CT Perfusion Imaging in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Premorbid Statin Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Imaging Protocol
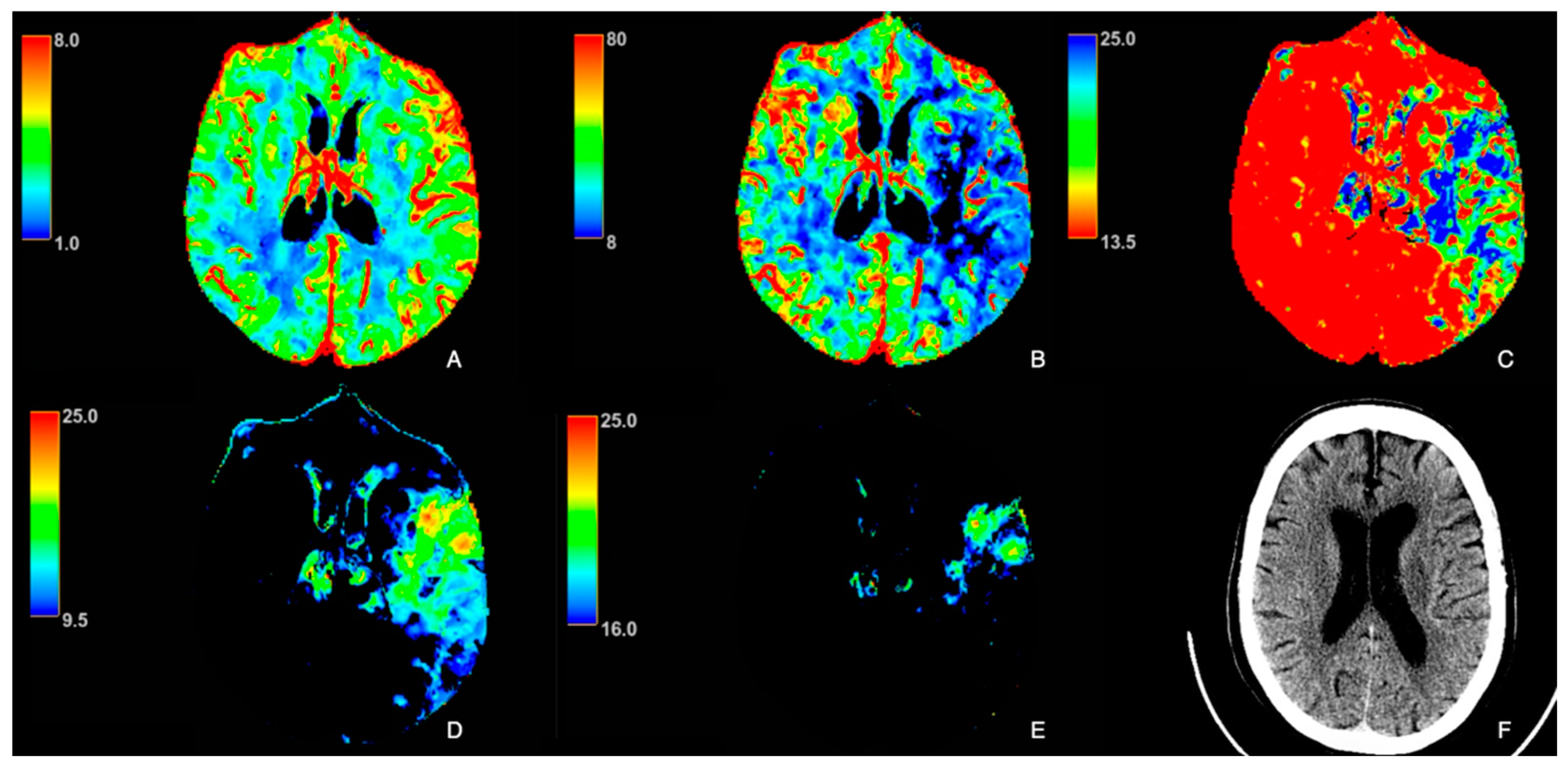
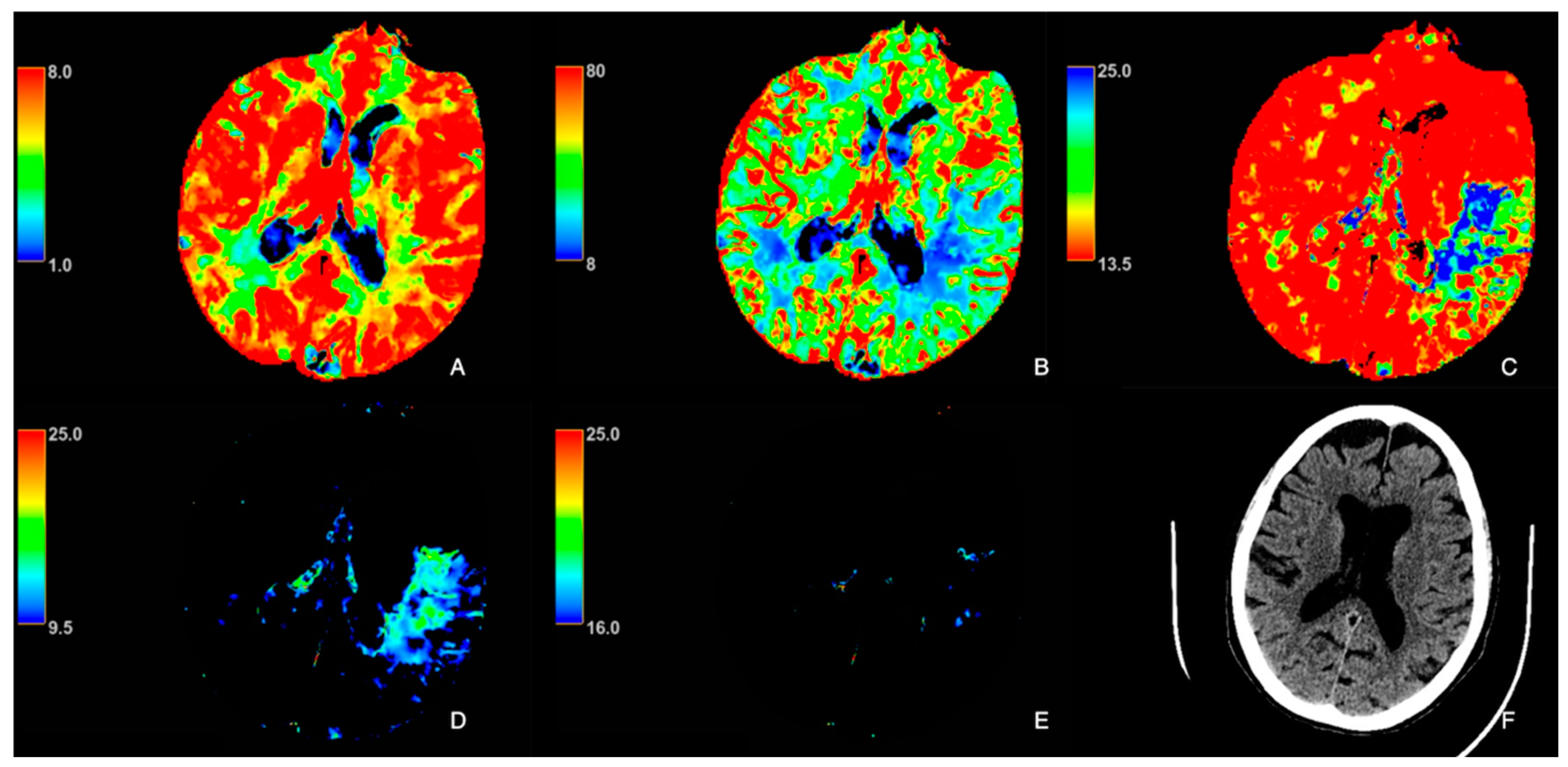
2.2. Image Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| CBV | Cerebral blood volume |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CTP | Computed tomography perfusion |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| EVT | Endovascular therapy |
| LVO | Large vessel occlusion |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
| mCTA | Computed tomography angiography |
| MTT | Mean transit time |
| NCCT | Axial non-contrast CT |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| PROACT | Prolyse in Acute Cerebral Thromboembolism |
| ROI | Region of interest |
References
- Hong, K.-S.; Lee, J.S. Statins in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review. J. Stroke 2015, 17, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Xu, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Dong, W. Prestroke statins use reduces oxidized low density lipoprotein levels and improves clinical outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation related acute ischemic stroke. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) Investigators. High-Dose Atorvastatin after Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.C.; Lee, J.S.; Park, T.H.; Cho, Y.-J.; Park, J.-M.; Kang, K.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, S.-J.; Ko, Y.; Lee, J.; et al. Effect of pre-stroke statin use on stroke severity and early functional recovery: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chróinín, D.N.; Asplund, K.; Åsberg, S.; Callaly, E.; Cuadrado-Godia, E.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; Di Napoli, M.; Engelter, S.T.; Furie, K.L.; Giannopoulos, S.; et al. Statin Therapy and Outcome After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, K.; Safouris, A.; Goyal, N.; Arthur, A.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Katsanos, A.H.; Sargento-Freitas, J.; Ribo, M.; Molina, C.; Chung, J.-W.; et al. Association of statin pretreatment with collateral circulation and final infarct volume in acute ischemic stroke patients: A meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2019, 282, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharek, A.; Chen, J.; Cui, X.; Yang, Y.; Chopp, M. Simvastatin Increases Notch Signaling Activity and Promotes Arteriogenesis After Stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, L.B. Statins and ischemic stroke severity: Cytoprotection. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2009, 11, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, M.; Laufs, U.; Huang, Z.; Nakamura, T.; Huang, P.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Liao, J.K. Stroke protection by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibitors mediated by endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8880–8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahi, M.; Huang, Z.; Thomas, S.; Yoshimura, S.; Sumii, T.; Mori, T.; Qiu, J.