Comparison of the Size Measurement of Gallbladder Polyps by Three Different Radiologists in Abdominal Ultrasonography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Image Acquisition of GB Polyps
2.3. Data Acquisition of Study Patients
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of GB Polyps
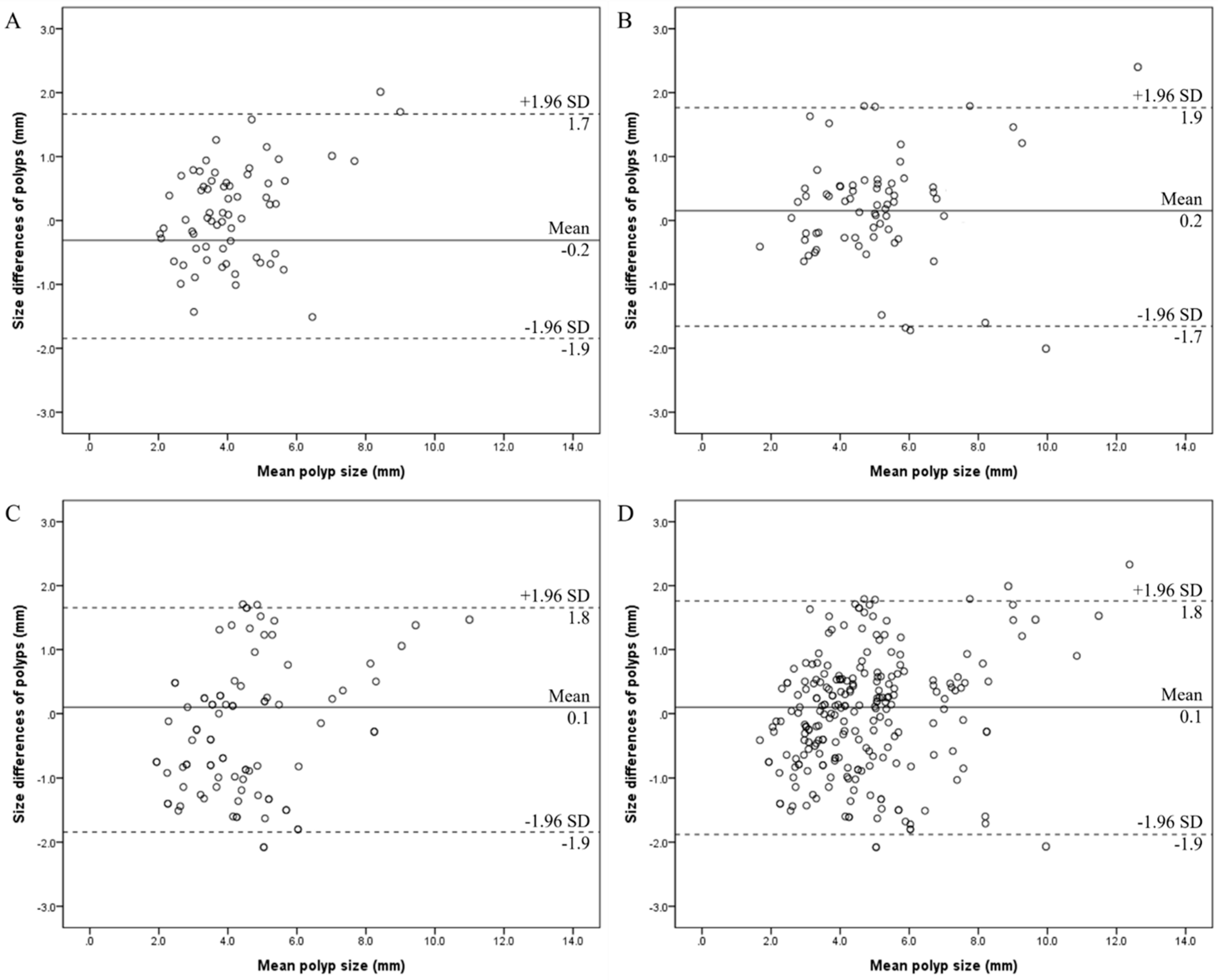
3.2. Intra-Reader Agreements for Size Measurements of GB Polyps
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jørgensen, T.; Jensen, K.H. Polyps in the gallbladder. A prevalence study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1990, 25, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.D.; Murakata, L.A.; Rohrmann, C.A., Jr. Gallbladder carcinoma: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2001, 21, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundal, R.; Shaffer, E.A. Gallbladder cancer: Epidemiology and outcome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diep, R.; Lombardo, P.; Schneider, M. The growth rates of solitary gallbladder polyps compared to multi-polyps: A quantitative analysis. Australas. J. Ultrasound Med. 2022, 25, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasry, M.; Lindop, D.; Dunne, D.F.J.; Malik, H.; Poston, G.J.; Fenwick, S.W. The risk of malignancy in ultrasound detected gallbladder polyps: A systematic review. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 33, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adsay, V.; Jang, K.T.; Roa, J.C.; Dursun, N.; Ohike, N.; Bagci, P.; Basturk, O.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Cheng, J.D.; Sarmiento, J.M.; et al. Intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasms (ICPN) of the gallbladder (neoplastic polyps, adenomas, and papillary neoplasms that are ≥1.0 cm): Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 123 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1279–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennmacker, S.Z.; de Savornin Lohman, E.A.; Hasami, N.A.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Boermeester, M.A.; Verheij, J.; Bilgen, E.J.S.; Meijer, J.W.; Bosscha, K.; van der Linden, J.C.; et al. Overtreatment of nonneoplastic gallbladder polyps due to inadequate routine ultrasound assessment. Dig. Surg. 2021, 38, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennmacker, S.Z.; van Dijk, A.H.; Raessens, J.H.; van Laarhoven, C.J.; Drenth, J.P.; de Reuver, P.R.; Nagtegaal, I.D. Polyp size of 1 cm is insufficient to discriminate neoplastic and non-neoplastic gallbladder polyps. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Yoon, Y.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Ryu, J.K.; Yoon, W.J.; Lee, S.H.; Yu, S.-J.; Kang, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, M.J. Management strategies for gallbladder polyps: Is it possible to predict malignant gallbladder polyps? Gut Liver 2008, 2, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.P.; Shaffer, E.A.; Beck, P.L. Gallbladder polyps: Epidemiology, natural history and management. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 16, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.F.; Wong, J.; Li, J.C.M.; San Lai, P.B. Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 188, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpakowski, J.L.; Tucker, L.Y. Outcomes of gallbladder polyps and their association with gallbladder cancer in a 20-year cohort. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e205143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Lin, N.; You, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y. Risk factors to discriminate neoplastic polypoid lesions of gallbladder: A large-scale case-series study. Asian J. Surg. 2021, 44, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, A.; Fung, C.; Szpakowski, J.L.; Fetzer, D.T.; Walsh, A.J.; Alimi, Y.; Bingham, D.B.; Corwin, M.T.; Dahiya, N.; Gabriel, H.; et al. Management of incidentally detected gallbladder polyps: Society of Radiologists in ultrasound consensus conference recommendations. Radiology 2022, 305, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, A.J.; Bingham, D.B.; Kamaya, A. Longitudinal ultrasound assessment of changes in size and number of incidentally detected gallbladder polyps. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 218, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, R.; Thoeni, R.F.; Barbu, S.T.; Vashist, Y.K.; Rafaelsen, S.R.; Dewhurst, C.; Arvanitakis, M.; Lahaye, M.; Soltes, M.; Perinel, J.; et al. Management and follow-up of gallbladder polyps: Joint guidelines between the European Society of Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Radiology (ESGAR), European Association for Endoscopic Surgery and other Interventional Techniques (EAES), International Society of Digestive Surgery-European Federation (EFISDS) and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE). Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 3856–3866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foley, K.G.; Lahaye, M.J.; Thoeni, R.F.; Soltes, M.; Dewhurst, C.; Barbu, S.T.; Vashist, Y.K.; Rafaelsen, S.R.; Arvanitakis, M.; Perinel, J.; et al. Management and follow-up of gallbladder polyps: Updated joint guidelines between the ESGAR, EAES, EFISDS and ESGE. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3358–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jung, H.K.; Hahn, S.; Baek, H.J. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability in sonographic size measurements of gallbladder polyps. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.; Ryu, J.K.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Paik, W.H.; Kwon, W.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Quantitative contrastenhanced US helps differentiating neoplastic vs non-neoplastic gallbladder polyps. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3772–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.W.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Ahn, S.J.; Joo, I.; Han, J.K. Risk stratification of gallbladder polyps larger than 10 mm using highresolution ultrasonography and texture analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, N.R.; Gillis, A.; Smoothey, C.O.; Awan, F.N.; Ridgway, P.F. Evidence based management of polyps of the gall bladder: A systematic review of the risk factors of malignancy. Surgeon 2016, 14, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, V.; Neal, C.P.; Dennison, A.R.; Garcea, G. Risk and costeffectiveness of surveillance followed by cholecystectomy for gallbladder polyps. Arch Surg 2012, 147, 078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Yoon, D.Y.; Seo, Y.L.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, S.; Lim, K.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Yun, E.J. Intraobserver and interobserver variability in ultrasound measurements of thyroid nodules. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegnander, E.; Eik-Nes, S.H. The examiner’s ultrasound experience has a significant impact on the detection rate of congenital heart defects at the second-trimester fetal examination. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 28, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.Y.; Kim, H.L.; Ha, E.J.; Park, S.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Han, M. Computer-aided diagnosis system for thyroid nodules on ultrasonography: Diagnostic performance and reproducibility based on the experience level of operators. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pt. No | Age | Sex | Maximal Diameter on Pathology (mm) | Maximal Diameter on Ultrasonography (mm) | Reader | Size Difference between Radiology and Pathology Reports (mm) | Interval Periods (Days) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44 | Male | 5.1 | 6.2 | A | −1.1 | 92 |
