Correlations of Lumbar Interspinous Distance with Neuroforaminal Dimensions, Disc Space Height, and Patient Demographic Factors
Abstract
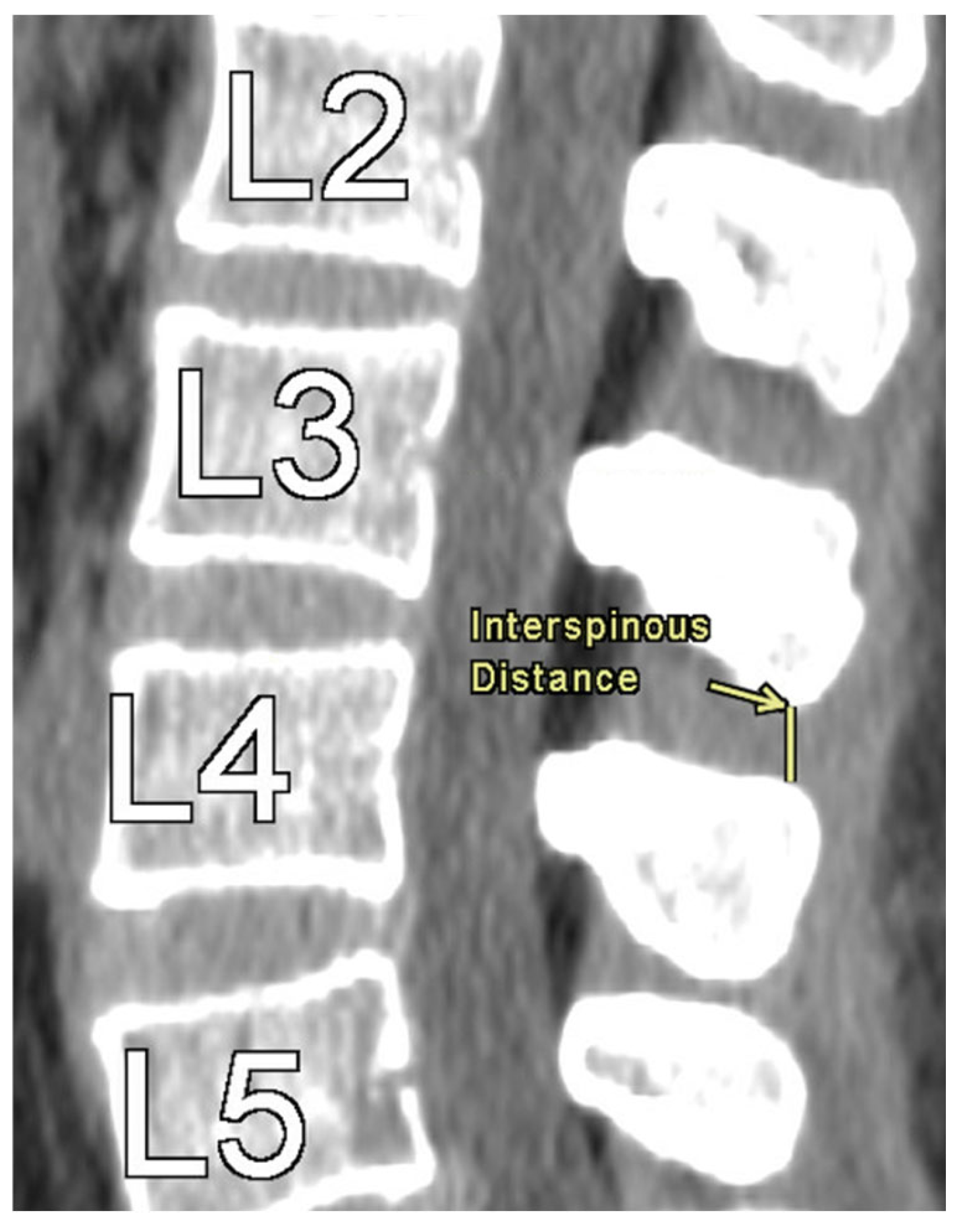
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ISD | Interspinous Distance |
| DSH | Disc Space Height |
| NFD | Neuroforaminal Dimension |
| AP | Anterior–Posterior |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
Appendix A
| Level | Mean (mm) | SD |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | 11.91 | 3.47 |
| L2 | 10.29 | 3.14 |
| L3 | 7.76 | 2.95 |
| L4 | 6.08 | 2.55 |
| L5 | 6.21 | 2.8 |
| Level | Variable | Mean (mm) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Anterior DSH | 5.54 | 1.75 |
| Middle DSH | 6.63 | 1.35 | |
| Posterior DSH | 3.15 | 1.19 | |
| L2 | Anterior DSH | 6.46 | 1.81 |
| Middle DSH | 8.02 | 1.58 | |
| Posterior DSH | 4.13 | 1.27 | |
| L3 | Anterior DSH | 7.71 | 1.86 |
| Middle DSH | 8.94 | 1.57 | |
| Posterior DSH | 4.73 | 1.40 | |
| L4 | Anterior DSH | 9.19 | 2.06 |
| Middle DSH | 9.43 | 1.69 | |
| Posterior DSH | 4.91 | 1.53 | |
| L5 | Anterior DSH | 10.68 | 2.71 |
| Middle DSH | 8.24 | 1.97 | |
| Posterior DSH | 3.80 | 1.45 |
| Level/Side | Variable | Mean (mm) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 Left | Axial AP Width | 9.20 | 2.07 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 17.53 | 2.23 | |
| Foraminal Area | 129.71 | 31.37 | |
| L1 Right | Axial AP Width | 9.19 | 2.04 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 17.46 | 2.22 | |
| Foraminal Area | 130.63 | 31.45 | |
| L2 Left | Axial AP Width | 8.93 | 1.90 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 18.63 | 2.20 | |
| Foraminal Area | 139.79 | 33.98 | |
| L2 Right | Axial AP Width | 9.04 | 1.97 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 18.64 | 2.33 | |
| Foraminal Area | 141.38 | 33.85 | |
| L3 Left | Axial AP Width | 8.74 | 1.92 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 18.73 | 2.39 | |
| Foraminal Area | 140.13 | 33.97 | |
| L3 Right | Axial AP Width | 8.73 | 1.87 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 18.54 | 2.38 | |
| Foraminal Area | 139.46 | 34.20 | |
| L4 Left | Axial AP Width | 8.09 | 1.89 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 18.06 | 2.55 | |
| Foraminal Area | 131.79 | 32.20 | |
| L4 Right | Axial AP Width | 8.10 | 2.00 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 17.80 | 2.37 | |
| Foraminal Area | 130.44 | 30.88 | |
| L5 Left | Axial AP Width | 8.23 | 2.33 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 15.63 | 2.65 | |
| Foraminal Area | 118.04 | 31.09 | |
| L5 Right | Axial AP Width | 8.51 | 2.37 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 15.55 | 2.63 | |
| Foraminal Area | 119.85 | 30.92 |
References
