An Anthropomorphic Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Simulation and Analysis of Breast DCE MRI Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
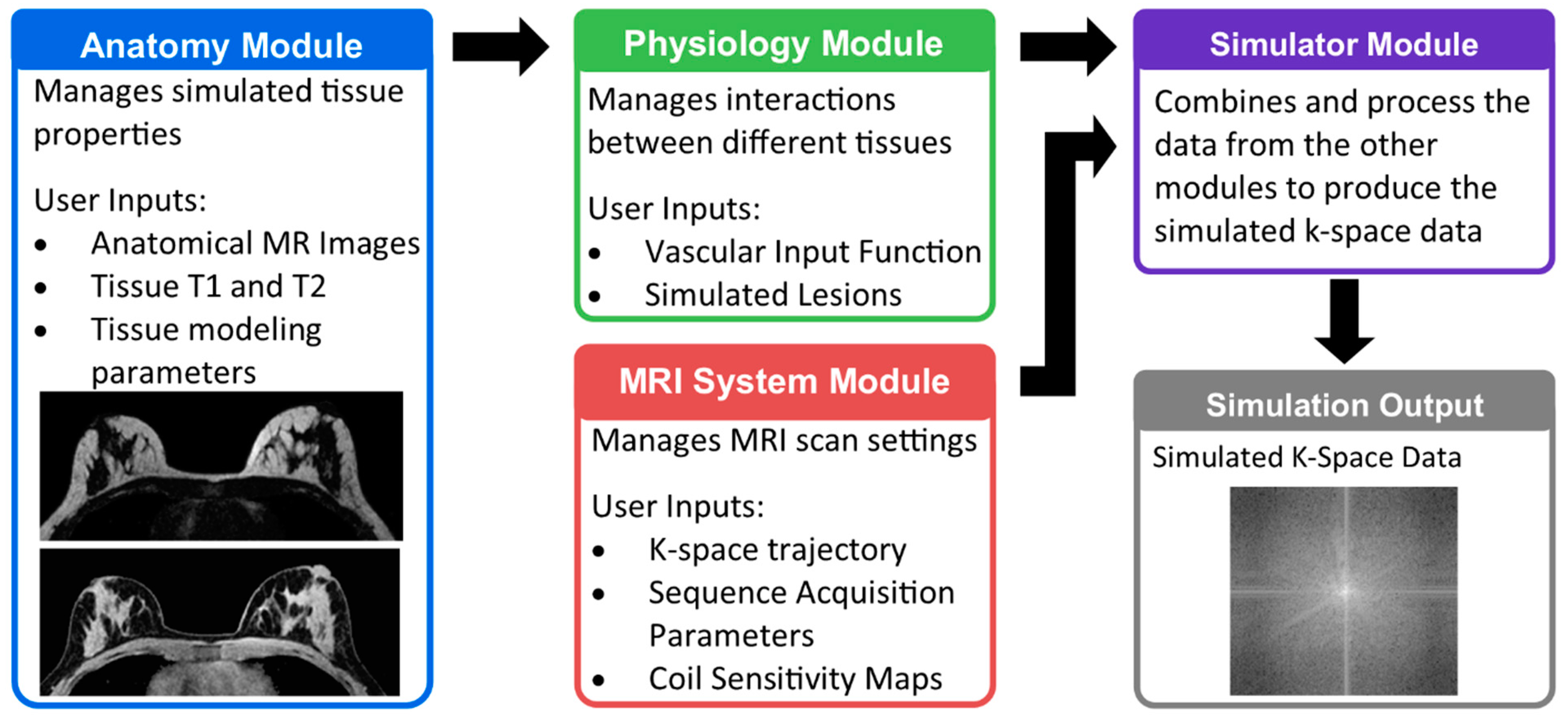
2.1. Breast MRI DRO Overview
- Different MRI input images including anatomy and chemical species content
- Different coil sensitivity profiles
- Contrast enhancement based on user desired kinetic models
- Simulation of MRI physics
- Simulation of k-space sampling in both time and space.
