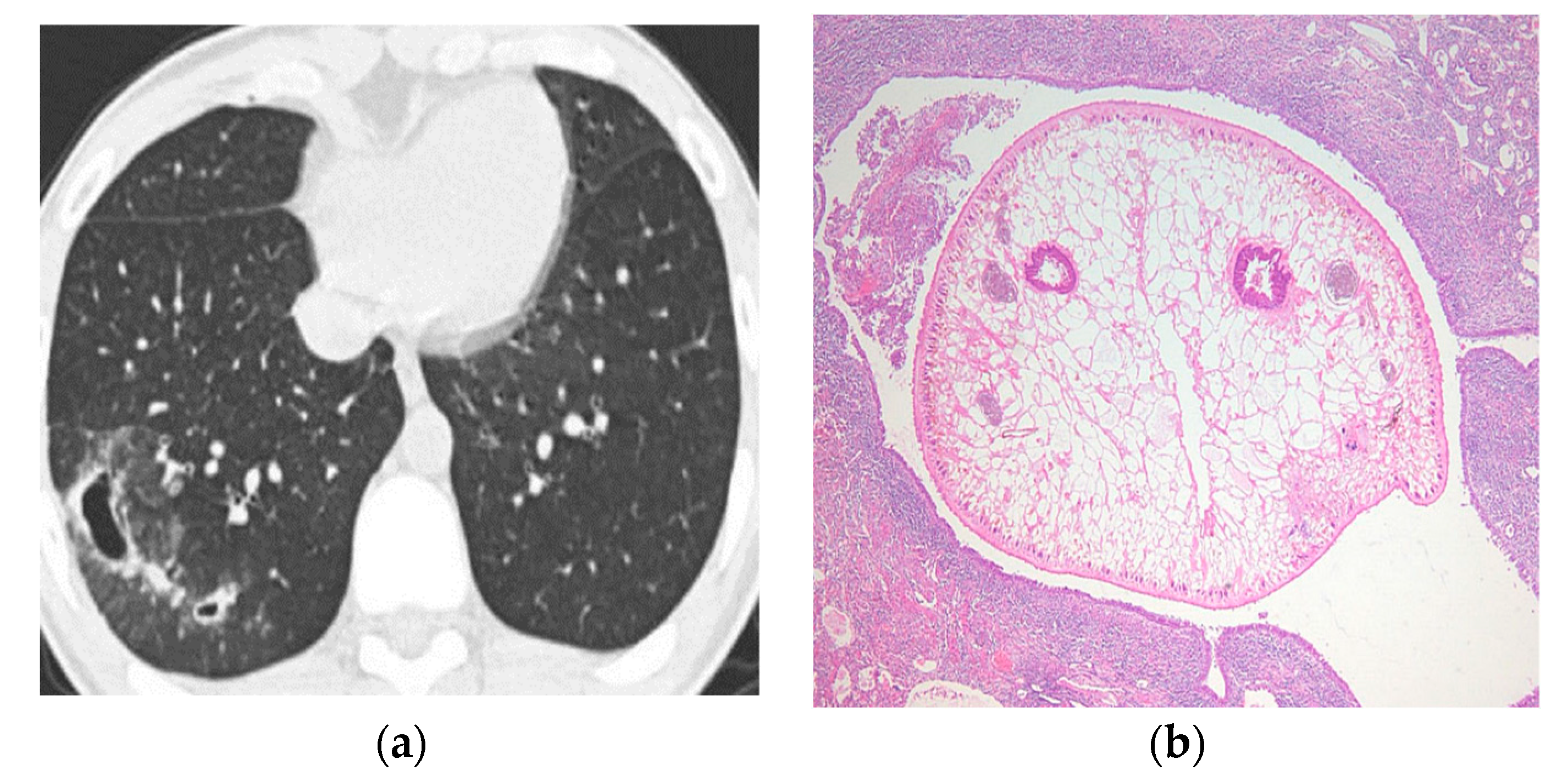
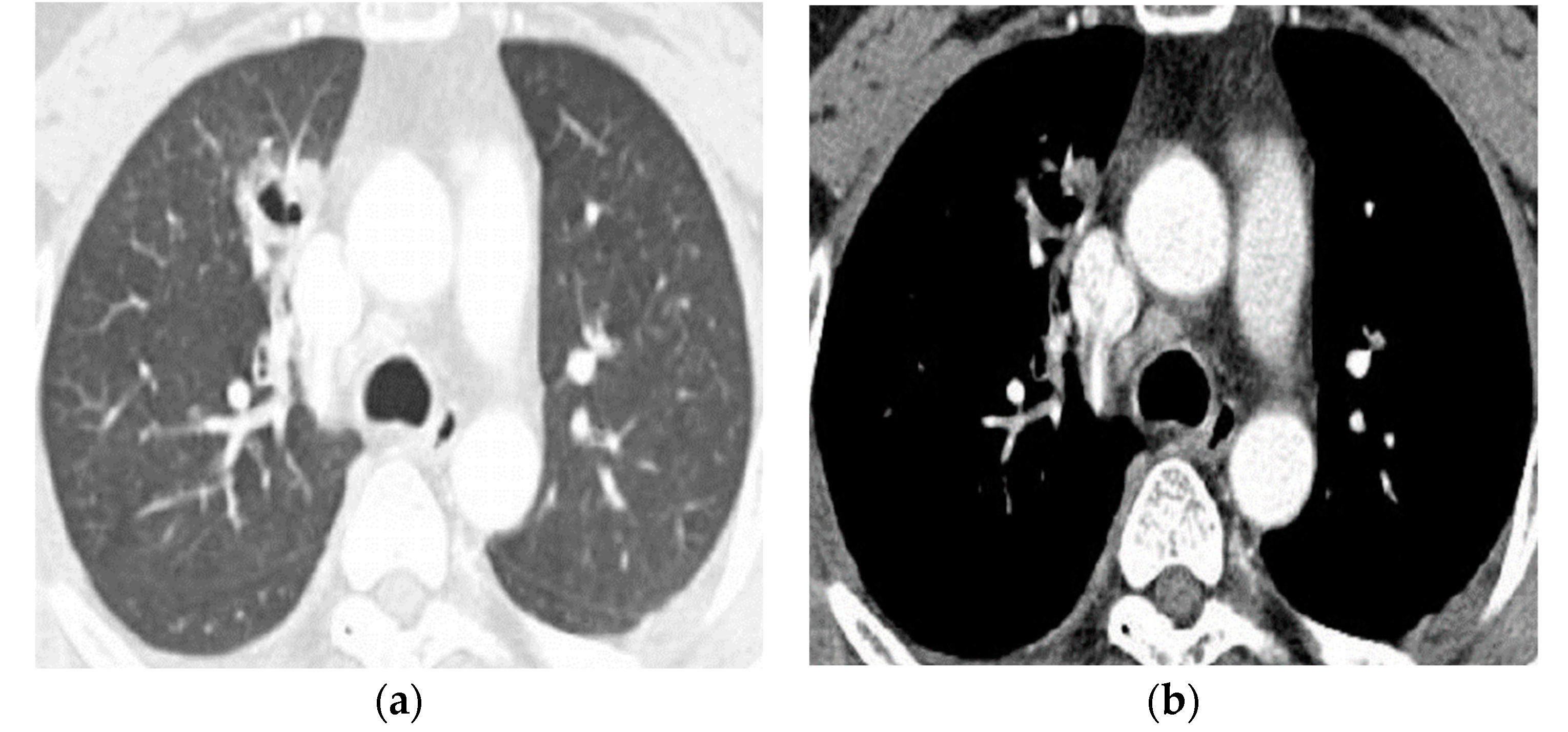
| Type of Questionnaire | Response Rates | Responses (n, %) |
|---|---|---|
| History of eating | 98.1% (101/103) | yes (n = 14, 13.9), no (n = 8, 7.9), unknown (n = 79, 78.2) |
| Leukocytosis * | 99.0% (102/103) | yes (n = 25, 24.5), no (n = 77, 75.5) |
| Eosinophilia ** | 94.2% (97/103) | yes (n = 84, 86.6), no (n = 13, 13.4) |
| Symptoms * | 100% (103/103) | blood-tinged sputum (n = 23, 23.3), hemoptysis (n = 18, 17.5), dyspnea (n = 23, 23.3), chest pain (n = 25, 24.3), cough (n = 15, 14.6), fever (n = 3, 2.9), sputum (n = 3, 2.9), abdominal pain (n = 2, 1.9), hemiparesis (n = 2, 1.9), no symptoms (n = 11, 10.7) |
| Diagnostic Tools | Rates of Compliance (%) | Positivity Rates (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sputum examination (n = 39) | 38.2 | 15.4 |
| ELISA (n = 97) | 95.1 | 99.0 |
| Bronchoscopy & BAL* (n = 40) | 39.2 | 5.0 |
| Tissue biopsy (n = 44) | 43.1 | 43.2 |
| Parenchymal Findings | n (%) | Initial CT Diagnosis | p Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correct (%) | Incorrect (%) | |||
| Locations (n = 94) | ||||
| upper lobes | 54 (57.4) | 26/54 (48.1) | 28/54(51.9) | 0.481 |
| lower lobes | 33 (35.1) | 15/33 (45.5) | 18/33 (54.5) | 0.454 |