- Katz, J.N.; Zimmerman, Z.E.; Mass, H.; Makhni, M.C. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albietz, J.S.; Rosasarellano, P.; Fleming, J.C.; Gurr, K.R.; Bailey, S.I.; Bailey, C.S. An Anatomic Study of the Interspinous Space of the Lumbosacral Spine. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.; Wang, Y.; Kärrholm, J.; Malchau, H.; Nordwall, A. Determination of Inter-Spinous Process Distance in the Lumbar Spine. Eur. Spine J. 1999, 8, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzouk, J.; Vyhmeister, E.; Carter, D.; Sajdak, G.; Nguyen, K.; Carter, M.; Kagabo, W.; Ramos, O.; Wycliffe, N.; Cheng, W.; et al. Normative Measurements of L1 to S1 Neuroforaminal Dimensions Derived From Plain Film Radiography, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Spine 2024, 49, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, K.; Ford, J.; Foley, R.; Januszewski, J.; Murtagh, R.; Decker, S.; Uribe, J.S. Morphometric Analysis of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Height: An Imaging Study. World Neurosurg. 2019, 124, e106–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Vyhmeister, E.; Im, D.; Fay, A.; Faehner, O.; Cabrera, A.; Bouterse, A.; Seo, L.; Bedward, D.; Carter, M.; et al. Lumbar Disc Space Height in Relation to Neural Foraminal Dimensions and Patient Characteristics: A Morphometric Analysis from L1-S1 Using Computed Tomography. Brain Spine 2024, 5, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobottke, R.; Schlüter-Brust, K.; Kaulhausen, T.; Röllinghoff, M.; Joswig, B.; Stützer, H.; Eysel, P.; Simons, P.; Kuchta, J. Interspinous Implants (X Stop®, Wallis®, Diam®) for the Treatment of LSS: Is There a Correlation between Radiological Parameters and Clinical Outcome? Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, G.; Giambartino, F.; Iacopino, D.G. Clinical Analysis Following Lumbar Interspinous Devices Implant: Where We Are and Where We Go. Spinal Cord 2014, 52, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hida, K.; Seki, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Minoru, A. An Interspinous Process Distractor (X STOP) for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis in Elderly Patients: Preliminary Experiences in 10 Consecutive Cases. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2004, 17, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harianja, G.; Razzouk, J.; Lindsey, W.; Urbina, B.; Cabrera, A.; Thomas, L.; Bouterse, A.; Wycliffe, N.; Cheng, W.; Danisa, O. Anatomic Assessment of L1-S1 Neuroforaminal Dimensions Using Computed Tomography. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2023, 105, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Shin, B.; Brandt, Z.; Nguyen, K.; Battikha, A.; Carter, D.; Carter, M.; Razzouk, J.; Wycliffe, N.; Cheng, W.; et al. Morphometric Analysis of Cervical Disc Space Height and Interpedicular Distance Using Computed Tomography. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2024, 15, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzouk, J.; Case, T.; Vyhmeister, E.; Nguyen, K.; Carter, D.; Carter, M.; Sajdak, G.; Kricfalusi, M.; Taylor, R.; Bedward, D.; et al. Morphometric Analysis of Cervical Neuroforaminal Dimensions from C2–T1 Using Computed Tomography of 1,000 Patients. Spine J. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancey, C.; Reidy, J. Statistics Without Maths for Psychology, 4th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, S.M.R.; Gupta, S.R.; Casey, A.T.H. Lumbar Interspinous Spacers: A Systematic Review of Clinical and Biomechanical Evidence. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010, 35, E1499–E1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poetscher, A.W.; Gentil, A.F.; Ferretti, M.; Lenza, M. Interspinous Process Devices for Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Spine Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Teng, H. The Correlation between Lumbar Interlaminar Space Size on Plain Radiograph and Spinal Stenosis. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinotti, G.; De Santis, P.; Nofroni, I.; Postacchini, F. Stenosis of Lumbar Intervertebral Foramen: Anatomic Study on Predisposing Factors. Spine 2002, 27, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Been, E.; Barash, A.; Pessah, H.; Peleg, S. A New Look at the Geometry of the Lumbar Spine. Spine 2010, 35, E1014–E1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.D.; Shaw, D.L.; Cooperman, D.R.; Eubanks, J.D.; Li, L.; Kim, D.H. Characterization of Lumbar Spinous Process Morphology: A Cadaveric Study of 2,955 Human Lumbar Vertebrae. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya Ayvaz, D.; Kervancıoğlu, P.; Bahşi, A.; Bahşi, İ. A Radiological Evaluation of Lumbar Spinous Processes and Interspinous Spaces, Including Clinical Implications. Cureus 2021, 13, e19454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, J.; Fornaciari, P.; Senteler, M.; Roth, T.; Snedeker, J.G.; Farshad, M. Kinematics of the Spine Under Healthy and Degenerative Conditions: A Systematic Review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 1491–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Been, E.; Li, L.; Hunter, D.J.; Kalichman, L. Geometry of the Vertebral Bodies and the Intervertebral Discs in Lumbar Segments Adjacent to Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis: Pilot Study. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganau, M.; Ennas, F.; Bellisano, G.; Ganau, L.; Ambu, R.; Faa, G.; Maleci, A. Synovial Cysts of the Lumbar Spine—Pathological Considerations and Surgical Strategy. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2013, 53, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, G.E.; Morone, N.; Weiner, D.K. Degenerative Lumbar Disc and Facet Disease in Older Adults. Spine 2009, 34, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Level | Measurements | ρ (Spearman’s Correlation) | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| L1 | Anterior Disc Space Height | 0.02 | −0.06 | 0.11 | 0.56 |
| Middle Disc Space Height | −0.03 | −0.11 | 0.05 | 0.46 | |
| Posterior Disc Space Height | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.07 | |
| L2 | Anterior Disc Space Height | −0.05 | −0.12 | 0.04 | 0.26 |
| Middle Disc Space Height | −0.11 | −0.19 | −0.02 | <0.01 | |
| Posterior Disc Space Height | 0.07 | −0.01 | 0.15 | 0.09 | |
| L3 | Anterior Disc Space Height | 0.00 | −0.08 | 0.08 | 0.97 |