2.2. Anatomy Module
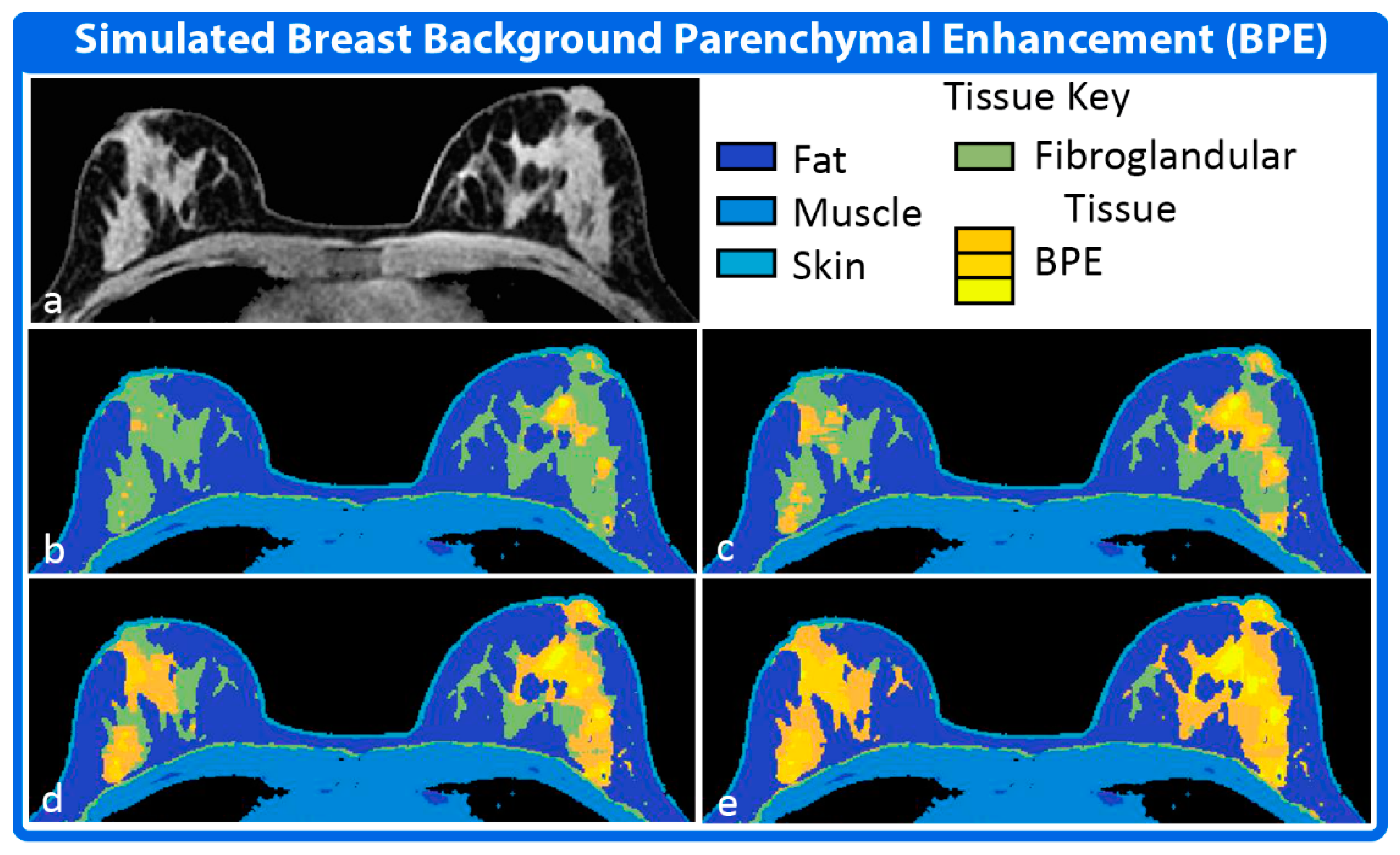
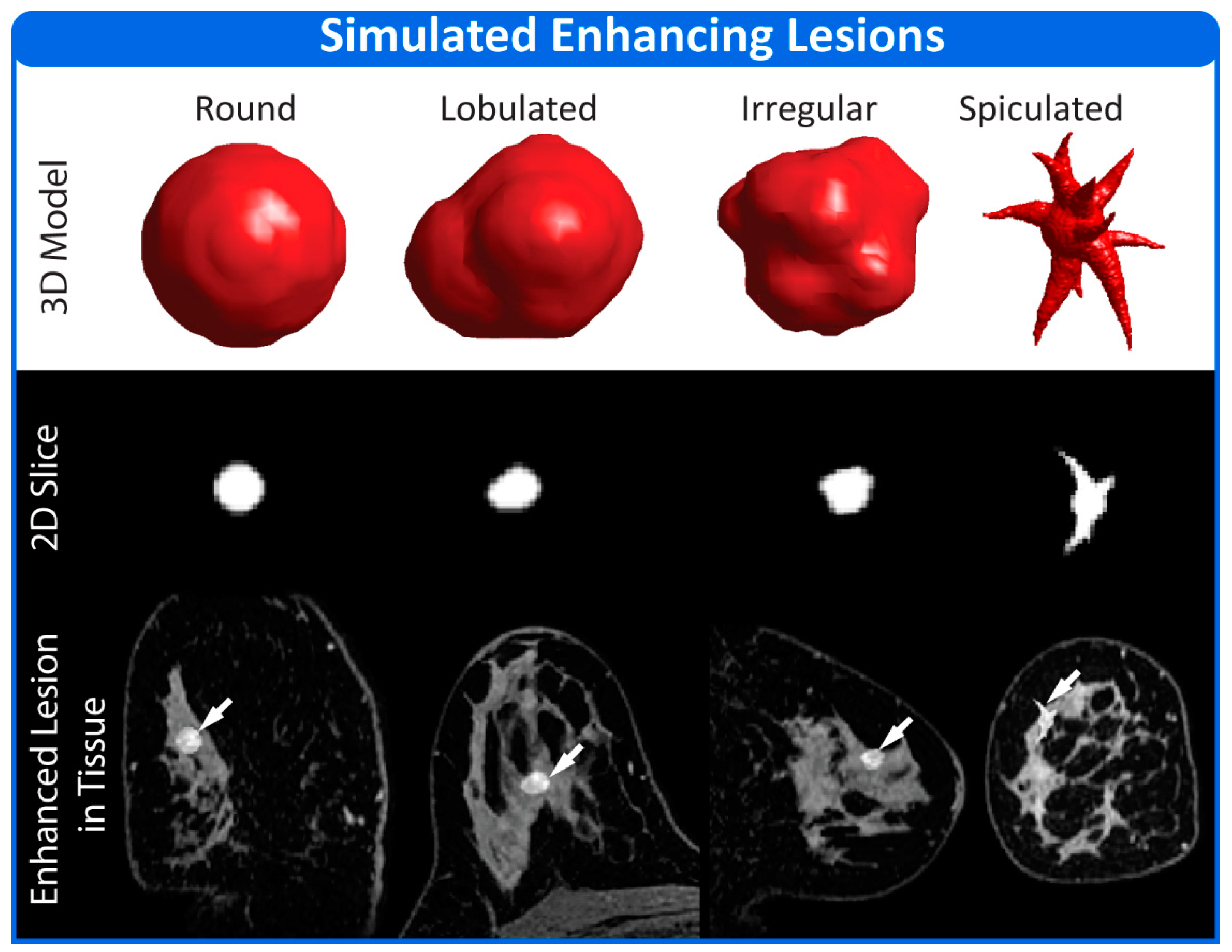
2.3. Physiology Module
2.4. MRI System Module
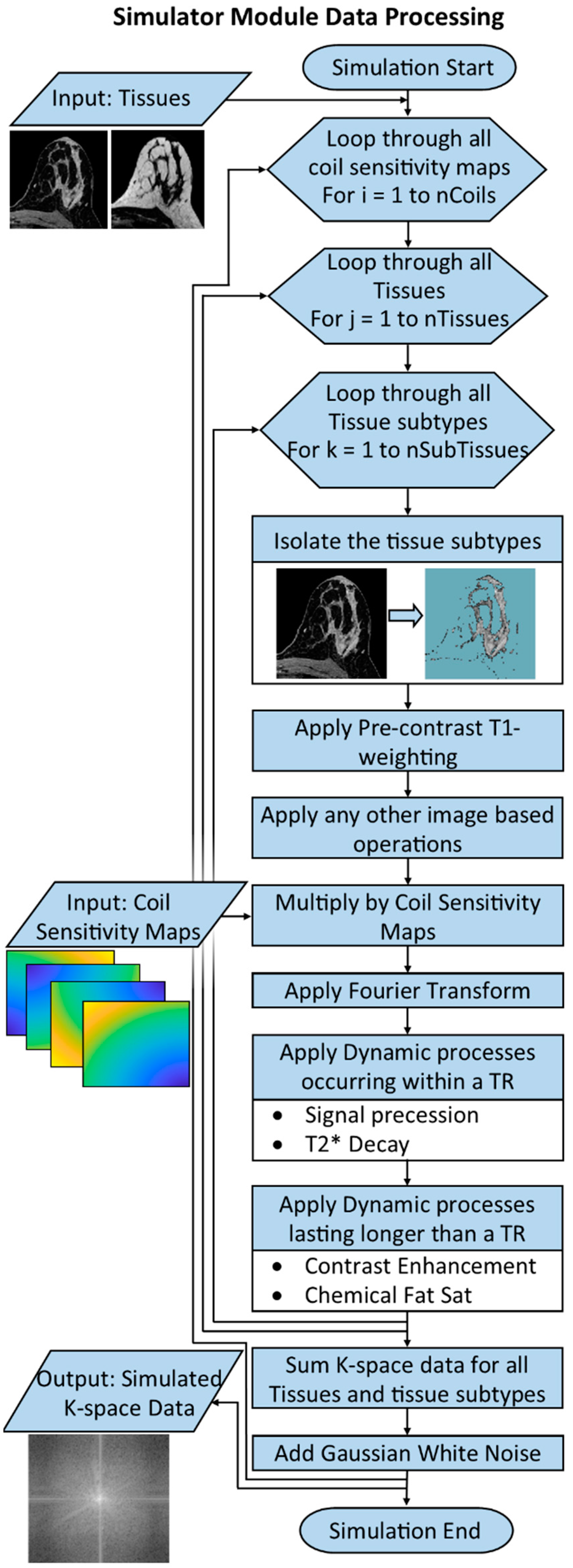
2.5. Simulator Module
2.6. Example Simulations Using the Breast DRO
2.6.1. Simulation 1
2.6.2. Simulation 2
2.6.3. Simulation 3
2.6.4. Simulation 4
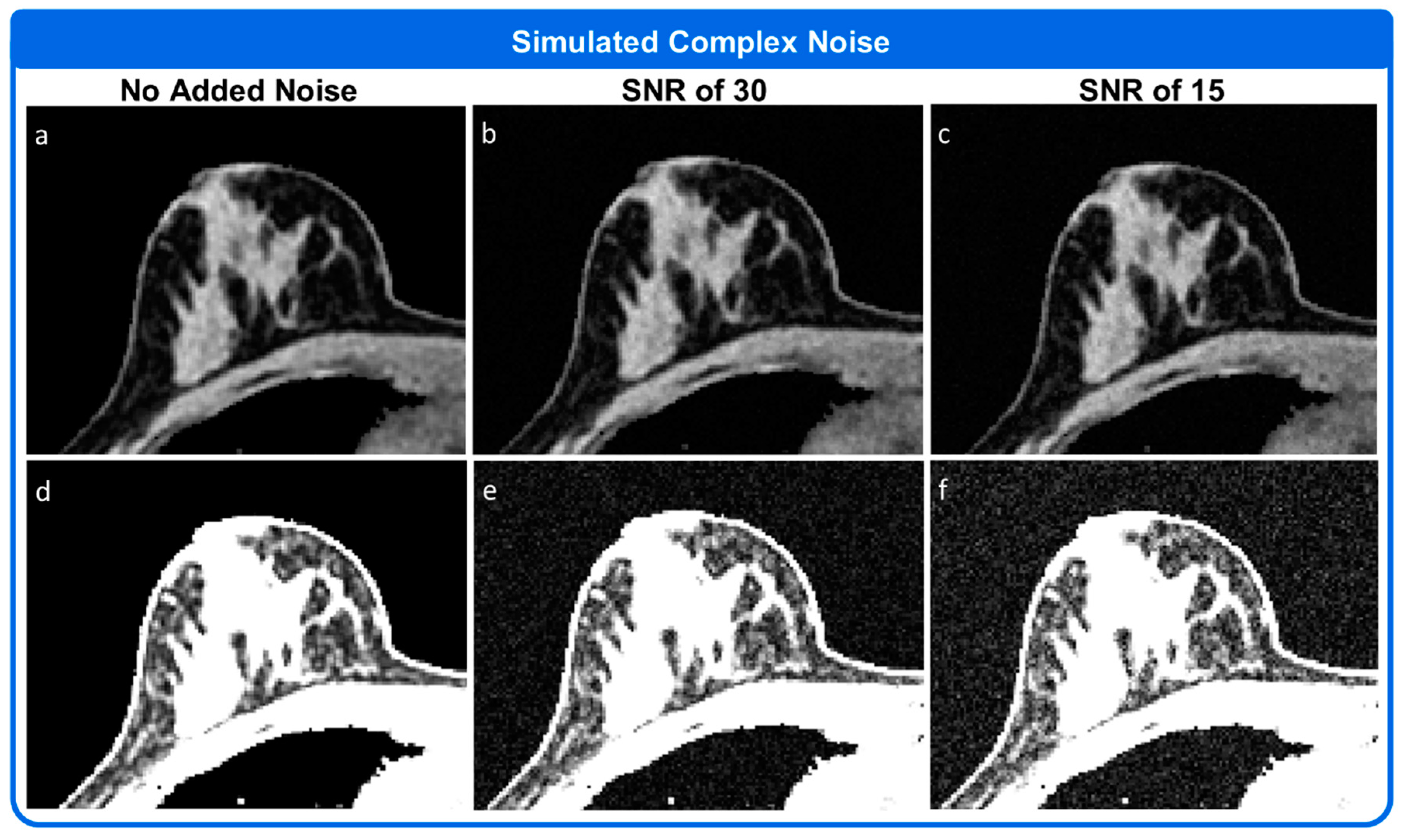
2.6.5. Simulation 5
3. Results
3.1. Simulation 1
3.2. Simulation 2
3.3. Simulation 3
3.4. Simulation 4
3.5. Simulation 5
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DCE MRI Technical Committee. DCE MRI Quantification Profile. Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance. Version 1.0. Profile Stage: Reviewed Draft. 1 July 2012. Available online: httpp://rsna.org/QIBA_.aspx (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Chenevert, T.L.; Jambawalikar, S.; Schwartz, L.H.; Malyarenko, D.; Huang, W.; Noworolski, S.M.; Young, R.J.; Shiroishi, M.S.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers alliance (QIBA) recommendations for improved precision of DWI and DCE-MRI derived biomarkers in multicenter oncology trials. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2019, 49, e101–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H. Variability in Quantitative DCE-MRI: Sources and Solutions. J. Nat. Sci. 2018, 4, e484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2021; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, R.M.; Mus, R.D.; van Zelst, J.; Geppert, C.; Karssemeijer, N.; Platel, B. A novel approach to contrast-enhanced breast magnetic resonance imaging for screening: High-resolution ultrafast dynamic imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2014, 49, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garimella, V.; Qutob, O.; Fox, J.N.; Long, E.D.; Chaturvedi, A.; Turnbull, L.W.; Drew, P.J. Recurrence rates after DCE-MRI image guided planning for breast-conserving surgery following neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 33, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Yin, F.F.; Horton, J.; Chang, Z. Review of treatment assessment using DCE-MRI in breast cancer radiation therapy. World J. Methodol. 2014, 4, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofts, P.S.; Brix, G.; Buckley, D.L.; Evelhoch, J.L.; Henderson, E.; Knopp, M.V.; Larsson, H.B.; Lee, T.Y.; Mayr, N.A.; Parker, G.J.; et al. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T(1)-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: Standardized quantities and symbols. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 1999, 10, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rooney, W.D.; Springer, C.S., Jr. A unified magnetic resonance imaging pharmacokinetic theory: Intravascular and extracellular contrast reagents. Magn. Reason. Med. 2005, 54, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankeelov, T.E.; Rooney, W.D.; Li, X.; Springer, C.S., Jr. Variation of the relaxographic “shutter-speed” for transcytolemmal water exchange affects the CR bolus-tracking curve shape. Magn. Reason. Med. 2003, 50, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovanni, P.; Azlan, C.A.; Ahearn, T.S.; Semple, S.I.; Gilbert, F.J.; Redpath, T.W. The accuracy of pharmacokinetic parameter measurement in DCE-MRI of the breast at 3 T. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman-Haran, E.; Grobgeld, D.; Kelcz, F.; Degani, H. Critical role of spatial resolution in dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2001, 13, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Gaonkar, B.; Mies, C.; DeMichele, A.; Rosen, M.; Davatzikos, C.; Kontos, D. Breast DCE-MRI Kinetic Heterogeneity Tumor Markers: Preliminary Associations with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response. Transl. Oncol. 2015, 8, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Schild, H.H.; Morakkabati, N. Dynamic bilateral contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast: Trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution. Radiology 2005, 236, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, P.D.; Swaminathan, S.V.; Smith, R. SENSE imaging of the breast. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, K.H.; Baltzer, P.A.; Dietzel, M.; Krumbein, I.; Geppert, C.; Kaiser, W.A.; Reichenbach, J.R. Resolving arterial phase and temporal enhancement characteristics in DCE MRM at high spatial resolution with TWIST acquisition. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2011, 34, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudorica, L.A.; Oh, K.Y.; Roy, N.; Kettler, M.D.; Chen, Y.; Hemmingson, S.L.; Afzal, A.; Grinstead, J.W.; Laub, G.; Li, X.; et al. A feasible high spatiotemporal resolution breast DCE-MRI protocol for clinical settings. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2012, 30, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saranathan, M.; Rettmann, D.W.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Lipson, J.A.; Daniel, B.L. Variable spatiotemporal resolution three-dimensional Dixon sequence for rapid dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2014, 40, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Vaals, J.J.; Brummer, M.E.; Dixon, W.T.; Tuithof, H.H.; Engels, H.; Nelson, R.C.; Gerety, B.M.; Chezmar, J.L.; den Boer, J.A. “Keyhole” method for accelerating imaging of contrast agent uptake. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 1993, 3, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.A.; Haraldseth, O.; Muller, T.B.; Rinck, P.A.; Oksendal, A.N. K-space substitution: A novel dynamic imaging technique. Magn. Reason. Med. 1993, 29, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranathan, M.; Rettmann, D.W.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Clarke, S.E.; Vasanawala, S.S. DIfferential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO): A high spatio-temporal resolution Dixon imaging sequence for multiphasic contrast enhanced abdominal imaging. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2012, 35, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.K.; Dougherty, L. Dynamic MRI with projection reconstruction and KWIC processing for simultaneous high spatial and temporal resolution. Magn. Reason. Med. 2004, 52, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.P. Spatiotemporal imaging with partially separable functions. In Proceedings of the 2007 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Macro to Nano, Arlington, VA, USA, 12–15 April 2007; Volume 1–3, pp. 988–991. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, J.E.; Strigel, R.M.; Johnson, K.M.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Reeder, S.B.; Block, W.F. Feasibility of high spatiotemporal resolution for an abbreviated 3D radial breast MRI protocol. Magn. Reason. Med. 2018, 80, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Grimm, R.; Block, K.T.; Chandarana, H.; Kim, S.; Xu, J.; Axel, L.; Sodickson, D.K.; Otazo, R. Golden-angle radial sparse parallel MRI: Combination of compressed sensing, parallel imaging, and golden-angle radial sampling for fast and flexible dynamic volumetric MRI. Magn. Reason. Med. 2014, 72, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jimenez, J.E.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Strigel, R.M.; Johnson, K.M.; Reeder, S.B.; Block, W.F. Non-Cartesian Compressed Sensing with Fat/Water Decomposition: Feasibility Study for High Performance Breast DCE-MRI. In Proceedings of the 23rd ISMRM Scientific Meeting 2015, Toronto, ON, Canada, 30 May–5 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hernando, D.; Haldar, J.P.; Sutton, B.P.; Ma, J.; Kellman, P.; Liang, Z.P. Joint estimation of water/fat images and field inhomogeneity map. Magn. Reason. Med. 2008, 59, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Block, K.T.; Uecker, M.; Frahm, J. Undersampled radial MRI with multiple coils. Iterative image reconstruction using a total variation constraint. Magn. Reason. Med. 2007, 57, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.W.; Ramsay, E.A.; Cheung, E.Y.; Plewes, D.B. The influence of radial undersampling schemes on compressed sensing reconstruction in breast MRI. Magn. Reason. Med. 2012, 67, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikina, J.V.; Alexander, A.L.; Samsonov, A. Accelerating MR parameter mapping using sparsity-promoting regularization in parametric dimension. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.N.; Velikina, J.V.; Strigel, R.M.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Samsonov, A.A.; Cashen, T.A.; Wang, K.; Kelcz, F.; Johnson, K.M.; Korosec, F.R.; et al. Comparison of data-driven and general temporal constraints on compressed sensing for breast DCE MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 3071–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.L.; Zijdenbos, A.P.; Kollokian, V.; Sled, J.G.; Kabani, N.J.; Holmes, C.J.; Evans, A.C. Design and construction of a realistic digital brain phantom. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, B.; Comerci, M.; Larobina, M.; Prinster, A.; Hornak, J.P.; Selvan, S.E.; Amato, U.; Quarantelli, M.; Tedeschi, G.; Brunetti, A.; et al. An MRI digital brain phantom for validation of segmentation methods. Med. Image Anal. 2011, 15, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert-Broche, B.; Evans, A.C.; Collins, L. A new improved version of the realistic digital brain phantom. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert-Broche, B.; Griffin, M.; Pike, G.B.; Evans, A.C.; Collins, D.L. Twenty new digital brain phantoms for creation of validation image data bases. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2006, 25, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosca, R.J.; Jackson, E.F. Creating an anthropomorphic digital MR phantom-an extensible tool for comparing and evaluating quantitative imaging algorithms. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliesener, Y.; Lingala, S.G.; Haldar, J.P.; Nayak, K.S. Impact of (k,t) sampling on DCE MRI tracer kinetic parameter estimation in digital reference objects. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antolak, A.G.; Jackson, E.F. Development and evaluation of an arterial spin-labeling digital reference object for quality control and comparison of data analysis applications. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 02NT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, A.; Chang, K.; Brown, J.; Zhu, X.; Sengupta, D.; Willke, T.L.; Gerstner, E.; Rosen, B.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J. Anatomical DCE-MRI Phantoms Generated from Glioma Patient Data. In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2018: Physics of Medical Imaging, Houston, TX, USA, 12–15 February 2018; p. 105732U. [Google Scholar]
- Semmineh, N.B.; Stokes, A.M.; Bell, L.C.; Boxerman, J.L.; Quarles, C.C. A Population-Based Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Optimizing Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC)-MRI Methods for Clinical Trials. Tomography 2017, 3, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikaios, N.; Arridge, S.; Hamy, V.; Punwani, S.; Atkinson, D. Direct parametric reconstruction from undersampled (k, t)-space data in dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2014, 18, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.C.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hamilton, J.; Grimm, R.; Griswold, M.; Gulani, V.; Seiberlich, N. Realistic 4D MRI abdominal phantom for the evaluation and comparison of acquisition and reconstruction techniques. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.; Magnin, I.E.; Clarysse, P. A new fully-digital anthropomorphic and dynamic thorax/heart model. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 6000–6003. [Google Scholar]
