Anatomical Variations and Morphometry of Carotid Sinus: A Computed Tomography Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Image Acquisition and Data Collection for Carotid Sinus Variations and Morphometry
2.2. Statistical Analysis
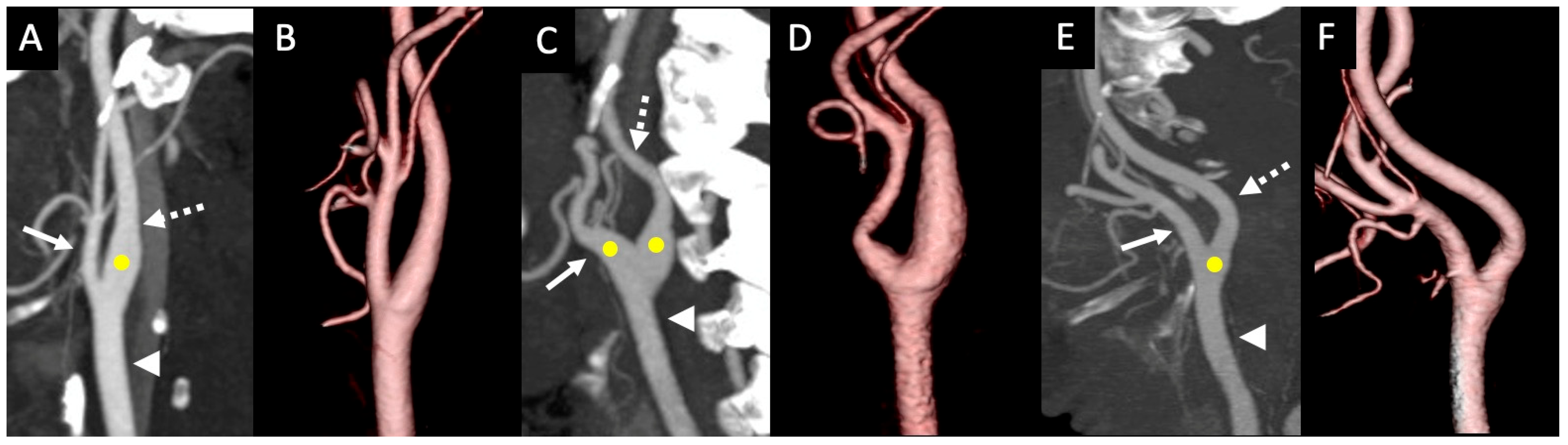
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- West, C.T.; Brassett, C.; Gaunt, M.E. Variations in carotid sinus anatomy and their relevance to carotid interventions. Folia Morphol. 2018, 77, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuta, S.; Iwanaga, J.; Kusukawa, J.; Tubbs, R.S. Carotid Sinus Nerve: A Comprehensive Review of Its Anatomy, Variations, Pathology, and Clinical Applications. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toorop, R.J.; Visser, R.F.; Moll, F.L.; Scheltinga, M.R. Long term safety and efficacy of internal carotid artery adventitial stripping in carotid sinus syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2014, 10, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andani, R.; Khan, Y.S. Anatomy, Head and Neck: Carotid Sinus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baz, R.A.; Scheau, C.; Rusali, A.C.; Bordei, P. Computed tomography-assessed variations of the carotid sinus. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2022, 44, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, D.; Bijari, P.B.; Morbiducci, U.; Qiao, Y.; Xie, Y.J.; Etesami, M.; Habets, D.; Lakatta, E.G.; Wasserman, B.A.; Steinman, D.A. Segment-specific associations between local haemodynamic and imaging markers of early atherosclerosis at the carotid artery: An in vivo human study. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saho, T.; Onishi, H. Quantitative analysis of effects of hemodynamic stress on temporal variations of cardiac phases in models of human carotid bulbs. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2017, 10, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.R.; Archie, J.P., Jr.; Kleinstreuer, C. Effect of carotid artery geometry on the magnitude and distribution of wall shear stress gradients. J. Vasc. Surg. 1996, 23, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijari, P.B.; Wasserman, B.A.; Steinman, D.A. Carotid bifurcation geometry is an independent predictor of early wall thickening at the carotid bulb. Stroke 2014, 45, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Show, S.; Biswas, N.; Datta, A. Atherosclerosis risk assessment in human carotid artery with variation in sinus length: A numerical approach. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed Engin. 2024, 27, 2288–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.K.; Sung, P.H.; Wu, C.J.; Yu, C.M. Carotid stenting and endarterectomy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 214, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, S.; Li, S.; Pu, F.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Li, D. Flow patterns and wall shear stress distribution in human internal carotid arteries: The geometric effect on the risk for stenoses. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G. Hemodynamic changes and baroreflex sensitivity associated with carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting. Interv. Neurol. 