Understanding the Dermoscopic Patterns of Basal Cell Carcinoma Using Line-Field Confocal Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubin, A.I.; Chen, E.H.; Ratner, D. Basal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, C.; Srinivasan, B.; Sayan, A.; Ilankovan, V. Epidemiology of basal cell carcinoma: A 10-year comparative study. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, M.C.; Lee, E.; Hibler, B.P.; Barker, C.A.; Mori, S.; Cordova, M.; Nehal, K.S.; Rossi, A.M. Basal cell carcinoma: Epidemiology; pathophysiology; clinical and histological subtypes; and disease associations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuka, A.G.; Book, S.E. Basal cell carcinoma: Pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reiter, O.; Mimouni, I.; Gdalevich, M.; Marghoob, A.A.; Levi, A.; Hodak, E.; Leshem, Y.A. The diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for basal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, S.W. Dermoscopy of pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 20, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, S.; Cecilia, N.; Malvehy, J. Dermoscopic criteria and basal cell carcinoma. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 147, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Altamura, D.; Menzies, S.W.; Argenziano, G.; Zalaudek, I.; Soyer, H.P.; Sera, F.; Avramidis, M.; DeAmbrosis, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Peris, K. Dermatoscopy of basal cell carcinoma: Morphologic variability of global and local features and accuracy of diagnosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, M.C.; Lee, E.; Hibler, B.P.; Giordano, C.N.; Barker, C.A.; Mori, S.; Cordova, M.; Nehal, K.S.; Rossi, A.M. Basal cell carcinoma: Contemporary approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heibel, H.D.; Hooey, L.; Cockerell, C.J. A Review of Noninvasive Techniques for Skin Cancer Detection in Dermatology. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Sattler, E.; Welzel, J. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography-Practical applications in dermatology and comparison with established imaging methods. Ski. Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzi, A.E.; Micali, G.; Lacarrubba, F. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography May Enhance Monitoring of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Imiquimod 5% Cream: A Pilot Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvel-Picard, J.; Chauvel-Picard, J.; Bérot, V.; Tognetti, L.; Orte Cano, C.; Fontaine, M.; Lenoir, C.; Pérez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Dubois, A.