- Tobon-Gomez, C.; Sukno, F.M.; Bijnens, B.H.; Huguet, M.; Frangi, A.F. Realistic simulation of cardiac magnetic resonance studies modeling anatomical variability, trabeculae, and papillary muscles. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissmann, L.; Santelli, C.; Segars, W.P.; Kozerke, S. MRXCAT: Realistic numerical phantoms for cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2014, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Segars, W.P.; Tourassi, G.D.; Boone, J.M.; Dobbins, J.T. Methodology for generating a 3D computerized breast phantom from empirical data. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 3122–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiarashi, N.; Lo, J.Y.; Lin, Y.; Ikejimba, L.C.; Ghate, S.V.; Nolte, L.W.; Dobbins, J.T.; Segars, W.P.; Samei, E. Development and Application of a Suite of 4-D Virtual Breast Phantoms for Optimization and Evaluation of Breast Imaging Systems. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Sisternes, L.; Brankov, J.G.; Zysk, A.M.; Schmidt, R.A.; Nishikawa, R.M.; Wernick, M.N. A computational model to generate simulated three-dimensional breast masses. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 1098–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erickson, D.W.; Wells, J.R.; Sturgeon, G.M.; Samei, E.; Dobbins, J.T.; Segars, W.P.; Lo, J.Y. Population of 224 realistic human subject-based computational breast phantoms. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballo, M.; Mann, R.; Sechopoulos, I. Patient-based 4D digital breast phantom for perfusion contrast-enhanced breast CT imaging. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 4448–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, E.; Davis, S.K.; Lazebnik, M.; Kelcz, F.; Van Veen, B.D.; Hagness, S.C. Development of anatomically realistic numerical breast phantoms with accurate dielectric properties for modeling microwave interactions with the human breast. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuncay, A.H.; Akduman, I. Realistic microwave breast models through T1-weighted 3-D MRI data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Y.; Kipfer, H.; Majidi, S.; Holz, S.; Dale, B.; Geppert, C.; Kroeker, R.; Lin, C. Application of time-resolved angiography with stochastic trajectories (TWIST)-Dixon in dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) breast MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.A.; Comstock, C.E.; Lee, C.H.; Lehman, C.D.; Ikeda, D.M.; Newstead, G.M.; Tozaki, M.; Hylton, N.; Helbich, T.H.; Kuhl, C.; et al. ACR BI-RADS Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Henze, L.C.; Smith, M.R.; Moran, C.J.; Xu, D.; King, K.F.; Samsonov, A.; Kelcz, F.; Block, W.F. Deterministic Comparisons of Nonlinear Acceleration Methods Using a Realistic Digital Phantom. In Proceedings of the Joint Annual Meeting of the ISMRM-ESMRMB 2010, Stockholm, Sweden, 1–7 May 2010; p. 2931. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Henze Bancroft, L.; Kecksemeti, S.; Reeder, S.B.; Block, W.F. Prediction and Removal of Aliased Signal in Undersampled IDEAL: Simulation Using a Digital Breast Phantom. In Proceedings of the 2012 ISMRM Workshop on Fat-Water Separation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 19–22 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Wu, D.; Bosca, R.J.; Morrison, C.K.; Block, W.F.; Korosec, F.R.; Strigel, R.M. The