| right middle lobes | 7 (7.5) | 4/7 (57.1) | 3/7 (42.9) | 0.571 |
| peripheral | 73 (77.7) | 36/73 (49.3) | 37/73 (50.7) | 0.493 |
| central | 13 (13.8) | 7/13 (53.8) | 6/13 (46.2) | 0.538 |
| both | 8 (8.5) | 2/8 (25) | 6/8 (75) | 0.250 |
| findings (n = 94) | ||||
| nodules | 53 (56.4) | 31/53 (58.5) | 22/53 (41.5) | 0.585 |
| non-cavitary | 31 (33.0) | 16/31 (51.6) | 15/31 (48.9) | 0.516 |
| cavitary | 22 (23.4) | 15/22 (68.2) | 7/22 (31.8) | 0.682 |
| air-space consolidation | 25 (26.6) | 7/25 (28) | 18/25 (72) | 0.280 |
| mass | 8 (8.5) | 2/8 (25) | 6/8 (75) | 0.250 |
| linear density | 5 (5.3) | 3/5 (60) | 2/5 (40) | 0.600 |
| others | 3 (3.2) | |||
| migrating worm track (n = 94) | ||||
| presence | 17 (18.1) | 12/17 (70.6) | 5/17 (29.4) | 0.706 |
| Pleural Findings (n = 102) | Numbers (%) | Initial CT Diagnosis | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correct | Incorrect | |||
| absence | 43 (42.2) | 17/43 (39.5) | 26/43 (60.5) | 0.395 |
| presence | 59 (57.8) | 29/59 (49.2) | 30/59 (50.8) | 0.492 |
| pleural effusion | 40 (67.8) | 16/40 (40) | 24/40 (60) | 0.400 |
| diffuse pleural thickening | 21 (35.6) | 7/21 (33.3) | 14/21 (66.7) | 0.333 |
| hydropneumothorax | 9 (15.3) | 6/9 (66.7) | 3/9 (33.3) | 0.667 |
| focal pleural thickening | 8 (13.6) | 4/8 (50) | 4/8 (50) | 0.500 |
