IRIS—Intelligent Rapid Interactive Segmentation for Measuring Liver Cyst Volumes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Intelligent Rapid Interactive Segmentation (IRIS) Method and Implementation
2.2. Patient Population
2.3. Data Analysis
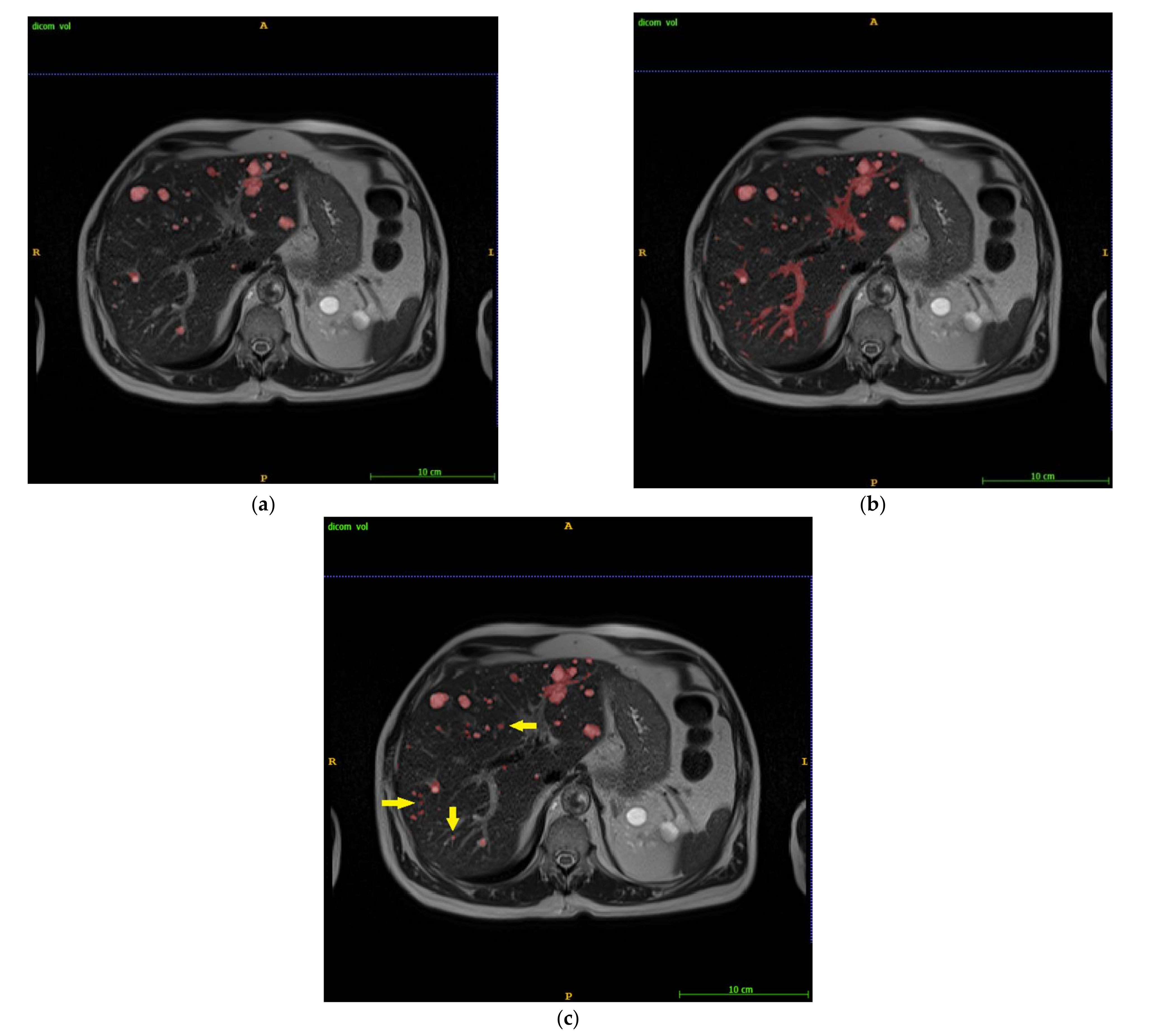
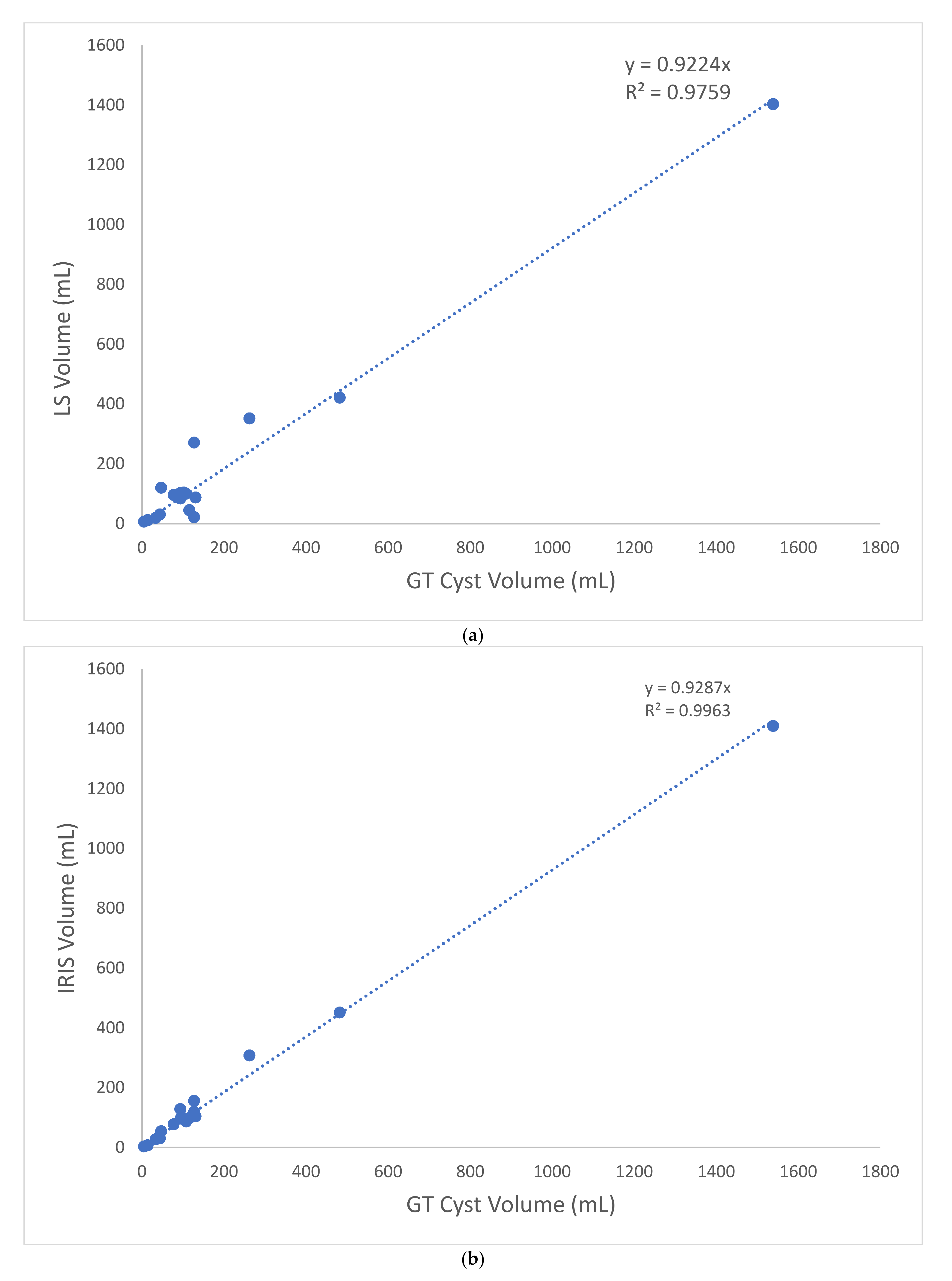
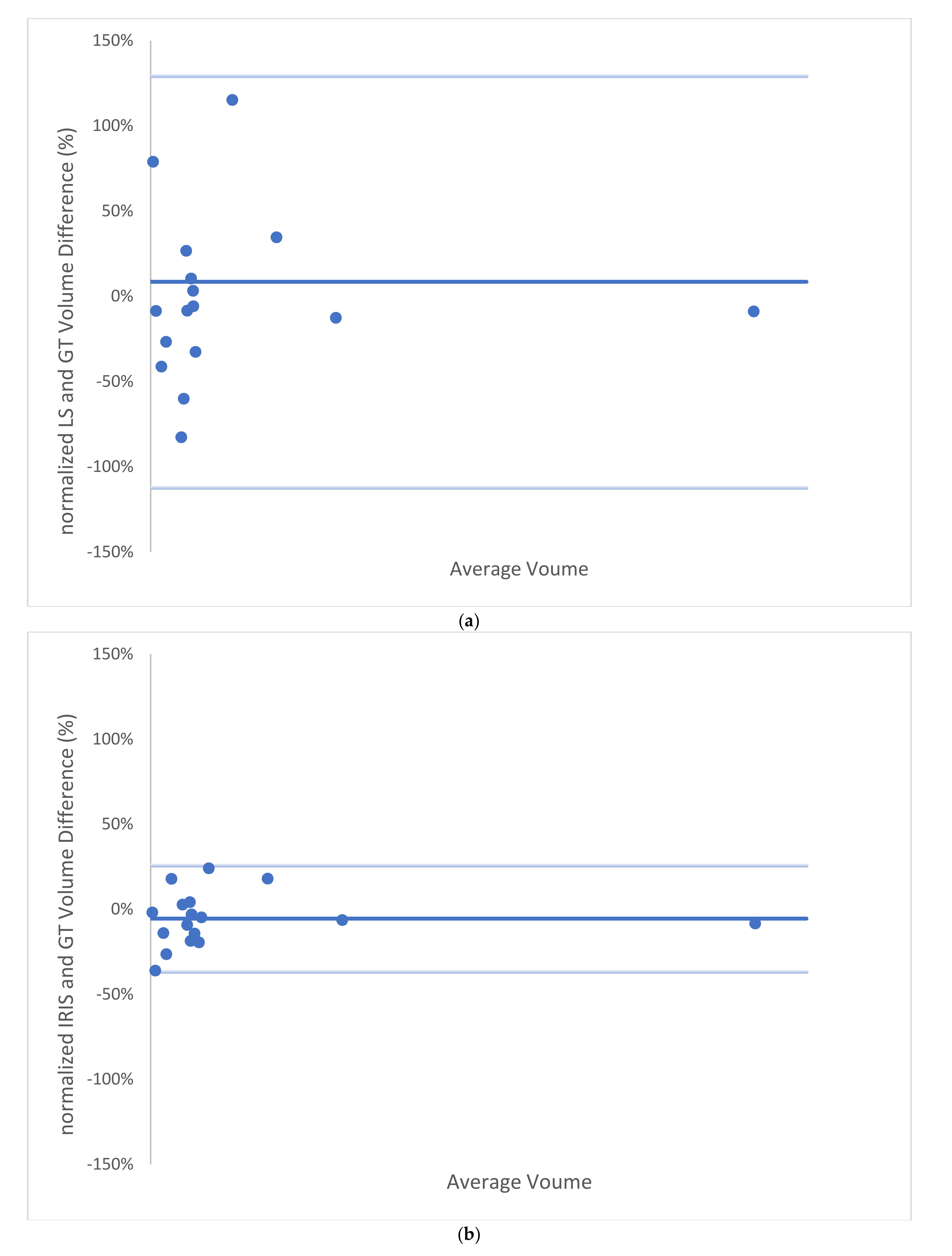
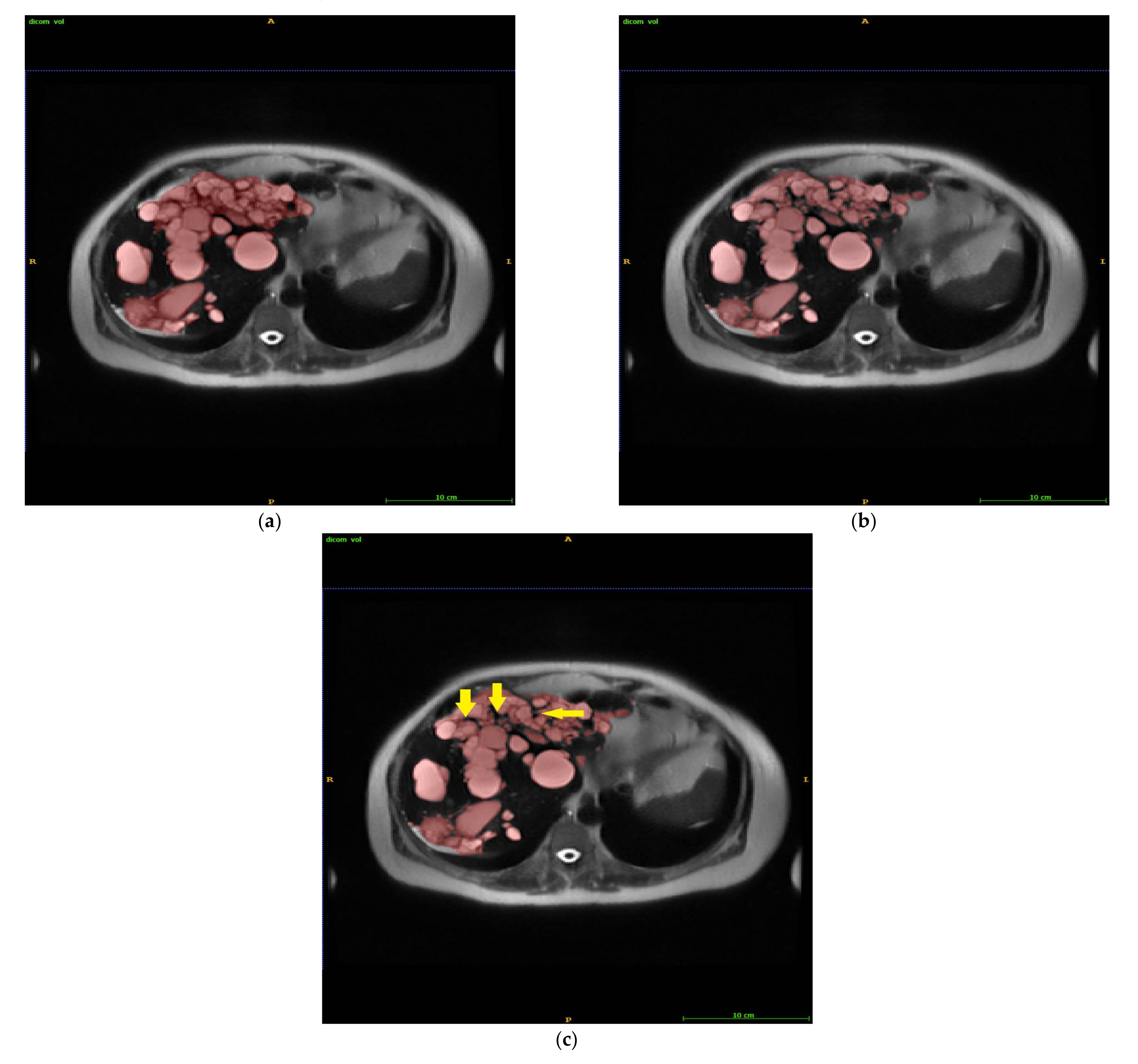
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cnossen, W.R.; Drenth, J.P.H. Polycystic liver disease: An overview of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Keimpema, L.; De Koning, D.B.; Van Hoek, B.; Van Den Berg, A.P.; Van Oijen, M.G.; De Man, R.A.; Nevens, F.; Drenth, J.P. Patients with isolated polycystic liver disease referred to liver centres: Clinical characterization of 137 cases. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, S.; Ando, M.; Nishio, S.; Hanaoka, K.; Ubara, Y.; Narita, I.; Kamura, K.; Mochizuki, T.; Tsuchiya, K.; Tsuruya, K.; et al. The relationship between liver cyst volume and QOL in Japanese ADPKD patients. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, F.; Nordenskjold, R.; Strand, R.; Kullberg, J. SmartPaint: A tool for interactive segmentation of medical volume images. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng.-Imaging Vis. 2017, 5, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Bae, S.K.; Cheng, T.; Tao, C.; Ge, Y.; Chapman, A.B.; Torres, V.E.; Yu, A.S.L.; Mrug, M.; Bennett, W.M.; et al. Automated segmentation of liver and liver cysts from bounded abdominal MR images in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 