| Middle Disc Space Height | −0.01 | −0.09 | 0.07 | 0.85 | |
| Posterior Disc Space Height | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| L4 | Anterior Disc Space Height | −0.01 | −0.09 | 0.07 | 0.77 |
| Middle Disc Space Height | 0.01 | −0.07 | 0.09 | 0.78 | |
| Posterior Disc Space Height | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| L5 | Anterior Disc Space Height | −0.18 | −0.25 | −0.10 | <0.01 |
| Middle Disc Space Height | −0.13 | −0.21 | −0.04 | <0.01 | |
| Posterior Disc Space Height | −0.05 | −0.13 | 0.04 | 0.26 | |
| Level | Measurements | ρ (Spearman’s Correlation) | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| L1 Left | Axial AP Width | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.21 | <0.01 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.26 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.33 | <0.01 | |
| L1 Right | Axial AP Width | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.20 | <0.01 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.25 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.35 | <0.01 | |
| L2 Left | Axial AP Width | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.24 | <0.01 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.22 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.27 | <0.01 | |
| L2 Right | Axial AP Width | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.24 | <0.01 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.23 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.28 | <0.01 | |
| L3 Left | Axial AP Width | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0.26 | <0.01 | |
| L3 Right | Axial AP Width | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.08 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.24 | <0.01 | |
| L4 Left | Axial AP Width | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.05 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.21 | <0.01 | |
| L4 Right | Axial AP Width | 0.07 | −0.01 | 0.15 | 0.10 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.24 | <0.01 | |
| L5 Left | Axial AP Width | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.20 | <0.01 |
| Craniocaudal Height | 0.03 | −0.05 | 0.11 | 0.46 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.22 | <0.01 | |
| L5 Right | Axial AP Width | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.19 | <0.01 |
| Craniocaudal Height | −0.03 | −0.11 | 0.05 | 0.47 | |
| Foraminal Area | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.25 | <0.01 | |
| Level | Caucasian | Hispanic/Latino | African American | Asian | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | ||
| L1 | 12.60 | 5.08 | 11.70 | 4.60 | 10.70 | 5.08 | 12.45 | 2.83 | 0.01 |
| L2 | 10.50 | 4.40 | 10.30 | 4.00 | 9.45 | 5.58 | 11.00 | 6.00 | 0.04 |
| L3 | 7.20 | 4.30 | 7.50 | 3.65 | 6.65 | 4.68 | 7.75 | 3.48 | 0.18 |
| L4 | 5.70 | 3.40 | 5.80 | 3.20 | 4.95 | 3.85 | 6.00 | 3.50 | 0.16 |
| L5 | 5.80 | 3.30 | 5.80 | 3.20 | 5.05 | 3.43 | 6.20 | 4.10 | 0.41 |