| pneumothorax | 4 (6.8) | 2/4 (50) | 2/4 (50) | 0.500 |
| Initial Diagnosis | Numbers |
|---|---|
| pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis | 46 (44.7) |
| pneumonia | 18 (17.5) |
| tuberculosis | 14 (13.6) |
| lung cancer | 7 (6.8) |
| pleural effusion | 7 (6.8) |
| solitary pulmonary nodule | 4 (3.9) |
| lung abscess | 4 (3.9) |
| eosinophilic pneumonia | 3 (2.9) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.K.; Jin, G.Y.; Kwon, K.S. What Findings on Chest CTs Can Delay Diagnosis of Pleuropulmonary Paragonimiasis? Tomography 2022, 8, 1493-1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030122
Li KK, Jin GY, Kwon KS. What Findings on Chest CTs Can Delay Diagnosis of Pleuropulmonary Paragonimiasis? Tomography. 2022; 8(3):1493-1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030122
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kai Ke, Gong Yong Jin, and Keun Sang Kwon. 2022. "What Findings on Chest CTs Can Delay Diagnosis of Pleuropulmonary Paragonimiasis?" Tomography 8, no. 3: 1493-1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030122
APA StyleLi, K. K., Jin, G. Y., & Kwon, K. S. (2022). What Findings on Chest CTs Can Delay Diagnosis of Pleuropulmonary Paragonimiasis? Tomography, 8(3), 1493-1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030122






