Autoencoder-Assisted Stacked Ensemble Learning for Lymphoma Subtype Classification: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Introducing a novel hybrid pipeline combining a Convolutional Autoencoder (CAE) with a stacked ensemble classifier for robust subtype classification of lymphoma.
- Leveraging PCA-reduced unsupervised deep features from CAE to train multiple classifiers.
- Demonstrating superior diagnostic performance over conventional and deep learning baselines, achieving 99.04% accuracy and 0.9998 AUC.
- Highlighting clinical utility by integrating explainability into predictions.
Related Work
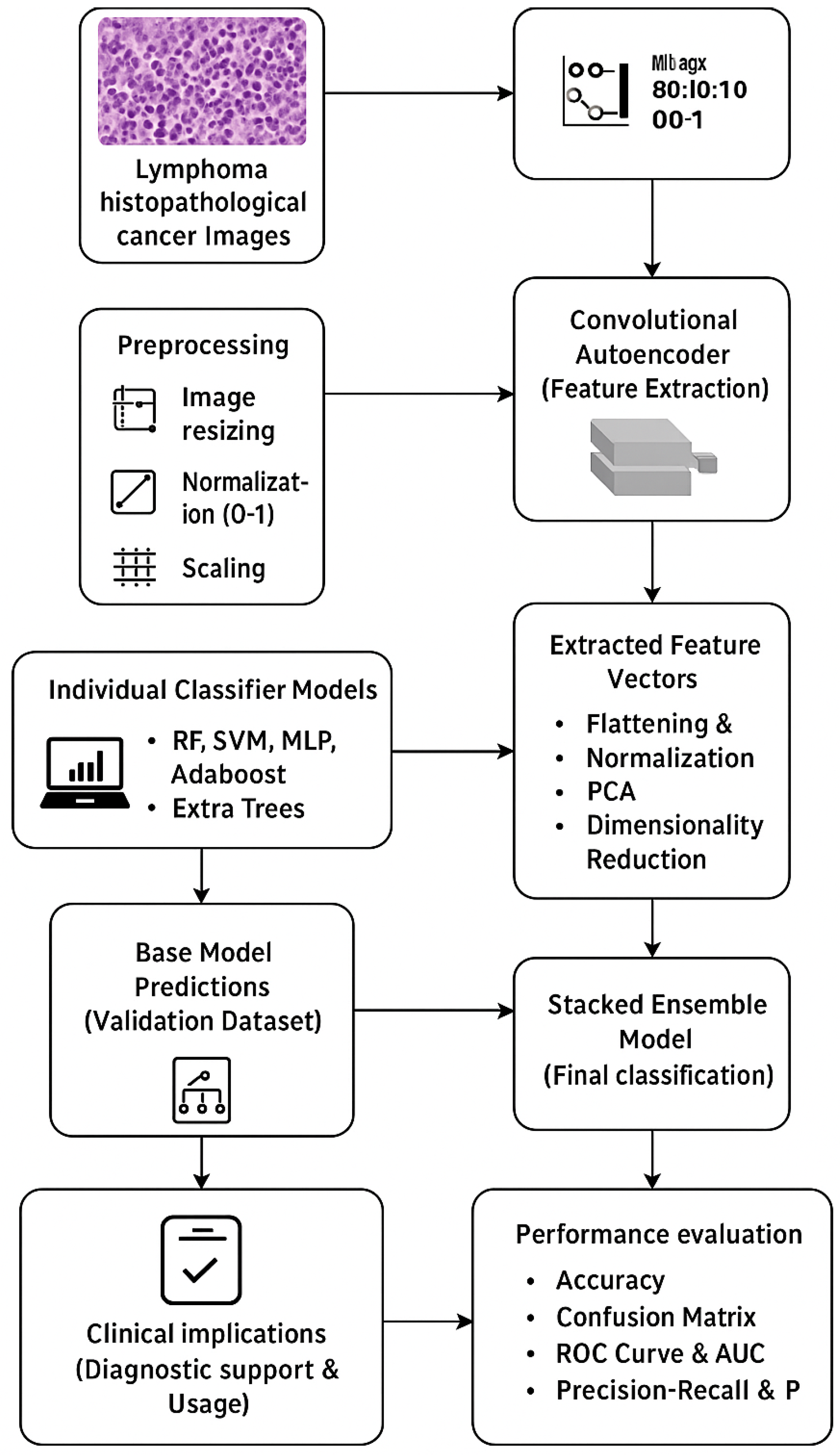
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Description and Preprocessing
2.2. Autoencoder-Based Feature Extraction
2.3. Dimensionality Reduction
2.4. Classification Models and Stacked Ensemble Learning
2.5. Stacked Ensemble Model
| #Step 1: Train Base Classifiers train_base_classifiers(X_train, y_train): RF = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=200, criterion=‘gini’).fit(X_train, y_train) SVM = SVC (kernel=‘rbf’, C=1.0, probability=True).fit(X_train, y_train) MLP = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(128, 64), activation=‘relu’, max_iter=500).fit(X_train, y_train) AdaBoost = AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=150, learning_rate=1.0).fit(X_train, y_train) ExtraTrees = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=150, criterion=‘entropy’).fit(X_train, y_train) return RF, SVM, MLP, AdaBoost, ExtraTrees # Step 2: Generate Meta-Features generate_meta_features(X_val, base_classifiers): meta_features = [] for clf in base_classifiers: meta_features.append(clf.predict_proba(X_val)) return np.hstack(meta_features) # Step 3: Train Meta-Classifier (GBM) train_meta_classifier(meta_features, y_val): GBM = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=150, learning_rate=0.05, max_depth=3) GBM.fit(meta_features, y_val) return GBM # Step 4: Final Prediction predict (X_test, base_classifiers, meta_classifier): meta_test_features = generate_meta_features(X_test, base_classifiers) return meta_classifier.predict(meta_test_features) # Execution Pipeline base_classifiers = train_base_classifiers(X_train, y_train) meta_features = generate_meta_features(X_val, base_classifiers) meta_classifier = train_meta_classifier(meta_features, y_val) y_pred = predict (X_test, base_classifiers, meta_classifier |
2.6. Training Strategy
2.7. Performance Evaluation
- Confusion Matrix: This is a table used to illustrate the performance of a classification model by indicating the number of true positive (TP), true negative (TN), false positive (FP), and false negative (FN) predictions [31].
