Temporal Shift When Comparing Contrast-Agent Concentration Curves Estimated Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) and ΔR2*: The Association Between Vortex Parameters and Oxygen Extraction Fraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Measurements
2.2. Image Processing and Data Analysis
2.2.1. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
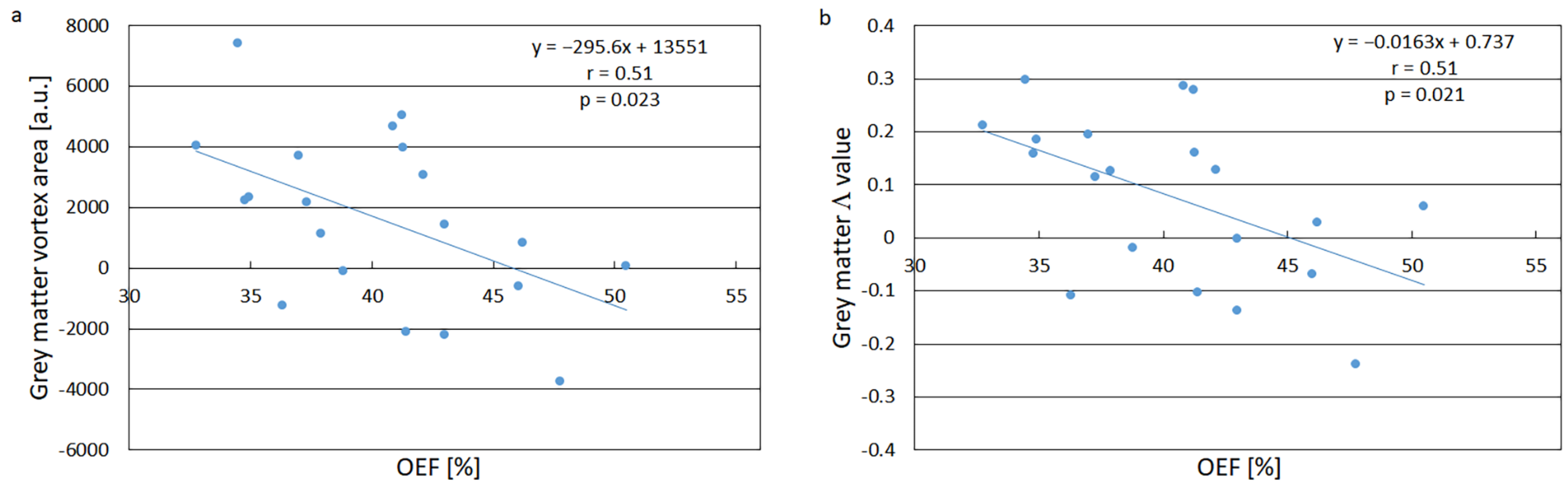
2.2.2. Oxygen Extraction Fraction
2.2.3. Vortex Curves from Dynamic GRE Data
2.2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Vortex Curves
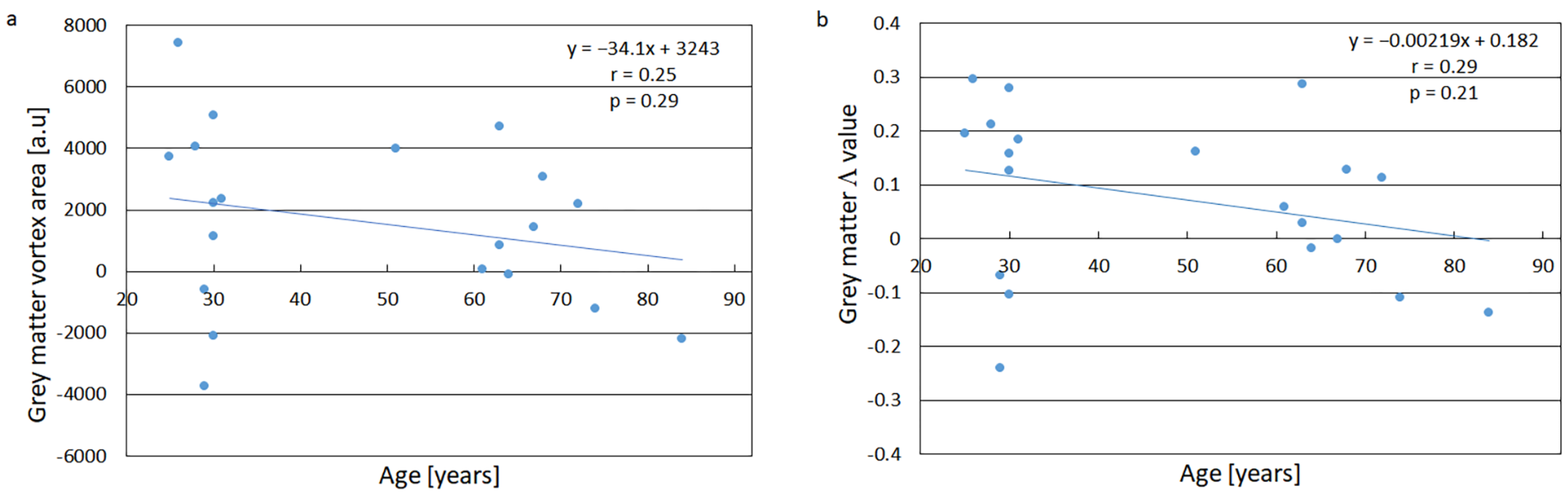
3.2. Age Dependence of the Vortex Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boxerman, J.L.; Hamberg, L.M.; Rosen, B.R.; Weisskoff, R.M. MR contrast due to intravascular magnetic susceptibility perturbations. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Kiselev, V.G.; Strecker, R.; Ziyeh, S.; Speck, O.; Hennig, J. Vessel size imaging in humans. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Kiselev, V.G.; Möller, H.E.; Fiebach, J.B. Dynamic hysteresis between gradient echo and spin echo attenuations in dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 981–991. [Google Scholar]
- Emblem, K.E.; Mouridsen, K.; Bjornerud, A.; Farrar, C.T.; Jennings, D.; Borra, R.J.; Wen, P.Y.; Ivy, P.; Batchelor, T.T.; Rosen, B.R.; et al. Vessel architectural imaging identifies cancer patient responders to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, A.; Zhang, K.; Mooshage, C.M.; Jende, J.M.E.; Rotkopf, L.T.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Bendszus, M.; Wick, W.; Kurz, F.T. Whole-brain vascular architecture mapping identifies region-specific microvascular profiles in vivo. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2024, 45, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Stadlbauer, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Oberndorfer, S.; Doerfler, A.; Buchfelder, M.; Heinz, G.; Roessler, K. Vascular hysteresis loops and vascular architecture mapping in patients with glioblastoma treated with antiangiogenic therapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8508. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Park, J.E.; Emblem, K.; Bjørnerud, A.; Kim, H.S. Vessel type determined by vessel architectural imaging improves differentiation between early tumor progression and pseudoprogression in glioblastoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.I.; Ryu, C.W.; Kim, S.; Rhee, H.Y.; Jahng, G.H. Changes in microvascular morphology in subcortical vascular dementia: A study of vessel size magnetic resonance imaging. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 545450. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Schmidt, W.U.; Villringer, K.; Brunecker, P.; Kiselev, V.; Gall, P.; Fiebach, J.B. Vessel size imaging reveals pathological changes of microvessel density and size in acute ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.E.; Lou, K.W.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Chang, K.; Gidwani, M.; Hoebel, K.; Patel, J.B.; Cleveland, M.C.; Singh, P.; Bridge, C.P.; et al. Abnormal vascular structure and function within brain metastases is linked to pembrolizumab resistance. Neuro Oncol. 2024, 26, 965–974. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, E.; Knutsson, L.; Ståhlberg, F.; Wirestam, R. Dynamic contrast-enhanced QSM for perfusion imaging: A systematic comparison of ΔR2*- and QSM-based contrast agent concentration time curves in blood and tissue. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. 2020, 33, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, B.; Klose, U. The in vivo influence of white matter fiber orientation towards B0 on T2* in the human brain. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cho, Z.H.; Lee, J. Origin of B0 orientation dependent R2* (=1/T2*) in white matter. Neuroimage 2013, 73, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Torres, E.; Kassner, N.; Forkert, N.D.; Wei, L.; Wiggermann, V.; Daemen, M.; Machan, L.; Traboulsee, A.; Li, D.; Rauscher, A. Anisotropic cerebral vascular architecture causes orientation dependency in cerebral blood flow and volume measured with dynamic susceptibility contrast magnetic resonance imaging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Denk, C.; Hernandez Torres, E.; MacKay, A.; Rauscher, A. The influence of white matter fibre orientation on MR signal phase and decay. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibgatulin, R.; Güllmar, D.; Deistung, A.; Ropele, S.; Reichenbach, J.R. In vivo assessment of anisotropy of apparent magnetic susceptibility in white matter from a single orientation acquisition. Neuroimage 2021, 241, 118442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blomqvist, L.; Nordberg, G.F.; Nurchi, V.M.; Aaseth, J.O. Gadolinium in medical imaging: Usefulness, toxic reactions and possible countermeasures—A review. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutsson, L.; Lindgren, E.; Ahlgren, A.; van Osch, M.J.; Bloch, K.M.; Surova, Y.; Ståhlberg, F.; van Westen, D.; Wirestam, R. Dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI with a prebolus contrast agent administration design for improved absolute quantification of perfusion. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 996–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Wirestam, R.; Lundberg, A.; Chakwizira, A.; van Westen, D.; Knutsson, L.; Lind, E. Test-retest analysis of cerebral oxygen extraction estimates in healthy volunteers: Comparison of methods based on quantitative susceptibility mapping and dynamic susceptibility contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; de Rochefort, L.; Ledoux, J.; Khalidov, I.; Chen, W.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wisnieff, C.; Spincemaille, P.; Prince, M.R.; et al. Morphology enabled dipole inversion for quantitative susceptibility mapping using structural consistency between the magnitude image and the susceptibility map. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomir, R.; de Senneville, B.D.; Moonen, C.T.W. A fast calculation method for magnetic field inhomogeneity due to an arbitrary distribution of bulk susceptibility. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2003, 19, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, J.P.; Bowtell, R. Application of a Fourier-based method for rapid calculation of field inhomogeneity due to spatial variation of magnetic susceptibility. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2005, 25, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- de Rochefort, L.; Liu, T.; Kressler, B.; Liu, J.; Spincemaille, P.; Lebon, V.