7864–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farooq, Z.; Behzadi, A.H.; Blumenfeld, J.D.; Zhao, Y.; Prince, M.R. Comparison of MRI segmentation techniques for measuring liver cyst volumes in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin. Imaging 2018, 47, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutasa, S.; Varada, S.; Goel, A.; Wong, T.T.; Rasiej, M.J. Advanced Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Automated Femoral Neck Fracture Detection and Classification. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codella, N.C.F.; Weinsaft, J.W.; Cham, M.D.; Janik, M.; Prince, M.R.; Wang, Y. Left Ventricle: Automated Segmentation by Using Myocardial Effusion Threshold Reduction and Intravoxel Computation at MR Imaging. Radiology 2008, 248, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codella, N.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Fieno, D.S.; Chen, D.W.; Hurtado-Rua, S.; Kochar, M.; Finn, J.P.; Judd, R.; Goyal, P.; Schenendorf, J.; et al. Improved left ventricular mass quantification with partial voxel interpolation: In vivo and necropsy validation of a novel cardiac MRI segmentation algorithm. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.A.; Blumenfeld, J.D.; Chhabra, S.; Dutruel, S.P.; Thimmappa, N.D.; Bobb, W.O.; Donahue, S.; Rennert, H.E.; Tan, A.Y.; Giambrone, A.E.; et al. Pancreatic Cysts in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Prevalence and Association with PKD2 Gene Mutations. Radiology 2016, 280, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montagnon, E.; Cerny, M.; Cadrin-Chênevert, A.; Hamilton, V.; Derennes, T.; Ilinca, A.; Vandenbroucke-Menu, F.; Turcotte, S.; Kadoury, S.; Tang, A. Deep learning workflow in radiology: A primer. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, K.; Jiang, B.; Shang, D. The overview of the deep learning integrated into the medical imaging of liver: A review. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Frimmel, H.; Smedby, Ö. Fast level-set based image segmentation using coherent propagation. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 073501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoogi, A.; Subramaniam, A.; Veerapaneni, R.; Rubin, D.L. Adaptive Estimation of Active Contour Parameters Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Texture Analysis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatos, I.; Tsantis, S.; Karamesini, M.; Spiliopoulos, S.; Karnabatidis, D.; Hazle, J.D.; Kagadis, G.C. Focal liver lesions segmentation and classification in nonenhanced T2-weighted MRI. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 3695–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Grist, T.M.; Korosec, F.R.; Christy, P.S.; Alley, M.T.; Polzin, J.A.; Mistretta, C.A. Respiratory Blur in 3D Coronary MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 33, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ehman, R.L. Retrospective adaptive motion correction for navigator-gated 3D coronary MR angiography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 11, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spincemaille, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Prince, M.R.; Wang, Y. Kalman filtering for real-time navigator processing. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rossman, P.J.; Grimm, R.C.; Wilman, A.H.; Riederer, S.J.; Ehman, R.L. 3D MR angiography of pulmonary arteries using realtime navigator gating and magnetization preparation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saake, M.; Seuß, H.; Riexinger, A.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Hammon, M.; Uder, M.; Laun, F.B. Image Quality and Detection of Small Focal Liver Lesions in Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Comparison of Navigator Tracking and Free-Breathing Acquisition. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilligan, L.A.; Dillman, J.R.; Tkach, J.A.; Trout, A.T. Comparison of navigator-gated and breath-held image acquisition techniques for multi-echo quantitative dixon imaging of the liver in children and young adults. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motosugi, U.; Hernando, D.; Bannas, P.; Holmes, J.H.; Wang, K.; Shimakawa, A.; Iwadate, Y.; Taviani, V.; Rehm, J.L.; Reeder, S.B. Quantification of liver fat with respiratory-gated quantitative chemical shift encoded MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokuda, J.; Morikawa, S.; Dohi, T.; Hata, N. Motion tracking in MR-guided liver therapy by using navigator echoes and projection profile matching. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 11, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Senan, R.; Newhouse, J. CT Volumetry of Convoluted Objects—A Simple Method Using Volume Averaging. Tomography 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Time (s) | GT | LS | IRIS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 2159 | 6 | 202 |
| Median | 2145 | 5 | 187 |
| [Min, Max] | [293, 5427] | [2, 28] | [75, 338] |
| STD | 1312 | 6 | 84 |
| Dice Score | GT—LS | GT—IRIS |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 63.1% | 79.0% |