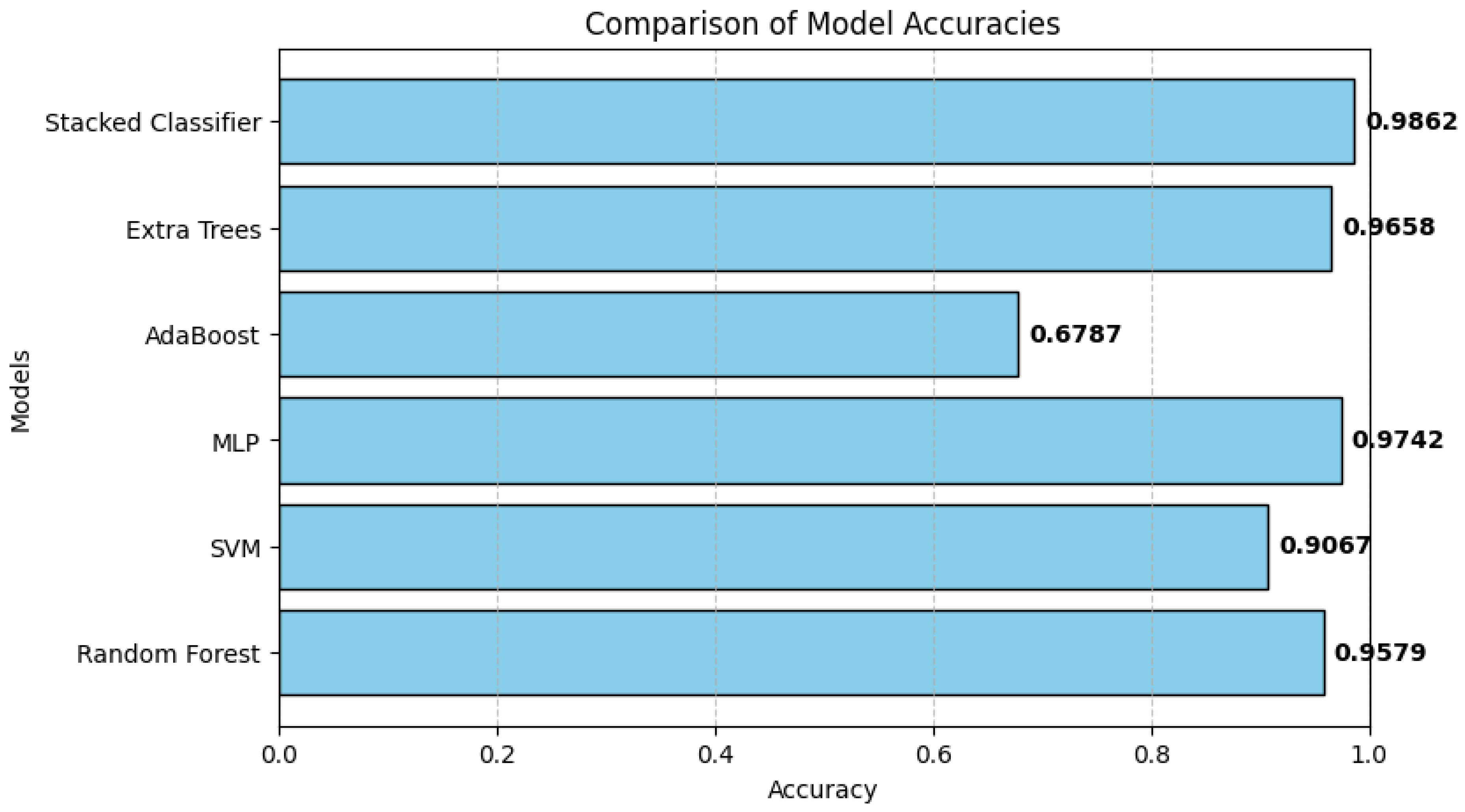
- Accuracy Score: Accuracy computes the proportion of instances correctly classified to the total number of instances. It is given as:
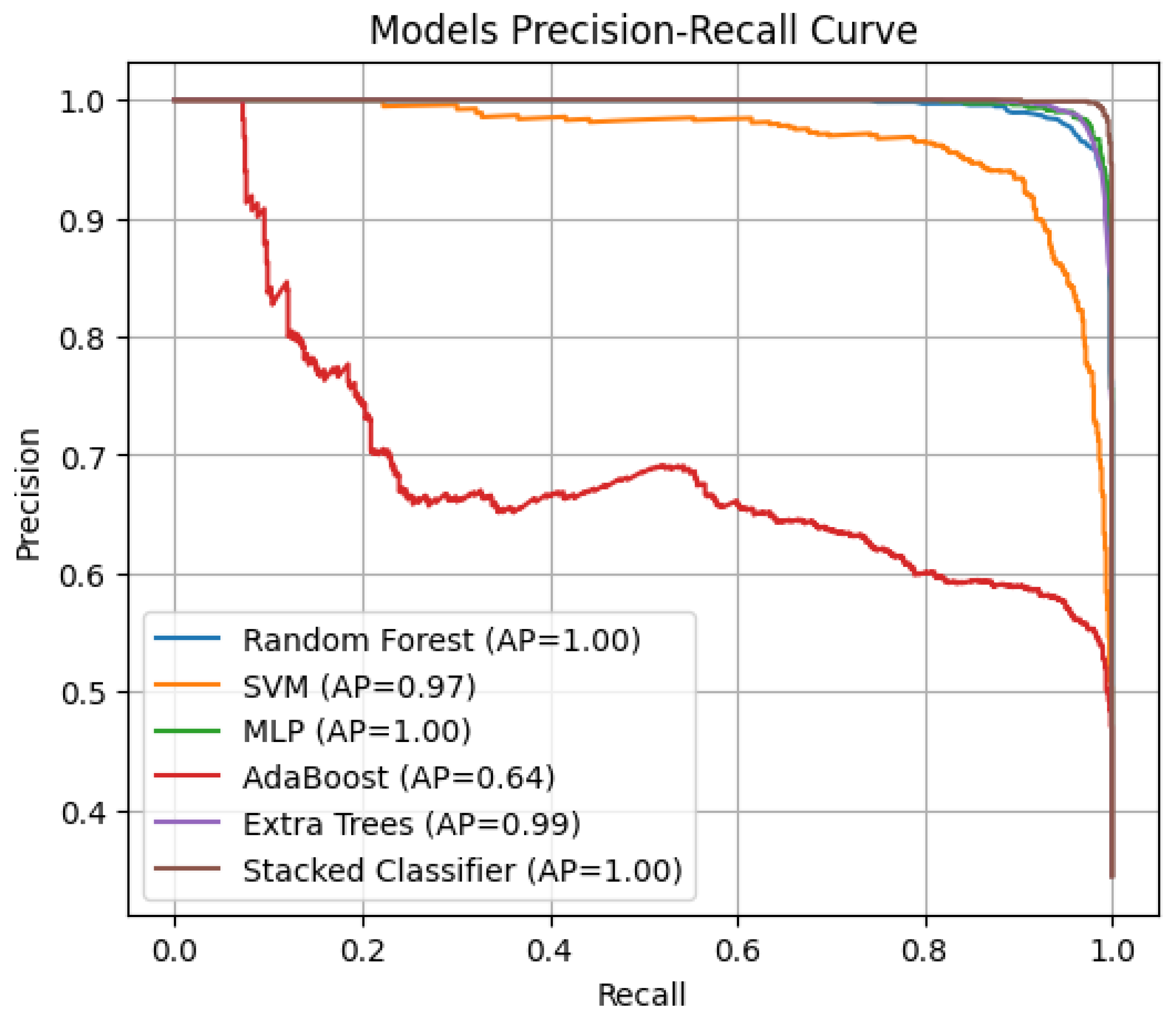
- Precision–Recall (PR) and Average Precision (AP): This plots precision vs. recall at different classification thresholds [31]).