2015, 3, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigaudo-Roussel, D.; Evans, D.H.; Naylor, A.R.; Panerai, R.B.; London, N.L.; Bell, P.; Gaunt, M.E. Deterioration in carotid baroreflex during carotid endarterectomy. J. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 36, 793–798. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.S.; Lim, Y.J.; Bahk, J.H.; Do, S.H.; Ham, B.M. Coronary artery spasm induced by carotid sinus stimulation during neck surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2003, 90, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Ozgur, Z.; Govsa, F.; Ozgur, T. Anatomic evaluation of the carotid artery bifurcation in cadavers: Implications for open and endovascular therapy. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2008, 30, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.; Lieber, B.B.; Wakhloo, A.K. Morphological age-dependent development of the human carotid bifurcation. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.; Jeong, W.; Smith, N.; Towner, R.A. Hemodynamic effects of long-term morphological changes in the human carotid sinus. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, U.G.; Rothwell, P.M. Major variation in carotid bifurcation anatomy: A possible risk factor for plaque development? Stroke 2001, 32, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, B.R.; Bäck, M.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Caligiuri, G.; Daemen, M.J.; Davies, P.F.; Hoefer, I.E.; Holvoet, P.; Jo, H.; Krams, R.; et al. Biomechanical factors in atherosclerosis: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 3013–3020d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalinos, A.; Chatzimarkos, M.; Arkadopoulos, N.; Safioleas, M.; Troupis, T. Anatomical Considerations on Surgical Anatomy of the Carotid Bifurcation. Anat. Res. Int. 2016, 6907472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Brink, R.B.; de Lange, F.J. Carotismassage is geen onschuldige interventie [Carotid sinus massage is not a benign intervention]. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2017, 161, D1312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crouse, J.R.; Goldbourt, U.; Evans, G.; Pinsky, J.; Sharrett, A.R.; Sorlie, P.; Riley, W.; Heiss, G. Arterial enlargement in the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) cohort. In vivo quantification of carotid arterial enlargement. The ARIC Investigators. Stroke 1994, 25, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannami, T.; Baba, S.; Ogata, J. Potential of carotid enlargement as a useful indicator affected by high blood pressure in a large general population of a Japanese city: The Suita study. Stroke 2000, 31, 2958–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonithon-Kopp, C.; Touboul, P.J.; Berr, C.; Magne, C.; Ducimetière, P. Factors of carotid arterial enlargement in a population aged 59 to 71 years: The EVA study. Stroke 1996, 27, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagargoje, M.; Gupta, R. Effect of sinus size and position on hemodynamics during pulsatile flow in a carotid artery bifurcation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 192, 105440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | CS Type I | CS Type II | CS Type III |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 754) | 87.67 (661/754) | 9.02 (68/754) | 3.32 (25/754)) |