| Median | 63.8% | 81.0% |
| [Min, Max] | [29.7%, 90.5%] | [58.2%, 93.5%] |
| STD | 18.0% | 9.2% |
| Metric | |VGT−VLS|/VGT | |VGT−VIRIS|/VGT |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 42.22% | 13.44% |
| Median | 26.84% | 13.87% |
| [Min, Max] | [3.34%, 161.58%] | [1.74%, 35.90%] |
| STD | 44.49% | 9.70% |
| Metric | LS | IRIS |
|---|---|---|
| ICC | 98.91% | 99.54% |
| RMSE | 66.4 mL | 35.9 mL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Romano, D.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, H.; Prince, M.R.; Wang, Y. IRIS—Intelligent Rapid Interactive Segmentation for Measuring Liver Cyst Volumes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Tomography 2022, 8, 447-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010037
Li C, Romano D, Wang SJ, Zhang H, Prince MR, Wang Y. IRIS—Intelligent Rapid Interactive Segmentation for Measuring Liver Cyst Volumes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Tomography. 2022; 8(1):447-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Collin, Dominick Romano, Sophie J. Wang, Hang Zhang, Martin R. Prince, and Yi Wang. 2022. "IRIS—Intelligent Rapid Interactive Segmentation for Measuring Liver Cyst Volumes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease" Tomography 8, no. 1: 447-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010037
APA StyleLi, C., Romano, D., Wang, S. J., Zhang, H., Prince, M. R., & Wang, Y. (2022). IRIS—Intelligent Rapid Interactive Segmentation for Measuring Liver Cyst Volumes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Tomography, 8(1), 447-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010037