Impact of Accelerated Imaging on Breast DCE MRI: Analysis of a 3D Radial Reconstruction using a Digital Breast Phantom. In Proceedings of the ISMRM Workshop MRI in the Management of Breast Disease: Past, Present and Future, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–15 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, C.K.; Wu, D.; Bosca, R.J.; Block, W.F.; Strigel, R.M.; Korosec, F.R.; Henze Bancroft, L.C. Impact of k-space Segmentation and View Sharing on Lesion Enhancement Curves in Breast DCE MRI: A Digital Phantom Study. In Proceedings of the ISMRM Workshop MRI in the Management of Breast Disease: Past, Present and Future, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–15 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, J.E.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Strigel, R.; Johnson, K.M.; Reeder, S.B.; Block, W.F. In Silico Platform for Evaluation of Constrained Reconstruciton in DCE-MRI. In Proceedings of the Joint Annual Meeting of the ISMRM-ESMRMB 2018, Paris, France, 16–21 June 2018; p. 4338. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Henze Bancroft, L.; Jimenez, J.E.; van der Kolk, A.; Field, A.; Ahmed, A.; Strigel, R.; Block, W.F. Brain Tumor Simulator: Creating Ground Truth for Evaluation of Complex MR Acquisition and Reconstruction Methodologies. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 27th Annual Meeting & Exhibition 2019, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–16 May 2019; p. 898. [Google Scholar]
- Henze, L.C.; Moran, C.J.; Smith, M.R.; Kelcz, F.; Samsonov, A.; Fain, S.B.; Block, W.F. Digital Breast Phantom for Evaluating Dynamic Accelerated Imaging Methods. In Proceedings of the Joint Annual Meeting of the ISMRM-ESMRMB 2010, Stockholm, Sweden, 1–7 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB; R2018b; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2018.
- Kuhl, C.K.; Bieling, H.B.; Gieseke, J.; Kreft, B.P.; Sommer, T.; Lutterbey, G.; Schild, H.H. Healthy premenopausal breast parenchyma in dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast: Normal contrast medium enhancement and cyclical-phase dependency. Radiology 1997, 203, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, V.; Brooks, J.D.; Bernstein, J.L.; Reiner, A.S.; Pike, M.C.; Morris, E.A. Background parenchymal enhancement at breast MR imaging and breast cancer risk. Radiology 2011, 260, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giess, C.S.; Yeh, E.D.; Raza, S.; Birdwell, R.L. Background parenchymal enhancement at breast MR imaging: Normal patterns, diagnostic challenges, and potential for false-positive and false-negative interpretation. Radiographics 2014, 34, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greengard, L.; Lee, J.Y. Accelerating the nonuniform fast Fourier transform. Siam. Rev. 2004, 46, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrara, M. NUFFT, NFFT, USFFT. Available online: http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/25135-nufft--nfft--usfft (accessed on 1 October 2014).
