Voxel Size and Field of View Influence on Periodontal Bone Assessment Using Four CBCT Systems: An Experimental Ex Vivo Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
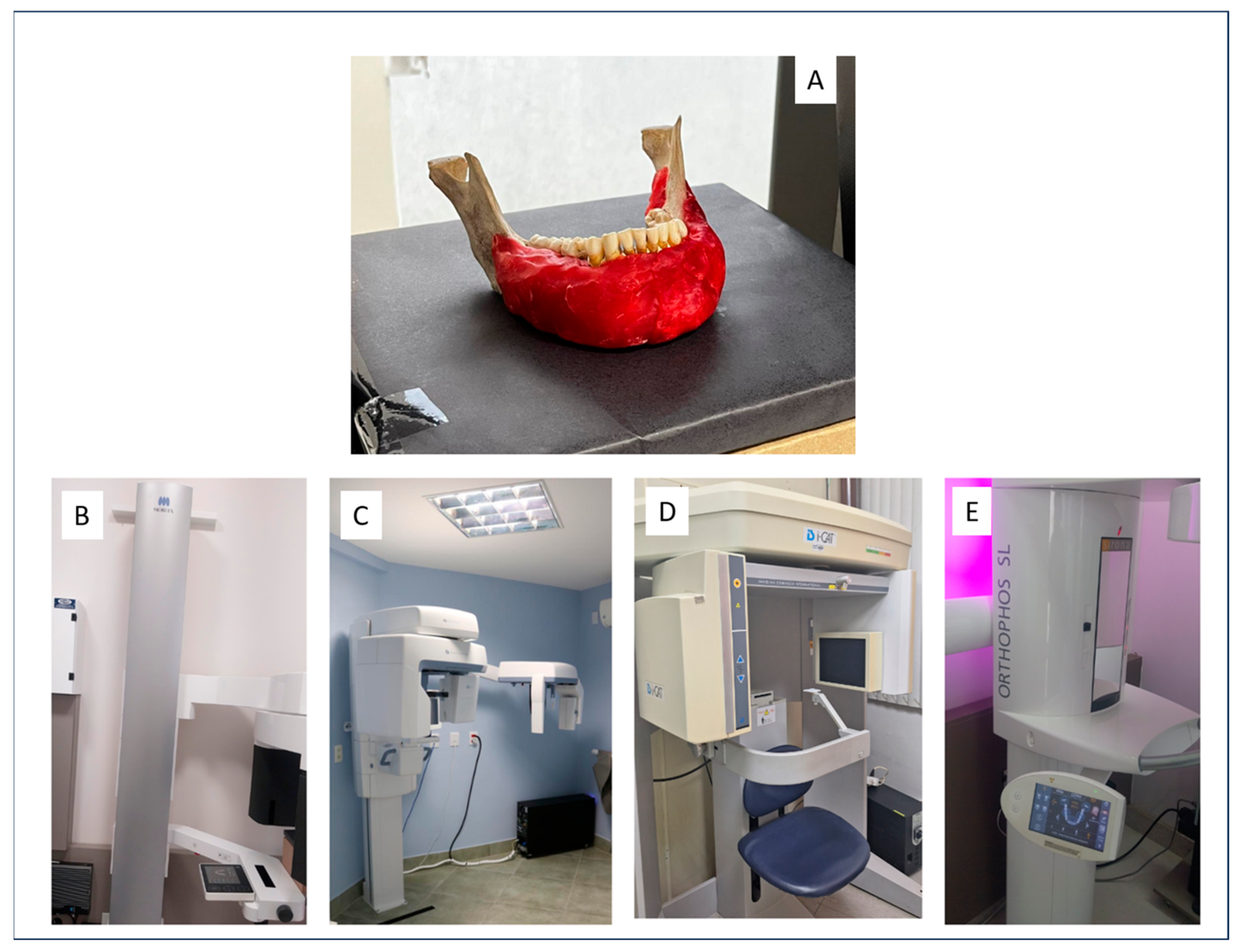
2.2. Specimen Preparation
2.3. CBCT Image Acquisition
- Veraview® X800 (J. Morita MFG. Corp., Tokyo, Japan);
- OP300 Pro® (Instrumentarium Dental, Tuusula, Finland);
- I-CAT Next Generation® (Imaging Sciences International, Hatfield, PA, USA);
- Orthophos XG 5 (Dentsply Sirona, Bensheim, Germany).