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Huang, P.L.; Liao, J.K.; et al. Protective Effects of Statins Involving Both eNOS and tPA in Focal Cerebral Ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallustio, F.; Diomedi, M.; Centonze, D.; Stanzione, P. Saving the Ischemic Penumbra: Potential Role for Statins and Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2007, 5, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretnar-Oblak, J.; Sabovic, M.; Sebestjen, M.; Pogacnik, T.; Zaletel, M. Influence of Atorvastatin Treatment on L-Arginine Cerebrovascular Reactivity and Flow-Mediated Dilatation in Patients With Lacunar Infarctions. Stroke 2006, 37, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebeskind, D.S. Collaterals in acute stroke: Beyond the clot. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2005, 15, 553–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, A.M.; Colò, F.; Brunetti, V.; Valente, I.; Frisullo, G.; Pedicelli, A.; Scarcia, L.; Rollo, C.; Falcou, A.; Milonia, L.; et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in minor stroke due to isolated M2 occlusion: A multicenter retrospective matched analysis. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, E198–E203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Ros, V.; Scaggiante, J.; Sallustio, F.; Lattanzi, S.; Bandettini, M.; Sgreccia, A.; Rolla-Bigliani, C.; Lafe, E.; Sanfilippo, G.; Diomedi, M.; et al. Carotid Stenting and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Tandem Occlusions: Antithrombotic Treatment and Functional Outcome. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakomkin, N.; Dhamoon, M.; Carroll, K.; Singh, I.P.; Tuhrim, S.; Lee, J.; Fifi, J.T.; Mocco, J. Prevalence of large vessel occlusion in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke: A 10-year systematic review of the literature. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Biller, J.; Coffey, C.S.; Hoh, B.L.; Jauch, E.C.; Johnston, K.C.; Johnston, S.C.; Khalessi, A.A.; Kidwell, C.S.; et al. 2015 American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Focused Update of the 2013 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke Regarding Endovascular Treatment. Stroke 2015, 46, 3020–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minosse, S.; Garaci, F.; Martucci, A.; Lanzafame, S.; Di Giuliano, F.; Picchi, E.; Cesareo, M. Disruption of brain network organization in primary open angle glaucoma. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS 2019), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 4338–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoli, A.; Motta, C.; Koch, G.; Diomedi, M.; Napolitano, S.; Giordano, A.; Panella, M.; Morosetti, D.; Fabiano, S.; Floris, R.; et al. Pretreatment predictors of malignant evolution in patients with ischemic stroke undergoing mechanical thrombectomy. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 10, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luitse, M.J.A.; van Seeters, T.; Horsch, A.D.; Kool, H.A.; Velthuis, B.K.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biessels, G.J. Admission Hyperglycaemia and Cerebral Perfusion Deficits in Acute Ischaemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 35, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Churilov, L.; Kanesan, L.; Dowling, R.; Mitchell, P.; Dong, Q.; Davis, S.; Yan, B. Blood Pressure May Be Associated with Arterial Collateralization in Anterior Circulation Ischemic Stroke before Acute Reperfusion Therapy. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.C.; Dillon, W.P.; Liu, S.; Adler, F.; Smith, W.S.; Wintermark, M. Systematic comparison of perfusion-CT and CT-angiography in acute stroke patients. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, P.; Schellinger, P.D.; Fiebach, J.B.; Heiland, S.; Jansen, O.; Knauth, M.; Hacke, W.; Sartor, K. Comparison of CT and CT angiography source images with diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with acute stroke within 6 hours after onset. Stroke 2002, 33, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Esterre, C.D.; Boesen, M.E.; Ahn, S.H.; Pordeli, P.; Najm, M.; Minhas, P.; Davari, P.; Fainardi, E.; Rubiera, M.; Khaw, A.V.; et al. Time-Dependent Computed Tomographic Perfusion Thresholds for Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, 3390–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giuliano, F.; Picchi, E.; Sallustio, F.; Ferrazzoli, V.; Alemseged, F.; Greco, L.; Minosse, S.; Da Ros, V.; Diomedi, M.; Garaci, F.; et al. Accuracy of advanced CT imaging in prediction of functional outcome after endovascular treatment in patients with large-vessel occlusion. Neuroradiol. J. 2019, 32, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.J.; De Sarno, D.; Lee, T.Y. CT perfusion stroke lesion threshold calibration between deconvolution algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlen, I.; Sprügel, M.; Hoelter, P.; Hock, S.; Knott, M.; Huttner, H.B.; Schwab, S.; Kallmünzer, B.; Doerfler, A. Comparison of Two Automated Computed Tomography Perfusion Applications to Predict the Final Infarct Volume After Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction 3 Recanalization. Stroke 2022, 53, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rava, R.A.; Snyder, K.V.; Mokin, M.; Waqas, M.; Allman, A.B.; Senko, J.L.; Podgorsak, A.; Bhurwani, M.S.; Hoi, Y.; Siddiqui, A.; et al. Assessment of a Bayesian Vitrea CT Perfusion Analysis to Predict Final Infarct and Penumbra Volumes in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Comparison with RAPID. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainardi, E.; Busto, G.; Rosi, A.; Scola, E.; Casetta, I.; Bernardoni, A.; Saletti, A.; Arba, F.; Nencini, P.; Limbucci, N.; et al. Tmax Volumes Predict Final Infarct Size and Functional Outcome in Ischemic Stroke Patients Receiving Endovascular Treatment. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 91, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, A.; Higashida, R.; Wechsler, L.; Gent, M.; Rowley, H.; Kase, C.; Pessin, M.; Ahuja, A.; Callahan, F.; Clark, W.M.; et al. Intra-arterial Prourokinase for Acute Ischemic Stroke: The PROACT II Study: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Jama 1999, 282, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagal, A.; Menon, B.K.; Foster, L.D.; Livorine, A.; Yeatts, S.D.; Qazi, E.; D’Esterre, C.; Shi, J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Hill, M.D.; et al. Association Between CT Angiogram Collaterals and CT Perfusion in the