| Comparison Groups | Level | Hodges–Lehmann Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval | Adjusted p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| Asian VS Black | L1 | 1.10 | −0.50 | 2.80 | 1.00 |
| L2 | 1.90 | 0.10 | 3.60 | 0.17 | |
| Asian VS Hispanic/Latino | L1 | 0.30 | −1.00 | 1.50 | 1.00 |
| L2 | 0.70 | −0.70 | 2.20 | 1.00 | |
| Asian VS White | L1 | −0.50 | −2.00 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
| L2 | 0.50 | −1.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 | |
| Black VS Hispanic/Latino | L1 | −0.90 | −1.90 | 0.10 | 0.54 |
| L2 | −1.10 | −2.10 | −0.10 | 0.18 | |
| Black VS White | L1 | −1.80 | −2.90 | −0.70 | 0.01 |
| L2 | −1.40 | −2.40 | −0.30 | 0.05 | |
| Hispanic/Latino VS White | L1 | −0.80 | −1.50 | −0.20 | 0.06 |
| L2 | −0.30 | −0.80 | 0.30 | 1.00 | |
| Level | Female | Male | Hodges–Lehmann Estimator | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| L1 | 11.6 | 4.8 | 12.3 | 4.45 | −0.60 | −1.20 | −0.00003 | 0.04 |
| L2 | 10.2 | 4.2 | 10.5 | 4.65 | −0.40 | −0.90 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| L3 | 7.5 | 4.1 | 7.2 | 3.7 | 0.10 | −0.40 | 0.60 | 0.70 |
| L4 | 5.65 | 3.6 | 5.8 | 3.4 | −0.30 | −0.70 | 0.10 | 0.17 |
| L5 | 5.4 | 3.1 | 6 | 3.6 | −0.70 | −1.10 | −0.30 | <0.01 |
| Level | ρ (Spearman’s Correlation) | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| L1 | −0.09 | −0.17 | −0.003 | 0.051 |
| L2 | −0.07 | −0.15 | 0.02 | 0.14 |
| L3 | −0.001 | −0.09 | 0.09 | 0.98 |
| L4 | 0.07 | −0.02 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| L5 | −0.00002 | −0.08 | 0.09 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cummings, C.; Brandt, Z.; Nguyen, K.; Isaac, A.; Gutierrez, J.-C.; Kempf, A.; Cheng, D.; Carson, J.D.; Novak, E.; Razzouk, J.; et al. Correlations of Lumbar Interspinous Distance with Neuroforaminal Dimensions, Disc Space Height, and Patient Demographic Factors. Tomography 2025, 11, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11090100
Cummings C, Brandt Z, Nguyen K, Isaac A, Gutierrez J-C, Kempf A, Cheng D, Carson JD, Novak E, Razzouk J, et al. Correlations of Lumbar Interspinous Distance with Neuroforaminal Dimensions, Disc Space Height, and Patient Demographic Factors. Tomography. 2025; 11(9):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11090100
Chicago/Turabian StyleCummings, Carson, Zachary Brandt, Kai Nguyen, Asael Isaac, Jean-Carlos Gutierrez, Ashley Kempf, David Cheng, Joel D. Carson, Emily Novak, Jacob Razzouk, and et al. 2025. "Correlations of Lumbar Interspinous Distance with Neuroforaminal Dimensions, Disc Space Height, and Patient Demographic Factors" Tomography 11, no. 9: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11090100
APA StyleCummings, C., Brandt, Z., Nguyen, K., Isaac, A., Gutierrez, J.-C., Kempf, A., Cheng, D., Carson, J. D., Novak, E., Razzouk, J., Danisa, O., & Cheng, W. (2025). Correlations of Lumbar Interspinous Distance with Neuroforaminal Dimensions, Disc Space Height, and Patient Demographic Factors. Tomography, 11(9), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11090100