2.4. Image Processing and Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. OP300 System
3.2. Veraview X800 System
3.3. Orthophos XG5 System
3.4. I-CAT System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, A.L.E.; Reis, I.N.R.; Bitencourt, F.V.; Salgado, D.M.R.A.; Costa, C.; Spin-Neto, R. Accuracy of linear measurements for implant planning based on low-dose cone beam CT protocols: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2024, 53, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.M.; Bassir, S.H. When Is Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Imaging Appropriate for Diagnostic Inquiry in the Management of Inflammatory Periodontitis? An American Academy of Periodontology Best Evidence Review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 978–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseh, I.; Al-Rawi, W. Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 62, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic-Jakoba, N.; Spin-Neto, R.; Wenzel, A. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography for Detection of Intrabony and Furcation Defects: A Systematic Review Based on a Hierarchical Model for Diagnostic Efficacy. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrmann, P.; Kühl, S.; Dagassan-Berndt, D.; Bornstein, M.M.; Zitzmann, N.U. Radiographic assessment of the peri-implant site. Periodontol. 2000 2024, 95, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macêdo, P.T.S. Influence of Different Cone-Beam CT Image Acquisition Protocols in the Visualization of Periodontal Structures and in the Bone Height Determination: In-Vitro Study. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Odontologia de Piracicaba. Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Spin-Neto, R.; Stavropoulos, A.; Dias Pereira, L.A.; Marcantonio, E., Jr.; Wenzel, A. Fate of autologous and fresh-frozen allogeneic block bone grafts used for ridge augmentation. A CBCT-based analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaju, P.P.; Jaju, S.P. Cone-beam computed tomography: Time to move from ALARA to ALADA. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2015, 45, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, K.F.; Evangelista, K.; Rodrigues, C.; Estrela, C.; de Sousa, T.; Silva, M. Detection of periodontal bone loss using cone beam CT and intraoral radiography. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2012, 41, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillenseger, J.P.; Gros, C.I.; Sayeh, A.; Rasamimanana, J.; Lawniczak, F.; Leminor, J.M.; Matern, J.F.; Constantinesco, A.; Bornert, F.; Choquet, P. Image quality evaluation of small FOV and large FOV CBCT devices for oral and maxillofacial radiology. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2017, 46, 20160285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misch, K.A.; Yi, E.S.; Sarment, D.P. Accuracy of Cone Beam Computed Tomography for Periodontal Defect Measurements. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.L.F.; Barbosa, B.V.; Perez-Gomes, J.P.; Calle, A.J.M.; Santamaria, M.P.; Lopes, S.L.P.C. Influence of voxel size on the accuracy of linear measurements of the condyle in images of cone beam computed tomography: A pilot study. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2018, 10, e876–e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbauy, W.D.; Moraes, L.C.; Lima, F.R.; Médici-Filho, E. An evaluation of alveolar bone loss in patients referred to periodontist: A radiographic study. Rev. Odontol. UNESP 2000, 29, 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Larato, D.C. Alveolar plate fenestrations and dehiscences of the human skull. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 1970, 29, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.; Metska, M.E.; Ozok, A.R.; van der Stelt, P.; Wesselink, P.R. Detection of Vertical Root Fractures in Endodontically Treated Teeth by a Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scan. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, E.; Soman, C.; Alasqah, M.; Alqahtani, S.; Alshehri, F.; Alyami, H.; Alzahrani, K.; Alqahtani, S.; Peeran, S.W.; Murugan, M.S. Comparative Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Surgical Measurements of Periodontal Bone Defects in Periodontitis Patients: An In Vivo Study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2024, 25, 772–777. [Google Scholar]
- Assiri, H.; Dawasaz, A.A.; Alahmari, A.; Asiri, Z. Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) in periodontal diseases: A Systematic review based on the efficacy model. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icen, M.; Orhan, K.; Şeker, Ç.; Geduk, G.; Cakmak Özlü, F.; Cengiz, M.İ. Comparison of CBCT with different voxel sizes and intraoral scanner for detection of periodontal defects: An in vitro study. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2020, 49, 20190197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsuz, M.E.; Bagis, N.; Orhan, K.; Avsever, H.; Demiralp, K.Ö. Comparison of the influence of FOV sizes and different voxel resolutions for the assessment of periodontal defects. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2015, 44, 20150070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintström, E.; Smedby, O.; Klintström, B.; Brismar, T.B.; Moreno, R. Trabecular bone histomorphometric measurements and contrast-to-noise ratio in CBCT. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2014, 43, 20140196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quereshy, F.A.; Savell, T.A.; Palomo, J.M. Applications of cone beam computed tomography in the practice of oral and maxillofacial surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetmili, H.; Tassoker, M.; Sener, S. Comparison of cone-beam computed tomography with bitewing radiography for detection of periodontal bone loss and assessment of effects of different voxel resolutions: An in vitro study. Oral Radiol. 2019, 35, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedke, G.S.; Silveira, H.E.D.; Silveira, H.L.D.; Dutra, V.; Figueiredo, J.A.P. Influence of voxel size in the diagnostic ability of cone beam tomography to evaluate simulated external root resorption. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Reis, L.; Gaêta-Araujo, H.; Rosado, L.P.L.; Mouzinho-Machado, S.; Oliveira-Santos, C.; Freitas, D.Q.; Correr-Sobrinho, L. Do cone-beam computed tomography low-dose protocols affect the evaluation of the temporomandibular joint? J. Oral Rehabil. 2023, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, A.; Gutierrez, B.L.; Fischer, K.; Sekula, M.; Santaella, G.M.; Scarfe, W.; Brasil, D.M.; Oliveira-Santos, C. Filtered back projection vs. iterative reconstruction for CBCT: Effects on image noise and processing time. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2023, 52, 20230109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomier, A.S.; Gaweesh, Y.S.E.; Taalab, M.R.; Sadat, S.A.E. Efficacy of low-dose cone beam computed tomography and metal artifact reduction tool for assessment of peri-implant bone defects: An in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.S.; Kehrwald, R.; Matheus, R.A.; Gomes, A.F.; Queiroz, P.M. Influence of Low-Dose Protocols of CBCT on Dental Implant Planning. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2021, 36, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, C.C.; Janson, G.; Massaro, C.S.; Cambiaghi, L.; Garib, D.G. Precision, reproducibility, and accuracy of bone crest level measurements of CBCT cross sections using different resolutions. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.; Brown, L.F.; Parashos, P. CBCT in contemporary endodontics. Aust. Dent. J. 2023, 68 (Suppl. S1), S39–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreppel, M.; Zöller, J. Ameloblastoma-Clinical, radiological, and therapeutic findings. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| CBCT System | FOV (H × D) (cm) | Voxel (mm) | Specifications (kVp/mA/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OP300 | 8 × 15 | 0.4SAR/0.32SAR/0.25SAR/0.4AR 0.32AR/0.25AR | 90 kVp/3.2 mA/2.3 s 90 kVp/6.3 mA/4.5 s |
| 8 × 8 | 0.32SAR/0.3SAR/0.2SAR/0.32AR 0.3 AR/0.2 AR | 90 kVp/3.2 mA/1.2 s 90 kVp/8.0 mA/2.3 s | |
| 6 × 8 | 0.32SAR/0.3SAR/0.2SAR/0.32AR 0.3 AR/0.2 AR | 90 kVp/3.2 mA/1.2 s 90 kVp/8.0 mA/2.3 s | |
| 5 × 5 | 0.28 SAR. AR. LE/0.2 SAR. AR. LE/0.125 SAR. AR. LE 0.085 SAR. AR. LE/0.28 SAR. AR. LD/0.2 SAR. AR. LD 0.125 SAR. AR. LD/0.085 SAR. AR. LD | 90 kVp/3.2 mA/1.2 s 90 kVp/6.3 mA/8.7 s 90 kVp/6.3 mA/6.1 s | |
| 13 × 15 | 0.42 AR/0.38 AR/0.32 AR/0.48SAR 0.38SAR/0.32SAR | 90 kVp/3.2 mA/4.5 s 90 kVp/5.0 mA/8.1 s | |
| Veraview X800 | 4 × 4 (Endo) | 0.08 RS. LS | 100 kVp/8.0 mA/10.0 s |
| 4 × 4 | 0.08 RS. LS | 100 kVp/8.0 mA/8.5 s | |
| 8 × 4/8 × 5/8 × 8/ 10 × 4/10 × 5/10 × 8 | 0.125 | 100 kVp/8.0 mA/8.3 s 100 kVp/8.0 mA/7.6 s | |
| 15 × 5/15 × 7.5 | 0.25 | 101 kVp/8.0 mA/2.5 s | |
| Ortophos XG5 | 5 × 5.5 | 0.08 RS. LS | 85 kVp/7.0 mA/7.5 s |
| 8 × 8/11 x10 | 0.16 | 85 kVp/6.0 mA/5.8 s | |
| I-CAT Next Generation | 7.1 × 16 | 0.4/0.3/0.25/0.2 | 120 kVp/36 mA/8.0 s |
| 6.1 × 16 | 0.4 | 89 kVp/8.0 mA/12.0 s |
| Protocol | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOV = 6 × 8 Res = 0.3 | 2.50 | 0.36 | 1.73 | 3.05 | 0.940 |
| FOV = 6 × 8 Res = 0.2 | 2.52 | 0.13 | 2.30 | 2.74 | 0.995 |
| FOV = 5 × 5 Res = 0.125 | 2.56 | 0.13 | 2.37 | 2.75 | 1.000 |
| FOV = 5 × 5 Res = 0.085 | 2.56 | 0.11 | 2.38 | 2.77 | 1.000 |
| FOV = 5 × 5 Res = 0.2 | 2.65 | 0.14 | 2.37 | 2.91 | 0.911 |
| FOV = 8 × 8 Res = 0.2 | 2.65 | 0.19 | 2.33 | 2.95 | 0.862 |
| FOV = 8 × 15 Res = 0.25 | 2.69 | 0.14 | 2.38 | 2.88 | 0.526 |
| FOV = 8 × 8 Res = 0.32 | 2.73 | 0.20 | 2.40 | 3.20 | 0.190 |
| FOV = 5 × 5 Res = 0.28 | 2.76 | 0.18 | 2.35 | 3.03 | 0.071 |
| FOV = 8 × 8 Res = 0.3 | 2.76 | 0.23 | 2.41 | 3.19 | 0.081 |
| FOV = 13 × 15 Res = 0.32 | 2.82 | 0.20 | 2.50 | 3.30 | 0.007 |
| FOV = 6 × 8 Res = 0.32 | 2.84 | 0.19 | 2.50 | 3.20 | 0.003 |
| FOV = 13 × 15 Res = 0.38 | 2.85 | 0.22 | 2.50 | 3.40 | 0.001 |
| FOV = 8 × 15 Res = 0.32 | 2.95 | 0.21 | 2.40 | 3.20 | <0.001 |
| FOV = 13 × 15 Res = 0.42 | 2.97 | 0.28 | 2.50 | 3.40 | <0.001 |
| FOV = 8 × 15 Res = 0.4 | 3.13 | 0.22 | 2.80 | 3.60 | <0.001 |
| Gold standard | 2.57 | 0.20 | 2.30 | 2.97 |
| Protocol | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOV = 8 × 5 Res = 0.125 | 2.24 | 0.26 | 1.93 | 2.60 | 0.019 |
| FOV = 8 × 8 Res = 0.125 | 2.32 | 0.35 | 1.73 | 2.88 | 0.133 |
| FOV = 8 × 4 Res = 0.125 | 2.34 | 0.30 | 1.97 | 2.86 | 0.200 |
| FOV = 10 × 5 Res = 0.125 | 2.38 | 0.18 | 2.11 | 2.69 | 0.387 |
| FOV = 15 × 5 Res = 0.25 | 2.38 | 0.16 | 2.17 | 2.69 | 0.392 |
| FOV = 10 × 8 Res = 0.125 | 2.39 | 0.31 | 1.91 | 2.83 | 0.438 |
| FOV = 10 × 4 Res = 0.125 | 2.50 | 0.31 | 1.97 | 2.86 | 0.989 |
| FOV = 4 × 4 Res = 0.08 | 2.50 | 0.30 | 1.97 | 2.93 | 0.965 |
| FOV = 15 × 7.5 Res = 0.25 | 2.54 | 0.17 | 2.31 | 2.89 | 1.000 |
| Gold standard | 2.57 | 0.20 | 2.30 | 2.97 |
| Protocol | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOV = 5 × 5.5 Res = 0.08 | 2.35 | 0.26 | 1.93 | 2.70 |
| FOV = 11 × 10 Res = 0.16 | 2.39 | 0.10 | 2.25 | 2.58 |