Interventional Management of Stroke III Trial. Stroke 2016, 47, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanen, H.; Saarinen, J.T.; Sillanpää, N. Collateral Circulation Predicts the Size of the Infarct Core and the Proportion of Salvageable Penumbra in Hyperacute Ischemic Stroke Patients Treated with Intravenous Thrombolysis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 40, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Ma, M.; Fang, J.; Bao, J.; Dong, S.; Chen, N.; Guo, Y.; He, L. Prestroke statin use enhances collateralization in acute ischemic stroke patients. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2020, 38, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Chiang, H.F.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chou, C.L.; Jhou, Z.Y.; Hou, T.Y.; Shaw, J.S. Using Deep-Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Technique to Automatically Evaluate the Collateral Status of Multiphase CTA in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Tomography 2023, 9, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, H.; Han, H.; Sun, J.; Wu, X. Collateral Status and Clinical Outcomes after Mechanical Thrombectomy in Patients with Anterior Circulation Occlusion. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7796700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannoni, S.; Sirimarco, G.; Cereda, C.W.; Lambrou, D.; Strambo, D.; Eskandari, A.; Mosimann, P.J.; Wintermark, M.; Michel, P. Determining factors of better leptomeningeal collaterals: A study of 857 consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violi, F.; Calvieri, C.; Ferro, D.; Pignatelli, P. Statins as Antithrombotic Drugs. Circulation 2013, 127, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessinger, C.W.; Kim, J.W.; Henke, P.K.; Thompson, B.; McCarthy, J.R.; Hara, T.; Sillesen, M.; Margey, R.J.P.; Libby, P.; Weissleder, R.; et al. Statins improve the resolution of established murine venous thrombosis: Reductions in thrombus burden and vein wall scarring. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Savitz, S.; Schlaug, G.; Caplan, L.; Selim, M. Antiplatelets, ACE inhibitors, and statins combination reduces stroke severity and tissue at risk. Neurology 2006, 66, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matetzky, S.; Fefer, P.; Shenkman, B.; Shechter, M.; Novikov, I.; Savion, N.; Varon, D.; Hod, H. Statins have an early antiplatelet effect in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Platelets 2011, 22, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austein, F.; Riedel, C.; Kerby, T.; Meyne, J.; Binder, A.; Lindner, T.; Huhndorf, M.; Wodarg, F.; Jansen, O. Comparison of Perfusion CT Software to Predict the Final Infarct Volume after Thrombectomy. Stroke 2016, 47, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivard, A.; Levi, C.; Spratt, N.; Parsons, M. Perfusion CT in acute stroke: A comprehensive analysis of infarct and penumbra. Radiology 2013, 267, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, A.; Christensen, S.; Straka, M.; Mlynash, M.; Liggins, J.; Bammer, R.; Thijs, V.; Lemmens, R.; Albers, G.W.; Lansberg, M.G. A comparison of relative time to peak and tmax for mismatch-based patient selection. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muizelaar, J.P.; Fatouros, P.P.; Schröder, M.L. A new method for quantitative regional cerebral blood volume measurements using computed tomography. Stroke 1997, 28, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavilala, M.S.; Lee, L.A.; Lam, A.M. Cerebral blood flow and vascular physiology. Anesthesiol. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 20, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, N.A. Normal average value of cerebral blood flow in younger adults is 50 ml/100 g/min. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1985, 5, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient Characteristics | Statins (n = 29) | No Statins (n = 32) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age [range] (in years) | 75.7 [58–87] | 72.7 [45–86] | 0.5 |
| Sex (male/female) | 11/18 | 11/21 | 0.6 |
| Risk factors, n (%) | |||
| -Atrial fibrillation | 14 (48.3) | 9 (29.0) | 0.1 |
| -Systemic hypertension | 25 (86.2) | 23 (74.2) | 0.2 |
| -Smoking | 10 (34.5) | 5 (16.1) | 0.1 |
| -Diabetes | 12 (41.4) | 6 (19.3) | 0.1 |
| -Hypercholesterolemia | 19 (65.5) | 5 (16.1) | <0.001 * |
| -Transient ischemic attack/ictus | 6 (20.7) | 5 (16.1) | 0.7 |
| -Coronary artery disease | 9 (31.0) | 4 (12.9) | 0.1 |
| Admission NIHSS, median (IQR) | 13 [7–16] | 17 [15–20] | <0.001 * |
| Variables [cm3] | Statins (n = 29) | No Statins (n = 32) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24.7 [4.23, 33.06] | 35.46 [15.71, 54.96] | 0.165 | |
| 37.59 [16.08, 102.43] | 107.00 [75.05, 173.50] | <0.001 * | |
| CBVv | 3.60 [0.65, 12.40] | 11.85 [5.37, 30.56] | 0.015 * |
| CBFv | 25.6 [7.84, 59.75] | 56.84 [31.26, 87.67] | 0.037 * |
| − CBFv | 5.63 [−14.75, 27.75] | 40.52 [−9.65, 102.47] | 0.035 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picchi, E.; Di Giuliano, F.; Pucci, N.; Sallustio, F.; Minosse, S.; Mascolo, A.P.; Marrama, F.; Ferrazzoli, V.; Da Ros, V.; Diomedi, M.; et al. CT Perfusion Imaging in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Premorbid Statin Treatment. Tomography 2025, 11, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11050054
Picchi E, Di Giuliano F, Pucci N, Sallustio F, Minosse S, Mascolo AP, Marrama F, Ferrazzoli V, Da Ros V, Diomedi M, et al. CT Perfusion Imaging in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Premorbid Statin Treatment. Tomography. 2025; 11(5):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11050054
Chicago/Turabian StylePicchi, Eliseo, Francesca Di Giuliano, Noemi Pucci, Fabrizio Sallustio, Silvia Minosse, Alfredo Paolo Mascolo, Federico Marrama, Valentina Ferrazzoli, Valerio Da Ros, Marina Diomedi, and et al. 2025. "CT Perfusion Imaging in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Premorbid Statin Treatment" Tomography 11, no. 5: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11050054
APA StylePicchi, E., Di Giuliano, F., Pucci, N., Sallustio, F., Minosse, S., Mascolo, A. P., Marrama, F., Ferrazzoli, V., Da Ros, V., Diomedi, M., Federici, M., & Garaci, F. (2025). CT Perfusion Imaging in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Premorbid Statin Treatment. Tomography, 11(5), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11050054