2.8. Experimentation Setup
3. Results and Discussion
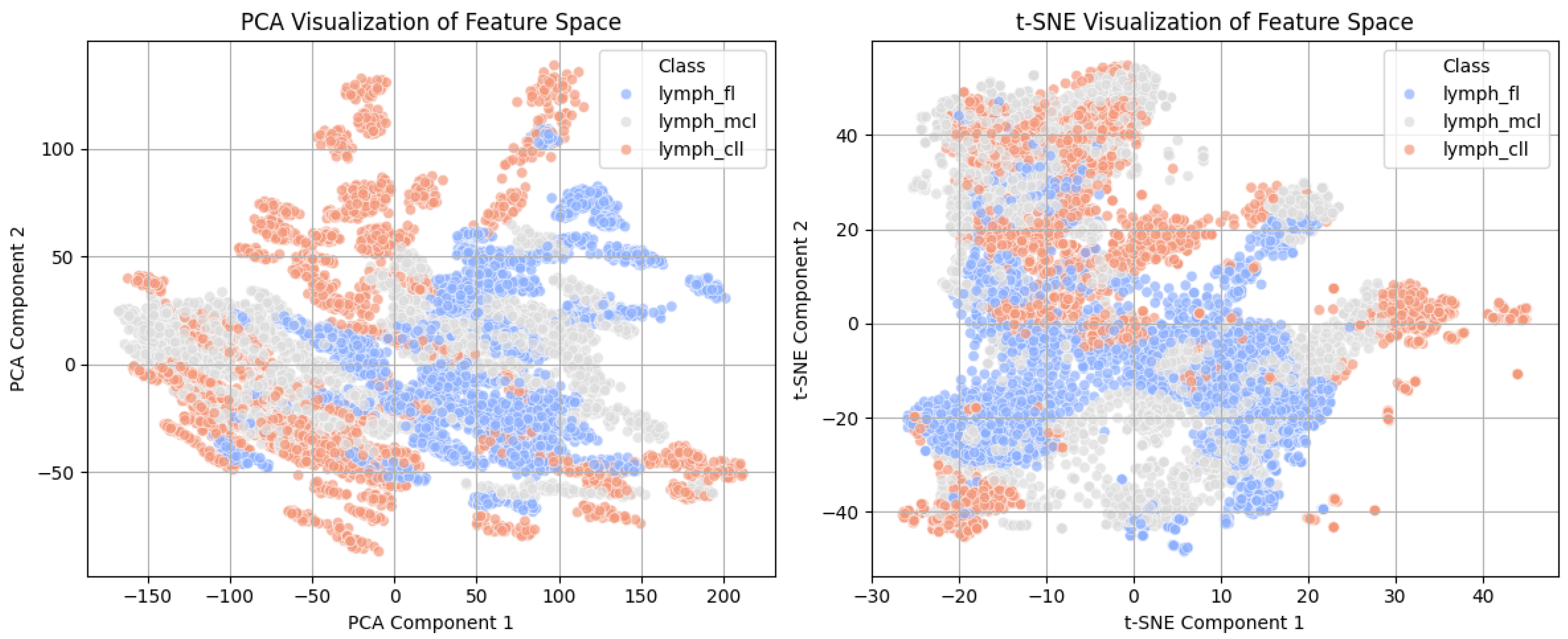
3.1. Feature Space Visualization Using PCA and t-SN
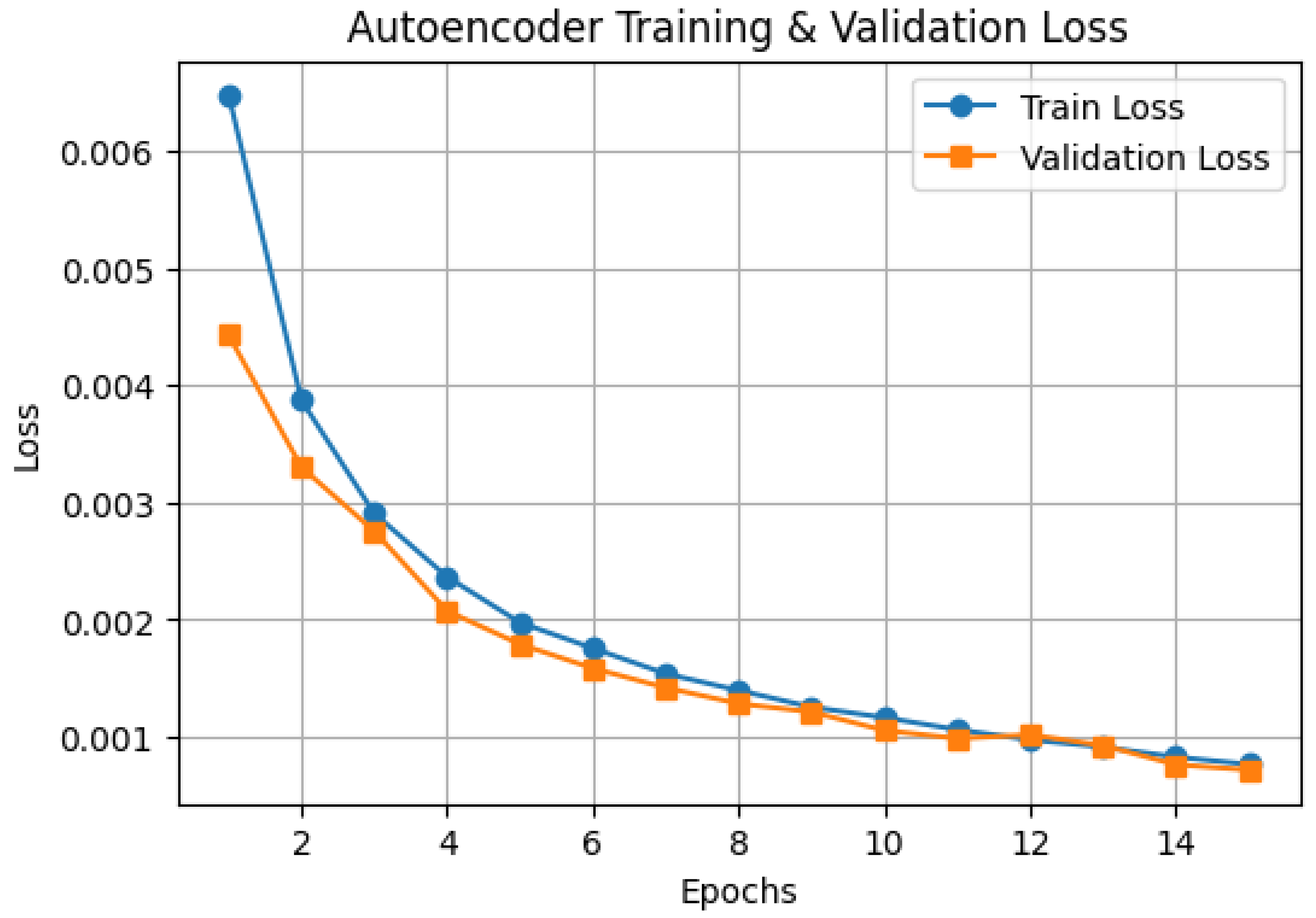
3.2. Autoencoder Training Performance
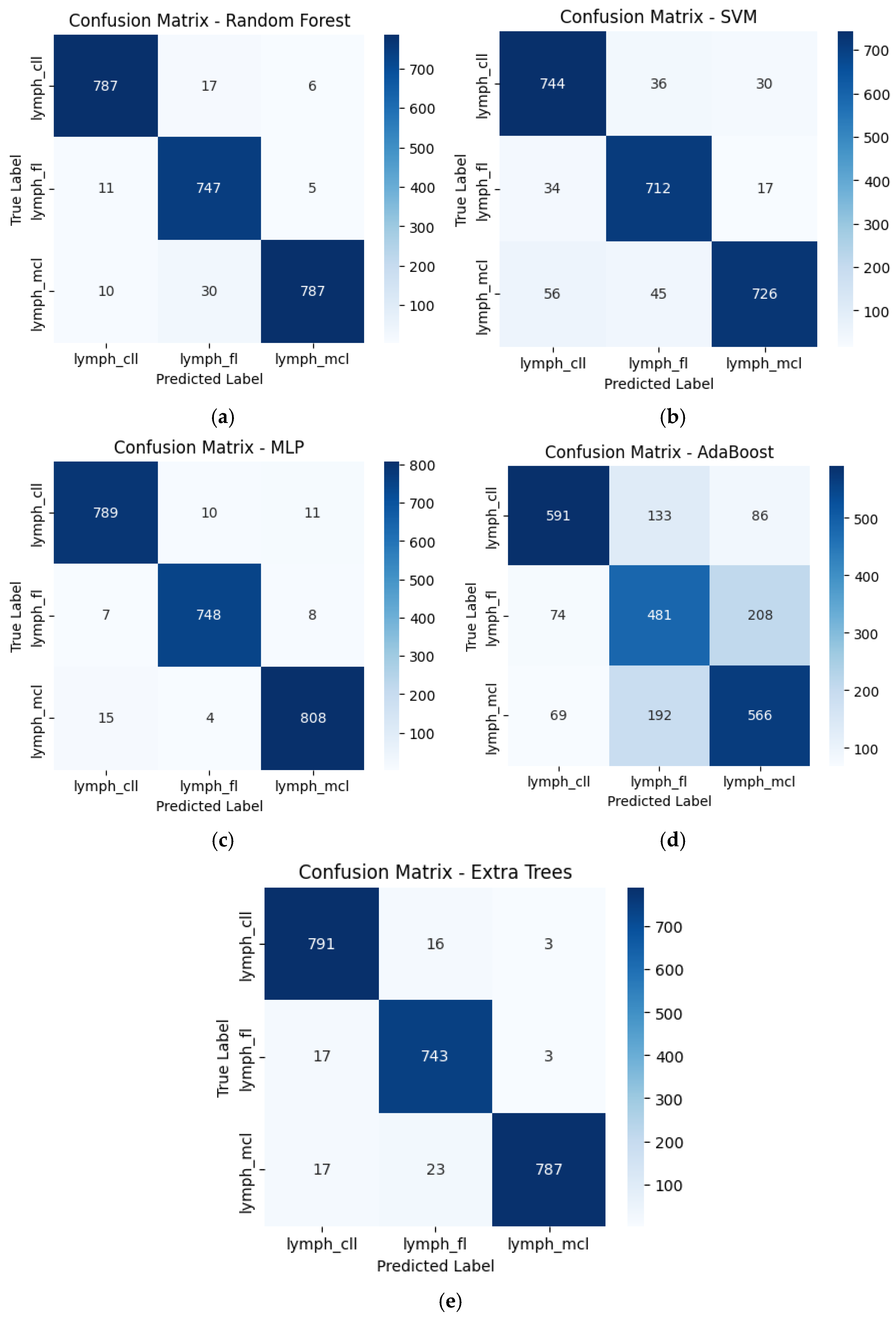
3.3. Classification Performance of Individual Models
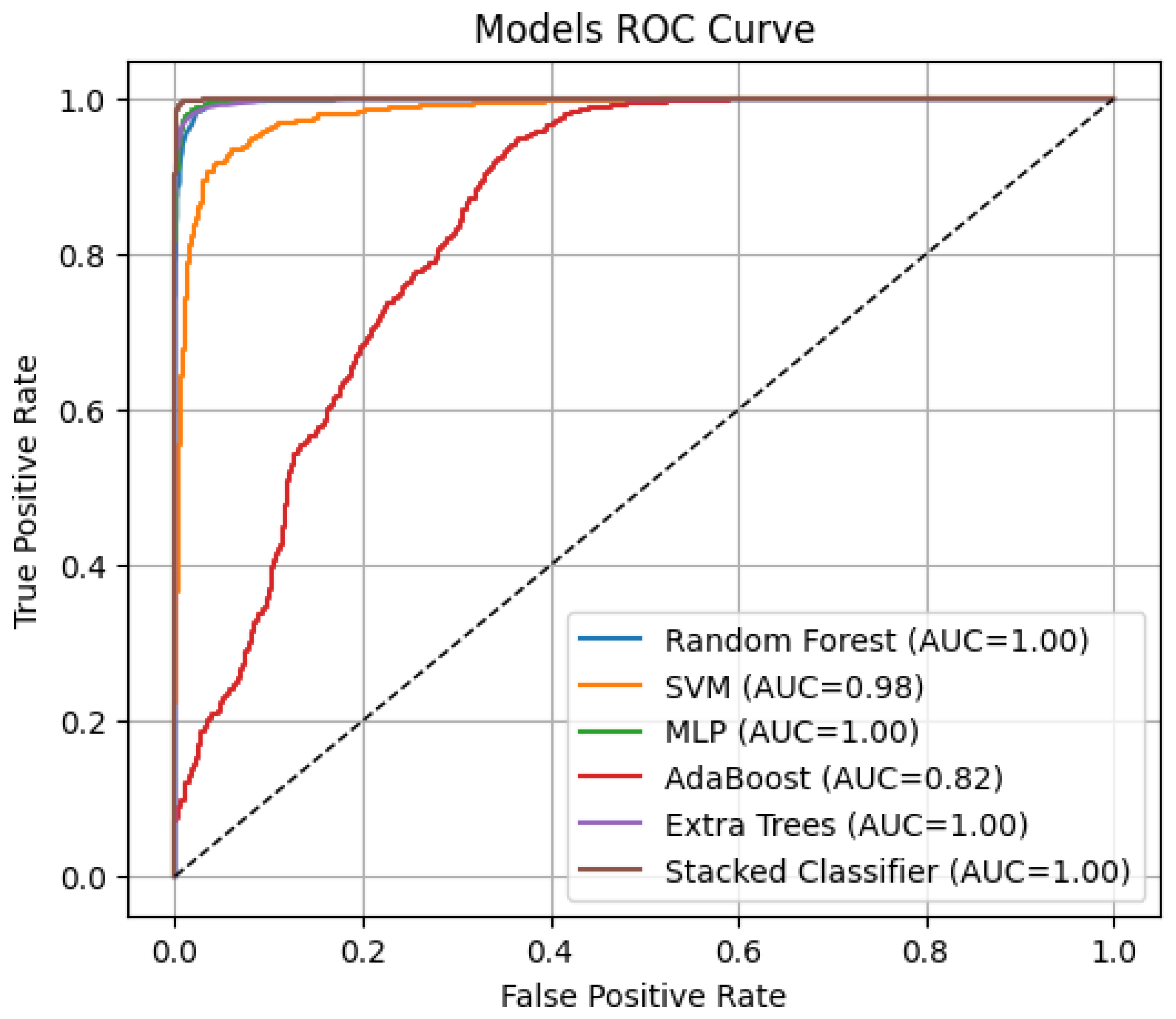
3.4. Stacked Ensemble Classifier Performance
3.5. Comparative Evaluation of Model Performance
3.6. Discussion and Clinical Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, J.; Han, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, D. Fast Virtual Stenting for Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair of Aortic Dissection Using Graph Deep Learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2025, 29, 4374–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Gao, J.; Zhao, D. A review of the application of deep learning in medical image classification and segmentation. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S.; Yu, X.; Lei, S.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Xue, X.; Ding, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhu, B. Deep learning for fast super-resolution ultrasound microvessel imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 245023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.I. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, H.; Liao, M.; Peng, Y. MvMRL: A multi-view molecular representation learning method for molecular property prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Seo, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.G. Comparison between deep learning and conventional machine learning in classifying iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis upon CT venography. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.P.; Samala, R.K.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Zhou, C. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Deep Learn. Med. Image Anal. Chall. Appl. 2020, 1213, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, B.; Hao, A. CenterFormer: A Novel Cluster Center Enhanced Transformer for Unconstrained Dental Plaque Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 10965–10978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.; Hossain, M.A.F.; Ali, M.; Sukanya, M.I.; Mahmud, T.; Fattah, S.A. AutoCovNet: Unsupervised feature learning using autoencoder and feature merging for detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 1685–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Luan, S.; Lei, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z.; Xue, X.; Ma, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, B. Deep learning for fast denoising filtering in ultrasound localization microscopy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 205002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Long, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Fu, L.; Luo, D. Evaluation of a three-gene methylation model for correlating lymph node metastasis in postoperative early gastric cancer adjacent samples. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1432869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbuss, G.; Kriegsmann, M.; Zgorzelski, C.; Brobeil, A.; Goeppert, B.; Dietrich, S.; Mechtersheimer, G.; Kriegsmann, K. Deep learning for the classification of non-Hodgkin lymphoma on histopathological images. Cancers 2021, 13, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Du, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H. Merge-and-Split Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Interaction Recognition. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, B.; Fu, Z.; Li, Z.; Tu, C. Deciphering the role of liquid-liquid phase separation in sarcoma: Implications for pathogenesis and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2025, 616, 217585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Zhou, J.; Ai, Q.; Li, L.H.; Liu, X.H.; Zhou, L. Clinical significance of PCT, CRP, IL-6, NLR, and TyG Index in early diagnosis and severity assessment of acute pancreatitis: A retrospective analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakasa, W.; Viriri, S. Stacked ensemble deep learning for pancreas cancer classification using extreme gradient boosting. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1232640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.P.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Helvie, M.A.; Richter, C.D. Generalization error analysis for deep convolutional neural network with transfer learning in breast cancer diagnosis. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Luo, Y.; Ge, M.; Yao, W.; Hei, Z.; Chen, C. A Supervised Explainable Machine Learning Model for Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorder in Liver-Transplantation Patients and External Validation on the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV Database: Retrospective Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e55046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanas, G.; Ge, W.; Quek, R.G.; Keeven, K.; Nersesyan, K.; Arnason, J.E. Epidemiology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL) in the United States and Western Europe: Population-level projections for 2020–2025. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafabadi, M.M.; Villanustre, F.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Seliya, N.; Wald, R.; Muharemagic, E. Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics. J. Big Data 2015, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekkal, R.N.; Bereksi-Reguig, F.; Ruiz-Fernandez, D.; Dib, N.; Sekkal, S. Automatic sleep stage classification: From classical machine learning methods to deep learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 77, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirocchi, C.; Bogliolo, A.; Montagna, S. Medical-informed machine learning: Integrating prior knowledge into medical decision systems. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24 (Suppl. 4), 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, D.; Soto-Rey, I.; Kramer, F. An analysis on ensemble learning optimized medical image classification with deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 66467–66480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, J.; Akila Agnes, S.; Pandian, S.I.A.; Bruntha, M. Deep-stacked autoencoder for medical image classification. In Evolving Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: New AI Techniques for Real-Time Interventions; Kumar, A., Dubey, A.K., Bhatia, S., Kumar, S.A., Le, D.N., Eds.; Institution of Engineering and Technology: Hertfordshire, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Tong, L.; Qian, B.; Yu, J.; Xiao, C. Self-attention-based conditional variational auto-encoder generative adversarial networks for hyperspectral classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Deng, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Huang, B. Artificial Intelligence in Lymphoma Histopathology: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e62851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, N.; Ko, K.; Yokota, T.; Kohno, K.; Nakaguro, M.; Nakamura, S.; Takeuchi, I.; Hontani, H. Subtype classification of malignant lymphoma using immunohistochemical staining pattern. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2022, 17, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundokun, R.O.; Odusami, M.; Sisodia, D.S.; Awotunde, J.B.; Tiwari, D.P. A Novel PCA-Logistic Regression for Intrusion Detection System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems and Management Science, Msida, Malta, 6–9 October 2022; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 575–588. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, T. Principal component analysis (PCA). In Computer Vision: A Reference Guide; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1013–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Ogundokun, R.O.; Awotunde, J.B.; Akande, H.B.; Lee, C.C.; Imoize, A.L. Deep transfer learning models for mobile-based ocular disorder identification on retinal images. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 80, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihan, P.; Saygılı, A.; Ermutlu, C.Ş.; Aydın, U.; Aksoy, Ö. AI-aided cardiovascular disease diagnosis in cattle from retinal images: Machine learning vs. deep learning models. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volovăț, S.R.; Boboc, D.-I.; Ostafe, M.-R.; Buzea, C.G.; Agop, M.; Ochiuz, L.; Rusu, D.I.; Vasincu, D.; Ungureanu, M.I.; Volovăț, C.C. Utilizing Vision Transformers for Predicting Early Response of Brain Metastasis to Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Stage Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Treatment. Tomography 2025, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble methods in machine learning. In International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ganaie, M.A.; Hu, M.; Malik, A.K.; Tanveer, M.; Suganthan, P.N. Ensemble deep learning: A review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, R.; Luttrell, J.; Zhang, C. Deep learning based analysis of histopathological images of breast cancer. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 426920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, X.; Bing, P.; He, B.; Tian, G.; et al. Evaluating cancer-related biomarkers based on pathological images: A systematic review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 763527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, M.; Li, X. Progress on deep learning in digital pathology of breast cancer: A narrative review. Gland Surg. 2022, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Nabi, H.; Ali, M.; Awajan, A.; Daoud, M.; Alazrai, R.; Suganthan, P.N.; Ali, T. A comprehensive review of the deep learning-based tumor analysis approaches in histopathological images: Segmentation, classification and multi-learning tasks. Clust. Comput. 2023, 26, 3145–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kather, J.N.; Krisam, J.; Charoentong, P.; Luedde, T.; Herpel, E.; Weis, C.A.; Gaiser, T.; Marx, A.; Valous, N.A.; Ferber, D.; et al. Predicting survival from colorectal cancer histology slides using deep learning: A retrospective multicenter study. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komura, D.; Ishikawa, S. Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanella, G.; Hanna, M.G.; Geneslaw, L.; Miraflor, A.; Werneck Krauss Silva, V.; Busam, K.J.; Brogi, E.; Reuter, V.E.; Klimstra, D.S.; Fuchs, T.J. Clinical-grade computational pathology using weakly supervised deep learning on whole slide images. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejnordi, B.E.; Veta, M.; Van Diest, P.J.; Van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; Litjens, G.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Hermsen, M.; Manson, Q.F.; Balkenhol, M.; et al. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA 2017, 318, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, N.K.; Bhushan, B.; Aurangzeb, K. Intelligent Green AI Technologies for Promoting Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Smart Cities. In Establishing AI-Specific Cloud Computing Infrastructure; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 393–414. [Google Scholar]
- Bandi, P.; Geessink, O.; Manson, Q.; Van Dijk, M.; Balkenhol, M.; Hermsen, M.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Lee, B.; Paeng, K.; Zhong, A.; et al. From detection of individual metastases to classification of lymph node status at the patient level: The camelyon17 challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Methodology | Key Findings | Application Domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litjens et al. [1] | Survey of DL in medical imaging | CNNs outperform traditional ML methods | Medical imaging |