| FOV = 8 × 8 Res = 0.16 | 2.41 | 0.29 | 1.93 | 2.72 |
| Gold standard | 2.57 | 0.20 | 2.30 | 2.97 |
| Protocol | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOV = 7.1 × 16 Res = 0.4 | 3.22 | 0.35 | 2.80 | 3.70 | <0.001 |
| FOV = 6.1 × 16 Res = 0.4 | 3.00 | 0.12 | 2.80 | 3.20 | <0.001 |
| FOV = 7.1 × 16 Res = 0.3 | 2.74 | 0.15 | 2.51 | 3.08 | 0.039 |
| FOV = 7.1 × 16 Res = 0.2 | 2.70 | 0.10 | 2.50 | 2.88 | 0.166 |
| FOV = 7.1 × 16 Res = 0.25 | 2.60 | 0.18 | 2.08 | 2.89 | 0.988 |
| Gold standard | 2.57 | 0.20 | 2.30 | 2.97 |
| CBCT System | Protocol (FOV/Voxel) | Mode/Side | Mean (mm) | p-Value | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP300 | 5 × 5/0.125 | SAR, AR, LE | 2.56 | 1.000 | Accurate (+ +) |
| 5 × 5/0.125 | SAR, AR, LD | 2.56 | 1.000 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| 5 × 5/0.085 | SAR, AR, LE | 2.56 | 1.000 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| 5 × 5/0.085 | SAR, AR, LD | 2.56 | 1.000 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| 6 × 8/0.2 | SAR | 2.52 | 0.995 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| 13 × 15/0.32 | AR | 2.82 | 0.007 | Moderately different (+ −) | |
| 13 × 15/0.38 | AR | 2.85 | 0.001 | Significantly different (− −) | |
| 8 × 15/0.4 | SAR | 3.13 | <0.001 | Significantly different (− −) | |
| Veraview X800 | 4 × 4/0.08 | RS, LS | 2.50 | 0.965 | Accurate (+ +) |
| 15 × 7.5/0.25 | Standard | 2.54 | 1.000 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| 8 × 5/0.125 | Standard | 2.24 | 0.019 | Moderately different (+ −) | |
| Orthophos XG5 | 5 × 5.5/0.08 | RS, LS | 2.35 | >0.05 | Accurate (+ +) |
| 8 × 8/0.16 | Standard | 2.41 | >0.05 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| 11 × 10/0.16 | Standard | 2.39 | >0.05 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| I-CAT Next Generation | 7.1 × 16/0.25 | Standard | 2.60 | 0.988 | Accurate (+ +) |
| 7.1 × 16/0.2 | Standard | 2.70 | 0.166 | Accurate (+ +) | |
| 7.1 × 16/0.3 | Standard | 2.74 | 0.039 | Moderately different (+ −) | |
| 7.1 × 16/0.4 | Standard | 3.22 | <0.001 | Significantly different (− −) | |
| 6.1 × 16/0.4 | Standard | 3.00 | <0.001 | Significantly different (− −) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, V.G.B.; Queiroz, P.M.; Simões, A.R.; Alves, M.G.O.; Jardini, M.A.N.; Costa, A.L.F.; Lopes, S.L.P.d.C. Voxel Size and Field of View Influence on Periodontal Bone Assessment Using Four CBCT Systems: An Experimental Ex Vivo Analysis. Tomography 2025, 11, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11070074
de Oliveira VGB, Queiroz PM, Simões AR, Alves MGO, Jardini MAN, Costa ALF, Lopes SLPdC. Voxel Size and Field of View Influence on Periodontal Bone Assessment Using Four CBCT Systems: An Experimental Ex Vivo Analysis. Tomography. 2025; 11(7):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11070074
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Victória Geisa Brito, Polyane Mazucatto Queiroz, Alessandra Rocha Simões, Mônica Ghislaine Oliveira Alves, Maria Aparecida Neves Jardini, André Luiz Ferreira Costa, and Sérgio Lucio Pereira de Castro Lopes. 2025. "Voxel Size and Field of View Influence on Periodontal Bone Assessment Using Four CBCT Systems: An Experimental Ex Vivo Analysis" Tomography 11, no. 7: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11070074
APA Stylede Oliveira, V. G. B., Queiroz, P. M., Simões, A. R., Alves, M. G. O., Jardini, M. A. N., Costa, A. L. F., & Lopes, S. L. P. d. C. (2025). Voxel Size and Field of View Influence on Periodontal Bone Assessment Using Four CBCT Systems: An Experimental Ex Vivo Analysis. Tomography, 11(7), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11070074