| Men (n = 428) | 89.72 * (384/428) | 7.94 (34/428) | 2.34 (10/428) |
| Women (n = 326) | 84.97 * (277/326) | 10.43 (34/326) | 4.60 (15/326) |
| Right side (n = 380) | 89.47 (340/380) | 6.58 (25/380) | 3.95 (15/380) |
| Left side (n = 374) | 85.83 (321/374) | 11.5 (43/374) | 2.67 (10/374) |
| Vessel Max Diameter | Men (n = 428) | Women (n = 326) | p Value * | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | ||||
| Type I | 7.53 ± 0.04 (n = 384) | 6.76 ± 0.06 (n = 277) | <0.001 # | 15.10 |
| Type II | 8.04 ± 0.23 (n = 34) | 7.57 ± 0.20 (n = 34) | 0.13 | NA |
| Type III | 5.92 ± 0.14 (n = 10) | 6.13 ± 0.39 (n = 15) | 0.67 | NA |
| Overall | 7.53 ± 0.05 (n = 428) | 6.81 ± 0.06 (n = 326) | <0.001 # | 13.03 |
| ECA | ||||
| Type I | 5.05 ± 0.37 (n = 384) | 4.47 ± 0.04 (n = 277) | <0.001 # | 13.04 |
| Type II | 5.89 ± 0.15 (n = 34) | 5.69 ± 0.17 (n = 34) | 0.38 | NA |
| Type III | 4.78 ± 0.31 (n = 10) | 4.77 ± 0.21 (n = 15) | 0.98 | NA |
| Overall | 5.11 ± 0.04 (n = 428) | 4.62 ± 0.04 (n = 326) | <0.001 # | 12.25 |
| CCA | ||||
| Type I | 9.54 ± 0.64 (n = 384) | 8.60 ± 0.07 (n = 277) | <0.001 # | 2.06 |
| Type II | 10.79 ± 0.23 (n = 34) | 9.93 ± 0.20 (n = 34) | 0.01 | NA |
| Type III | 8.70 ± 0.34 (n = 10) | 9.02 ± 0.42 (n = 15) | 0.59 | NA |
| Overall | 8.76 ± 0.07 (n = 428) | 9.61 ± 0.06 (n = 326) | <0.001 # | 13.04 |
| Sinus length | ||||
| Type I | 12.72 ± 0.08 (n = 384) | 11.75 ± 0.09 (n = 277) | <0.001 # | 11.39 |
| Type II | 13.72 ± 0.311 (n = 34) | 12.92 ± 0.23 (n = 34) | 0.04 | NA |
| Overall | 12.80 ± 0.07 (n = 418) | 11.88 ± 0.086 (n = 311) | <0.001 # | 11.41 |
| Vessel with max diameter at sinus | ||||
| CCA | 9.64 ± 0.06 (n = 423) | 8.77 ± 0.07 (n = 324) | <0.001 # | 13.34 |
| ICA | 8.42 ± 0.40 (n = 5) | 7.30 ± 0.40 (n = 2) | 0.17 | NA |
| Vessel Max Diameter | Right Side (n = 380) | Left Side (n = 374) | p Value # |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | |||
| Type I | 7.15 ± 0.06 (n = 340) | 7.27 ± 0.06 (n = 321) | 0.18 |
| Type II | 7.84 ± 0.30 (n = 25) | 7.78 ± 0.18 (n = 43) | 0.85 |
| Type III | 6.05 ± 0.33 (n = 15) | 6.04 ± 0.36 (n = 10) | 0.99 |
| Overall | 7.15 ± 1.22 (n = 380) | 7.30 ± 1.56 (n = 374) | 0.10 |
| ECA | |||
| Type I | 4.85 ± 0.42 (n = 340) | 4.75 ± 0.04 (n = 321) | 0.08 |
| Type II | 5.67 ± 0.20 (n = 25) | 5.86 ± 0.14 (n = 43) | 0.44 |
| Type III | 4.97 ± 0.25 (n = 15) | 4.47 ± 0.17 (n = 10) | 0.11 |
| Overall | 4.92 ± 0.81 (n = 380) | 4.87 ± 0.84 (n = 374) | 0.48 |
| CCA | |||
| Type I | 9.10 ± 0.07 (n = 340) | 9.19 ± 0.07 (n = 321) | 0.38 |
| Type II | 10.32 ± 0.30 (n = 25) | 10.38 ± 0.19 (n = 43) | 0.53 |
| Type III | 9.02 ± 0.39 (n = 15) | 8.70 ± 0.42 (n = 10) | 0.59 |
| Overall | 9.18 ± 1.36 (n = 380) | 9.32 ± 1.34 (n = 374) | 0.17 |
| Sinus length | |||
| Type I | 12.28 ± 0.09 (n = 340) | 12.34 ± 0.09 (n = 321) | 0.63 |