| Chan et al. [8] | Early DL systems for lesion detection | DL performance matches or exceeds that of radiologists | Lesion detection |
| Hwang et al. [7] | VGG16 vs. handcrafted feature classifier | VGG16 slightly outperformed traditional models | Deep vein thrombosis |
| Rashid et al. [10] | Unsupervised feature learning | Generalizes better with limited labelled data | Medical image analysis |
| Anitha et al. [25] | Stacked autoencoder for skin lesion classification | Outperformed conventional classifiers with higher accuracy | Skin lesion classification |
| Chen et al. [26] | Conditional VAE for anomaly detection | Detected cancer via feature variations | Histopathology anomaly detection |
| Bakasa & Viriri [17] | Stacked ensemble DL with CNN + XGBoost | Achieved 98.8% accuracy, improved robustness | Pancreas tumour classification |
| Müller et al. [24] | Comparison of ensemble strategies | Stacking boosted F1 scores by up to 13% | Medical image classification |
| Steinbuss et al. [13] | EfficientNet-based lymphoma subtype model | Achieved 95.6% accuracy on nodal lymphoma classification | Lymphoma classification |
| Fu et al. [27] | Systematic review of AI in lymphoma pathology | 95–100% accuracy in B-cell subtypes (e.g., FL, CLL, MCL) | Lymphoma histopathology |
| Hashimoto et al. [28] | MIL with typicality-driven instance selection | Improved accuracy from 66.4% to 68.3% | Lymphoma subtype classification |
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | AP |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.9671 | 0.9977 | 0.9953 |
| SVM | 0.9092 | 0.9825 | 0.9669 |
| MLP | 0.9771 | 0.9986 | 0.9973 |
| AdaBoost | 0.6825 | 0.8194 | 0.6424 |
| Extra Tree | 0.9671 | 0.9972 | 0.9943 |
| Stacked Classifier | 0.9904 | 0.9998 | 0.9996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogundokun, R.O.; Owolawi, P.A.; Tu, C.; van Wyk, E. Autoencoder-Assisted Stacked Ensemble Learning for Lymphoma Subtype Classification: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach. Tomography 2025, 11, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080091
Ogundokun RO, Owolawi PA, Tu C, van Wyk E. Autoencoder-Assisted Stacked Ensemble Learning for Lymphoma Subtype Classification: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach. Tomography. 2025; 11(8):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080091
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgundokun, Roseline Oluwaseun, Pius Adewale Owolawi, Chunling Tu, and Etienne van Wyk. 2025. "Autoencoder-Assisted Stacked Ensemble Learning for Lymphoma Subtype Classification: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach" Tomography 11, no. 8: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080091
APA StyleOgundokun, R. O., Owolawi, P. A., Tu, C., & van Wyk, E. (2025). Autoencoder-Assisted Stacked Ensemble Learning for Lymphoma Subtype Classification: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach. Tomography, 11(8), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080091