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Quantitative susceptibility map reconstruction from MR phase data using Bayesian regularization: Validation and application to brain imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 194–206. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Liu, J.; de Rochefort, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Khalidov, I.; Ledoux, J.R.; Wang, Y. Morphology enabled dipole inversion (MEDI) from a single-angle acquisition: Comparison with COSMOS in human brain imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 777–783. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wisnieff, C.; Lou, M.; Chen, W.; Spincemaille, P.; Wang, Y. Nonlinear formulation of the magnetic field to source relationship for robust quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 467–476. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Khalidov, I.; de Rochefort, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Liu, J.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wang, Y. A novel background field removal method for MRI using projection onto dipole fields (PDF). NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, E.; Knutsson, L.; Kämpe, R.; Ståhlberg, F.; Wirestam, R. Assessment of MRI contrast agent concentration by quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): Application to estimation of cerebral blood volume during steady state. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. 2017, 30, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Weisskoff, R.M.; Kiihne, S. MRI susceptometry: Image-based measurement of absolute susceptibility of MR contrast agents and human blood. Magn. Reson. Med. 1992, 24, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Eldeniz, C.; Binkley, M.M.; Fields, M.; Guilliams, K.; Ragan, D.K.; Chen, Y.; Lee, J.M.; Ford, A.L.; An, H. Bulk volume susceptibility difference between deoxyhemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin for HbA and HbS: A comparative study. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.L.; Dumas, J.A.; Park, D.C.; Liu, P.; Filbey, F.M.; McAdams, C.J.; Pinkham, A.E.; Adinoff, B.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H. Age-related increase of resting metabolic rate in the human brain. Neuroimage 2014, 98, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, A.; Lind, E.; Olsson, H.; Helms, G.; Knutsson, L.; Wirestam, R. Comparison of MRI methods for measuring whole-brain oxygen extraction fraction under different geometric conditions at 7T. J. Neuroimaging 2022, 32, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Rochefort, L.; Nguyen, T.; Brown, R.; Spincemaille, P.; Choi, G.; Weinsaft, J.; Prince, M.R.; Wang, Y. In vivo quantification of contrast agent concentration using the induced magnetic field for time-resolved arterial input function measurement with MRI. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 5328–5339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thilmann, O. LUPE: An extensible modular framework for evaluation of DSC-acquired perfusion images. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. 2004, 16 (Suppl. S1), 537. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.J.; Swinscow, T.V.D. Statistics at Square One, 11th ed.; BMJ Books, Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Emblem, K.E.; Farrar, C.T.; Gerstner, E.R.; Batchelor, T.T.; Borra, R.J.; Rosen, B.R.; Sorensen, A.G.; Jain, R.K. Vessel calibre—A potential MRI biomarker of tumour response in clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 566–584. [Google Scholar]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Videen, T.O.; Yundt, K.D.; Fritsch, S.M.; Carpenter, D.A.; Grubb, R.L.; Powers, W.J. Variability of cerebral blood volume and oxygen extraction: Stages of cerebral haemodynamic impairment revisited. Brain 2002, 125, 595–607. [Google Scholar]