- Fessler, J.A. On NUFFT-based gridding for non-Cartesian MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 188, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foo, T.K.; Sawyer, A.M.; Faulkner, W.H.; Mills, D.G. Inversion in the steady state: Contrast optimization and reduced imaging time with fast three-dimensional inversion-recovery-prepared GRE pulse sequences. Radiology 1994, 191, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, W. Simple proton spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 1984, 153, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, S.; Wen, Z.; Yu, H.; Pineda, A.; Gold, G.; Markl, M.; Pelc, N. Multicoil Dixon chemical species separation with an iterative least-squares estimation method. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 51, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.B.; Song, Y.C.; Park, D.J. Adaptive template filtering for signal-to-noise ratio enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bydder, M.; Girard, O.; Hamilton, G. Mapping the double bonds in triglycerides. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 29, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakow-Penner, R.; Daniel, B.; Yu, H.; Sawyer-Glover, A.; Glover, G.H. Relaxation times of breast tissue at 1.5T and 3T measured using IDEAL. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 23, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.; Henze Bancroft, L.C.; Hernando, D.; Zea, R.; Reeder, S.B.; Strigel, R.M. Gradient tracing for semiautomatic full breast segmentation of low resolution, low contrast breast MR images. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 25th Annual Meeting & Exhibition 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 26 April 2017; p. 2131. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, S.; Querleux, B.; Bittoun, J.; Idy-Peretti, I.; Jolivet, O.; Cermakova, E.; Leveque, J.L. In vivo proton relaxation times analysis of the skin layers by magnetic resonance imaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, G.E.; Han, E.; Stainsby, J.; Wright, G.; Brittain, J.; Beaulieu, C. Musculoskeletal MRI at 3.0 T: Relaxation times and image contrast. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 183, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboriak, D.P.; MacFall, J.R.; Viglianti, B.L.; Dewhirst Dvm, M.W. Comparison of three physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models for the prediction of contrast agent distribution measured by dynamic MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Jentoft, M.E.; Murray, D.L.; Thielen, K.R.; Williamson, E.E.; Eckel, L.J. Intracranial Gadolinium Deposition after Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging. Radiology 2015, 275, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.H.; Yin, F.F.; Segars, W.P.; Chang, Z.; Ren, L. Development of a Computerized 4-D MRI Phantom for Liver Motion Study. Technol. Cancer Res. Trans. 2017, 16, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.N.; Strigel, R.M.; Fischer, A.; Wang, K.; Velikina, J.V.; Korosec, F.R.; Cashen, T.A.; Johnson, K.M.; Holmes, J.H. Comparison of Radial and Cartesian Acquisitions in Breast MRI for Improved Visualization of the Axilla. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 25th ISMRM Scientific Meeting 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–27 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.N.; Velikina, J.; Samsonov, A.; Estkowski, L.; Cashen, T.A.; Kelcz, F.; Strigel, R.; Korosec, F.R.; Erson, A.; Holmes, J.H. Feasibility of respiratory self-gated free breathing supine breast DCE-MRI using data-driven model consistency condition reconstruction. In Proceedings of the ISMRM & SMRT Annual Meeting and Exhibition 2021, Online, 15–20 May 2021. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henze Bancroft, L.; Holmes, J.; Bosca-Harasim, R.; Johnson, J.; Wang, P.; Korosec, F.; Block, W.; Strigel, R. An Anthropomorphic Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Simulation and Analysis of Breast DCE MRI Techniques. Tomography 2022, 8, 1005-1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020081
Henze Bancroft L, Holmes J, Bosca-Harasim R, Johnson J, Wang P, Korosec F, Block W, Strigel R. An Anthropomorphic Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Simulation and Analysis of Breast DCE MRI Techniques. Tomography. 2022; 8(2):1005-1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020081
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenze Bancroft, Leah, James Holmes, Ryan Bosca-Harasim, Jacob Johnson, Pingni Wang, Frank Korosec, Walter Block, and Roberta Strigel. 2022. "An Anthropomorphic Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Simulation and Analysis of Breast DCE MRI Techniques" Tomography 8, no. 2: 1005-1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020081
APA StyleHenze Bancroft, L., Holmes, J., Bosca-Harasim, R., Johnson, J., Wang, P., Korosec, F., Block, W., & Strigel, R. (2022). An Anthropomorphic Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Simulation and Analysis of Breast DCE MRI Techniques. Tomography, 8(2), 1005-1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020081