| 2 | 42 | Male | 14.9 | 13.0 | B | 1.9 | 21 |
| 3 | 45 | Female | 9.1 | 8.2 | A | 0.9 | 66 |
| 4 | 41 | Male | 9.5 | 9.3 | A | 0.2 | 45 |
| 5 | 38 | Male | 13.0 | 11.5 | C | 1.5 | 28 |
| 6 | 40 | Male | 8.2 | 9.1 | C | −0.9 | 28 |
| 7 | 52 | Male | 8.0 | 7.1 | A | 0.9 | 87 |
| 8 | 47 | Male | 11.3 | 10.0 | B | 1.3 | 25 |
| 9 | 39 | Male | 6.5 | 4.8 | A | 1.7 | 388 |
| 10 | 46 | Male | 10.3 | 9.6 | B | 0.7 | 54 |
| 11 | 48 | Female | 8.5 | 9.1 | B | −0.6 | 48 |
| 12 | 51 | Female | 9.8 | 9.5 | C | 0.3 | 50 |
| Characteristics | Reader A | Reader B | Reader C | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 65 | 77 | 86 | 228 |
| Age (years) | 44.4 ± 8.0 | 41.6 ± 7.6 | 45.4 ± 7.4 | 43.8 ± 7.8 |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Men | 54 (83.1) | 67 (87.0) | 68 (79.1) | 189 (82.9) |
| Women | 11 (16.9) | 10 (13.0) | 18 (20.9) | 39 (17.1) |
| Size of polyps (mm) | ||||
| ≤5 mm, n (%) | 44 (67.7) | 51 (66.2) | 43 (50.0) | 138 (60.5) |
| >5 mm, n (%) | 21 (32.3) | 26 (33.8) | 43 (50.0) | 90 (39.5) |
| Location of polyps, n (%) | ||||
| Neck | 27 (41.5) | 30 (39.0) | 38 (44.2) | 92 (40.4) |
| Body | 35 (53.9) | 44 (57.1) | 39 (45.3) | 121 (53.0) |
| Fundus | 3 (4.6) | 3 (3.9) | 9 (10.5) | 15 (6.6) |
| Type of polyps, n (%) | ||||
| Sessile | 8 (12.3) | 9 (11.7) | 13 (15.1) | 30 (13.2) |
| Pedunculated | 47 (72.3) | 58 (75.3) | 55 (64.0) | 160 (70.2) |
| N/A * | 10 (15.4) | 10 (13.0) | 18 (20.9) | 38 (16.6) |
| Reader A | Reader B | Reader C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All measured polyps † | 0.859 (0.774–0.911) | 0.947 (0.917–0.966) | 0.948 (0.920–0.966) |
| Size | |||
| ≤5 mm | 0.726 (0.445–0.876) | 0.808 (0.675–0.886) | 0.840 (0.677–0.921) |
| >5 mm | 0.821 (0.507–0.932) | 0.920 (0.795–0.969) | 0.902 (0.823–0.947) |
| Location | |||
| Neck | 0.924 (0.934–0.965) | 0.933 (0.858–0.968) | 0.936 (0.878–0.967) |
| Body | 0.823 (0.605–0.925) | 0.957 (0.921–0.976) | 0.951 (0.910–0.973) |
| Fundus | 0.934 (0.070–0.998) | 0.901 (0.083–0.997) | 0.964 (0.732–0.996) |
| Type | |||
| Sessile | 0.837 (0.536–0.938) | 0.966 (0.758–0.995) | 0.947 (0.673–0.992) |
| Pedunculated | 0.875 (0.780–0.940) | 0.920 (0.866–0.952) | 0.941 (0.903–0.964) |
| N/A * | 0.832 (0.470–0.938) | 0.974 (0.903–0.994) | 0.971 (0.905–0.992) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-C.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, D.-K. Comparison of the Size Measurement of Gallbladder Polyps by Three Different Radiologists in Abdominal Ultrasonography. Tomography 2024, 10, 1031-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070077
Lee K-C, Kim J-K, Kim D-K. Comparison of the Size Measurement of Gallbladder Polyps by Three Different Radiologists in Abdominal Ultrasonography. Tomography. 2024; 10(7):1031-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070077
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kyu-Chong, Jin-Kyem Kim, and Dong-Kyu Kim. 2024. "Comparison of the Size Measurement of Gallbladder Polyps by Three Different Radiologists in Abdominal Ultrasonography" Tomography 10, no. 7: 1031-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070077
APA StyleLee, K.-C., Kim, J.-K., & Kim, D.-K. (2024). Comparison of the Size Measurement of Gallbladder Polyps by Three Different Radiologists in Abdominal Ultrasonography. Tomography, 10(7), 1031-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070077