| Type II | 13.48 ± 0.41 (n = 25) | 13.22 ± 0.20 (n = 43) | 0.53 |
| Overall | 12.37 ± 0.88 (n = 365) | 12.45 ± 0.08 (n = 364) | 0.50 |
| Vessel with max diameter at sinus | |||
| CCA | 9.20 ± 0.07 (n = 377) | 9.33 ± 0.07 (n = 370) | 0.16 |
| ICA | 8.07 ± 0.88 (n = 3) | 8.13 ± 0.22 (n = 4) | 0.94 |
| Vessel Max Diameter | Age Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | 18–39 (n = 210) | 40–69 (n = 486) | ≥70 (n = 58) | p Value * |
| Type I | 7.13 ± 0.08 (n = 191) | 7.25 ± 0.056 (n = 422) | 7.09 ± 0.15 (n = 48) | 0.36 |
| Type II | 7.02 ± 0.78 (n = 10) | 7.95 ± 1.33 (n = 54) | 10.48 ± 1.66 (n = 4) | 0.11 |
| Type III | 6.38 ± 1.77 (n = 9) | 5.76 ± 0.81 (n = 10) | 6.03 ± 0.66 (n = 6) | 0.56 |
| Overall | 7.09 ± 1.17 (n = 210) | 7.30 ± 1.20 (n = 486) | 7.03 ± 1.07 (n = 58) | 0.05 |
| ECA | ||||
| Type I | 4.79 ± 0.06 (n = 191) | 4.82 ± 0.03 (n = 422) | 4.73 ± 0.09 (n = 48) | 0.75 |
| Type II | 5.85 ± 1.25 (n = 10) | 5.81 ± 0.91 (n = 54) | 5.32 ± 0.57 (n = 4) | 0.60 |
| Type III | 5.25 ± 0.91 (n = 9) | 4.22 ± 0.57 (n = 10) | 4.97 ± 0.75 (n = 6) | 0.02 |
| Overall | 4.86 ± 0.85 (n = 210) | 4.92 ± 0.83 (n = 486) | 4.80 ± 0.69 (n = 58) | 0.49 |
| CCA | ||||
| Type I | 9.15 ± 0.096 (n = 191) | 9.18 ± 0.063 (n = 422) | 8.86 ± 0.17 (n = 48) | 0.29 |
| Type II | 10.20 ± 1.26 (n = 10) | 10.38 ± 1.35 (n = 54) | 10.48 ± 1.66 (n = 4) | 0.91 |
| Type III | 9.17 ± 1.71 (n = 9) | 8.47 ± 1.44 (n = 10) | 9.18 ± 0.82 (n = 6) | 0.50 |
| Overall | 9.20 ± 1.36 (n = 210) | 9.29 ± 1.36 (n = 486) | 9.01 ± 1.35 (n = 58) | 0.26 |
| Sinus length | ||||
| Type I | 12.43 ± 1.62 (n = 191) | 12.30 ± 1.57 (n = 422) | 11.97 ± 1.41 (n = 48) | 0.20 |
| Type II | 12.61 ± 1.16 (n = 10) | 13.53 ± 1.68 (n = 54) | 12.30 ± 0.96 (n = 4) | 0.11 |
| Overall | ||||
| Vessel with max diameter at sinus | ||||
| CCA | 9.22 ± 1.37 (n = 210) | 9.31 ± 1.38 (n = 480) | 9.08 ± 1.22 (n = 57) | 0.43 |
| ICA | - | 8.05 ± 1.01 (n = 6) | 8.40 ± 0.00 (n = 1) | 0.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fazaldad, N.; Sirasanagandla, S.R.; Al-Shuaili, A.; Mogali, S.R.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Dhuhli, H.A.; Al-Ajmi, E. Anatomical Variations and Morphometry of Carotid Sinus: A Computed Tomography Study. Tomography 2025, 11, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040045
Fazaldad N, Sirasanagandla SR, Al-Shuaili A, Mogali SR, Chandrasekaran R, Dhuhli HA, Al-Ajmi E. Anatomical Variations and Morphometry of Carotid Sinus: A Computed Tomography Study. Tomography. 2025; 11(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleFazaldad, Noor, Srinivasa Rao Sirasanagandla, Anwar Al-Shuaili, Sreenivasulu Reddy Mogali, Ramya Chandrasekaran, Humoud Al Dhuhli, and Eiman Al-Ajmi. 2025. "Anatomical Variations and Morphometry of Carotid Sinus: A Computed Tomography Study" Tomography 11, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040045
APA StyleFazaldad, N., Sirasanagandla, S. R., Al-Shuaili, A., Mogali, S. R., Chandrasekaran, R., Dhuhli, H. A., & Al-Ajmi, E. (2025). Anatomical Variations and Morphometry of Carotid Sinus: A Computed Tomography Study. Tomography, 11(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040045