- Rudko, D.A.; Klassen, L.M.; de Chickera, S.N.; Gati, J.S.; Dekaban, G.A.; Menon, R.S. Origins of R2* orientation dependence in gray and white matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E159–E167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doucette, J.; Wei, L.; Hernández-Torres, E.; Kames, C.; Forkert, N.D.; Aamand, R.; Lund, T.E.; Hansen, B.; Rauscher, A. Rapid solution of the Bloch-Torrey equation in anisotropic tissue: Application to dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI of cerebral white matter. NeuroImage 2019, 185, 198–207. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Shin, H.G.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Li, X. Exploiting gradient-echo frequency evolution: Probing white matter microstructure and extracting bulk susceptibility-induced frequency for quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 1676–1693. [Google Scholar]
- Raichle, M.E.; MacLeod, A.M.; Snyder, A.Z.; Powers, W.J.; Gusnard, D.A.; Shulman, G.L. A default mode of brain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 676–682. [Google Scholar]
- Leenders, K.L.; Perani, D.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Heather, J.D.; Buckingham, P.; Jones, T.; Healy, M.J.R.; Gibbs, J.M.; Wise, R.J.S.; Hatazawa, J.; et al. Cerebral blood flow, blood volume and oxygen utilization. Normal values and effect of age. Brain 1990, 113 Pt 1, 27–47. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wirestam, R.; Lundberg, A.; Knutsson, L.; Lind, E. Temporal Shift When Comparing Contrast-Agent Concentration Curves Estimated Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) and ΔR2*: The Association Between Vortex Parameters and Oxygen Extraction Fraction. Tomography 2025, 11, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040046
Wirestam R, Lundberg A, Knutsson L, Lind E. Temporal Shift When Comparing Contrast-Agent Concentration Curves Estimated Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) and ΔR2*: The Association Between Vortex Parameters and Oxygen Extraction Fraction. Tomography. 2025; 11(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleWirestam, Ronnie, Anna Lundberg, Linda Knutsson, and Emelie Lind. 2025. "Temporal Shift When Comparing Contrast-Agent Concentration Curves Estimated Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) and ΔR2*: The Association Between Vortex Parameters and Oxygen Extraction Fraction" Tomography 11, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040046
APA StyleWirestam, R., Lundberg, A., Knutsson, L., & Lind, E. (2025). Temporal Shift When Comparing Contrast-Agent Concentration Curves Estimated Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) and ΔR2*: The Association Between Vortex Parameters and Oxygen Extraction Fraction. Tomography, 11(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11040046