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography as a tool for three-dimensional in vivo quantification of healthy epidermis: A pilot study. J. Biophotonics 2022, 15, e202100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Gust, C.; Kendziora, B.; Frommherz, L.; French, L.E.; Hartmann, D.; Welzel, J.; Sattler, E. Line-field optical coherence tomography: In vivo diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma subtypes compared with histopathology. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwet, K.L. Computing inter-rater reliability and its variance in the presence of high agreement. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2008, 61 Pt 1, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brereton, R.G. Contingency tables, confusion matrices, classifiers and quality of prediction. J. Chemom. 2021, 35, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallas, A.; Apalla, Z.; Ioannides, D.; Argenziano, G.; Castagnetti, F.; Moscarella, E.; Longo, C.; Palmieri, T.; Ramundo, D.; Zalaudek, I. Dermoscopy in the diagnosis and management of basal cell carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallas, A.; Apalla, Z.; Argenziano, G.; Longo, C.; Moscarella, E.; Specchio, F.; Raucci, M.; Zalaudek, I. The dermatoscopic universe of basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2014, 4, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelamos, O.; Braun, R.P.; Liopyris, K.; Wolner, Z.J.; Kerl, K.; Gerami, P.; Marghoob, A.A. Dermoscopy and dermatopathology correlates of cutaneous neoplasms. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabanlioglu Onan, D.; Sahin, S.; Gököz, O.; Erkin, G.; Cakır, B.; Elçin, G.; Kayıkçıoğlu, A. Correlation between the dermatoscopic and histopathological features of pigmented basal cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perino, F.; Suarez, R.; Perez-Anker, J.; Carrera, C.; Rezze, G.G.; Primiero, C.A.; Alos, L.L.; Díaz, A.; Barreiro, A.; Puig, S. Concordance of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy and horizontal-sectioning histology in skin tumours. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 38, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, G.; Denaro, N.; Boggio, F.; Nazzaro, G.; Benzecry, V.; Bortoluzzi, P.; Passoni, E.; Garrone, O.; Marzano, A. Basosquamous Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools, and Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2023, 12, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gust, C.; Schuh, S.; Welzel, J.; Daxenberger, F.; Hartmann, D.; French, L.E.; Ruini, C.; Sattler, E.C. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography Increases the Diagnostic Accuracy and Confidence for Basal Cell Carcinoma in Equivocal Lesions: A Prospective Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinotti, E.; Brunetti, T.; Cartocci, A.; Tognetti, L.; Suppa, M.; Malvehy, J.; Perez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Perrot, J.L.; Rubegni, P. Diagnostic Accuracy of Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, C.; Suppa, M.; Tognetti, L.; Perrot, J.L.; Calabrese, L.; Pérez-Anker, J.; Malvehy, J.; Rubegni, P.; Cinotti, E. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas: Real-Life Data over Three Years. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 8853–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppa, M.; Fontaine, M.; Dejonckheere, G.; Cinotti, E.; Yélamos, O.; Diet, G.; Tognetti, L.; Miyamoto, M.; Orte Cano, C.; Perez-Anker, J.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography of basal cell carcinoma: A descriptive study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, G.; Orte Cano, C.; Fontaine, M.; Lenoir, C.; Cinotti, E.; Tognetti, L.; Rubegni, P.; Perez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J.; et al. Dermoscopic criteria explained by LC-OCT: Negative maple leaf-like areas. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 38, e271–e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomel, J.; Zalaudek, I. Dermoscopy of superficial basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 1710–1713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Micantonio, T.; Gulia, A.; Altobelli, E.; Di Cesare, A.; Fidanza, R.; Riitano, A.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Peris, K. Vascular patterns in basal cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, A. Dermoscopy-pathology relationship in seborrheic keratosis. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, O.; Mimouni, I.; Dusza, S.; Halpern, A.C.; Leshem, Y.A.; Marghoob, A.A. Dermoscopic features of basal cell carcinoma and its subtypes: A systematic review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallas, A.; Argenziano, G.; Kyrgidis, A.; Apalla, Z.; Moscarella, E.; Longo, C.; Ferrara, G.; Piana, S.; Benati, E.; Zendri, E.; et al. Dermoscopy uncovers clinically undetectable pigmentation in basal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 170, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Overall, n (%) (n = 100) | |
|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 53 (53) |
| Age at diagnosis, mean (SD) | 65.46 (13.36) |
| BCC localization | |
| Trunk, n (%) | 25 (25) |
| Inferior extremities, n (%) | 12 (12) |
| Superior extremities, n (%) | 6 (6) |
| Head and neck, n (%) | 57 (57) |
| Dermoscopic pigmented BCC, n (%) | 59 (59) |
| BCC histological subtypes, n (%) | |
| Superficial, n (%) | 54 (54) |
| Nodular, n (%) | 20 (20) |
| Infiltrating, n (%) | 16 (16) |
| Micronodular, n (%) | 5 (5) |
| Basosquamous, n (%) | 5 (5) |
| Overall (n = 100) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermoscopy Criteria | LC-OCT Criteria | Dermoscopy | LC-OCT | P | CCR | Concordance | p Concordance |
| Ulceration or erosion | Ulceration or erosion | 7 (7.0) | 7 (7.0) | 1 | 1 | 1 | <0.001 |
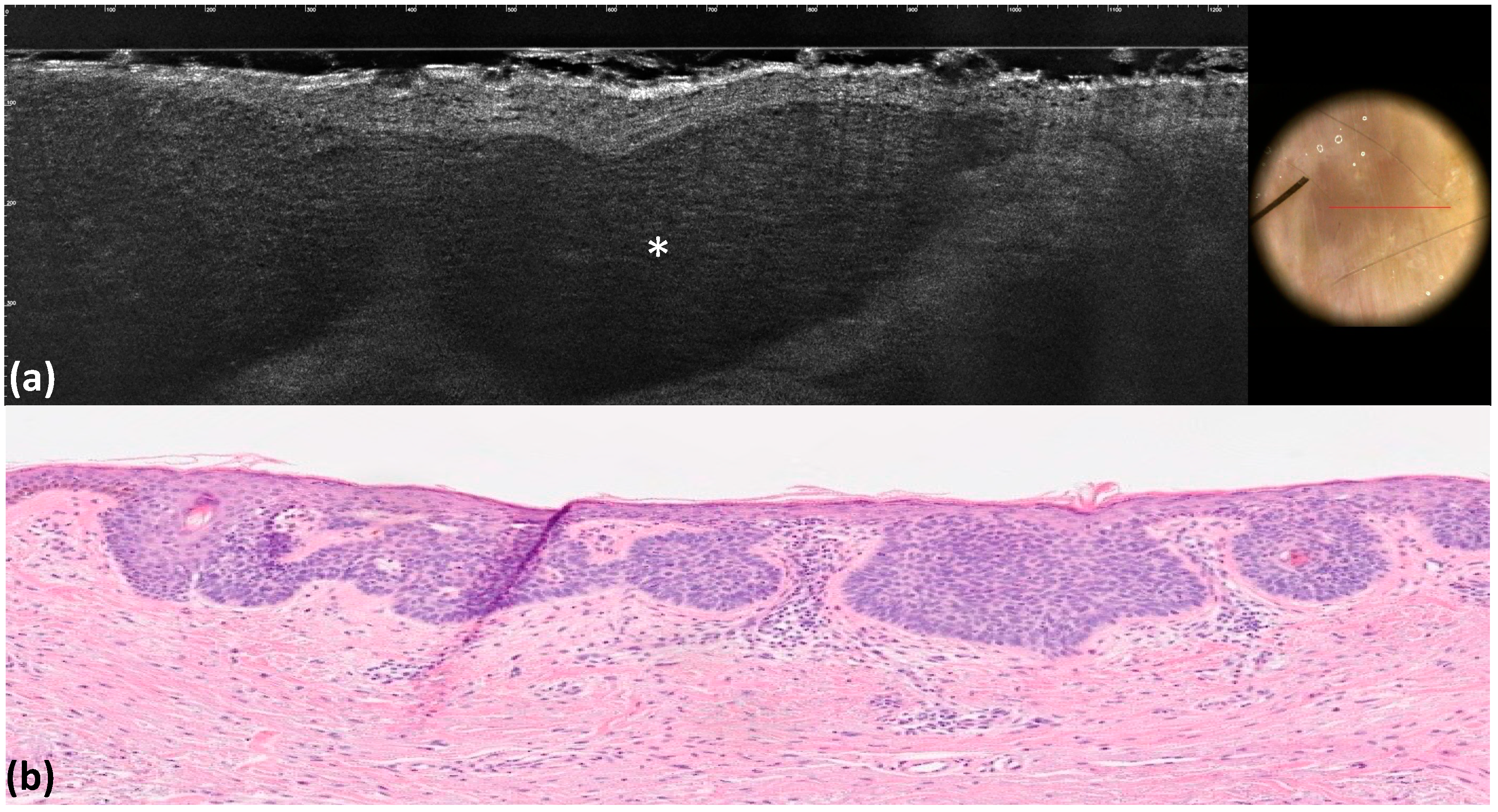
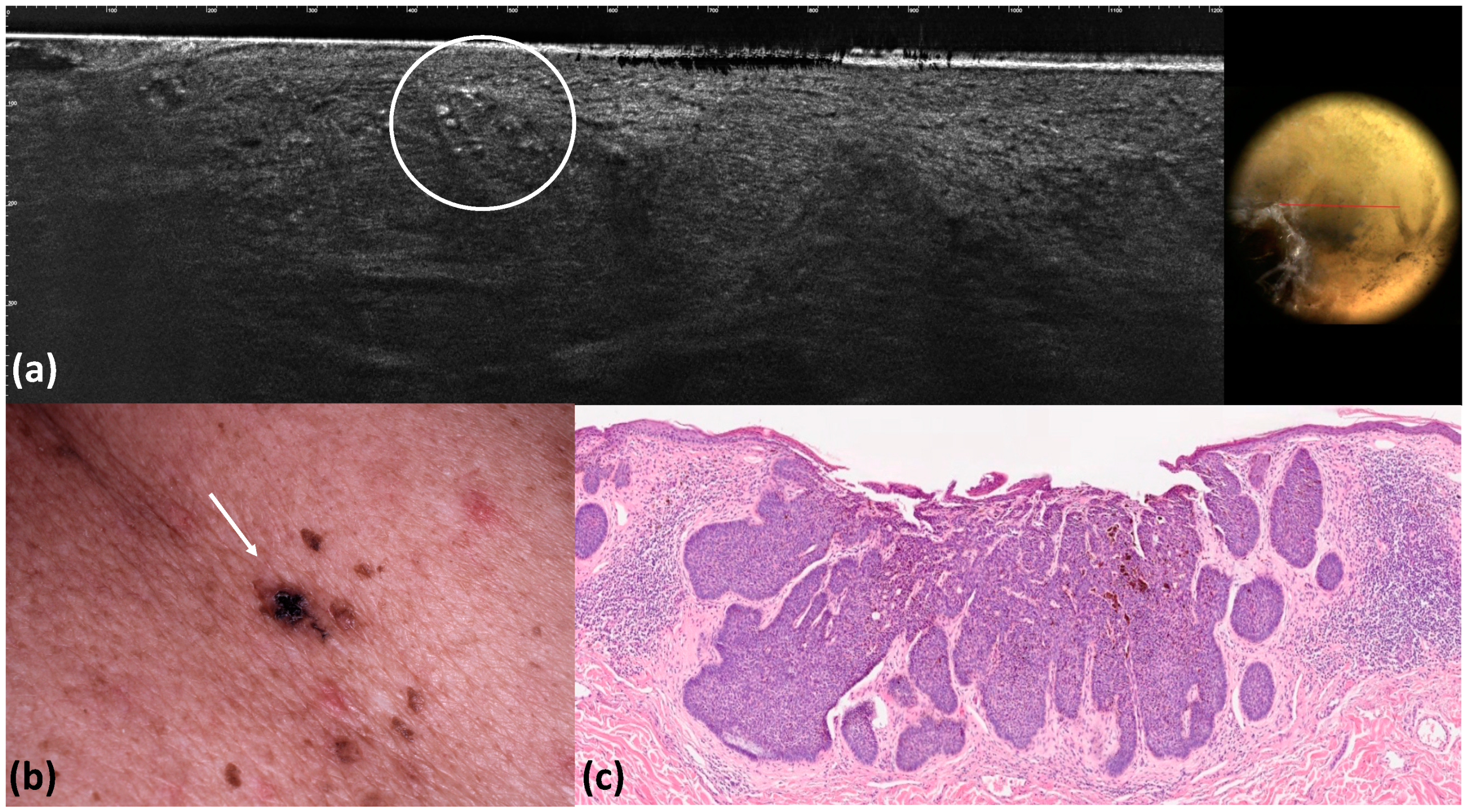
| Maple-leaf figures | Medium-reflective lobules with maple-leaf shapes attached to the epidermis | 12 (12.0) | 12 (12.0) | 1 | 1 | 1 | <0.001 |
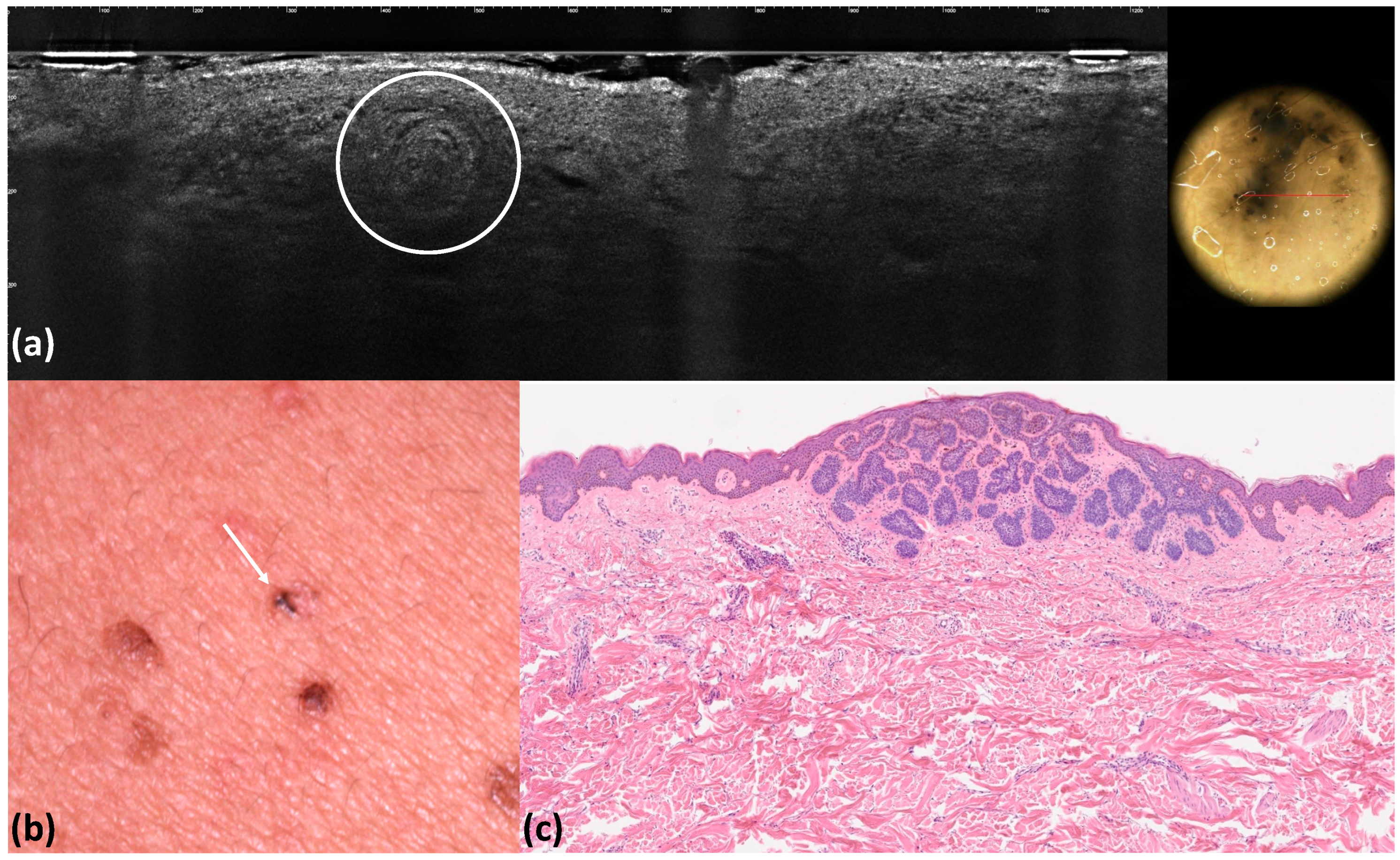
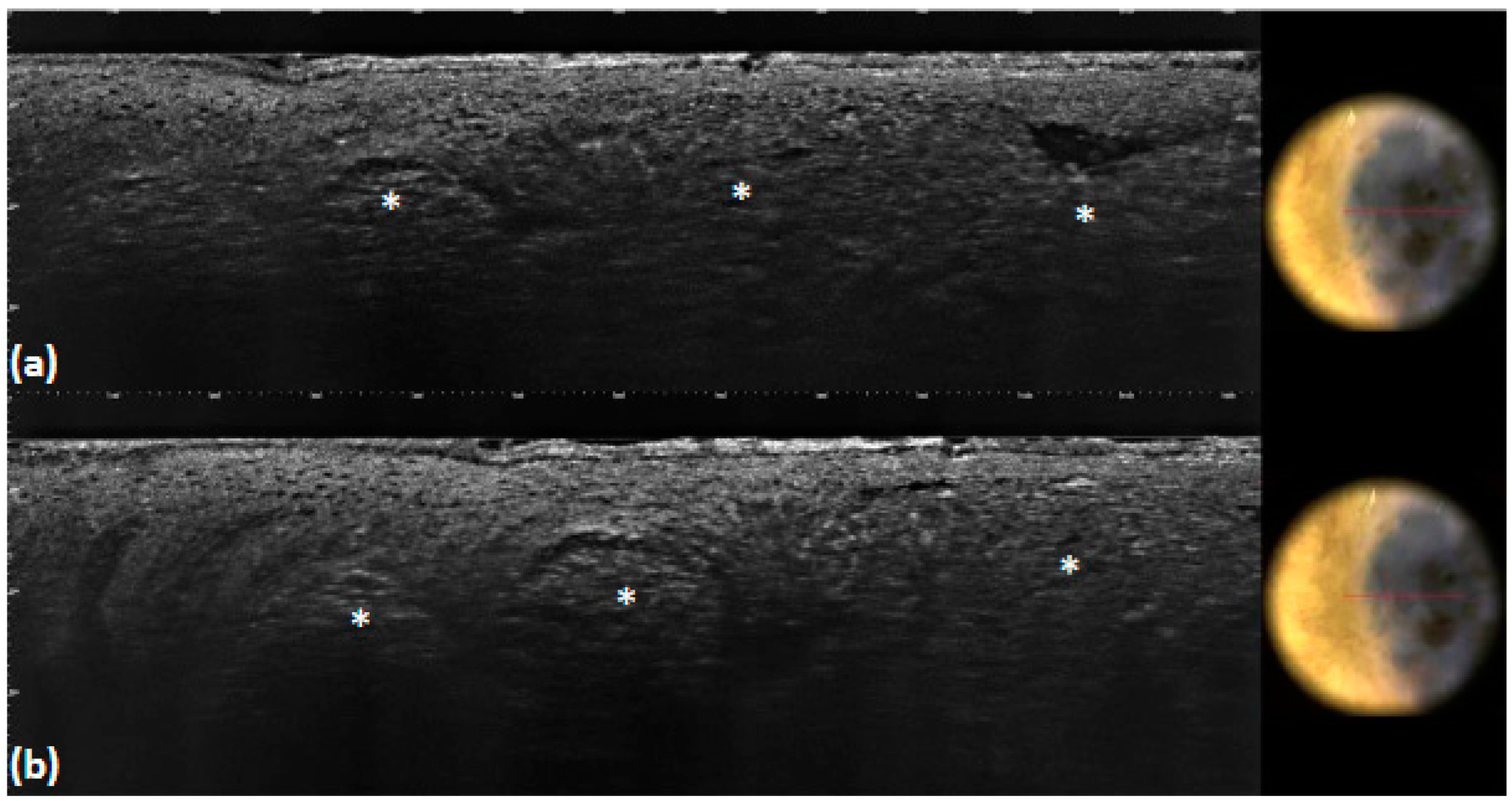
| Blue–gray globules | Roundish medium-reflective tumor lobules detached from the epidermis with variable hyper-reflective spots | 40 (40.0) | 36 (36.0) | 0.662 | 0.96 | 0.92 | <0.001 |
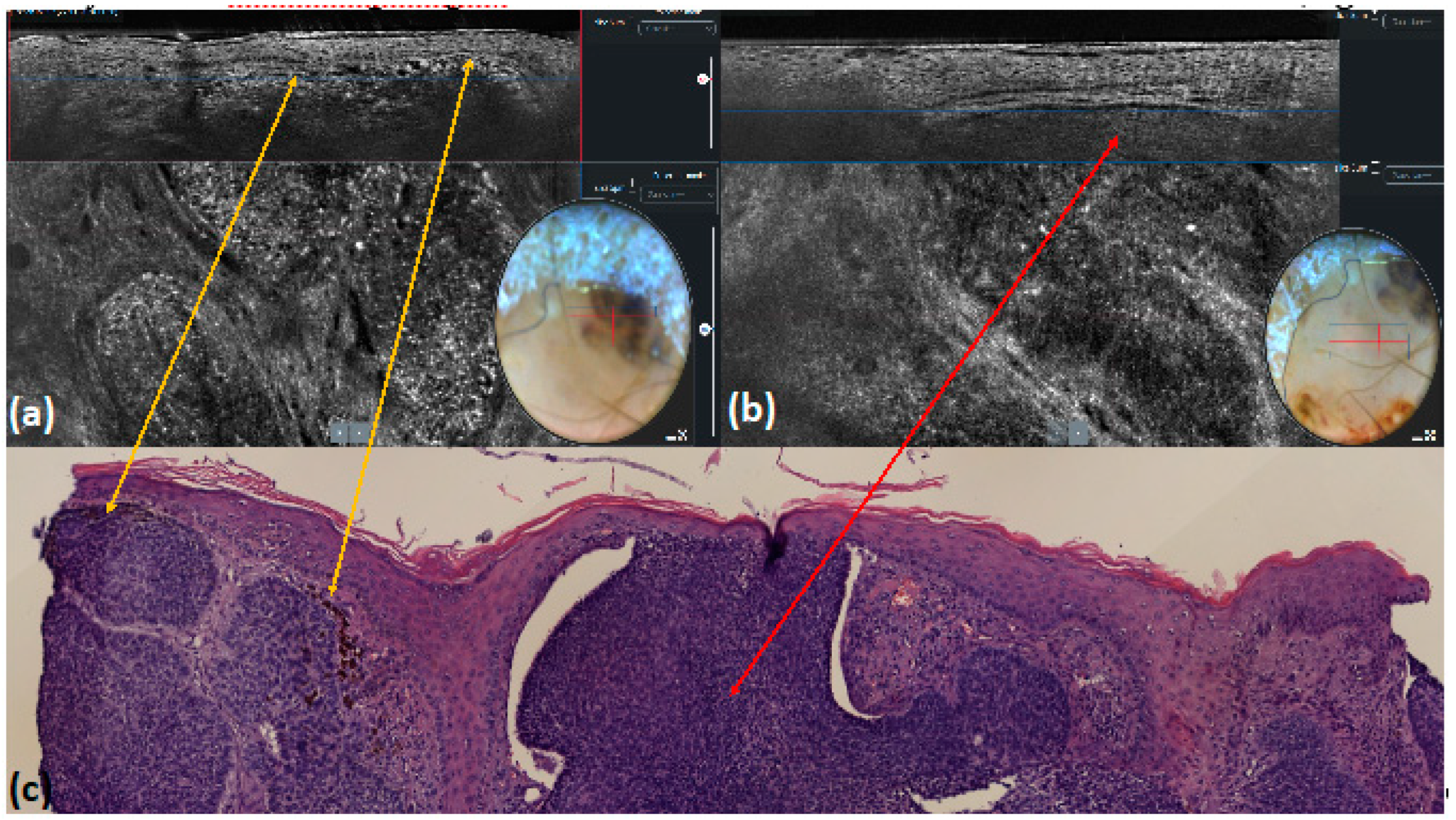
| Blue–gray ovoid nests | Medium-reflective tumor lobules detached from the epidermis with variable hyper-reflective spots | 10 (10.0) | 9 (9.0) | 1 | 0.99 | 0.99 | <0.001 |
| Telangiectasia or arborizing vessels | Telangiectasia or arborizing vessels | 51 (51.0) | 39 (39.0) | 0.118 | 0.88 | 0.76 | <0.001 |
| Multiple blue–gray dots | Hyper-reflective roundish small areas inside tumor lobules | 18 (18.0) | 13 (13.0) | 0.435 | 0.95 | 0.93 | <0.001 |
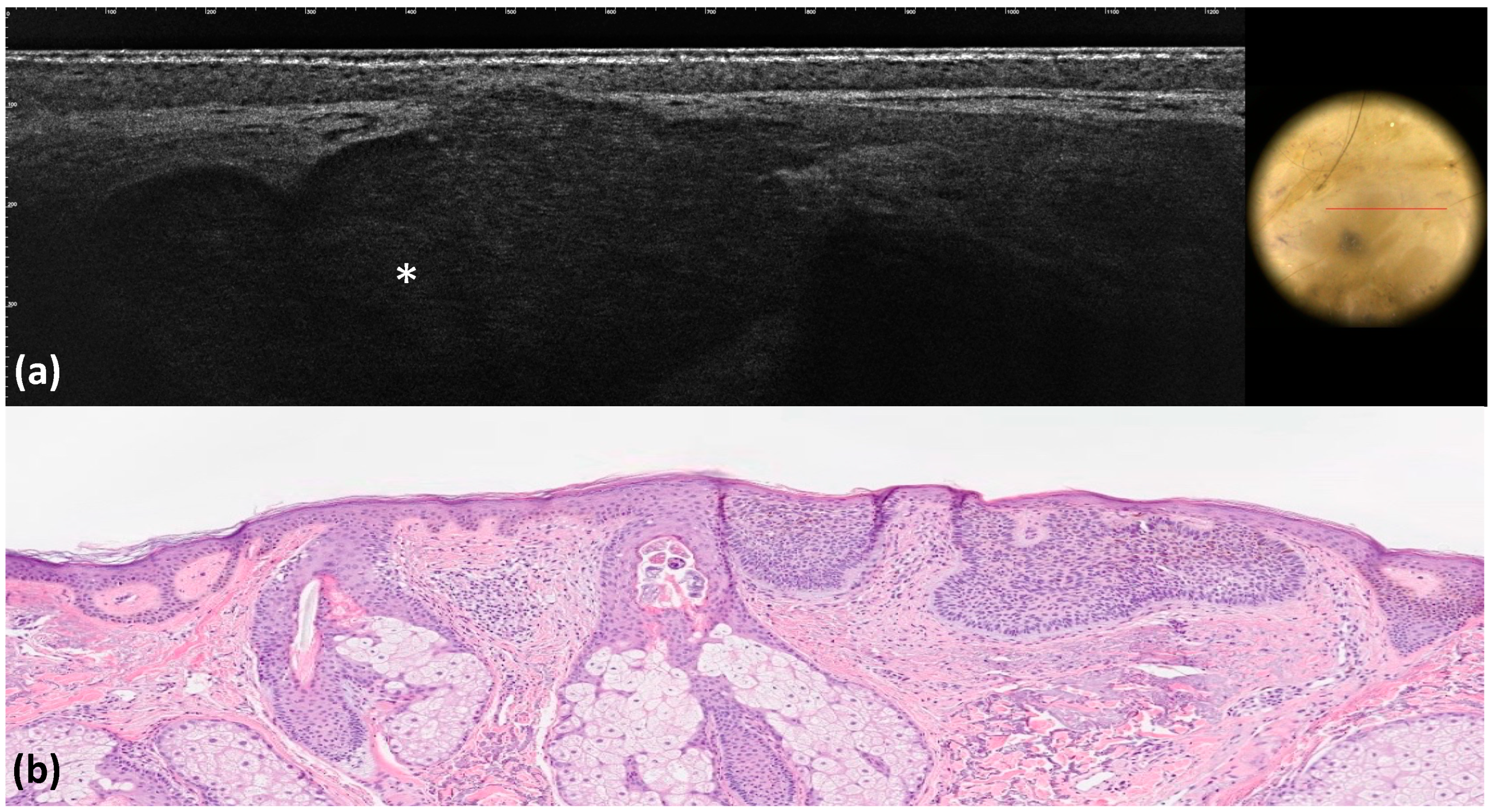
| Pink–white areas | Medium-reflective lobules | 10 (10.0) | 8 (8.0) | 0.805 | 0.98 | 0.98 | <0.001 |
| Blue-whitish veils | Hyper-reflective lobules in the entire dermis | 9 (9.0) | 9 (9.0) | 1 | 1 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Milia-like cysts | Milia-like cysts | 9(9.0) | 5 (5.0) | 0.406 | 0.90 | 0.89 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbarossa, L.; D’Onghia, M.; Cartocci, A.; Suppa, M.; Tognetti, L.; Cappilli, S.; Peris, K.; Perez-Anker, J.; Malvehy, J.; Baldino, G.; et al. Understanding the Dermoscopic Patterns of Basal Cell Carcinoma Using Line-Field Confocal Tomography. Tomography 2024, 10, 826-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060063
Barbarossa L, D’Onghia M, Cartocci A, Suppa M, Tognetti L, Cappilli S, Peris K, Perez-Anker J, Malvehy J, Baldino G, et al. Understanding the Dermoscopic Patterns of Basal Cell Carcinoma Using Line-Field Confocal Tomography. Tomography. 2024; 10(6):826-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060063
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbarossa, Lorenzo, Martina D’Onghia, Alessandra Cartocci, Mariano Suppa, Linda Tognetti, Simone Cappilli, Ketty Peris, Javiera Perez-Anker, Josep Malvehy, Gennaro Baldino, and et al. 2024. "Understanding the Dermoscopic Patterns of Basal Cell Carcinoma Using Line-Field Confocal Tomography" Tomography 10, no. 6: 826-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060063
APA StyleBarbarossa, L., D’Onghia, M., Cartocci, A., Suppa, M., Tognetti, L., Cappilli, S., Peris, K., Perez-Anker, J., Malvehy, J., Baldino, G., Militello, C., Perrot, J. L., Rubegni, P., & Cinotti, E. (2024). Understanding the Dermoscopic Patterns of Basal Cell Carcinoma Using Line-Field Confocal Tomography. Tomography, 10(6), 826-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060063







